Arakan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Arakan ( or ) is a historic coastal region in

 Arakan came under strong Indic influence from the
Arakan came under strong Indic influence from the
 After the Burmese invasion,
After the Burmese invasion,
 Min Saw Mon's successors in the
Min Saw Mon's successors in the  Even after independence from the Sultans of Bengal, the Arakanese kings continued the custom of maintaining Muslim titles. They compared themselves to
Even after independence from the Sultans of Bengal, the Arakanese kings continued the custom of maintaining Muslim titles. They compared themselves to
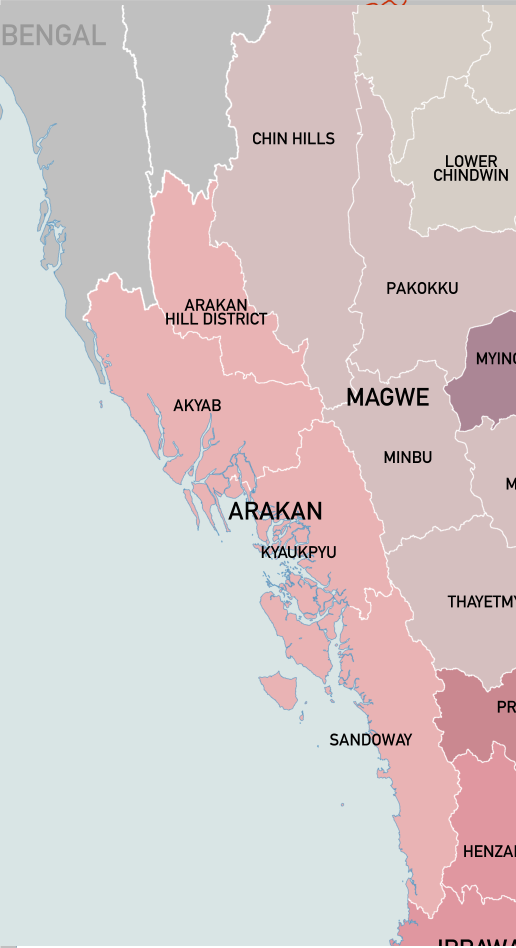 The Burmese Empire ceded Arakan to the
The Burmese Empire ceded Arakan to the
 Arakan is a coastal geographic region in
Arakan is a coastal geographic region in
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
. Its borders faced the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
to its west, the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
to its north and Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
proper to its east. The Arakan Mountains
The Arakan Mountains ( my, ရခိုင်ရိုးမ), also known as the Rakhine Yoma, are a mountain range in western Myanmar, between the coast of Rakhine State and the Central Myanmar Basin, in which flows the Irrawaddy River. It is th ...
isolated the region and made it accessible only by the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
and the sea. The region now forms the Rakhine State
Rakhine State (; , , ; formerly known as Arakan State) is a Administrative divisions of Myanmar, state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady R ...
in Myanmar.
Arakan became one of the earliest regions in Southeast Asia to embrace Dharmic religions
Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, and Sikhism,Adams, C. J."Classification of ...
, particularly Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
and Hinduism. Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
arrived with Arab merchants in the 8th century. The Kingdom of Mrauk U
The Kingdom of Mrauk-U ( Arakanese: မြောက်ဦး နေပြည်တော်,) was a kingdom that existed on the Arakan littoral from 1429 to 1785. Based out of the capital Mrauk-U, near the eastern coast of the Bay of Bengal, t ...
emerged as an independent Arakanese kingdom for 300 years. During the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafarin ...
and Bengal Subah
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Ben ...
's major economic development, Arakan caught the interest of the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
and the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the l ...
. In the middle of the 17th century, it was dominated by the Islamic Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
. Arakan steadily declined from the 18th century onwards after its loss to the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
.
After conquest by the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
, Arakan became one of the divisions of British India
The Divisions of British India were administrative units of the Government of the British Raj or Indian Empire.''Imperial Gazetteer of India''. Published under the authority of His Majesty's Secretary of State for India in Council. Oxford: Claren ...
and received settlers from the neighboring Chittagong Division
Chittagong Division, officially known as Chattogram Division, is geographically the largest of the eight administrative divisions of Bangladesh. It covers the south-easternmost areas of the country, with a total area of and a population at the 2 ...
of the Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and ...
. In 1937, it became a division of British Burma
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
. Arakan Division
Arakan Division ( my, ရခိုင်တိုင်း) was an administrative division of the British Empire, covering modern-day Rakhine State, Myanmar, which was the historical region of Arakan. It bordered the Bengal Presidency of British ...
was once a leading rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
exporter. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the region was occupied by Imperial Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent forma ...
. The Allied Forces liberated Arakan during the Burma Campaign. It continued to be an administrative division after Burmese independence; and later became a province. In the early 1960s, the northern part of Arakan was governed from Rangoon
Yangon ( my, ရန်ကုန်; ; ), formerly spelled as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar (also known as Burma). Yangon served as the capital of Myanmar until 2006, when the military government ...
as the Mayu Frontier District
The Mayu Frontier District ( my, မေယုနယ်ခြားခရိုင်) was a short-lived administrative zone of Burma (present-day Myanmar) which existed between 1961 and 1964. It covered the Maungdaw District of present-day Rakhine ...
.
In 1982, the Burmese nationality law
The Nationality law of Myanmar currently recognises three categories of citizens, namely citizen, associate citizen and naturalised citizen, according to the 1982 Citizenship Law. Citizens, as defined by the 1947 Constitution, are persons who b ...
stripped many inhabitants of the region, most notably the Rohingya, of their citizenship. In 1989, the Burmese military junta changed the official name of Burma to Myanmar. In the 1990s, the junta changed the name of Arakan State to Rakhine State
Rakhine State (; , , ; formerly known as Arakan State) is a Administrative divisions of Myanmar, state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady R ...
— a name reflecting the dominance of the Rakhine majority. Many in the Rohingya
The Rohingya people () are a stateless Indo-Aryan ethnic group who predominantly follow Islam and reside in Rakhine State, Myanmar (previously known as Burma). Before the Rohingya genocide in 2017, when over 740,000 fled to Bangladesh, an ...
minority strongly opposed the change. The region has seen conflict between the Burmese state, Rakhine nationalists and Rohingya rebels. In more recent times, Rakhine State has been notable for the exodus of refugees into neighboring countries because of military operations by the Tatmadaw
Tatmadaw (, , ) is the official name of the armed forces of Myanmar (formerly Burma). It is administered by the Ministry of Defence and composed of the Myanmar Army, the Myanmar Navy and the Myanmar Air Force. Auxiliary services include th ...
(Myanmar Armed Forces).
Etymology
Claudius Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance ...
identified Arakan as ''Argyré''. Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
records spelled the name as ''Arracao''. The name was spelled as ''Araccan'' in many old European maps and publications. The region was named as Arakan Division
Arakan Division ( my, ရခိုင်တိုင်း) was an administrative division of the British Empire, covering modern-day Rakhine State, Myanmar, which was the historical region of Arakan. It bordered the Bengal Presidency of British ...
during British rule in Burma
( Burmese)
, conventional_long_name = Colony of Burma
, common_name = Burma
, era = Colonial era
, event_start = First Anglo-Burmese War
, year_start = 1824
, date_start = ...
.
History
Early inhabitants
It is unclear who the earliest inhabitants were; some historians believe the earliest settlers included the Burmese Mro tribe but there is a lack of evidence and no clear tradition of their origin or written records of their history. Arakanese traditional history holds that Arakan was inhabited by the Rakhine since 3000 BCE, but there is no archaeological evidence to support the claim. According to British historian Daniel George Edward Hall, who wrote extensively on the history of Burma, "The Burmese do not seem to have settled in Arakan until possibly as late as the tenth century AD. Hence earlier dynasties are thought to have been Indian, ruling over a population similar to that of Bengal. All the capitals known to history have been in the north near modern Akyab".Ancient Indic influence

 Arakan came under strong Indic influence from the
Arakan came under strong Indic influence from the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
, particularly the ancient kingdoms of the Ganges delta. Arakan was one of the first regions in Southeast Asia to adopt Dharmic religions
Indian religions, sometimes also termed Dharmic religions or Indic religions, are the religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent. These religions, which include Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism, and Sikhism,Adams, C. J."Classification of ...
. It became one of the earliest Indianized kingdoms
Greater India, or the Indian cultural sphere, is an area composed of many countries and regions in South and Southeast Asia that were historically influenced by Indian culture, which itself formed from the various distinct indigenous cultures ...
in Southeast Asia. Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
missionaries from the Mauryan Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
traveled through Arakan to other parts of Southeast Asia.
First states
Due to the evidence ofSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
inscriptions found in the region, historians believe the founders of the first Arakanese state were Indian. The first Arakanese state flourished in Dhanyawadi
Kingdom of Dhanyawaddy ( my, ဓညဝတီ; pi, Dhaññavatī) was the capital of the first Arakanese Kingdom, located in what is now Northern Rakhine State, Myanmar. The name is a corruption of the Pali word ''Dhannavati'', which means "large ...
between the 4th and 6th centuries. Sircar has dated King Chandrodaya at the start of 3rd century AD and there are king which are mentioned even prior to him. It is concluded that from King Chandrodaya a new religion of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
took root in Arakan as the prior kings are regarded less religious compared to the later. The city was the center of a large trade network linked to India, China and Persia. Power then shifted to the city of Waithali
Waithali ( my, ဝေသာလီမြို့, , pi, Vesālī) located in today's northern Rakhine State, Myanmar, was the capital of the Waithali Kingdom from 788 to 1018. The former capital site is approximately north-east of Sittwe, and ...
, where the Candra dynasty
The Chandra kingdom was a Buddhist kingdom, originating from the Indian subcontinent, which ruled the Samatata region of Bengal, as well as northern Arakan. Later it was a neighbor to the Pala Empire to the north. Rulers of Chandra kingdom were ...
ruled. Waithali became a wealthy trading port. The Chandra-ruled Harikela
Harikela () was an ancient empire located in the eastern region of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, it was a neighboring independent and independent township of ancient East Bengal, which had a continuous existence of about 500 years. The st ...
state was known as the Kingdom of Ruhmi to the Arabs.
Arrival of Islam
Since in the 8th century, Arab merchants began conducting missionary activities in southeast Asia. Some researchers have speculated that Muslims usedtrade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sing ...
s in the region to travel to India and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. A southern branch of the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
connected India, Burma and China since the neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
period.
Rakhine migration
It is unclear whether theRakhine people
The Rakhine people ( my, ရက္ခိုင်လူမျိုး, : , ), also known as the Arakanese people, are a Southeast Asian ethnic group in Myanmar (Burma) forming the majority along the coastal region of present-day Rakhine Stat ...
were one of the tribes of the Burmese Pyu city-states
, conventional_long_name = Pyu city-states
, common_name = Pyu City States
, era = Classical antiquity
, status = City
, event_start = Earliest Pyu presence in Upper Burma
, year_start = c. 2nd century BCE
, date_start =
, event_en ...
because the people in those states at the time spoke a Tibeto-Burman
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people spea ...
language while Arakan (Rakhine) speakers are from the Sino-Tibetan
Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Chinese languages. ...
language family. They began migrating to Arakan through the Arakan Mountains in the 9th century. The Rakhines settled in the valley of the Lemro River
The Lemro ( my, လေးမြို့မြစ်, ) originally called Aizannadi is a river of Myanmar flowing through Chin State and Rakhine State. It flows into the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian ...
. Their cities included Sambawak I, Pyinsa, Parein, Hkrit, Sambawak II, Myohaung, Toungoo and Launggret. The cities flourished between the 11th and 15th centuries. The Burmese invaded Arakan in 1406.
Indo-Islamic influence
 After the Burmese invasion,
After the Burmese invasion, Min Saw Mon
Narameikhla Min Saw Mon ( Arakanese:နရမိတ်လှ မင်းစောမွန်; , Arakanese transliteration: Meng Sao Mwan, Arakanese pronunciation: ; also known as Suleiman Shah; 1380–1433) was the last king of Launggyet Dynas ...
fled to Gaurh in the Bengal Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominan ...
, where he stayed in exile for 24 years after being granted asylum
Asylum may refer to:
Types of asylum
* Asylum (antiquity), places of refuge in ancient Greece and Rome
* Benevolent Asylum, a 19th-century Australian institution for housing the destitute
* Cities of Refuge, places of refuge in ancient Judea
...
by Sultan Ghiyasuddin Azam Shah
Ghiyasuddin A'zam Shah ( bn, গিয়াসউদ্দীন আজম শাহ, fa, ) was the third Sultan of Bengal and the Ilyas Shahi dynasty. He was one of the most prominent medieval Bengali sultans. He established diplomatic relatio ...
. The Bengal Sultanate was one of the major Islamic states established after the Muslim conquest of the Indian subcontinent
The Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent mainly took place from the 13th to 17th centuries. Earlier Muslim conquests include the invasions into what is now modern-day Pakistan and the Umayyad campaigns in India in eighth century and res ...
.
In 1430, Min Saw Mon regained control of Arakan with help from the Bengal Sultanate. He established his new capital in the city of Mrauk U
Mrauk U ( ) is a town in northern Rakhine State, Myanmar. It is the capital of Mrauk-U Township, a subregion of the Mrauk-U District.
Mrauk U is of great cultural importance to the local Rakhine (Arakanese) people, and is the location of many ...
. Arakan became a vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
of the Bengal Sultanate and recognized Bengali sovereignty over some territory of northern Arakan. Arakanese kings adopted Islamic titles and struck the Bengali taka. Min Saw Mon was styled as Suleiman Shah. Bengalis
Bengalis (singular Bengali bn, বাঙ্গালী/বাঙালি ), also rendered as Bangalee or the Bengali people, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the ...
settled in Arakan and formed their settlements.
Kingdom of Mrauk U
 Min Saw Mon's successors in the
Min Saw Mon's successors in the Kingdom of Mrauk U
The Kingdom of Mrauk-U ( Arakanese: မြောက်ဦး နေပြည်တော်,) was a kingdom that existed on the Arakan littoral from 1429 to 1785. Based out of the capital Mrauk-U, near the eastern coast of the Bay of Bengal, t ...
sought to end the Bengal Sultanate's hegemony. Min Khayi
Min Khayi ( my, မင်းခရီ, ; also spelled Meng Khari, Arakanese pronunciation: ; also known as Ali Khan; 1392–1459) was the second king of the Mrauk-U Kingdom from 1433 to 1459.
He began his reign as a vassal of the Bengal Sulta ...
(Ali Khan) was the first to challenge Bengali hegemony. Ba Saw Phyu
Ba Saw Phyu ( my, ဘစောဖြူ, ; also spelled Ba Saw Pru, Arakanese pronunciation: ; also known as Kalima Shah; 1430–1482) was king of Arakan from 1459 to 1482. He acquired Chittagong in 1459, and put down a rebellion there in 1481 ...
(Kalima Shah) defeated Bengal Sultan Rukunuddin Barbak Shah
Ruknuddīn Bārbak Shāh ( bn, রোকনউদ্দীন বারবক শাহ, fa, ; r. 1459–1474) was the son and successor of Sultan Nasiruddin Mahmud Shah. Initially appointed as the governor of Satgaon during the reign of his fa ...
in 1459. Min Bin
Min Bin ( Arakanese and my, မင်းဘင်, , Arakanese pronunciation: ; also known as Min Ba-Gyi (မင်းဗာကြီး, , Meng Ba-Gri, Arakanese pronunciation: ); 1493–1554) was a king of Arakan from 1531 to 1554, "whose re ...
(Zabuk Shah) conquered Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in B ...
. Taking advantage of the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
's invasion campaign of Bengal, the Arakan navy and pirate
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
s dominated a coastline of 1000 miles, spanning from the Sundarbans
Sundarbans (pronounced ) is a mangrove area in the delta formed by the confluence of the Padma, Brahmaputra and Meghna Rivers in the Bay of Bengal. It spans the area from the Baleswar River in Bangladesh's division of Khulna to the Hooghly R ...
to Moulmein
Mawlamyine (also spelled Mawlamyaing; , ; th, เมาะลำเลิง ; mnw, မတ်မလီု, ), formerly Moulmein, is the fourth-largest city in Myanmar (Burma), ''World Gazetteer'' south east of Yangon and south of Thaton, at th ...
. The kingdom's coastline was frequented by Arab, Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
and Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
traders. Control of the Kaladan River
The Kaladan River ( my, ကုလားတန်မြစ်, ; also Kysapnadi, Beino, Bawinu and Kolodyne) is a river in eastern Mizoram State of India, and in Chin State and Rakhine State of western Myanmar. The Kaladan River is called the Chh ...
and Lemro River valleys led to increased international trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories because there is a need or want of goods or services. (see: World economy)
In most countries, such trade represents a significant ...
, making Mrauk U prosperous. The reigns of Min Phalaung (Sikender Shah), Min Rajagiri (Salim Shah I) and grandson Min Khamaung (Hussein Shah) strengthened the wealth and power of Mrauk U. Arakan colluded in the slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
with the Portuguese settlement in Chittagong
Chittagong, the second largest city and main port of Bangladesh, was home to a thriving trading post of the Portuguese Empire in the East in the 16th and 17th centuries. The Portuguese first arrived in Chittagong around 1528 and left in 1666 af ...
. After conquering the port city of Syriam in the early 1600s, Arakan appointed the Portuguese mercenary Philip De Brito e Nicota as the governor of Syriam. But Nicota later transferred Syriam to the authority of Portuguese India
The State of India ( pt, Estado da Índia), also referred as the Portuguese State of India (''Estado Português da Índia'', EPI) or simply Portuguese India (), was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded six years after the discovery of a se ...
.
 Even after independence from the Sultans of Bengal, the Arakanese kings continued the custom of maintaining Muslim titles. They compared themselves to
Even after independence from the Sultans of Bengal, the Arakanese kings continued the custom of maintaining Muslim titles. They compared themselves to Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
s and fashioned themselves after Mughal rulers. They also continued to employ Indians and Muslims in prestigious positions within the royal administration. The court adopted Indian and Islamic fashions from neighbouring Bengal. Mrauk U hosted mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
s, temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
s, shrine
A shrine ( la, scrinium "case or chest for books or papers"; Old French: ''escrin'' "box or case") is a sacred or holy sacred space, space dedicated to a specific deity, ancestor worship, ancestor, hero, martyr, saint, Daemon (mythology), daem ...
s, seminaries
A seminary, school of theology, theological seminary, or divinity school is an educational institution for educating students (sometimes called ''seminarians'') in scripture, theology, generally to prepare them for ordination to serve as clergy, ...
and libraries
A library is a collection of materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display purposes. A library provides physical (hard copies) or digital access (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location or a vir ...
. Syed Alaol was a renowned poet of Arakan. Indian and Muslim influence continued on Arakanese affairs for 350 years.
In 1660, Shah Shuja, the brother of Emperor Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
and a claimant of the Peacock Throne
The Peacock Throne ( Hindustani: ''Mayūrāsana'', Sanskrit: मयूरासन, Urdu: تخت طاؤس, fa, تخت طاووس, ''Takht-i Tāvūs'') was a famous jewelled throne that was the seat of the emperors of the Mughal Empire in India ...
, received asylum in Mrauk U. Members of Shuja's entourage were recruited in the Arakanese army and court. They were kingmakers in Arakan until the Burmese conquest. Arakan suffered a major defeat to the forces of Mughal Bengal
The Bengal Subah ( bn, সুবাহ বাংলা; fa, ), also referred to as Mughal Bengal ( bn, মোগল বাংলা), was the largest subdivision of the Mughal Empire (and later an independent state under the Nawabs of Beng ...
during the Battle of Chittagong in 1666, when Mrauk U lost control of southeast Bengal. The Mrauk U dynasty's reign continued until the 18th century.
Burmese conquest
TheKonbaung Dynasty
The Konbaung dynasty ( my, ကုန်းဘောင်ခေတ်, ), also known as Third Burmese Empire (တတိယမြန်မာနိုင်ငံတော်) and formerly known as the Alompra dynasty (အလောင်းဘ ...
conquered Arakan in 1784. Mrauk U was devastated during the invasion. The Burmese Empire executed thousands of men and deported a considerable portion of people from the Arakanese population to central Burma.
British Empire
 The Burmese Empire ceded Arakan to the
The Burmese Empire ceded Arakan to the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
in the 1826 Treaty of Yandabo
The Treaty of Yandabo ( my, ရန္တပိုစာချုပ် ) was the peace treaty that ended the First Anglo-Burmese War. The treaty was signed on 24February 1826, nearly two years after the war formally broke out on 5March 1824, by ...
. Arakan became one of the divisions of British India
The Divisions of British India were administrative units of the Government of the British Raj or Indian Empire.''Imperial Gazetteer of India''. Published under the authority of His Majesty's Secretary of State for India in Council. Oxford: Claren ...
. Initially governed as part of the Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency, officially the Presidency of Fort William and later Bengal Province, was a subdivision of the British Empire in India. At the height of its territorial jurisdiction, it covered large parts of what is now South Asia and ...
, it received many settlers from neighboring Chittagong Division
Chittagong Division, officially known as Chattogram Division, is geographically the largest of the eight administrative divisions of Bangladesh. It covers the south-easternmost areas of the country, with a total area of and a population at the 2 ...
. The settlers became influential in commerce, agriculture and shipping. In 1937, Arakan became part of Burma Province
( Burmese)
, conventional_long_name = Colony of Burma
, common_name = Burma
, era = Colonial era
, event_start = First Anglo-Burmese War
, year_start = 1824
, date_start = ...
, which was separated from India into a distinct crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Counci ...
. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Arakan endured the Japanese occupation of Burma
The Japanese occupation of Burma was the period between 1942 and 1945 during World War II, when Burma was occupied by the Empire of Japan. The Japanese had assisted formation of the Burma Independence Army, and trained the Thirty Comrades, who ...
. The Burma National Army
The Burma Independence Army (BIA), was a collaborationist and revolutionary army that fought for the end of British rule in Burma by assisting the Japanese in their conquest of the country in 1942 during World War II. It was the first post-c ...
and the pro-British V Force
V Force was a reconnaissance, intelligence-gathering and guerrilla organisation established by the British against Japanese forces during the Burma Campaign in World War II.
Establishment and organisation
In April 1942, when the Japanese drove t ...
were active in the region. Sectarian tensions flared during the Arakan massacres in 1942. Japanese rule ended with the successful Burma Campaign by Allied forces.
During British rule, Arakan Division was one of the largest rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
exporters in the world. The division's seaport and capital Akyab were dominated by Arakanese Indians, which caused tension with Arakanese Burmese. Both groups were represented as natives in the Legislative Council of Burma
The Legislative Council of Burma was the legislative body of British Burma from 1897 to 1936.
Establishment
It was established in 1897 as an advisory council to the British colonial governor, the Lieutenant-Governor of Burma, in drafting legisl ...
and the Legislature of Burma
The Burma Legislature was the legislative body of British Burma from 1936 to 1947. As an elected body, the Legislature of Burma was a bicameral legislature consisting of the 36-seat Senate and the 132-seat House of Representatives.
Establishment ...
. In the 1940s, Arakanese Muslims appealed to Muhammad Ali Jinnah
Muhammad Ali Jinnah (, ; born Mahomedali Jinnahbhai; 25 December 1876 – 11 September 1948) was a barrister, politician, and the founder of Pakistan. Jinnah served as the leader of the All-India Muslim League from 1913 until the ...
to incorporate the townships of the Mayu River valley into the Dominion of Pakistan
Between 14 August 1947 and 23 March 1956, Pakistan was an independent federal dominion in the Commonwealth of Nations, created by the passing of the Indian Independence Act 1947 by the British parliament, which also created the Dominion of I ...
.
Burmese independence
Arakan became one of theUnion of Burma
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
's divisions after independence from British rule. Burma was a parliamentary democracy
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
until the 1962 Burmese coup d'état
The 1962 Burmese coup d'état on 2 March 1962 marked the beginning of one-party rule and the political dominance of the army in Burma (now Myanmar) which spanned the course of 26 years. In the coup, the military replaced the civilian AFPFL-g ...
. The northern part of Arakan was governed by the central government in Rangoon
Yangon ( my, ရန်ကုန်; ; ), formerly spelled as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar (also known as Burma). Yangon served as the capital of Myanmar until 2006, when the military government ...
in the early 1960s. Known as the Mayu Frontier District
The Mayu Frontier District ( my, မေယုနယ်ခြားခရိုင်) was a short-lived administrative zone of Burma (present-day Myanmar) which existed between 1961 and 1964. It covered the Maungdaw District of present-day Rakhine ...
, it covered townships near the border with East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a Pakistani province established in 1955 by the One Unit Scheme, One Unit Policy, renaming the province as such from East Bengal, which, in modern times, is split between India and Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India ...
.
In 1982, the Burmese junta
Junta may refer to:
Government and military
* Junta (governing body) (from Spanish), the name of various historical and current governments and governing institutions, including civil ones
** Military junta, one form of junta, government led by ...
enacted the Burmese nationality law
The Nationality law of Myanmar currently recognises three categories of citizens, namely citizen, associate citizen and naturalised citizen, according to the 1982 Citizenship Law. Citizens, as defined by the 1947 Constitution, are persons who b ...
which did not recognize Arakanese Indians as one of Burma's ethnic groups, thereby stripping them of their citizenship. In 1989, the Burmese government altered the country's name from Burma to Myanmar. In the 1990s, the State Peace and Development Council
The State Peace and Development Council ( my, နိုင်ငံတော် အေးချမ်းသာယာရေး နှင့် ဖွံ့ဖြိုးရေး ကောင်စီ ; abbreviated SPDC or , ) was the offi ...
changed the name of Arakan State to Rakhine State
Rakhine State (; , , ; formerly known as Arakan State) is a Administrative divisions of Myanmar, state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady R ...
. The province was renamed after the Rakhine ethnic group. However, the new name is not accepted as legitimate by many in both the Rakhine and Rohingya
The Rohingya people () are a stateless Indo-Aryan ethnic group who predominantly follow Islam and reside in Rakhine State, Myanmar (previously known as Burma). Before the Rohingya genocide in 2017, when over 740,000 fled to Bangladesh, an ...
communities, instead preferring the historical term Arakan.
Rakhine-led groups like the Arakan Liberation Army
The Arakan Liberation Army ( my, ရခိုင်ပြည် လွတ်မြောက်ရေး တပ်မတော်; abbreviated ALA) is a Rakhine insurgent group in Myanmar (Burma). It is the armed wing of the Arakan Liberation ...
have sought independence for the region. Other groups, including the Arakan Rohingya National Organization
The Arakan Rohingya National Organisation (ARNO) is a Rohingya political organisation based in London, United Kingdom.
Ideology
The proclaimed beliefs and objectives of ARNO are as follows:
* The right of self-determination of the Rohingya p ...
, have demanded autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ...
. The region witnessed military crackdowns during Operation King Dragon in 1978; in 1991 and 1992 after the 8888 uprising
The 8888 Uprising ( my, ၈၈၈၈ အရေးအခင်း), also known as the People Power UprisingYawnghwe (1995), pp. 170 and the 1988 Uprising, was a series of nationwide protests, marches, and riots in Burma (present-day Myanmar) th ...
and 1990 Burmese general election
General elections were held in Myanmar on 27 May 1990, the first multi-party elections since 1960, after which the country had been ruled by a military dictatorship. The elections were for a parliament-sized constitutional committee to draft ...
; the 2012 Rakhine State riots
The 2012 Rakhine State riots were a series of conflicts primarily between ethnic Rakhine Buddhists and Rohingya Muslims in northern Rakhine State, Myanmar, though by October Muslims of all ethnicities had begun to be targeted. The riots start ...
, the 2015 Rohingya refugee crisis
In 2015, tens of thousands of Rohingya people were forcibly displaced from their villages and IDP camps in Rakhine State, Myanmar, due to sectarian violence. Some fled to neighbouring Bangladesh, but most travelled to Southeast Asian countrie ...
and Rohingya persecution in Myanmar (2016-present).
Geography
Lower Burma
Lower Myanmar ( my, အောက်မြန်မာပြည်, also called Lower Burma) is a geographic region of Myanmar and includes the low-lying Irrawaddy Delta (Ayeyarwady Region, Ayeyarwady, Bago Region, Bago and Yangon Regions), as we ...
. It comprises a long narrow strip of land along the eastern seaboard of the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between ...
and stretches from the Naf River
The Naf River ( bn, নাফ নদী ''Naf Nodi'' ; my, နတ်မြစ် ; rki, ) is an international river marking the border of southeastern Bangladesh and northwestern Myanmar.
Geography
The Naf River's average depth is , and ma ...
estuary on the border of the Chittagong Hills area (in Bangladesh) in the north to the Gwa River in the south. The Arakan region is about 400 miles (640 km) long from north to south and is about 90 miles (145 km) wide at its broadest. The Arakan Mountains
The Arakan Mountains ( my, ရခိုင်ရိုးမ), also known as the Rakhine Yoma, are a mountain range in western Myanmar, between the coast of Rakhine State and the Central Myanmar Basin, in which flows the Irrawaddy River. It is th ...
(also called Arakan Yoma), a range that forms the eastern boundary of the region, isolates Arakan from the rest of Burma. The coast has several sizable offshore islands, including Cheduba
Cheduba Island ( my, မာန်အောင်ကျွန်း; also known as Manaung Island) is an island in the Bay of Bengal close to Ramree Island and belongs to Myanmar, formerly Burma. It has a maximum length of , with an area of approxi ...
and Ramree. The region's principal rivers are the Nāf estuary and the Mayu Mayu may refer to:
* Mayu (given name), a feminine Japanese given name
* Mayu (river), a river of Burma
* Mayu Frontier District, a former administrative zone of Burma
* Mayu Island (妈屿), Shantou, China
* Mayu, Jinzhou, Hebei (马于镇), a tow ...
, Kaladan, and Lemro rivers. One-tenth of Arakan's generally hilly land is cultivated. Rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
is the dominant crop in the delta areas, where most of the population is concentrated. Other crops include fruits, chilies, dha and tobacco.
The main towns are coastal and include Sittwe
Sittwe (; ; formerly Akyab) is the capital of Rakhine State, Myanmar (Burma). Sittwe, pronounced ''sait-tway'' in the Rakhine language, is located on an estuarial island created at the confluence of the Kaladan, Mayu, and Lay Mro rivers emptyi ...
(Akyab), Sandoway
Thandwe ("Thandway" in Arakanese; ; formerly Sandoway) is a town and major seaport in Rakhine State, the westernmost part of Myanmar. Thandwe is very ancient, and is said to have been at one time the capital of Rakhine State, then called Arakan. ...
, Kyaukpyu
Kyaukpyu ( my, ကျောက်ဖြူမြို့ ; also spelt Kyaukphyu) is a major town in Rakhine State, in western Myanmar. It is located on the north western corner of Yanbye Island on Combermere Bay, and is 250 miles (400 ...
and Taungup
Taungup, Toungup or Toungok ( my, တောင်ကုတ်မြို့) is a principal town of the Taungup Township in the Rakhine State of westernmost part of Myanmar. As of May 2020, there is one case of COVID-19, one of two cases in not ...
.
Demographics
The people of Arakan have historically been called the Arakanese. The population consists ofTibeto-Burman
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people spea ...
s and Indo-Aryans
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of Indo-European peoples speaking Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent. Historically, Aryan were the Indo-European pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and intr ...
. Tibeto-Burman Arakanese mostly speak the Arakanese language
, pronunciation =
, ethnicity = Rakhine, Kamein
, states = Myanmar, Bangladesh, India
, region = * Rakhine State (Myanmar)
* Bandarban, Khagrachari, Patuakhali, Barguna (Bangladesh)
* Tripura (India)
, speaker ...
, also known as ''Rakhine'' and closely related to Burmese. Most Indo-Aryan Arakanese speak the Rohingya language
Rohingya (), also known as Ruáingga ( Hanifi Rohingya: ; ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Rohingya people of Rakhine State, Myanmar. It is an Eastern Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Bengali–Assamese branch, and is closely r ...
. Other languages spoken by smaller communities in Rakhine state include the Tibeto-Burman Chak, Asho Chin, Ekai, Kumi, Laitu, Mru, Songlai, Sumtu and Uppu
''Uppu'' ( ml, ഉപ്പ്, en, Salt, french: Le Sel) is a 1987 Indian Malayalam film, directed by V. K. Pavithran and written by K. M. A. Rahim. The film is about the atavistic Muslim practice of male polygamy. The film is entirely on t ...
, as well as the Indo-Aryan Chakma.
The government of Myanmar
Myanmar ( also known as Burma) operates ''de jure'' as a unitary assembly-independent republic under its 2008 constitution. On 1 February 2021, Myanmar's military took over the government in a coup, causing ongoing anti-coup protests.
P ...
recognizes Tibeto-Burman Arakanese as the Rakhine people
The Rakhine people ( my, ရက္ခိုင်လူမျိုး, : , ), also known as the Arakanese people, are a Southeast Asian ethnic group in Myanmar (Burma) forming the majority along the coastal region of present-day Rakhine Stat ...
. It also recognizes sections of the Muslim community, including the Kamein
The Kamein ( my, ကမန်လူမျိုး), also known as the Kaman (), are a Southeast Asian ethnic group indigenous to Rakhine State, Myanmar, where they primarily reside in, and who predominantly follow Islam. The name ''Kaman'' comes ...
. But Myanmar does not recognize the Rohingya
The Rohingya people () are a stateless Indo-Aryan ethnic group who predominantly follow Islam and reside in Rakhine State, Myanmar (previously known as Burma). Before the Rohingya genocide in 2017, when over 740,000 fled to Bangladesh, an ...
.
Arakan Division had the largest percentage of Indians in British Burma
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
.
See also
* Military history of Arakan *History of Southeast Asia
The history of Southeast Asia covers the people of Southeast Asia from prehistory to the present in two distinct sub-regions: Mainland Southeast Asia (or Indochina) and Maritime Southeast Asia (or Insular Southeast Asia). Mainland Southeast As ...
References
Sources
* * *External links
*{{commons category-inline . Historical regions in Myanmar Regions of Myanmar Former countries in Burmese history