Battle of Chantilly on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Battle of Chantilly (or Ox Hill, the Confederate name) took place on September 1, 1862, in
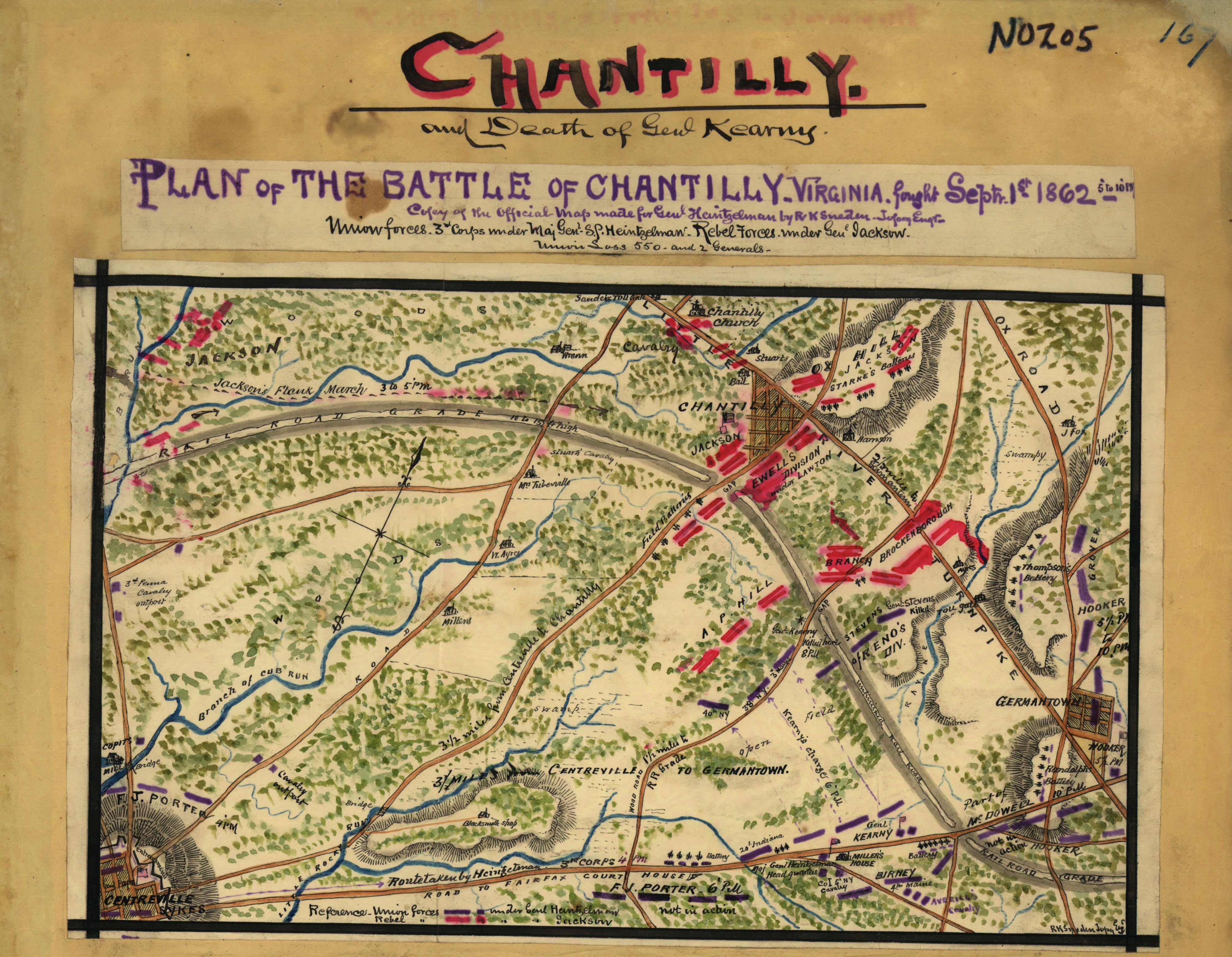 On the morning of September 1, Pope ordered Maj. Gen. Edwin V. Sumner of the II Corps, Army of the Potomac, to send a brigade north to reconnoiter; the army's cavalry was too exhausted for the mission. But at the same time, he continued his movement in the direction of Washington, sending McDowell's corps to Germantown (on the western border of modern-day
On the morning of September 1, Pope ordered Maj. Gen. Edwin V. Sumner of the II Corps, Army of the Potomac, to send a brigade north to reconnoiter; the army's cavalry was too exhausted for the mission. But at the same time, he continued his movement in the direction of Washington, sending McDowell's corps to Germantown (on the western border of modern-day  A severe thunderstorm erupted about this time, resulting in limited visibility and an increased dependence on the bayonet, as the rain soaked the ammunition of the infantry and made it useless. Kearny arrived about this time with his division to find Stevens' units disorganized. Perceiving a gap in the line he deployed Brig. Gen. David B. Birney's brigade on Stevens's left, ordering it to attack across the field. Birney managed to maneuver close to the Confederate line but his attack stalled in hand-to-hand combat with Maj. Gen. A.P. Hill's division. Kearny mistakenly rode into the Confederate lines during the battle and was killed. As Kearny's other two brigades arrived on the field, Birney used the reinforcements as a rear guard as he withdrew the remainder of the Union force to the southern side of the farm fields, ending the battle.
A severe thunderstorm erupted about this time, resulting in limited visibility and an increased dependence on the bayonet, as the rain soaked the ammunition of the infantry and made it useless. Kearny arrived about this time with his division to find Stevens' units disorganized. Perceiving a gap in the line he deployed Brig. Gen. David B. Birney's brigade on Stevens's left, ordering it to attack across the field. Birney managed to maneuver close to the Confederate line but his attack stalled in hand-to-hand combat with Maj. Gen. A.P. Hill's division. Kearny mistakenly rode into the Confederate lines during the battle and was killed. As Kearny's other two brigades arrived on the field, Birney used the reinforcements as a rear guard as he withdrew the remainder of the Union force to the southern side of the farm fields, ending the battle.
Library of Congress
* Hennessy, John J. ''Return to Bull Run: The Campaign and Battle of Second Manassas''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1993. . * Ropes, John Codman. ''The Army in the Civil War''. Vol. 4, ''The Army under Pope''. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1881. . * Salmon, John S. ''The Official Virginia Civil War Battlefield Guide''. Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books, 2001. . * Taylor, Paul. ''He Hath Loosed the Fateful Lightning: The Battle of Ox Hill (Chantilly), September 1, 1862''. Shippensburg, PA: White Mane Publishers, 2003. .
CWSAC Report Update
* Welker, David A. "Tempest at Ox Hill: The Battle of Chantilly." New York: DaCapo, 2002. .
Animated maps, histories, photos, and preservation news. (
''The Battle of Chantilly (Ox Hill)'', a docudrama about the battle
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chantilly
Fairfax County, Virginia
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a County (United States), county in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia. With a population of 1,150,309 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the most p ...
, as the concluding battle of the Northern Virginia Campaign of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson's corps of the Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was a field army of the Confederate States Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was also the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed agains ...
attempted to cut off the line of retreat of the Union Army of Virginia following the Second Battle of Bull Run
The Second Battle of Bull Run or Battle of Second Manassas was fought August 28–30, 1862, in Prince William County, Virginia, as part of the American Civil War. It was the culmination of the Northern Virginia Campaign waged by Confederate ...
but was attacked by two Union divisions. During the ensuing battle, Union division commanders Isaac Stevens
Isaac Ingalls Stevens (March 25, 1818 – September 1, 1862) was an American military officer and politician who served as governor of the Territory of Washington from 1853 to 1857, and later as its delegate to the United States House of Represe ...
and Philip Kearny
Philip Kearny Jr. (; June 1, 1815 – September 1, 1862) was a United States Army officer, notable for his leadership in the Mexican–American War and American Civil War. He served in Emperor of the French, French Emperor Napoleon III's Imperial ...
were both killed, but the Union attack halted Jackson's advance.
Background
Defeated in theSecond Battle of Bull Run
The Second Battle of Bull Run or Battle of Second Manassas was fought August 28–30, 1862, in Prince William County, Virginia, as part of the American Civil War. It was the culmination of the Northern Virginia Campaign waged by Confederate ...
on August 30, Union Maj. Gen. John Pope ordered his Army of Virginia to retreat to Centreville. The movement began after dark, with Maj. Gen. Irvin McDowell
Irvin McDowell (October 15, 1818 – May 4, 1885) was an American army officer. He is best known for his defeat in the First Battle of Bull Run, the first large-scale battle of the American Civil War. In 1862, he was given command of the ...
's III Corps providing cover. The army crossed Bull Run and the last troops across, Maj. Gen. Franz Sigel's I Corps, destroyed Stone Bridge behind them. Gen. Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a general officers in the Confederate States Army, Confederate general during the American Civil War, who was appointed the General in Chief of the Armies of the Confederate ...
decided not to press the advantage gained that day, largely because he knew his Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was a field army of the Confederate States Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was also the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most often arrayed agains ...
was exhausted from two weeks of nearly constant marching and nearly three days of battle, so the Union retreat went unmolested. Lee's decision also allowed the Army of Virginia's II Corps, under Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks
Nathaniel Prentice (or Prentiss) Banks (January 30, 1816 – September 1, 1894) was an American politician from Massachusetts and a Union Army, Union general during the American Civil War, Civil War. A millworker, Banks became prominent in local ...
, to consolidate with the bulk of Pope's army, marching in from Bristoe Station, where they had been guarding the army's trains. More importantly, Lee's decision bought time for the Union to push to the front the Army of the Potomac's II, V, and VI Corps, which had been brought from the Peninsula
A peninsula is a landform that extends from a mainland and is only connected to land on one side. Peninsulas exist on each continent. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula.
Etymology
The word ''peninsula'' derives , . T ...
and—much to Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan (December 3, 1826 – October 29, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 24th governor of New Jersey and as Commanding General of the United States Army from November 1861 to March 186 ...
's dismay—placed under Pope's command.
By the morning of August 31, Pope began to lose his grasp on command of his army. The defeat at Second Bull Run seemed to have shattered his nerve and Pope was unsure what to do next; he knew Washington wanted an attack but he feared Lee might strike first and destroy his reforming force before it was ready to fight again. Calling a conference of his corps commanders—something he had been loath to do previously in the Virginia Campaign—in his Centreville headquarters, Pope agreed with their decision to retreat further into the Washington defenses. But a message from General-in-Chief Henry W. Halleck directed him to attack and he ordered an advance on Lee's forces on the Manassas field.
Lee, however, had already set in motion his own plan that would rob Pope of the initiative to attack. Lee directed Maj. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson to march his troops around Pope's right flank to get behind the Union position at Centreville. Leading the way and scouting for any Union blocking force was Confederate cavalry under the command of Maj. Gen. J.E.B. Stuart. Maj. Gen. James Longstreet
James Longstreet (January 8, 1821January 2, 1904) was a General officers in the Confederate States Army, Confederate general during the American Civil War and was the principal subordinate to General Robert E. Lee, who called him his "Old War Ho ...
's command would remain in place for the day to deceive Pope into believing that Lee's entire force remained in his front, while Jackson's command would make its flanking march north and then east to take strategically important Germantown, Virginia
Germantown is a historic unincorporated rural community in Fauquier County, Virginia, United States. It is located in and around current-day C. M. Crockett Park, which contains the popular local fishing destination of Germantown Lake. Chief J ...
, where Pope's only two routes to Washington—the Warrenton Pike (modern U.S. Route 29
U.S. Route 29 or U.S. Highway 29 (US 29) is a north–south United States Numbered Highway that runs for from Pensacola, Florida, to Ellicott City, Maryland, just west of Baltimore, Baltimore, Maryland, in the Eastern United Stat ...
) and the Little River Turnpike (modern U.S. Route 50
U.S. Route 50 or U.S. Highway 50 (US 50) is a major east–west route of the U.S. Highway system, stretching from Interstate 80 (I-80) in West Sacramento, California, to Maryland Route 528 (MD 528) in Ocean City, Maryland, on the Atlantic ...
)—converged. Jackson's men, hungry and worn, moved slowly and bivouacked for the night at Pleasant Valley, three miles northeast of Centreville. As Pope settled down for the night on August 31, he was unaware that Jackson was on the verge of turning his flank.
During the night two events occurred that forced Pope to change his mind. A staff officer arrived from the Germantown position to report that a heavy force of cavalry had shelled the intersection before retreating. Pope initially dismissed the cavalry as little more than a patrol. But when, hours later, two Union cavalrymen reported seeing a large mass of infantry marching east down the Little River Turnpike, Pope realized that his army was in danger. He countermanded actions preparing for an attack and directed the army to retreat from Centreville to Washington; he also sent out a series of infantry probes up the roads that Lee might use to reach his troops as they pulled back.
Opposing forces
Union
Confederate
Battle
 On the morning of September 1, Pope ordered Maj. Gen. Edwin V. Sumner of the II Corps, Army of the Potomac, to send a brigade north to reconnoiter; the army's cavalry was too exhausted for the mission. But at the same time, he continued his movement in the direction of Washington, sending McDowell's corps to Germantown (on the western border of modern-day
On the morning of September 1, Pope ordered Maj. Gen. Edwin V. Sumner of the II Corps, Army of the Potomac, to send a brigade north to reconnoiter; the army's cavalry was too exhausted for the mission. But at the same time, he continued his movement in the direction of Washington, sending McDowell's corps to Germantown (on the western border of modern-day Fairfax, Virginia
Fairfax ( ) is an independent city (United States), independent city in Virginia and the county seat of Fairfax County, Virginia, in the United States. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 24,146.
Fairfax is pa ...
), where it could protect the important intersection of Warrenton Pike and Little River Turnpike that the army needed for the retreat. He also sent two brigades from Maj. Gen. Jesse L. Reno's IX Corps, under the command of Brig. Gen. Isaac Stevens
Isaac Ingalls Stevens (March 25, 1818 – September 1, 1862) was an American military officer and politician who served as governor of the Territory of Washington from 1853 to 1857, and later as its delegate to the United States House of Represe ...
, to block Jackson. Maj. Gen. Philip Kearny
Philip Kearny Jr. (; June 1, 1815 – September 1, 1862) was a United States Army officer, notable for his leadership in the Mexican–American War and American Civil War. He served in Emperor of the French, French Emperor Napoleon III's Imperial ...
's division from the III Corps followed later that afternoon.
Jackson resumed his march to the south, but his troops were tired and hungry and made poor progress as the rain continued. They marched only three miles and occupied Ox Hill, southeast of Chantilly Plantation, and halted, while Jackson himself took a nap. All during the morning, Confederate cavalry skirmished with Union infantry and cavalry. At about 3 p.m., Stevens' division arrived at Ox Hill. Despite being outnumbered, Stevens chose to attack across a grassy field against Brig. Gen. Alexander Lawton's division in the Confederate center. The Union attack was initially successful, routing the brigade of Colonel Henry Strong and driving in the flank of Captain William Brown, with Brown killed during the fighting. The Union division was driven back following a counterattack by Brig. Gen. Jubal Early
Jubal Anderson Early (November 3, 1816 – March 2, 1894) was an American lawyer, politician and military officer who served in the Confederate States Army during the Civil War. Trained at the United States Military Academy, Early resigned his ...
's brigade. Stevens was killed during this attack at about 5 p.m., by a shot through his temple.
 A severe thunderstorm erupted about this time, resulting in limited visibility and an increased dependence on the bayonet, as the rain soaked the ammunition of the infantry and made it useless. Kearny arrived about this time with his division to find Stevens' units disorganized. Perceiving a gap in the line he deployed Brig. Gen. David B. Birney's brigade on Stevens's left, ordering it to attack across the field. Birney managed to maneuver close to the Confederate line but his attack stalled in hand-to-hand combat with Maj. Gen. A.P. Hill's division. Kearny mistakenly rode into the Confederate lines during the battle and was killed. As Kearny's other two brigades arrived on the field, Birney used the reinforcements as a rear guard as he withdrew the remainder of the Union force to the southern side of the farm fields, ending the battle.
A severe thunderstorm erupted about this time, resulting in limited visibility and an increased dependence on the bayonet, as the rain soaked the ammunition of the infantry and made it useless. Kearny arrived about this time with his division to find Stevens' units disorganized. Perceiving a gap in the line he deployed Brig. Gen. David B. Birney's brigade on Stevens's left, ordering it to attack across the field. Birney managed to maneuver close to the Confederate line but his attack stalled in hand-to-hand combat with Maj. Gen. A.P. Hill's division. Kearny mistakenly rode into the Confederate lines during the battle and was killed. As Kearny's other two brigades arrived on the field, Birney used the reinforcements as a rear guard as he withdrew the remainder of the Union force to the southern side of the farm fields, ending the battle.
Aftermath
That night, Longstreet arrived to relieve Jackson's troops and to renew the battle in the morning. The lines were so close that some soldiers accidentally stumbled into the camps of the opposing army. The Union army withdrew to Germantown and Fairfax Court House that night, followed over the next few days by retreating to the defenses of Washington. The Confederate cavalry attempted a pursuit but failed to cause significant damage to the Union army. The fighting was tactically inconclusive. Although Jackson's turning movement was foiled and he was unable to block the Union retreat or destroy Pope's army, National Park Service historians count Chantilly as a strategic Confederate victory because it neutralized any threat from Pope's army and cleared the way for Lee to begin hisMaryland Campaign
The Maryland campaign (or Antietam campaign) occurred September 4–20, 1862, during the American Civil War. The campaign was Confederate States Army, Confederate General (CSA), General Robert E. Lee's first invasion of the Northern United Stat ...
. The Confederates claimed a tactical victory as well because they held the field after the battle. Two Union generals were killed, while one Confederate brigade commander was killed. Pope, recognizing the attack as an indication of continued danger to his army, continued his retreat to the fortifications around Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
Lee began the Maryland Campaign, which culminated in the Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam ( ), also called the Battle of Sharpsburg, particularly in the Southern United States, took place during the American Civil War on September 17, 1862, between Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virgi ...
, after Pope retreated from Virginia. The Army of the Potomac, under Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan (December 3, 1826 – October 29, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 24th governor of New Jersey and as Commanding General of the United States Army from November 1861 to March 186 ...
, absorbed the forces of Pope's Army of Virginia, which was disbanded as a separate army.
Battlefield today
The site of the battle, once rural farmland, is now surrounded by suburban development inFairfax County, Virginia
Fairfax County, officially the County of Fairfax, is a County (United States), county in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia. With a population of 1,150,309 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the most p ...
. The modern thoroughfares of U.S. Route 50
U.S. Route 50 or U.S. Highway 50 (US 50) is a major east–west route of the U.S. Highway system, stretching from Interstate 80 (I-80) in West Sacramento, California, to Maryland Route 528 (MD 528) in Ocean City, Maryland, on the Atlantic ...
(Lee-Jackson Memorial Highway) and State Route 286 (Fairfax County Parkway), as well as State Route 608 (West Ox Road) intersect near the location of the battle. A 4.8 acre (19,000 m2) memorial park, the Ox Hill Battlefield Park, is located off of West Ox Road and lies adjacent to the Fairfax Towne Center shopping area, and includes most of the Gen. Isaac Stevens portion of the battle, about 1.5% of the total ground. The park is under the jurisdiction of the Fairfax County Park Authority; in January 2005, the Authority approved a General Management Plan and Conceptual Development Plan that sets forth a detailed history and future management framework for the site.
A small yard located within the nearby Fairfax Towne Center has been preserved to mark the area crossed by Confederate troops to get to the Ox Hill battlefield.Taylor, p. 128.
Notes
References
* Esposito, Vincent J. ''West Point Atlas of American Wars''. New York: Frederick A. Praeger, 1959. . A copy is available online at thLibrary of Congress
* Hennessy, John J. ''Return to Bull Run: The Campaign and Battle of Second Manassas''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1993. . * Ropes, John Codman. ''The Army in the Civil War''. Vol. 4, ''The Army under Pope''. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 1881. . * Salmon, John S. ''The Official Virginia Civil War Battlefield Guide''. Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books, 2001. . * Taylor, Paul. ''He Hath Loosed the Fateful Lightning: The Battle of Ox Hill (Chantilly), September 1, 1862''. Shippensburg, PA: White Mane Publishers, 2003. .
CWSAC Report Update
* Welker, David A. "Tempest at Ox Hill: The Battle of Chantilly." New York: DaCapo, 2002. .
Further reading
* Mauro, Charles V. ''The Battle of Chantilly (Ox Hill): A Monumental Storm''. Fairfax, VA: Fairfax County History Commission, 2002. .External links
Animated maps, histories, photos, and preservation news. (
Civil War Trust
The American Battlefield Trust is a charitable organization (501(c)(3)) whose primary focus is in the preservation of battlefields of the Revolutionary War, the War of 1812, and the American Civil War, through the acquisition of battlefield lan ...
)
''The Battle of Chantilly (Ox Hill)'', a docudrama about the battle
{{DEFAULTSORT:Chantilly
Chantilly
Chantilly may refer to:
Places
France
*Chantilly, Oise, a city
** US Chantilly, a football club
*Château de Chantilly
United States
* Chantilly, Missouri, an unincorporated community
* Chantilly (Charlotte neighborhood), North Carolina ...
Chantilly
Chantilly may refer to:
Places
France
*Chantilly, Oise, a city
** US Chantilly, a football club
*Château de Chantilly
United States
* Chantilly, Missouri, an unincorporated community
* Chantilly (Charlotte neighborhood), North Carolina ...
Chantilly
Chantilly may refer to:
Places
France
*Chantilly, Oise, a city
** US Chantilly, a football club
*Château de Chantilly
United States
* Chantilly, Missouri, an unincorporated community
* Chantilly (Charlotte neighborhood), North Carolina ...
Chantilly
Chantilly may refer to:
Places
France
*Chantilly, Oise, a city
** US Chantilly, a football club
*Château de Chantilly
United States
* Chantilly, Missouri, an unincorporated community
* Chantilly (Charlotte neighborhood), North Carolina ...
Chantilly
Chantilly may refer to:
Places
France
*Chantilly, Oise, a city
** US Chantilly, a football club
*Château de Chantilly
United States
* Chantilly, Missouri, an unincorporated community
* Chantilly (Charlotte neighborhood), North Carolina ...
1862 in Virginia
1862 in the American Civil War
September 1862