Agrigento on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of
 Theron, a member of the Emmenid family, made himself tyrant of Acragas around 488 BC. He formed an alliance with
Theron, a member of the Emmenid family, made himself tyrant of Acragas around 488 BC. He formed an alliance with
 The period after the fall of the Emmenids is not well-known. An
The period after the fall of the Emmenids is not well-known. An

 The other temples are much more fragmentary, having been toppled by earthquakes long ago and quarried for their stones. The largest by far is the Temple of Olympian Zeus, built to commemorate the Battle of Himera in 480 BC: it is believed to have been the largest Doric temple ever built. Although it was apparently used, it appears never to have been completed; construction was abandoned after the Carthaginian invasion of 406 BC.
The other temples are much more fragmentary, having been toppled by earthquakes long ago and quarried for their stones. The largest by far is the Temple of Olympian Zeus, built to commemorate the Battle of Himera in 480 BC: it is believed to have been the largest Doric temple ever built. Although it was apparently used, it appears never to have been completed; construction was abandoned after the Carthaginian invasion of 406 BC.
 The remains of the temple were extensively quarried in the 18th century to build the jetties of
The remains of the temple were extensively quarried in the 18th century to build the jetties of 
 Many other Hellenistic and Roman sites can be found in and around the town. These include a pre-Hellenic cave sanctuary near a Temple of Demeter, over which the Church of San Biagio was built. A late Hellenistic funerary monument erroneously labelled the "Tomb of Theron" is situated just outside the sacred area, and a 1st-century AD '' heroon'' (heroic shrine) adjoins the 13th century Church of San Nicola a short distance to the north. A sizeable area of the Greco-Roman city has also been excavated, and several classical
Many other Hellenistic and Roman sites can be found in and around the town. These include a pre-Hellenic cave sanctuary near a Temple of Demeter, over which the Church of San Biagio was built. A late Hellenistic funerary monument erroneously labelled the "Tomb of Theron" is situated just outside the sacred area, and a 1st-century AD '' heroon'' (heroic shrine) adjoins the 13th century Church of San Nicola a short distance to the north. A sizeable area of the Greco-Roman city has also been excavated, and several classical
Yair Karelic's photos of the Valley of the TemplesAgrigento Old Town
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Sicily Municipalities of the Province of Agrigento 580s BC Dorian colonies in Magna Graecia Colonies of Gela 6th-century BC establishments in Italy Populated places established in the 6th century BC
 Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento
The Province of Agrigento ( it, Provincia di Agrigento; scn, Pruvincia di Girgenti; officially ''Libero consorzio comunale di Agrigento'') is a province in the autonomous island region of Sicily in Italy, situated on its south-western coast. Follo ...
. It was one of the leading cities of Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia (, ; , , grc, Μεγάλη Ἑλλάς, ', it, Magna Grecia) was the name given by the Romans to the coastal areas of Southern Italy in the present-day Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania and Sicily; these re ...
during the golden age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the ''Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages of Man, Ages, Gold being the first and the one during ...
of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
BC.
History
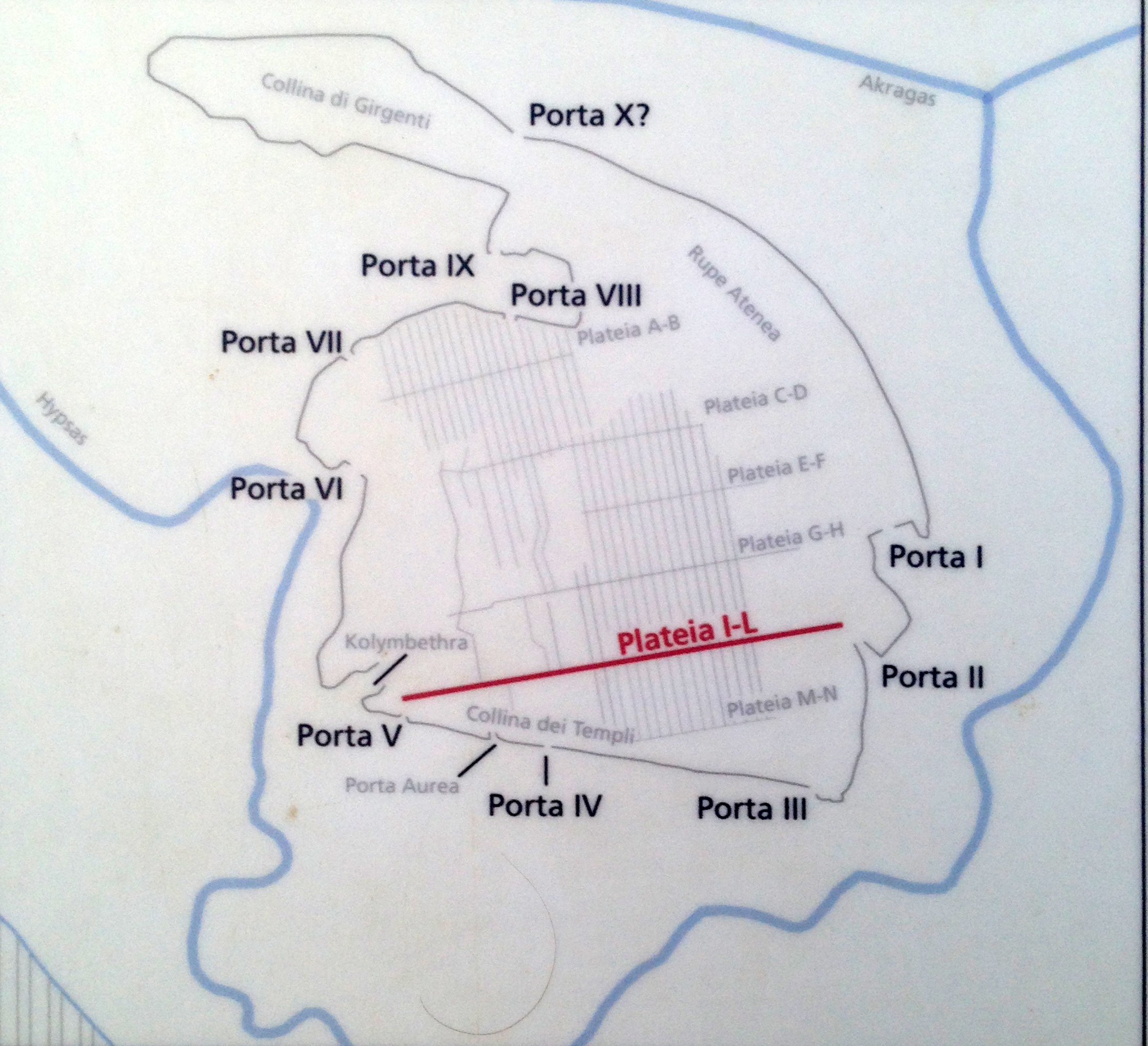
Akragas was founded on a plateau overlooking the sea, with two nearby rivers, the Hypsas and the Acragas, after which the settlement was originally named. A ridge, which offered a degree of natural fortification, links a hill to the north called Colle di Girgenti with another, called Rupe Atenea, to the east. According toThucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His ''History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of "scientifi ...
, it was founded around 582-580 BC by Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
colonists from Gela
Gela (Sicilian and ; grc, Γέλα) is a city and (municipality) in the Autonomous Region of Sicily, Italy; in terms of area and population, it is the largest municipality on the southern coast of Sicily. Gela is part of the Province of Cal ...
in eastern Sicily, with further colonists from Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
and Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the So ...
. The founders ( ''oikistai'') of the new city were Aristonous and Pystilus. It was the last of the major Greek colonies in Sicily to be founded.
Archaic period
The territory under Akragas's control expanded to comprise the whole area between the Platani and theSalso
The Salso ( Sicilian: ''Salsu''), also known as the Imera Meridionale (Greek: ; Latin Himera), is a river of Sicily. It rises in the Madonie Mountains (Latin: Nebrodes Mons; Sicilian: Munti Madunìi) and, traversing the provinces of Enna and Ca ...
, and reached deep into the Sicilian interior. Greek literary sources connect this expansion with military campaigns, but archaeological evidence indicates that this was a much longer term process which reached its peak only in the early fifth century BC. Most other Greek settlements in Sicily experienced similar territorial expansion in this period. Excavations at a range of sites in this region inhabited by the indigenous Sican people, such as Monte Sabbucina, Gibil-Gabil, Vasallaggi, San Angelo Muxano, and Mussomeli
Mussomeli (''Mussumeli'' in Sicilian) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Caltanissetta, Sicily, Italy.
History
Mussomeli is claimed to have been founded in the 14th century by Manfredo III Chiaramonte with the name Manfredi, but later ...
, show signs of the adoption of Greek culture. It is disputed how much of this expansion was carried out by violence and how much by commerce and acculturation. The territorial expansion provided land for the Greek settlers to farm, native slaves
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
to work these farms, and control of the overland route from Acragas to the city of Himera
Himera (Greek language, Greek: ), was a large and important ancient Greece, ancient Greek city, situated on the north coast of Sicily at the mouth of the river of the same name (the modern Imera Settentrionale), between Panormus (modern Palermo) ...
on the northern coast of Sicily. This was the main land route from the Straits of Sicily to the Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea (; it, Mar Tirreno , french: Mer Tyrrhénienne , sc, Mare Tirrenu, co, Mari Tirrenu, scn, Mari Tirrenu, nap, Mare Tirreno) is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy. It is named for the Tyrrhenian pe ...
and Acragas' control of it was a key factor in its economic prosperity in the sixth and fifth centuries BC, which became proverbial. Famously, Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, upon seeing the living standard of the inhabitants, was said to have remarked that "they build like they intend to live forever, yet eat like this is their last day." Perhaps as a result of this wealth, Acragas was one of the first communities in Sicily to begin minting its own coinage, around 520 BC.
Around 570 BC, the city came under the control of Phalaris
Phalaris ( el, Φάλαρις) was the tyrant of Akragas (now Agrigento) in Sicily, from approximately 570 to 554 BC.
History
Phalaris was renowned for his excessive cruelty. Among his alleged atrocities is cannibalism: he was said to have e ...
, a semi-legendary figure, who was remembered as the archetypal tyrant
A tyrant (), in the modern English usage of the word, is an absolute ruler who is unrestrained by law, or one who has usurped a legitimate ruler's sovereignty. Often portrayed as cruel, tyrants may defend their positions by resorting to rep ...
, said to have killed his enemies by burning them alive inside a bronze bull. In the ancient literary sources, he is linked with the military campaigns of territorial expansion, but this is probably anachronistic. He ruled until around 550 BC. The political history of Acragas in the second half of the sixth century is unknown, except for the names of two leaders, Alcamenes and Alcander. Acragas also expanded westwards over the course of the sixth century BC, leading to a rivalry with Selinus
Selinunte (; grc, Σελῑνοῦς, Selīnoûs ; la, Selīnūs , ; scn, Silinunti ) was a rich and extensive ancient Greek city on the south-western coast of Sicily in Italy. It was situated between the valleys of the Cottone and Modion ...
, the next Greek city to the west. The Selinuntines founded the city of Heraclea Minoa
Heraclea Minoa ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλεια Μινῴα, ''Hērákleia Minṓia''; it, Eraclea Minoa) was an ancient Greek city situated on the southern coast of Sicily near the mouth of the river Halycus (modern Platani), 25 km west of A ...
at the mouth of the Platani river, halfway between the two settlements, in the mid-sixth century BC, but the Acragantines conquered it around 500 BC.
Emmenid period
 Theron, a member of the Emmenid family, made himself tyrant of Acragas around 488 BC. He formed an alliance with
Theron, a member of the Emmenid family, made himself tyrant of Acragas around 488 BC. He formed an alliance with Gelon
Gelon also known as Gelo (Greek: Γέλων ''Gelon'', ''gen.'': Γέλωνος; died 478 BC), son of Deinomenes, was a Greek tyrant of the Sicilian cities Gela and Syracuse, and first of the Deinomenid rulers.
Early life
Gelon was the son o ...
, tyrant of Gela and Syracuse. Around 483 BC, Theron invaded and conquered Himera, Acragas’ neighbour to the north. The tyrant of Himera, Terillus
Terillus ( el, Τήριλλος; fl. early 5th century BC) was a son of Crinippus, tyrant of Himera, in Sicily.
Nothing is known about how Terillus rose to power. Nor is there any information available to historians about the duration or events ...
joined his son-in-law, Anaxilas
Anaxilas or Anaxilaus ( grc-gre, Ἀναξίλας, Ἀναξίλαος), son of Cretines, was a tyrant of Rhegium (modern Reggio Calabria). He was originally from Messenia, a region in the Peloponnese.
Life
Anaxilas was master of Rhegium in 494 ...
of Rhegium
Reggio di Calabria ( scn, label= Southern Calabrian, Riggiu; el, label=Calabrian Greek, Ρήγι, Rìji), usually referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the largest city in Calabria. It has an estimated popula ...
, and the Selinuntines in calling on the Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
to come and restore Terillus to power. The Carthaginians did invade in 480 BC, the first of the Greco-Punic Wars, but they were defeated by the combined forces of Theron and Gelon at the Battle of Himera. As a result, Acragas was affirmed in its control of the central portion of Sicily, an area of around 3,500 km2. A number of enormous construction projects were carried out in the Valle dei Templi
The Valle dei Templi (; scn, Vaddi di li Tempri), or Valley of the Temples, is an archaeological site in Agrigento (ancient Greek ''Akragas''), Sicily. It is one of the most outstanding examples of ancient Greek art and architecture, and is one ...
at this time, including the Temple of Olympian Zeus, which was one of the largest Greek temples ever built, and the construction of a massive Kolymbethra reservoir. According to Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
, they were built in commemoration of the Battle of Himera, using the prisoners captured in the war as slave labour. Archaeological evidence indicates that the boom in monumental construction actually began before the battle, but continued in the period after it. A major reconstruction of the city walls on a monumental scale also took place in this period. Theron sent teams to compete in the Olympic games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a var ...
and other Panhellenic competitions in mainland Greece. Several poems by Pindar
Pindar (; grc-gre, Πίνδαρος , ; la, Pindarus; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar is ...
and Simonides
Simonides of Ceos (; grc-gre, Σιμωνίδης ὁ Κεῖος; c. 556–468 BC) was a Greek lyric poet, born in Ioulis on Kea (island), Ceos. The scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria included him in the canonical list of the nine lyric p ...
commemorated victories by Theron and other Acragantines, which provide insights into Acragantine identity and ideology at this time. Greek literary sources generally praise Theron as a good tyrant, but accuse his son Thrasydaeus
Thrasydaeus ( grc, Θρασυδαῖος), tyrant of Agrigentum, was the son and successor of Theron. Already during his father's lifetime he had been appointed to the government of Himera, where, by his violent and arbitrary conduct, he alienated ...
, who succeeded him in 472 BC, of violence and oppression. Shortly after Theron's death, Hiero I of Syracuse
Hieron I ( el, Ἱέρων Α΄; usually Latinized Hiero) was the son of Deinomenes, the brother of Gelon and tyrant of Syracuse in Sicily from 478 to 467 BC. In succeeding Gelon, he conspired against a third brother, Polyzelos.
Life
During hi ...
(brother and successor of Gelon) invaded Acragas and overthrew Thrasydaeus. The literary sources say that Acragas then became a democracy, but in practice it seems to have been dominated by the civic aristocracy.
Classical and Hellenistic periods

oligarchic
Oligarchy (; ) is a conceptual form of power structure in which power rests with a small number of people. These people may or may not be distinguished by one or several characteristics, such as nobility, fame, wealth, education, or corporate, r ...
group called "the thousand" was in power for a few years in the mid-fifth century BC, but was overthrown - the literary tradition gives the philosopher Empedocles
Empedocles (; grc-gre, Ἐμπεδοκλῆς; , 444–443 BC) was a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is best known for originating the cosmogonic theory of the fo ...
a decisive role in this revolution, but some modern scholars have doubted this. In 451 BC, Ducetius
Ducetius ( grc, Δουκέτιος) (died 440 BCE) was a Hellenized leader of the Sicels and founder of a united Sicilian state and numerous cities.LiviusDucetius of Sicily Retrieved on 25 April 2006. It is thought he may have been born around th ...
, leader of a Sicel
The Sicels (; la, Siculi; grc, Σικελοί ''Sikeloi'') were an Italic tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily during the Iron Age. Their neighbours to the west were the Sicani. The Sicels gave Sicily the name it has held since antiquity, b ...
state opposed to the expansion of Syracuse and other Greeks into the interior of Sicily invaded Acragantine territory, conquering an outpost called Motyum. Ducetius was defeated in 450, but the Syracusan decision to let Ducetius go outraged the Acragantines and they went to war with Syracuse. They were defeated in a battle on the Salso river, which left Syracuse the pre-eminent power in eastern Sicily. The defeat was serious enough that Acragas ceased to mint coinage for a number of years.
Ancient sources considered Acragas to be a very large city at this time. Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
says that the population was 200,000 people, of which 20,000 were citizens. Diogenes Laertius
Diogenes Laërtius ( ; grc-gre, Διογένης Λαέρτιος, ; ) was a biographer of the Greek philosophers. Nothing is definitively known about his life, but his surviving ''Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers'' is a principal sour ...
put the population at an incredible 800,000. Some modern scholars have accepted Diodorus' numbers, but they seem to be far too high. Jos de Waele suggests a population of 16,000-18,000 citizens, while Franco de Angelis estimates a total population of around 30,000-40,000.
When Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
undertook the Sicilian Expedition
The Sicilian Expedition was an Athenian military expedition to Sicily, which took place from 415–413 BC during the Peloponnesian War between Athens on one side and Sparta, Syracuse and Corinth on the other. The expedition ended in a devas ...
against Syracuse from 415-413 BC, Acragas remained neutral. However, it was sacked by the Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
in 406 BC. Acragas never fully recovered its former status, though it revived following the invasion of Timoleon
Timoleon (Ancient Greek language, Greek: wikt:Τιμολέων, Τιμολέων), son of Timodemus, of Ancient Corinth, Corinth (c. 411–337 BC) was a Greek statesman and general.
As a brilliant general, a champion of Greece against Anci ...
in the late fourth century onwards and large-scale construction took place in the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
. During the early 3rd century BC, a tyrant called Phintias declared himself king in Akragas, also controlling a variety of other cities. His kingdom was however not long-lived.
Roman period
The city was disputed between theRomans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
and the Carthaginians during the First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
. The Romans laid siege to the city in 262 BC and captured it after defeating a Carthaginian relief force in 261 BC and sold the population into slavery. Although the Carthaginians recaptured the city in 255 BC the final peace settlement gave Punic Sicily and with it Akragas to Rome. It suffered badly during the Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
(218–201 BC) when both Rome and Carthage fought to control it. The Romans eventually captured Akragas in 210 BC and renamed it ''Agrigentum'', although it remained a largely Greek-speaking community for centuries thereafter. It became prosperous again under Roman rule and its inhabitants received full Roman citizenship following the death of Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
in 44 BC.
Middle Ages
After thefall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rul ...
, the city successively passed into the hands of the Vandalic Kingdom, the Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), existed under the control of the Germanic peoples, Germanic Ostrogoths in Italian peninsula, Italy and neighbouring areas from 493 to 553.
In Italy, the Ostrogoths led by Theodoric the ...
of Italy and then the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. During this period the inhabitants of Agrigentum largely abandoned the lower parts of the city and moved to the former acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens, ...
, at the top of the hill. The reasons for this move are unclear but were probably related to the destructive coastal raids of the Saracens
file:Erhard Reuwich Sarazenen 1486.png, upright 1.5, Late 15th-century Germany in the Middle Ages, German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek language, Greek and Latin writings, to refer ...
and other peoples around this time. In 828 AD the Saracens captured the diminished remnant of the city; the Arabic form of its name became () or ().
Following the Norman conquest of Sicily
The Norman conquest of southern Italy lasted from 999 to 1139, involving many battles and independent conquerors.
In 1130, the territories in southern Italy united as the Kingdom of Sicily, which included the island of Sicily, the southern th ...
, the city changed its name to the Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
version ''Girgenti''. In 1087, Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
Count Roger I established a Latin bishopric in the city. Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Fran ...
built the Castello di Agrigento to control the area. The population declined during much of the medieval period but revived somewhat after the 18th century.
Modern period
In 1860, as in the rest of Sicily, the inhabitants supported the arrival ofGiuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as ''Gioxeppe Gaibado''. In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as ''Jousé'' or ''Josep''. 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, patr ...
during the Expedition of the Thousand
The Expedition of the Thousand ( it, Spedizione dei Mille) was an event of the Italian Risorgimento that took place in 1860. A corps of volunteers led by Giuseppe Garibaldi sailed from Quarto, near Genoa (now Quarto dei Mille) and landed in Ma ...
(one of the most dramatic events of the Unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century Political movement, political and social movement that resulted in the Merger (politics), consolidation of List of historic stat ...
) which marked the end of Bourbon Bourbon may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bourbon whiskey, an American whiskey made using a corn-based mash
* Bourbon barrel aged beer, a type of beer aged in bourbon barrels
* Bourbon biscuit, a chocolate sandwich biscuit
* A beer produced by Bras ...
rule. In 1927, Benito Mussolini through the "Decree Law n. 159, July 12, 1927" introduced the current Italianized version of the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
name. The decision remains controversial as a symbol of Fascism and the eradication of local history. Following the suggestion of Andrea Camilleri
Andrea Calogero Camilleri (; 6 September 1925 – 17 July 2019) was an Italian writer.
Biography
Originally from Porto Empedocle, Girgenti, Sicily, Camilleri began university studies in the Faculty of Literature at the University of Palermo, b ...
, a Sicilian writer of Agrigentine origin, the historic city centre was renamed to the Sicilian name "Girgenti" in 2016. The city suffered a number of destructive bombing raids during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
.
Economy
Agrigento is a major tourist centre due to its extraordinarily rich archaeological legacy. It also serves as an agricultural centre for the surrounding region.Sulphur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
and potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.
were mined locally from Minoan
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age Aegean civilization on the island of Crete and other Aegean Islands, whose earliest beginnings were from 3500BC, with the complex urban civilization beginning around 2000BC, and then declining from 1450B ...
times until the 1970s, and were exported worldwide from the nearby harbour of Porto Empedocle
Porto Empedocle ( scn, 'a Marina) is a town and ''comune'' in Italy on the coast of the Strait of Sicily, administratively part of the province of Agrigento. It was named after Empedocles, a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of the ci ...
(named after the philosopher Empedocles
Empedocles (; grc-gre, Ἐμπεδοκλῆς; , 444–443 BC) was a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is best known for originating the cosmogonic theory of the fo ...
, who lived in ancient Akragas). In 2010, the unemployment rate
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the referen ...
in Agrigento was 19.2%, almost twice the national average.
Main sights
Ancient Akragas covers a huge area—much of which is still unexcavated today—but is exemplified by the famous ''Valle dei Templi'' ("Valley of the Temples", a misnomer, as it is a ridge, rather than a valley). This comprises a large sacred area on the south side of the ancient city where seven monumental Greek temples in theDoric style
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of col ...
were constructed during the 6th and 5th centuries BC. Now excavated and partially restored, they constitute some of the largest and best-preserved ancient Greek buildings outside of Greece itself. They are listed as a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
.
The best-preserved of the temples are two very similar buildings traditionally attributed to the goddesses Hera Lacinia and Concordia (though archaeologists believe this attribution to be incorrect). The latter temple is remarkably intact, due to its having been converted into a Christian church in 597 AD. Both were constructed to a peripteral
A peripteros (a peripteral building, grc-gre, περίπτερος) is a type of ancient Greek or Roman temple surrounded by a portico with columns. It is surrounded by a colonnade ('' pteron'') on all four sides of the ''cella'' (''naos''), crea ...
hexastyle
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cult ...
design. The area around the Temple of Concordia
The Temple of Concordia ( it, Tempio della Concordia) is an ancient Greek temple in the Valle dei Templi (Valley of the Temples) in Agrigento (Greek: Akragas) on the south coast of Sicily, Italy. It is the largest and best-preserved Doric temple ...
was later re-used by early Christians as a catacomb
Catacombs are man-made subterranean passageways for religious practice. Any chamber used as a burial place is a catacomb, although the word is most commonly associated with the Roman Empire.
Etymology and history
The first place to be referred ...
, with tombs hewn out of the rocky cliffs and outcrops.
 The remains of the temple were extensively quarried in the 18th century to build the jetties of
The remains of the temple were extensively quarried in the 18th century to build the jetties of Porto Empedocle
Porto Empedocle ( scn, 'a Marina) is a town and ''comune'' in Italy on the coast of the Strait of Sicily, administratively part of the province of Agrigento. It was named after Empedocles, a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of the ci ...
. Temples dedicated to Hephaestus
Hephaestus (; eight spellings; grc-gre, Ἥφαιστος, Hḗphaistos) is the Greek god of blacksmiths, metalworking, carpenters, craftsmen, artisans, sculptors, metallurgy, fire (compare, however, with Hestia), and volcanoes.Walter Burk ...
, Heracles
Heracles ( ; grc-gre, Ἡρακλῆς, , glory/fame of Hera), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive ...
and Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of ...
were also constructed in the sacred area, which includes a sanctuary of Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter (; Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although s ...
and Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after ...
(formerly known as the Temple of Castor and Pollux); the marks of the fires set by the Carthaginians in 406 BC can still be seen on the sanctuary's stones.
 Many other Hellenistic and Roman sites can be found in and around the town. These include a pre-Hellenic cave sanctuary near a Temple of Demeter, over which the Church of San Biagio was built. A late Hellenistic funerary monument erroneously labelled the "Tomb of Theron" is situated just outside the sacred area, and a 1st-century AD '' heroon'' (heroic shrine) adjoins the 13th century Church of San Nicola a short distance to the north. A sizeable area of the Greco-Roman city has also been excavated, and several classical
Many other Hellenistic and Roman sites can be found in and around the town. These include a pre-Hellenic cave sanctuary near a Temple of Demeter, over which the Church of San Biagio was built. A late Hellenistic funerary monument erroneously labelled the "Tomb of Theron" is situated just outside the sacred area, and a 1st-century AD '' heroon'' (heroic shrine) adjoins the 13th century Church of San Nicola a short distance to the north. A sizeable area of the Greco-Roman city has also been excavated, and several classical necropoleis
A necropolis (plural necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'', literally meaning "city of the dead".
The term usually im ...
and quarries are still extant.
Much of present-day Agrigento is modern but it still retains a number of medieval and Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
buildings. These include the 14th century cathedral and the 13th century Church of Santa Maria dei Greci ("St. Mary of the Greeks"), again standing on the site of an ancient Greek temple (hence the name). The town also has a notable archaeological museum displaying finds from the ancient city.
People
*Empedocles
Empedocles (; grc-gre, Ἐμπεδοκλῆς; , 444–443 BC) was a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is best known for originating the cosmogonic theory of the fo ...
(5th Century BC), the Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrates. Pre-Socratic philosophers were mostly interested in cosmology, the beginning and the substance of the universe, but the inquiries of thes ...
, was a citizen of ancient ''Akragas''.
* Tellias ( grc, Τελλίας) of Akragas, described in ancient sources as a hospitable man; when 500 horsemen were billeted with him during the winter, he gave each a tunic and cloak.
* Karkinos ( grc, Καρκίνος) of Akragas, a tragedian
* Tigellinus
Ofonius Tigellinus (c. 10 – 69) was a prefect of the Roman imperial bodyguard, known as the Praetorian Guard, from 62 until 68, during the reign of emperor Nero. Tigellinus gained imperial favour through his acquaintance wit ...
(born c10 AD), a Prefect of the Praetorian Guard
The Praetorian Guard (Latin: ''cohortēs praetōriae'') was a unit of the Imperial Roman army that served as personal bodyguards and intelligence agents for the Roman emperors. During the Roman Republic, the Praetorian Guard were an escort fo ...
and infamous associate of the Emperor Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68), was the fifth Roman emperor and final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 un ...
, belonged to a family of Greek descent in Agrigento - although he may have been born in Scyllaceum
Scylletium or Scolacium was an ancient seaside city in Calabria, southern Italy. Its ruins can be found at the ''frazione'' of Roccelletta, in the ''comune'' of Borgia, near Catanzaro, facing the Gulf of Squillace.
History
Scylletium was situat ...
in Southern Italy, where his father is supposed to have lived in exile.
* Paolo Girgenti
Paolo Girgenti (1767/69 – 1819) was an Italian painter of the late 18th and early 19th-centuries, active in Naples.
He was born in Agrigento, Sicily, known in Sicilian language as ''Girgenti''. He studied, along with a Giuseppe Camerata from S ...
(1767–1815), a painter active in Naples who served as president of the Accademia di Belle Arti di Napoli
The Accademia di Belle Arti di Napoli (Naples Academy of Fine Arts) is a university-level art school in Naples. In the past it has been known as the Reale Istituto di Belle Arti and the Reale Accademia di Belle Arti. Founded by King Charles VII ...
, was born in Agrigento.
* Luigi Pirandello
Luigi Pirandello (; 28 June 1867 – 10 December 1936) was an Italian dramatist, novelist, poet, and short story writer whose greatest contributions were his plays. He was awarded the 1934 Nobel Prize in Literature for "his almost magical power ...
(1867-1936), dramatist and Nobel prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
winner for literature, was born at contrada
A (plural: ) is a subdivision (of various types) of Italian city, now unofficial. Depending on the case, a will be a ''località'', a ''rione'', a ''quartiere'' (''terziere'', etc.), a '' borgo'', or even a suburb. The best-known are the 1 ...
''u Càvusu'' in Agrigento.
* Giovanni Leone
Giovanni Leone (; 3 November 1908 – 9 November 2001) was an Italian politician, jurist, and university professor. A founding member of the Christian Democracy (DC), Leone served as the President of Italy from December 1971 until June 1978. H ...
(b. 1967), an Italian geophysicist and volcanologist, was born in Agrigento.
* Vinnie Paz
Vincenzo Luvineri (born October 5, 1977), better known as Vinnie Paz (formerly known as Ikon the Verbal Hologram), is a Sicilian Americans, Sicilian American rapper and producer behind the Philadelphia underground hip hop group Jedi Mind Tricks ...
(b. 1977), the Italian-American rapper and lyricist behind Philadelphia underground hip-hop group Jedi Mind Tricks
Jedi Mind Tricks (JMT) are an American underground hip hop group from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, founded in 1996 by two high school friends, rapper Vinnie Paz (Vincenzo Luvineri) and producer Stoupe the Enemy of Mankind (Kevin Baldwin). In 19 ...
.
* Larry Page
Lawrence Edward Page (born March 26, 1973) is an American business magnate, computer scientist and internet entrepreneur. He is best known for co-founding Google with Sergey Brin.
Page was the chief executive officer of Google from 1997 unt ...
(b. 1973), co-founder of Google
Google LLC () is an American multinational technology company focusing on search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, artificial intelligence, and consumer electronics. ...
, became an honorary citizen of Agrigento on August 4, 2017.
Twin towns – sister cities
Agrigento is twinned with: *Perm
Perm or PERM may refer to:
Places
*Perm, Russia, a city in Russia
** Permsky District, the district
**Perm Krai, a federal subject of Russia since 2005
**Perm Oblast, a former federal subject of Russia 1938–2005
**Perm Governorate, an administra ...
, Russia
* Tampa
Tampa () is a city on the Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The city's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and the seat of Hillsborough County ...
, United States
* Valenciennes
Valenciennes (, also , , ; nl, label=also Dutch, Valencijn; pcd, Valincyinnes or ; la, Valentianae) is a commune in the Nord department, Hauts-de-France, France.
It lies on the Scheldt () river. Although the city and region experienced a s ...
, France
See also
* Siege of Akragas (406 BC) *Agrigentum inscription The Agrigentum inscription is a Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, Punic inscription (Kanaanäische und Aramäische Inschriften, KAI 302, Corpus Inscriptionum Semiticarum, CIS i 5510) found in 1934 during the excavations led by :fr:Gabriel-Guillaum ...
*Battle of Agrigentum (456)
{{Campaignbox Fall of Western Roman Empire
The Battle of Agrigentum was fought in 456 A.D. at Agrigentum, now Agrigento in modern-day Sicily. An army of the Western Roman Empire, led by the general Ricimer, drove off an invading force, a fleet of ...
* List of mayors of Agrigento
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * *External links
Yair Karelic's photos of the Valley of the Temples
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Sicily Municipalities of the Province of Agrigento 580s BC Dorian colonies in Magna Graecia Colonies of Gela 6th-century BC establishments in Italy Populated places established in the 6th century BC