acne vulgaris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term
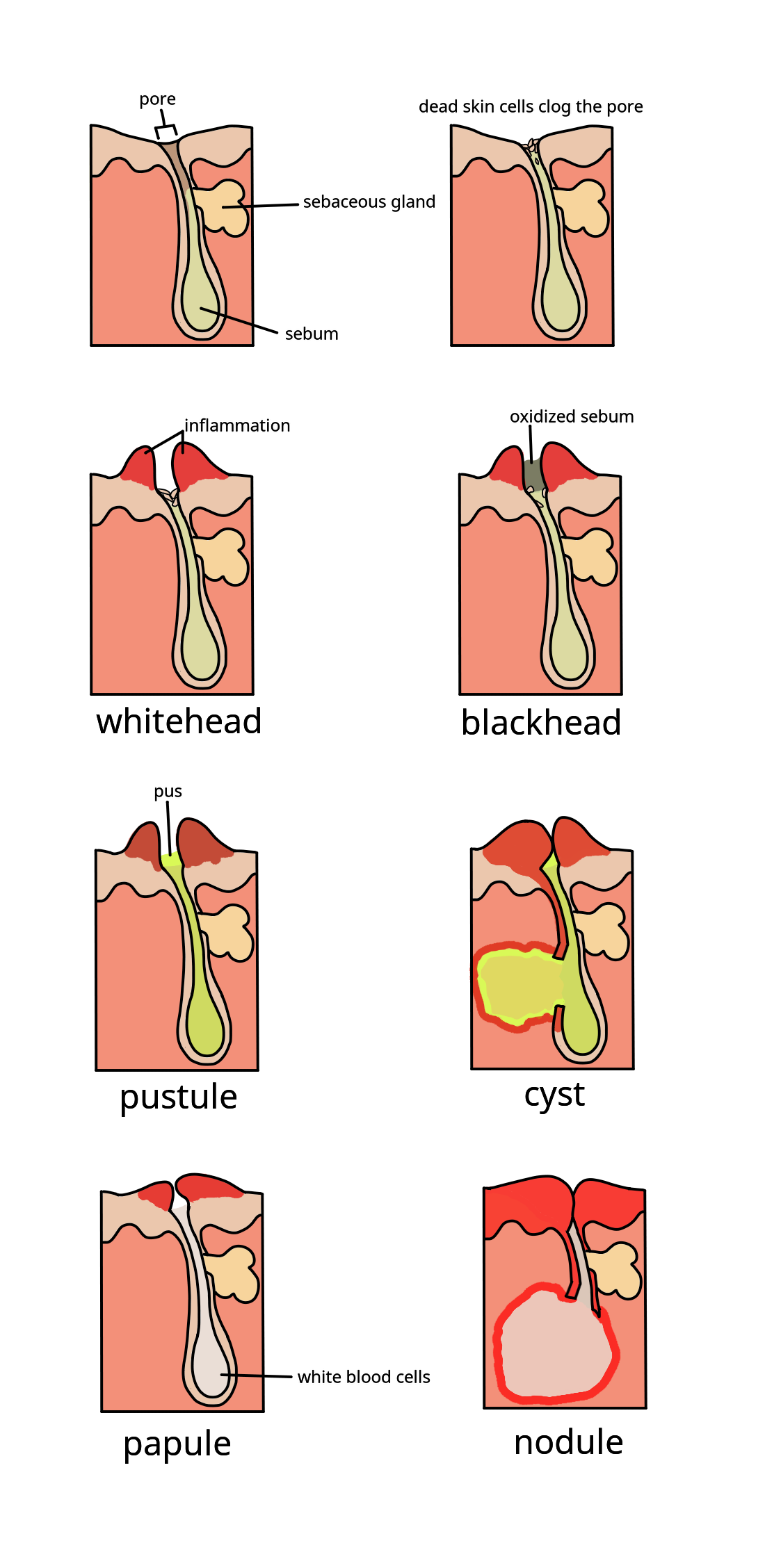
 Acne vulgaris is a chronic skin disease of the pilosebaceous unit and develops due to blockages in the skin's
Acne vulgaris is a chronic skin disease of the pilosebaceous unit and develops due to blockages in the skin's
 Benzoyl peroxide (BPO) is a first-line treatment for mild and moderate acne due to its effectiveness and mild side-effects (mainly
Benzoyl peroxide (BPO) is a first-line treatment for mild and moderate acne due to its effectiveness and mild side-effects (mainly
Acne Support
Expert, impartial advice on acne by the British Association of Dermatologists, BAD. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Acne Vulgaris Acneiform eruptions Cutaneous conditions Dermatology task force articles Puberty Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
skin condition
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this s ...
that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between h ...
s. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimple
A pimple is a kind of comedo that results from excess sebum and dead skin cells getting trapped in the pores of the skin. In its aggravated state, it may evolve into a pustule or papules. Pimples can be treated by acne medications, antibioti ...
s, oily skin, and possible scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a na ...
ring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
, reduced self-esteem
Self-esteem is confidence in one's own worth or abilities. Self-esteem encompasses beliefs about oneself (for example, "I am loved", "I am worthy") as well as emotional states, such as triumph, despair, pride, and shame. Smith and Mackie (2007) d ...
, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide.
Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or simply released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed ...
in the condition are unclear, and neither cleanliness
Cleanliness is both the state of being clean and free from germs, dirt, trash, or waste, and the habit of achieving and maintaining that state. Cleanliness is often achieved through cleaning. Culturally, cleanliness is usually a good quality, as ...
nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. In both sex
Sex is the trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing animal or plant produces male or female gametes. Male plants and animals produce smaller mobile gametes (spermatozoa, sperm, pollen), while females produce larger ones ( ova, of ...
es, hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
s called androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This inc ...
s appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest nu ...
. Another common factor is the excessive growth of the bacterium ''Cutibacterium acnes
''Cutibacterium acnes'' (formerly ''Propionibacterium acnes'') is the relatively slow-growing, typically aerotolerant anaerobic, gram-positive bacterium (rod) linked to the skin condition of acne; it can also cause chronic blepharitis and endopht ...
'', which is present on the skin.
Treatments for acne are available, including lifestyle changes, medications, and medical procedures. Eating fewer simple carbohydrates
Monosaccharides (from Greek ''monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
They are usually colorless, water-solub ...
such as sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
may minimize the condition. Treatments applied directly to the affected skin, such as azelaic acid
Azelaic acid (AzA) is an organic compound with the formula HOOC(CH2)7 COOH. This saturated dicarboxylic acid exists as a white powder. It is found in wheat, rye, and barley. It is a precursor to diverse industrial products including polymers an ...
, benzoyl peroxide, and salicylic acid, are commonly used. Antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention o ...
and retinoids are available in formulations
Formulation is a term used in various senses in various applications, both the material and the abstract or formal. Its fundamental meaning is the putting together of components in appropriate relationships or structures, according to a formul ...
that are applied to the skin and taken by mouth for the treatment of acne. However, resistance to antibiotics may develop as a result of antibiotic therapy. Several types of birth control pills Oral contraceptives, abbreviated OCPs, also known as birth control pills, are medications taken by mouth for the purpose of birth control.
Female
Two types of female oral contraceptive pill, taken once per day, are widely available:
* The combin ...
help prevent acne in women. Medical professionals typically reserve isotretinoin
Isotretinoin, also known as 13-''cis''-retinoic acid and sold under the brand name Accutane among others, is a medication primarily used to treat severe acne. It is also used to prevent certain skin cancers ( squamous-cell carcinoma), and in t ...
pills for severe acne, due to greater potential side effects. Early and aggressive treatment of acne is advocated by some in the medical community to decrease the overall long-term impact on individuals.
In 2015, acne affected approximately 633million people globally, making it the eighth-most common disease worldwide. Acne commonly occurs in adolescence
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of physical and psychological development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majority). Adolescence is usually associated with the t ...
and affects an estimated 80–90% of teenagers in the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and state (polity), states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
. Some rural societies report lower rates of acne than industrialized ones. Children and adults may also be affected before and after puberty. Although acne becomes less common in adulthood, it persists in nearly half of affected people into their twenties and thirties, and a smaller group continues to have difficulties in their forties.
Classification
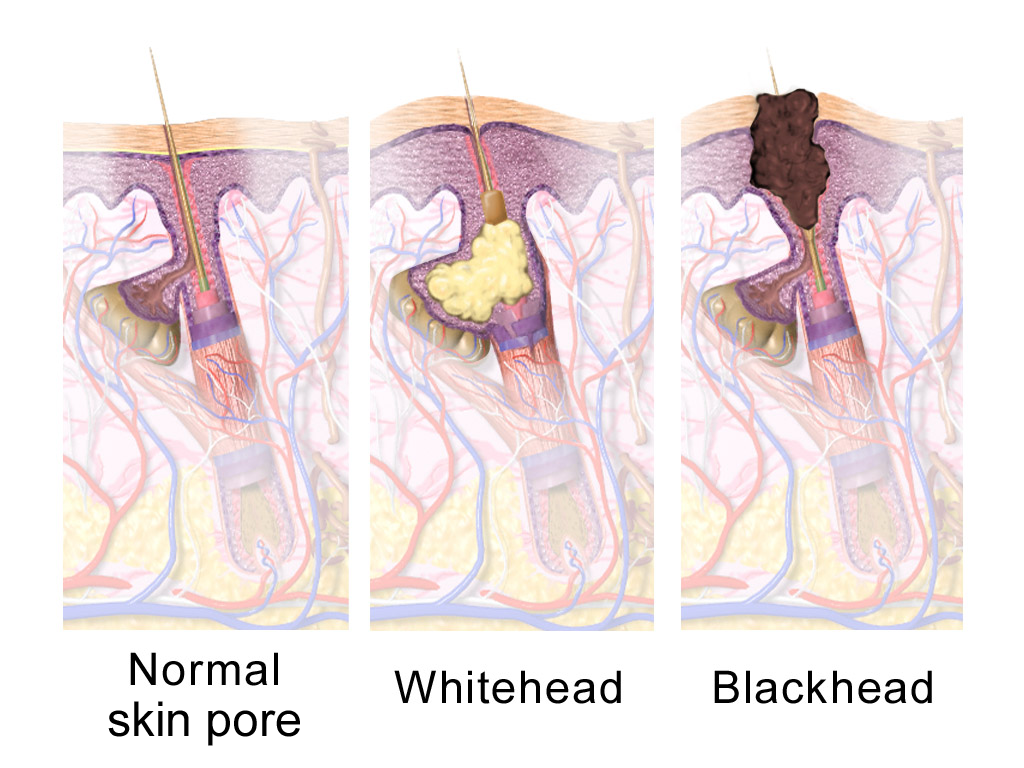
The severity of acne vulgaris (Gr. ἀκµή, "point" + L. ''vulgaris'', "common") can be classified as mild, moderate, or severe to determine an appropriate treatment regimen. There is no universally accepted scale for grading acne severity. The presence of clogged skin follicles (known ascomedo
A comedo is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin. Keratin (skin debris) combines with oil to block the follicle. A comedo can be open (blackhead) or closed by skin (whitehead) and occur with or without acne. The word "comedo" comes from the ...
nes) limited to the face with occasional inflammatory lesions defines mild acne. Moderate severity acne is said to occur when a higher number of inflammatory papule
A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the skin. It may have a rounded, pointed or flat top, and may have a dip. It can appear with a stalk, be thread-like or look warty. It can be soft or firm and its surface may be rough or smooth. Some h ...
s and pustule
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this s ...
s occur on the face, compared to mild cases of acne, and appear on the trunk of the body. Severe acne is said to occur when nodules (the painful 'bumps' lying under the skin) are the characteristic facial lesions, and involvement of the trunk is extensive.
Large nodules were previously called cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and cell division, division compared with the nearby Biological tissue, tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of Cell (biology), cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which ...
s. The term ''nodulocystic'' has been used in the medical literature to describe severe cases of inflammatory acne. True cysts are rare in those with acne, and the term ''severe nodular acne'' is now the preferred terminology.
''Acne inversa'' (L. invertō, "upside-down") and ''acne rosacea'' (rosa, "rose-colored" + -āceus, "forming") are not forms of acne and are alternate names that respectively refer to the skin conditions hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), sometimes known as acne inversa or Verneuil's disease, is a long-term dermatological condition characterized by the occurrence of inflamed and swollen lumps. These are typically painful and break open, releasing ...
(HS) and rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarg ...
. Although HS shares certain overlapping features with acne vulgaris, such as a tendency to clog skin follicles with skin cell debris, the condition otherwise lacks the hallmark features of acne and is therefore considered a distinct skin disorder.
Signs and symptoms
Typical features of acne include increased secretion of oilysebum
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest nu ...
by the skin, microcomedones, comedones, papules, nodules (large papules), pustules, and often results in scarring. The appearance of acne varies with skin color. It may result in psychological and social problems.
Scars
Acnescar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a na ...
s are caused by inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
within the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
and are estimated to affect 95% of people with acne vulgaris. Abnormal healing and dermal inflammation create the scar. Scarring is most likely to take place with severe acne but may occur with any form of acne vulgaris. Acne scars are classified based on whether the abnormal healing response following dermal inflammation leads to excess collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole ...
deposition or loss at the site of the acne lesion.
Atrophic acne scars have lost collagen from the healing response and are the most common type of acne scar (accounting for approximately 75% of all acne scars). Ice-pick scars, boxcar scars, and rolling scars are subtypes of atrophic acne scars. Boxcar scars are round or ovoid indented scars with sharp borders and vary in size from 1.5–4 mm across. Ice-pick scars are narrow (less than 2 mm across), deep scars that extend into the dermis. Rolling scars are broader than ice-pick and boxcar scars (4–5 mm across) and have a wave-like pattern of depth in the skin.
Hypertrophic scar
A hypertrophic scar is a cutaneous condition characterized by deposits of excessive amounts of collagen which gives rise to a raised scar, but not to the degree observed with keloids. Like keloids, they form most often at the sites of pimples, b ...
s are uncommon and are characterized by increased collagen content after the abnormal healing response. They are described as firm and raised from the skin. Hypertrophic scars remain within the original margins of the wound, whereas keloid scars
Keloid, also known as keloid disorder and keloidal scar,
is the formation of a type of scar which, depending on its maturity, is composed mainly of either type III (early) or type I (late) collagen. It is a result of an overgrowth of granulation t ...
can form scar tissue outside of these borders. Keloid scars from acne occur more often in men and people with darker skin, and usually occur on the trunk of the body.
In November 2021 a study was published exposing the consensus of twenty-four renowned international plastic surgeons and dermatologists about the most effective energy-based devices for the treatment of acne scars.
Pigmentation
After an inflamed nodular acne lesion resolves, it is common for the skin to darken in that area, which is known as postinflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). The inflammation stimulates specialized pigment-producing skin cells (known asmelanocyte
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea),
the inner ear,
vaginal epithelium, meninges,
bones,
and heart.
...
s) to produce more melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
pigment, which leads to the skin's darkened appearance. PIH occurs more frequently in people with darker skin color. Pigmented scar is a common term used for PIH, but is misleading as it suggests the color change is permanent. Often, PIH can be prevented by avoiding any aggravation of the nodule and can fade with time. However, untreated PIH can last for months, years, or even be permanent if deeper layers of skin are affected. Even minimal skin exposure to the sun's ultraviolet rays
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
can sustain hyperpigmentation. Daily use of SPF 15 or higher sunscreen
Sunscreen, also known as sunblock or sun cream, is a photoprotective topical product for the skin that mainly absorbs, or to a much lesser extent reflects, some of the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation and thus helps protect against sunburn and ...
can minimize such a risk.
Causes
Risk factors for the development of acne, other than genetics, have not been conclusively identified. Possible secondary contributors include hormones, infections, diet, and stress. Studies investigating the impact of smoking on the incidence and severity of acne have been inconclusive. Sunlight and cleanliness are not associated with acne.Genes
Acne appears to be highlyheritable
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic informa ...
; genetics explain 81% of the variation in the population. Studies performed in affected twins
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two em ...
and first-degree relatives further demonstrate the strongly inherited nature of acne. Acne susceptibility is likely due to the influence of multiple genes, as the disease does not follow a classic (Mendelian) inheritance pattern. These gene candidates include certain variations in tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), IL-1 alpha
Interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha) also known as hematopoietin 1 is a cytokine of the interleukin 1 family that in humans is encoded by the ''IL1A'' gene. In general, Interleukin 1 is responsible for the production of inflammation, as well as the p ...
, and CYP1A1
Cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 is a protein
that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP1A1'' gene.
The protein is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes.
Function
Metabolism of xenobiotics and drugs
CYP1A1 ...
genes, among others. The 308 G/A single nucleotide polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently larg ...
variation in the gene for TNF
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
is associated with an increased risk for acne. Acne can be a feature of rare genetic disorders such as Apert's syndrome. Severe acne may be associated with XYY syndrome
XYY syndrome, also known as Jacobs syndrome, is an aneuploid genetic condition in which a male has an extra Y chromosome. There are usually few symptoms. These may include being taller than average, acne, and an increased risk of learning disa ...
.
Hormones
Hormonal activity, such as occurs duringmenstrual cycles
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that make pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs ...
and puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. ...
, may contribute to the formation of acne. During puberty, an increase in sex hormones called androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This inc ...
s causes the skin follicle glands to grow larger and make more oily sebum. The androgen hormones testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondar ...
, dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 5α-DHT, androstanolone or stanolone) is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone. The enzyme 5α-reductase catalyzes the formation of DHT from testosterone in certain tissues includi ...
(DHT), and dehydroepiandrosterone
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), also known as androstenolone, is an endogenous steroid hormone precursor. It is one of the most abundant circulating steroids in humans. DHEA is produced in the adrenal glands, the gonads, and the brain. It fun ...
(DHEA) are all linked to acne. High levels of growth hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in h ...
(GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has anabolic effects in adults.
IGF-1 is a protein that in humans is ...
(IGF-1) are also associated with worsened acne. Both androgens and IGF-1 seem to be essential for acne to occur, as acne does not develop in individuals with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome
Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome (CAIS) is an AIS condition that results in the complete inability of the cell to respond to androgens. As such, the insensitivity to androgens is only clinically significant when it occurs in individuals ...
(CAIS) or Laron syndrome
Laron syndrome (LS), also known as growth hormone insensitivity or growth hormone receptor deficiency (GHRD), is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a lack of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1; somatomedin) production in response t ...
(insensitivity to GH, resulting in very low IGF-1 levels).
Medical conditions that commonly cause a high-androgen state, such as polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is the most common endocrine disorder in women of reproductive age. The syndrome is named after the characteristic cysts which may form on the ovaries, though it is important to note that this is a sign and no ...
, congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the synthesis of cortisol in the adrenal cortex. ...
, and androgen-secreting tumors, can cause acne in affected individuals. Conversely, people who lack androgenic hormones or are insensitive to the effects of androgens rarely have acne. Pregnancy can increase androgen levels, and consequently, oily sebum synthesis. Acne can be a side effect of testosterone replacement therapy
Androgen replacement therapy (ART), often referred to as testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) or hormone replacement therapy (HRT), is a form of hormone therapy in which androgens, often testosterone, are supplemented or replaced exogenously ...
or anabolic steroid
Anabolic steroids, also known more properly as anabolic–androgenic steroids (AAS), are steroidal androgens that include natural androgens like testosterone (medication), testosterone as well as synthetic androgens that are structurally related ...
use. Over-the-counter bodybuilding
Bodybuilding is the use of progressive resistance exercise to control and develop one's muscles (muscle building) by muscle hypertrophy for aesthetic purposes. It is distinct from similar activities such as powerlifting because it focuses ...
and dietary supplement
A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement one's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources or that are synthetic in order ...
s often contain illegally added anabolic steroids.
Infections
The anaerobic bacterial species ''Cutibacterium acnes
''Cutibacterium acnes'' (formerly ''Propionibacterium acnes'') is the relatively slow-growing, typically aerotolerant anaerobic, gram-positive bacterium (rod) linked to the skin condition of acne; it can also cause chronic blepharitis and endopht ...
'' (formerly ''Propionibacterium acnes'') contributes to the development of acne, but its exact role is not well understood. There are specific sub-strains of ''C. acnes'' associated with normal skin and others with moderate or severe inflammatory acne. It is unclear whether these undesirable strains evolve on-site or are acquired, or possibly both depending on the person. These strains have the capability of changing, perpetuating, or adapting to the abnormal cycle of inflammation, oil production, and inadequate sloughing of dead skin cells from acne pores. Infection with the parasitic mite ''Demodex
''Demodex'' is a genus of tiny mites that live in or near hair follicles of mammals. Around 65 species of ''Demodex'' are known. Two species live on humans: ''Demodex folliculorum'' and ''Demodex brevis'', both frequently referred to as eyelash ...
'' is associated with the development of acne. It is unclear whether eradication of the mite improves acne.
Diet
High- glycemic-load diets have been found to have different degrees of effect on acne severity. Multiplerandomized controlled trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical te ...
s and nonrandomized studies have found a lower-glycemic-load diet to be effective in reducing acne. There is weak observational evidence suggesting that dairy milk consumption is positively associated with a higher frequency and severity of acne. Milk contains whey protein
Whey protein is a mixture of proteins isolated from whey, the liquid material created as a by-product of cheese production. The proteins consist of α-lactalbumin, β-lactoglobulin, serum albumin and immunoglobulins. Glycomacropeptide also ma ...
and hormones such as bovine IGF-1 and precursors of dihydrotestosterone. Studies suggest these components promote the effects of insulin and IGF-1 and thereby increase the production of androgen hormones, sebum, and promote the formation of comedones. Available evidence does not support a link between eating chocolate or salt and acne severity. Few studies have examined the relationship between obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's we ...
and acne. Vitamin B12 may trigger skin outbreaks similar to acne (acneiform eruptions), or worsen existing acne when taken in doses exceeding the recommended daily intake
The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) is a system of nutrition recommendations from the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) of the National Academies (United States). It was introduced in 1997 in order to broaden the existing guidelines known as Reco ...
.
Stress
There are few high-quality studies to demonstrate that stress causes or worsens acne. Despite being controversial, some research indicates that increased acne severity is associated with high stress levels in certain contexts, such as hormonal changes seen inpremenstrual syndrome
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) refers to emotional and physical symptoms that regularly occur in the one to two weeks before the start of each menstrual period. Symptoms resolve around the time menstrual bleeding begins. Different women experienc ...
.
Other
Some individuals experience severe intensification of their acne when they are exposed to hot humid climates; this is due to bacteria and fungus thriving in warm, moist environments. This climate induced acne exacerbation has been termed tropical acne. Mechanical obstruction ofskin follicles
The hair follicle is an Organ (anatomy), organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the Dermis, dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a compl ...
with helmets or chinstraps can worsen pre-existing acne. However, when acne is caused by mechanical obstruction it is not considered a form of acne vulgaris when being very technical. It would be an other acneiform eruption
Acneiform eruptions are a group of dermatoses including acne vulgaris, rosacea, folliculitis, and perioral dermatitis. Restated, acneiform eruptions are follicular eruptions characterized by papules and pustules resembling acne.James, William; Be ...
known as Acne mechanica
Acne mechanica is an acneiform eruption that has been observed after repetitive physical trauma to the skin such as rubbing, occurring from clothing (belts and straps) or sports equipment (football helmets and shoulder pads).Freedberg, et al. ( ...
.
Several medications can also worsen pre-existing acne; this condition is the acne medicamentosa
Acne medicamentosa is acne that is caused or aggravated by medication. Because acne is generally a disorder of the pilosebaceous units caused by hormones, the medications that trigger acne medicamentosa most frequently are hormone analogs. It is a ...
form of acne. Examples of such medications include lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid el ...
, hydantoin, isoniazid
Isoniazid, also known as isonicotinic acid hydrazide (INH), is an antibiotic used for the treatment of tuberculosis. For active tuberculosis it is often used together with rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and either streptomycin or ethambutol. For la ...
, glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebr ...
, iodides, bromides
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant ...
, and testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondar ...
. When acne medicamentosa is specifically caused by anabolic–androgenic steroids it can simply be referred to as steroid acne
Steroid acne is an adverse reaction to corticosteroids, and presents as small, firm follicular papules on the forehead, cheeks, and chest.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. ...
.
Genetically susceptible individuals can get acne breakouts as a result of polymorphous light eruption
Polymorphous light eruption (PLE) presents with itchy red small bumps on sun-exposed skin, particularly face, neck, forearms and legs. It generally appears 30 minutes to a few hours after sun exposure and may last between one and 14 days. The b ...
; a condition triggered by sunlight and artificial UV light exposure. This form of acne is called Acne aestivalis
Acne aestivalis also called as acne mallorca, is a special kind of polymorphous light eruption induced by ultra violet A radiation. This condition is said to be seasonal, usually affecting people in springtime and goes away in autumn when there i ...
and it's specifically caused by intense UVA light exposure. Affected individuals usually experience seasonal acne breakouts on their upper arms, shoulder girdle, back, and chest. The breakouts typically occur one-to-three days after they've been exposed to intese UVA radiation. Unlike other forms of acne the condition spares the face; this could possibly be a result of the pathogenesis of polymorphous light eruption, in which areas of the skin that are ''newly'' exposed to intense ultraviolet radiation are affected. Since faces are typically left uncovered at all stages of life there's little-to-no likelihood for an eruption to appear there. Studies show that both polymorphous light eruption outbreaks and the acne aestivalis breakout response can be prevented by topical antioxidants combined with the application of a broad spectrum sunscreen.
Pathophysiology

 Acne vulgaris is a chronic skin disease of the pilosebaceous unit and develops due to blockages in the skin's
Acne vulgaris is a chronic skin disease of the pilosebaceous unit and develops due to blockages in the skin's hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between h ...
s. These blockages occur as a result of the following four abnormal processes: increased oily sebum
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest nu ...
production (influenced by androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning "man") is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This inc ...
s), excessive deposition of the protein keratin leading to comedo formation, colonization of the follicle by ''Cutibacterium acnes'' (''C. acnes'') bacteria, and the local release of pro-inflammatory chemicals in the skin.
The earliest pathologic change is the formation of a plug (a microcomedone), which is driven primarily by excessive growth, reproduction, and accumulation of skin cells
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
in the hair follicle. In healthy skin, the skin cells that have died come up to the surface and exit the pore of the hair follicle. In people with acne, the increased production of oily sebum causes the dead skin cells to stick together. The accumulation of dead skin cell debris and oily sebum blocks the pore of the hair follicle, thus forming the microcomedone. The ''C. acnes'' biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular ...
within the hair follicle worsens this process. If the microcomedone is superficial within the hair follicle, the skin pigment melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
is exposed to air, resulting in its oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
and dark appearance (known as a blackhead or open comedo). In contrast, if the microcomedone occurs deep within the hair follicle, this causes the formation of a whitehead (known as a closed comedo).
The main hormonal driver of oily sebum production in the skin is dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 5α-DHT, androstanolone or stanolone) is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone. The enzyme 5α-reductase catalyzes the formation of DHT from testosterone in certain tissues includi ...
. Another androgenic hormone responsible for increased sebaceous gland activity is DHEA-S
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, abbreviated as DHEA sulfate or DHEA-S, also known as androstenolone sulfate, is an endogenous androstane steroid that is produced by the adrenal cortex. It is the 3β-sulfate ester and a metabolite of dehydroep ...
. The adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which ...
s secrete higher amounts of DHEA-S during adrenarche
Adrenarche is an early stage in sexual maturation that happens in some higher primates and in humans, typically peaks at around 20 years of age, and is involved in the development of pubic hair, body odor, skin oiliness, axillary hair, sexual ...
(a stage of puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. ...
), and this leads to an increase in sebum production. In a sebum-rich skin environment, the naturally occurring and largely commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit fro ...
skin bacterium ''C. acnes'' readily grows and can cause inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
within and around the follicle due to activation of the innate immune system
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the ...
. ''C. acnes'' triggers skin inflammation in acne by increasing the production of several pro-inflammatory chemical signals (such as IL-1α
Interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha) also known as hematopoietin 1 is a cytokine of the interleukin 1 family that in humans is encoded by the ''IL1A'' gene. In general, Interleukin 1 is responsible for the production of inflammation, as well as the p ...
, IL-8, TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
, and LTB4); IL-1α is essential to comedo formation.
''C. acnes ability to bind and activate a class of immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
receptors known as toll-like receptor
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are Bitopic protein, single-pass membrane-spanning Receptor (biochemistry), receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophage ...
s (TLRs), especially TLR2
Toll-like receptor 2 also known as TLR2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR2'' gene. TLR2 has also been designated as CD282 (cluster of differentiation 282). TLR2 is one of the toll-like receptors and plays a role in the immune sys ...
and TLR4
Toll-like receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TLR4'' gene. TLR4 is a transmembrane protein, member of the toll-like receptor family, which belongs to the pattern recognition receptor (PRR) family. Its activation leads to an ...
, is a core mechanism of acne-related skin inflammation. Activation of TLR2 and TLR4 by ''C. acnes'' leads to increased secretion of IL-1α, IL-8, and TNF-α. The release of these inflammatory signals attracts various immune cells to the hair follicle, including neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying ...
s, macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s, and Th1 cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are consider ...
s. IL-1α stimulates increased skin cell activity and reproduction, which, in turn, fuels comedo development. Furthermore, sebaceous gland cells produce more antimicrobial peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for a ...
, such as HBD1 and HBD2, in response to the binding of TLR2 and TLR4.
''C. acnes'' also provokes skin inflammation by altering the fatty composition of oily sebum. Oxidation of the lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
squalene
Squalene is an organic compound. It is a triterpenoid with the formula C30H50. It is a colourless oil, although impure samples appear yellow. It was originally obtained from shark liver oil (hence its name, as ''Squalus'' is a genus of sharks). A ...
by ''C. acnes'' is of particular importance. Squalene oxidation activates NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in almost all animal cell types and is involved in cellular ...
(a protein complex) and consequently increases IL-1α levels. Additionally, squalene oxidation increases 5-lipoxygenase enzyme activity, which catalyzes the conversion of arachidonic acid to leukotriene B4
Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is a leukotriene involved in inflammation. It has been shown to promote insulin resistance in obese mice.
Biochemistry
Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is a leukotriene involved in inflammation. It is produced from leukocytes in r ...
(LTB4). LTB4 promotes skin inflammation by acting on the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α), also known as NR1C1 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group C, member 1), is a nuclear receptor protein functioning as a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ''PPARA'' gene ...
(PPARα) protein. PPARα increases the activity of activator protein 1
Activator protein 1 (AP-1) is a transcription factor that regulates gene expression in response to a variety of stimuli, including cytokines, growth factors, stress, and bacterial and viral infections. AP-1 controls a number of cellular proce ...
(AP-1) and NF-κB, thereby leading to the recruitment of inflammatory T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s. ''C. acnes ability to convert sebum triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and ''glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as w ...
s to pro-inflammatory free fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, fr ...
s via secretion of the enzyme lipase
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually tr ...
further explains its inflammatory properties. These free fatty acids spur increased production of cathelicidin
Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) is a polypeptide that is primarily stored in the lysosomes of macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs); in humans, the ''CAMP'' gene encodes the peptide precursor CAP-18 (18 kDa), which is proce ...
, HBD1, and HBD2, thus leading to further inflammation.
This inflammatory cascade typically leads to the formation of inflammatory acne lesions, including papule
A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the skin. It may have a rounded, pointed or flat top, and may have a dip. It can appear with a stalk, be thread-like or look warty. It can be soft or firm and its surface may be rough or smooth. Some h ...
s, infected pustule
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this s ...
s, or nodules. If the inflammatory reaction is severe, the follicle can break into the deeper layers of the dermis and subcutaneous tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macr ...
and cause the formation of deep nodules. The involvement of AP-1 in the aforementioned inflammatory cascade activates matrix metalloproteinase
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), also known as matrix metallopeptidases or matrixins, are metalloproteinases that are calcium-dependent zinc-containing endopeptidases; other family members are adamalysins, serralysins, and astacins. The MMPs be ...
s, which contribute to local tissue destruction and scar formation.
Along with the bacteria ''C. acnes'', the bacterial species ''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' (''S. epidermidis'') also takes a part in the physiopathology of acne vulgaris. The proliferation of ''S. epidermidis'' with ''C. acnes'' causes the formation of biofilms
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular po ...
, which blocks the hair follicles and pores, creating an anaerobic
Anaerobic means "living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen", as opposed to aerobic which means "living, active, or occurring only in the presence of oxygen." Anaerobic may also refer to:
* Anaerobic adhesive, a bonding a ...
environment under the skin. This enables for increased growth of both ''C. acnes'' and ''S. epidermidis'' under the skin. The proliferation of ''C. acnes'' causes the formation of biofilms
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular po ...
and a biofilm matrix, making it even harder to treat the acne.
Diagnosis
Acne vulgaris is diagnosed based on a medical professional's clinical judgment. The evaluation of a person with suspected acne should include taking a detailed medical history about a family history of acne, a review of medications taken, signs or symptoms of excessive production of androgen hormones, cortisol, and growth hormone. Comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) must be present to diagnose acne. In their absence, an appearance similar to that of acne would suggest a different skin disorder. Microcomedones (the precursor to blackheads and whiteheads) are not visible to the naked eye when inspecting the skin and require a microscope to be seen. Many features may indicate that a person's acne vulgaris is sensitive to hormonal influences. Historical and physical clues that may suggest hormone-sensitive acne include onset between ages 20 and 30; worsening the week before a woman's period; acne lesions predominantly over the jawline and chin; and inflammatory/nodular acne lesions. Several scales exist to grade the severity of acne vulgaris, but disagreement persists about the ideal one for diagnostic use. Cook's acne grading scale uses photographs to grade severity from 0 to 8, with higher numbers representing more severe acne. This scale was the first to use a standardized photographic protocol to assess acne severity; since its creation in 1979, the scale has undergone several revisions. The Leeds acne grading technique counts acne lesions on the face, back, and chest and categorizes them as inflammatory or non-inflammatory. Leeds scores range from 0 (least severe) to 10 (most severe) though modified scales have a maximum score of 12. The Pillsbury acne grading scale classifies the severity of the acne from grade 1 (least severe) to grade 4 (most severe).Differential diagnosis
Many skin conditions can mimic acne vulgaris, and these are collectively known asacneiform eruptions
Acneiform eruptions are a group of dermatoses including acne vulgaris, rosacea, folliculitis, and perioral dermatitis. Restated, acneiform eruptions are follicular eruptions characterized by papules and pustules resembling acne.James, William; Ber ...
. Such conditions include angiofibroma
Angiofibroma (AGF) is a descriptive term for a wide range of benign skin or mucous membrane (i.e. the outer membrane lining body cavities such as the mouth and nose) lesions in which individuals have: 1) benign papules, i.e. pinhead-sized elevation ...
s, epidermal cyst
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water relea ...
s, flat warts, folliculitis
Folliculitis is the infection and inflammation of one or more hair follicles. The condition may occur anywhere on hair-covered skin. The rash may appear as pimples that come to white tips on the face, chest, back, arms, legs, buttocks, or head.
...
, keratosis pilaris
Keratosis pilaris (KP; also follicular keratosis, lichen pilaris, or colloquially chicken skin) is a common, autosomal- dominant, genetic condition of the skin's hair follicles characterized by the appearance of possibly itchy, small, goosefle ...
, milia
A milium (''plural'' milia), also called a milk spot or an oil seed, is a clog of the eccrine sweat gland. It is a keratin-filled cyst that can appear just under the epidermis or on the roof of the mouth.Freedberg, et al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick' ...
, perioral dermatitis
Perioral dermatitis, also known as periorificial dermatitis, is a common type of skin rash. Symptoms include multiple small (1–2 mm) bumps and blisters sometimes with background redness and scale, localized to the skin around the mouth and ...
, and rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarg ...
, among others. Age is one factor that may help distinguish between these disorders. Skin disorders such as perioral dermatitis and keratosis pilaris can appear similar to acne but tend to occur more frequently in childhood. Rosacea tends to occur more frequently in older adults. Facial redness triggered by heat or the consumption of alcohol or spicy food is also more suggestive of rosacea. The presence of comedones helps health professionals differentiate acne from skin disorders that are similar in appearance. Chloracne
Chloracne is an acne-like eruption of blackheads, cysts, and pustules associated with exposure to certain halogenated aromatic compounds, such as chlorinated dioxins and dibenzofurans. The lesions are most frequently found on the cheeks, behind t ...
and occupational acne due to exposure to certain chemicals & industrial compounds, may look very similar to acne vulgaris.
Management
Many different treatments exist for acne. These includealpha hydroxy acid
α-Hydroxy acids, or alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), are a class of chemical compounds that consist of a carboxylic acid with a hydroxyl group substituent on the adjacent (alpha) carbon. Prominent examples are glycolic acid, lactic acid, mandelic aci ...
, anti-androgen medications, antibiotics, antiseborrheic medications, azelaic acid
Azelaic acid (AzA) is an organic compound with the formula HOOC(CH2)7 COOH. This saturated dicarboxylic acid exists as a white powder. It is found in wheat, rye, and barley. It is a precursor to diverse industrial products including polymers an ...
, benzoyl peroxide, hormonal
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required fo ...
treatments, keratolytic
Keratolytic () therapy is a type of medical treatment to remove warts, calluses and other lesions in which the epidermis produces excess skin. In this therapy, acidic topical medicines, such as Whitfield's ointment or Jessner's solution, are ap ...
soaps, nicotinamide
Niacinamide or Nicotinamide (NAM) is a form of vitamin B3 found in food and used as a dietary supplement and medication. As a supplement, it is used by mouth to prevent and treat pellagra (niacin deficiency). While nicotinic acid (niacin) may ...
, retinoids, and salicylic acid. Acne treatments work in at least four different ways, including the following: reducing inflammation, hormonal manipulation, killing ''C. acnes'', and normalizing skin cell shedding and sebum production in the pore to prevent blockage. Typical treatments include topical therapies such as antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide, and retinoids, and systemic therapies, including antibiotics, hormonal agents, and oral retinoids.
Recommended therapies for first-line use in acne vulgaris treatment include topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and topical or oral antibiotics. Procedures such as light therapy and laser therapy are not first-line treatments and typically have only an add on role due to their high cost and limited evidence. Blue light therapy is of unclear benefit. Medications for acne target the early stages of comedo
A comedo is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin. Keratin (skin debris) combines with oil to block the follicle. A comedo can be open (blackhead) or closed by skin (whitehead) and occur with or without acne. The word "comedo" comes from the ...
formation and are generally ineffective for visible skin lesions; acne generally improves between eight and twelve weeks after starting therapy.
People often view acne as a short-term condition, some expecting it to disappear after puberty. This misconception can lead to depending on self-management or problems with long-term adherence to treatment. Communicating the long-term nature of the condition and better access to reliable information about acne can help people know what to expect from treatments.
Skin care
In general, it is recommended that people with acne do not wash affected skin more than twice daily. The application of a fragrance-free moisturizer to sensitive and acne-prone skin may reduce irritation. Skin irritation from acne medications typically peaks at two weeks after onset of use and tends to improve with continued use. Dermatologists recommend using cosmetic products that specifically say non-comedogenic, oil-free, and won't clog pores. Acne vulgaris patients, even those with oily skin, should moisturize in order to support the skin's moisture barrier since skin barrier dysfunction may contribute to acne. Moisturizers, especially ceramide-containing moisturizers, as an adjunct therapy are particularly helpful for the dry skin and irritation that commonly results from topical acne treatment. Studies show that ceramide-containing moisturizers are important for optimal skin care; they enhance acne therapy adherence and complement existing acne therapies. In a study where acne patients used 1.2% clindamycin phosphate / 2.5% benzoyl peroxide gel in the morning and applied a micronized 0.05% tretinoin gel in the evening the overwhelming majority of patients experienced no cutaneous adverse events throughout the study. It was concluded that using ceramide cleanser and ceramide moisturizing cream caused the favorable tolerability, did not interfere with the treatment efficacy, and improved adherence to the regimen. The importance of preserving the acidic mantle and its barrier functions is widely accepted in the scientific community. Thus, maintaining a pH in the range 4.5 - 5.5 is essential in order to keep the skin surface in its optimal, healthy conditions.Diet
Causal
Causality (also referred to as causation, or cause and effect) is influence by which one event, process, state, or object (''a'' ''cause'') contributes to the production of another event, process, state, or object (an ''effect'') where the ca ...
relationship is rarely observed with diet/nutrition and dermatologic conditions. Rather, associations — some of them compelling — have been found between diet and outcomes including disease severity and the number of conditions experienced by a patient. Evidence is emerging in support of medical nutrition therapy as a way of reducing the severity and incidence of dermatologic diseases, including acne. Researchers observed a link between high glycemic index diets and acne. Dermatologists also recommend a diet low in simple sugars as a method of improving acne. As of 2014, the available evidence is insufficient to use milk restriction for this purpose.
Medications
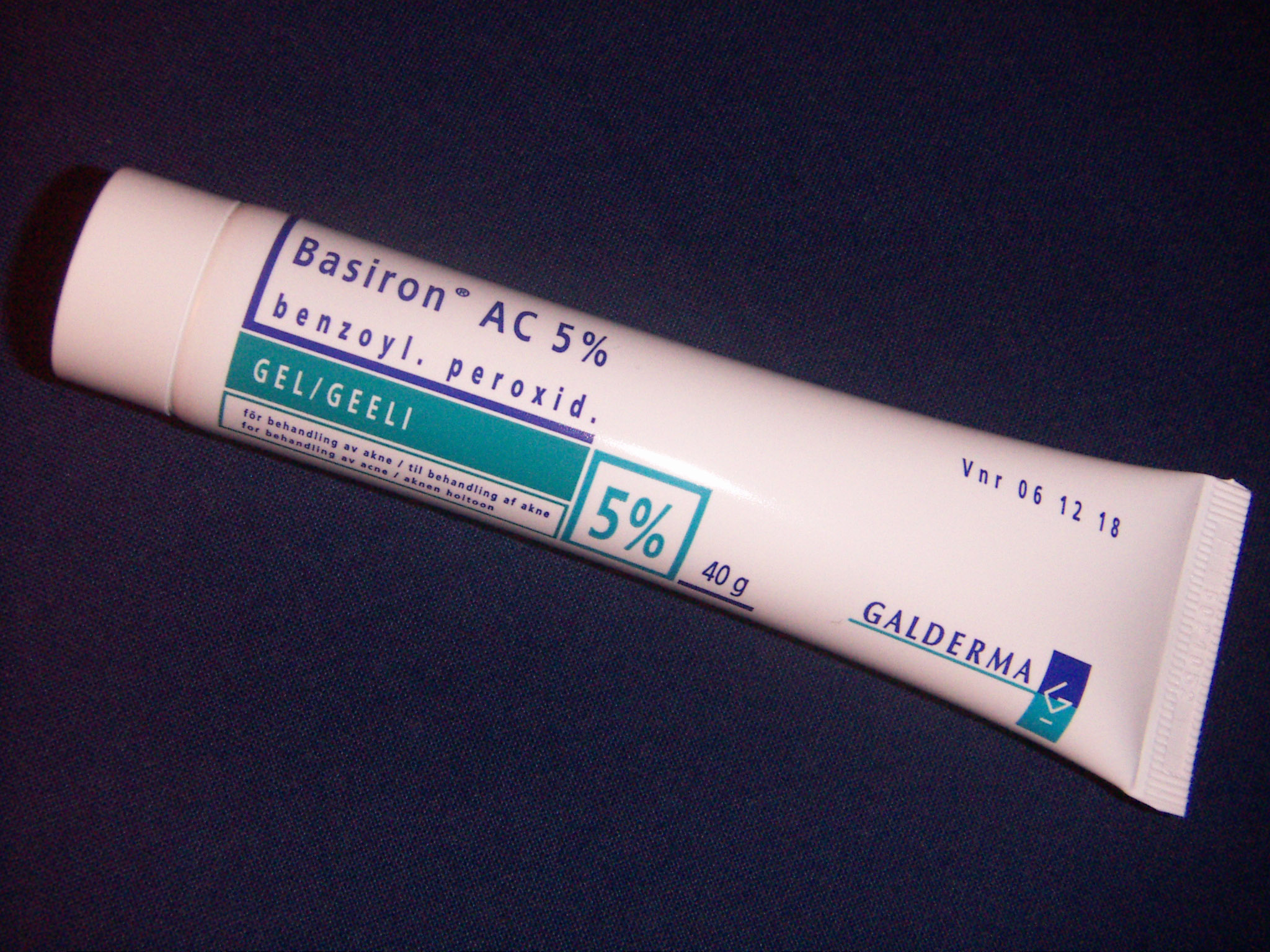
Benzoyl peroxide
 Benzoyl peroxide (BPO) is a first-line treatment for mild and moderate acne due to its effectiveness and mild side-effects (mainly
Benzoyl peroxide (BPO) is a first-line treatment for mild and moderate acne due to its effectiveness and mild side-effects (mainly skin irritation
Irritation, in biology and physiology, is a state of inflammation or painful reaction to allergy or cell-lining damage. A stimulus or agent which induces the state of irritation is an irritant. Irritants are typically thought of as chemical age ...
). In the skin follicle, benzoyl peroxide kills ''C. acnes'' by oxidizing its proteins through the formation of oxygen free radical
A daughter category of ''Ageing'', this category deals only with the biological aspects of ageing.
Ageing
Ailments of unknown cause
Biogerontology
Biological processes
Causes of death
Cellular processes
Gerontology
Life extension
Metabo ...
s and benzoic acid
Benzoic acid is a white (or colorless) solid organic compound with the formula , whose structure consists of a benzene ring () with a carboxyl () substituent. It is the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid. The name is derived from gum benzoin, wh ...
. These free radicals likely interfere with the bacterium's metabolism and ability to make proteins. Additionally, benzoyl peroxide is mildly effective at breaking down comedones and inhibiting inflammation. Combination products use benzoyl peroxide with a topical antibiotic or retinoid, such as benzoyl peroxide/clindamycin
Clindamycin/benzoyl peroxide is a topical gel used for the treatment of acne. It is a combination of clindamycin, an antibiotic, and benzoyl peroxide, an antiseptic.
Common side effects include peeling, itching, and dryness of the skin where ...
and benzoyl peroxide/adapalene, respectively. Topical benzoyl peroxide is effective at treating acne.
Side effects include increased skin photosensitivity, dryness, redness, and occasional peeling. Sunscreen use is often advised during treatment, to prevent sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and animals include: red or reddish skin that is ho ...
. Lower concentrations of benzoyl peroxide are just as effective as higher concentrations in treating acne but are associated with fewer side effects. Unlike antibiotics, benzoyl peroxide does not appear to generate bacterial antibiotic resistance.
Retinoids
Retinoids are medications that reduce inflammation, normalize the follicle cell life cycle, and reduce sebum production. They are structurally related tovitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin and an essential nutrient for humans. It is a group of organic compounds that includes retinol, retinal (also known as retinaldehyde), retinoic acid, and several provitamin A carotenoids (most notably bet ...
. Studies show dermatologists and primary care doctors underprescribe them for acne. The retinoids appear to influence the cell life cycle in the follicle lining. This helps prevent the accumulation of skin cells within the hair follicle that can create a blockage. They are a first-line acne treatment, especially for people with dark-colored skin. Retinoids are known to lead to faster improvement of postinflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Topical retinoids include adapalene
Adapalene is a third-generation topical retinoid primarily used in the treatment of mild-moderate acne, and is also used off-label to treat keratosis pilaris as well as other skin conditions. Studies have found adapalene is as effective as othe ...
, retinol
Retinol, also called vitamin A1, is a fat-soluble vitamin in the vitamin A family found in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to treat and prevent vitamin A deficiency, especially that which results in xeroph ...
, retinaldehyde
Retinal (also known as retinaldehyde) is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).
Some microorganisms use retin ...
, isotretinoin
Isotretinoin, also known as 13-''cis''-retinoic acid and sold under the brand name Accutane among others, is a medication primarily used to treat severe acne. It is also used to prevent certain skin cancers ( squamous-cell carcinoma), and in t ...
, tazarotene
Tazarotene, sold under the brand name Tazorac, among others, is a third-generation prescription topical retinoid. It is primarily used for the treatment of plaque psoriasis and acne. Tazarotene is also used as a therapeutic for photoaged and p ...
, trifarotene, and tretinoin
Tretinoin, also known as all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA), is a medication used for the treatment of acne and acute promyelocytic leukemia. For acne, it is applied to the skin as a cream, gel or ointment. For leukemia, it is taken by mouth ...
. They often cause an initial flare-up of acne and facial flushing
Flushing may refer to:
Places
* Flushing, Cornwall, a village in the United Kingdom
* Flushing, Queens, New York City
** Flushing Bay, a bay off the north shore of Queens
** Flushing Chinatown (法拉盛華埠), a community in Queens
** Flushing ...
and can cause significant skin irritation. Generally speaking, retinoids increase the skin's sensitivity to sunlight and are therefore recommended for use at night. Tretinoin is the least expensive of the topical retinoids and is the most irritating to the skin, whereas adapalene is the least irritating but costs significantly more. Most formulations of tretinoin are incompatible for use with benzoyl peroxide. Tazarotene is the most effective and expensive topical retinoid but is usually not as well tolerated. In 2019 a tazarotene lotion formulation, marketed to be a less irritating option, was approved by the FDA. Retinol is a form of vitamin A that has similar but milder effects and is present in many over-the-counter moisturizers and other topical products.
Isotretinoin is an oral retinoid that is very effective for severe nodular acne, and moderate acne that is stubborn to other treatments. One to two months of use is typically adequate to see improvement. Acne often resolves completely or is much milder after a 4–6 month course of oral isotretinoin. After a single round of treatment, about 80% of people report an improvement, with more than 50% reporting complete remission. About 20% of people require a second course, but 80% of those report improvement, resulting in a cumulative 96% efficacy rate.
There are concerns that isotretinoin is linked to adverse effects, like depression, suicidality
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and subs ...
, and anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, th ...
. There is no clear evidence to support some of these claims. Isotretinoin has been found in some studies to be superior to antibiotics or placebo in reducing acne lesions. However, a 2018 review comparing inflammatory lesions after treatment with antibiotics or isotretinoin found no difference. The frequency of adverse events was about twice as high with isotretinoin use, although these were mostly dryness-related events. No increased risk of suicide or depression was conclusively found.
Medical authorities strictly regulate isotretinoin use in women of childbearing age due to its known harmful effects in pregnancy. For such a woman to be considered a candidate for isotretinoin, she must have a confirmed negative pregnancy test
A pregnancy test is used to determine whether a female is pregnant or not. The two primary methods are testing for the female pregnancy hormone (human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)) in blood or urine using a pregnancy test kit, and scanning with ...
and use an effective form of birth control
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
. In 2008, the United States started the iPLEDGE program to prevent isotretinoin use during pregnancy. iPledge requires the woman to have two negative pregnancy tests and to use two types of birth control for at least one month before isotretinoin therapy begins and one month afterward. The effectiveness of the iPledge program is controversial due to continued instances of contraception nonadherence.
Antibiotics
People may apply antibiotics to the skin or take them orally to treat acne. They work by killing ''C. acnes'' and reducing inflammation. Although multiple guidelines call for healthcare providers to reduce the rates of prescribed oral antibiotics, many providers do not follow this guidance. Oral antibiotics remain the most commonly prescribed systemic therapy for acne. Widespreadbroad-spectrum antibiotic
A broad-spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic that acts on the two major bacterial groups, Gram-positive and Gram-negative, or any antibiotic that acts against a wide range of disease-causing bacteria. These medications are used when a bacterial inf ...
overuse for acne has led to higher rates of antibiotic-resistant ''C. acnes'' strains worldwide, especially to the commonly used tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an oral antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis.
Common side effects in ...
(e.g., doxycycline
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, an ...
) and macrolide antibiotics (e.g., topical erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used duri ...
). Therefore, dermatologists prefer antibiotics as part of combination therapy and not for use alone.
Commonly used antibiotics, either applied to the skin or taken orally, include clindamycin
Clindamycin is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media (middle ear infec ...
, erythromycin, metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vaginosis. It i ...
, sulfacetamide
Sulfacetamide is a sulfonamide antibiotic.
Uses
Sulfacetamide 10% topical lotion, sold under the brand name Klaron or Ovace, is approved for the treatment of acne and seborrheic dermatitis. When combined with sulfur, it is sold under the bran ...
, and tetracyclines (e.g., doxycycline or minocycline
Minocycline, sold under the brand name Minocin among others, is a tetracycline antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections such as pneumonia. It is generally less preferred than the tetracycline doxycycline. It is also ...
). Doxycycline 40 milligrams daily (low-dose) appears to have similar efficacy to 100 milligrams daily and has fewer gastrointestinal side effects. However, low-dose doxycycline is not FDA-approved for the treatment of acne. Antibiotics applied to the skin are typically used for mild to moderately severe acne. Oral antibiotics are generally more effective than topical antibiotics and produce faster resolution of inflammatory acne lesions than topical applications. Topical and oral antibiotics are not recommended for use together.
Oral antibiotics are recommended for no longer than three months as antibiotic courses exceeding this duration are associated with the development of antibiotic resistance and show no clear benefit over shorter durations. If long-term oral antibiotics beyond three months are used, then it is recommended that benzoyl peroxide or a retinoid be used at the same time to limit the risk of ''C. acnes'' developing antibiotic resistance.
The antibiotic dapsone
Dapsone, also known as 4,4'-sulfonyldianiline (SDA) or diaminodiphenyl sulfone (DDS), is an antibiotic commonly used in combination with rifampicin and clofazimine for the treatment of leprosy. It is a second-line medication for the treatment a ...
is effective against inflammatory acne when applied to the skin. It is generally not a first-line choice due to its higher cost and a lack of clear superiority over other antibiotics. Topical dapsone is sometimes a preferred therapy in women or for people with sensitive or darker-toned skin. It is not recommended for use with benzoyl peroxide due to the risk of causing yellow-orange skin discoloration with this combination. Minocycline is an effective acne treatment, but it is not a first-line antibiotic due to a lack of evidence that it is better than other treatments, and concerns about its safety compared to other tetracyclines.
Sarecycline is the most recent oral antibiotic developed specifically for the treatment of acne, and is FDA-approved for the treatment of moderate to severe inflammatory acne in patients nine years of age and older. It is a narrow-spectrum tetracycline antibiotic that exhibits the necessary antibacterial activity against pathogens related to acne vulgaris and a low propensity for inducing antibiotic resistance. In clinical trials, sarecycline demonstrated clinical efficacy in reducing inflammatory acne lesions as early as three weeks and reduced truncal (back and chest) acne.
Hormonal agents
In women, the use ofcombined birth control pill
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP), often referred to as the birth control pill or colloquially as "the pill", is a type of birth control that is designed to be taken orally by women. The pill contains two important hormones: proges ...
s can improve acne. These medications contain an estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal acti ...
and a progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic co ...
. They work by decreasing the production of androgen hormones by the ovaries and by decreasing the free and hence biologically active fractions of androgens, resulting in lowered skin production of sebum and consequently reduce acne severity. First-generation progestins such as norethindrone
Norethisterone, also known as norethindrone and sold under many brand names, is a progestin medication used in birth control pills, menopausal hormone therapy, and for the treatment of gynecological disorders. The medication is available in bo ...
and norgestrel have androgenic properties and may worsen acne. Although oral estrogens decrease IGF-1 levels in some situations, which could theoretically improve acne symptoms, combined birth control pills do not appear to affect IGF-1 levels in fertile women. Cyproterone acetate
Cyproterone acetate (CPA), sold alone under the brand name Androcur or Ethinylestradiol/cyproterone acetate, with ethinylestradiol under the brand names Diane or Diane-35 among others, is an antiandrogen and progestin medication used in the treat ...
-containing birth control pills seem to decrease total and free IGF-1 levels. Combinations containing third- or fourth-generation progestin
A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural product, natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a ''synthetic co ...
s, including desogestrel
Desogestrel is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills for women. It is also used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms in women. The medication is available and used alone or in combination with an estrogen. It is taken ...
, dienogest
Dienogest, sold under the brand name Visanne among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills and in the treatment of endometriosis. It is also used in menopausal hormone therapy and to treat heavy periods. Dienogest ...
, drospirenone
Drospirenone is a progestin and antiandrogen medication which is used in birth control pills to prevent pregnancy and in menopausal hormone therapy, among other uses. It is available both alone under the brand name Slynd and in combination wi ...
, or norgestimate, as well as birth control pills containing cyproterone acetate or chlormadinone acetate
Chlormadinone acetate (CMA), sold under the brand names Belara, Gynorelle, Lutéran, and Prostal among others, is a progestin and antiandrogen medication which is used in birth control pills to prevent pregnancy, as a component of menopausal hor ...
, are preferred for women with acne due to their stronger antiandrogenic effects. Studies have shown a 40 to 70% reduction in acne lesions with combined birth control pills. A 2014 review
A review is an evaluation of a publication, product, service, or company or a critical take on current affairs in literature, politics or culture. In addition to a critical evaluation, the review's author may assign the work a content rating, ...
found that oral antibiotics appear to be somewhat more effective than birth control pills at reducing the number of inflammatory acne lesions at three months. However, the two therapies are approximately equal in efficacy at six months for decreasing the number of inflammatory, non-inflammatory, and total acne lesions. The authors of the analysis suggested that birth control pills may be a preferred first-line acne treatment, over oral antibiotics, in certain women due to similar efficacy at six months and a lack of associated antibiotic resistance. In contrast to combined birth control pills, progestogen-only birth control
Progestogen-only contraception (or progestin-only contraception) relies on progestogens alone to achieve contraception. It is one of the two major types of hormonal contraception, with the other major type being combined hormonal contraceptive met ...
forms that contain androgenic progestins have been associated with worsened acne.
Antiandrogen
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs that prevent androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the ...
s such as cyproterone acetate and spironolactone
Spironolactone, sold under the brand name Aldactone among others, is a medication that is primarily used to treat fluid build-up due to heart failure, liver scarring, or kidney disease. It is also used in the treatment of high blood press ...
can successfully treat acne, especially in women with signs of excessive androgen production, such as increased hairiness or skin production of sebum, or scalp hair loss. Spironolactone is an effective treatment for acne in adult women. Unlike combined birth control pills, it is not approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
for this purpose. Spironolactone is an aldosterone antagonist
An antimineralocorticoid, also known as a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA or MCRA) or aldosterone antagonist, is a diuretic drug which antagonizes the action of aldosterone at mineralocorticoid receptors. This group of drugs is often u ...
and is a useful acne treatment due to its ability to additionally block the androgen receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in th ...
at higher doses. Alone or in combination with a birth control pill, spironolactone has shown a 33 to 85% reduction in acne lesions in women. The effectiveness of spironolactone for acne appears to be dose-dependent. High-dose cyproterone acetate alone reportedly decreases acne symptoms in women by 75 to 90% within three months. It is usually combined with an estrogen to avoid menstrual irregularities
Irregular menstruation is a menstrual disorder whose manifestations include irregular cycle lengths as well as metrorrhagia (vaginal bleeding between expected periods). The possible causes of irregular menstruation may vary. The common factors of ...
and estrogen deficiency
Hypoestrogenism, or estrogen deficiency, refers to a lower than normal level of estrogen. It is an umbrella term used to describe estrogen deficiency in various conditions. Estrogen deficiency is also associated with an increased risk of cardiov ...
. The medication appears to be effective in the treatment of acne in males, with one study finding that a high dosage reduced inflammatory acne lesions by 73%. However, spironolactone and cyproterone acetate's side effects in males, such as gynecomastia
Gynecomastia (also spelled gynaecomastia) is the abnormal non-cancerous enlargement of one or both breasts in males due to the growth of breast tissue as a result of a hormone imbalance between estrogens and androgens. Updated by Brent Wisse (1 ...
, sexual dysfunction, and decreased bone mineral density, generally make their use for male acne impractical.
Pregnant and lactating women should not receive antiandrogens for their acne due to a possibility of congenital disorder, birth disorders such as hypospadias and Feminization (biology), feminization of male babies. Women who are sexually active and who can or may become pregnant should use an effective method of contraception to prevent pregnancy while taking an antiandrogen. Antiandrogens are often combined with birth control pills for this reason, which can result in additive efficacy. The FDA added a Boxed warning, black-box warning to spironolactone about possible tumor risks based on preclinical research with very high doses (>100-fold clinical doses) and cautioned that unnecessary use of the medication should be avoided. However, several large epidemiological study, epidemiological studies subsequently found no greater risk of tumors in association with spironolactone in humans. Conversely, strong associations of cyproterone acetate with certain brain tumors have been discovered and its use has been restricted. The brain tumor risk with cyproterone acetate is due to its strong progestogen (medication), progestogenic actions and is not related to antiandrogenic activity nor shared by other antiandrogens.
Flutamide, a pure receptor antagonist, antagonist of the androgen receptor, is effective in treating acne in women. It appears to reduce acne symptoms by 80 to 90% even at low doses, with several studies showing complete acne clearance. In one study, flutamide decreased acne scores by 80% within three months, whereas spironolactone decreased symptoms by only 40% in the same period. In a large long-term study, 97% of women reported satisfaction with the control of their acne with flutamide. Although effective, flutamide has a risk of serious liver toxicity, and cases of death in women taking even low doses of the medication to treat androgen-dependent skin and hair conditions have occurred. As such, the use of flutamide for acne has become increasingly limited, and it has been argued that continued use of flutamide for such purposes is unethical. Bicalutamide, a pure androgen receptor antagonist with the same mechanism as flutamide and with comparable or superior antiandrogenic efficacy but with a far lower risk of liver toxicity, is an alternative option to flutamide in the treatment of androgen-dependent skin and hair conditions in women.
Clascoterone is a topical administration, topical antiandrogen that has demonstrated effectiveness in the treatment of acne in both males and females and was approved for clinical use for this indication in August 2020. It has shown no systemic absorption or associated antiandrogenic side effects. In a small direct head-to-head comparison, clascoterone showed greater effectiveness than topical isotretinoin. 5α-Reductase inhibitors such as finasteride and dutasteride may be useful for the treatment of acne in both males and females but have not been adequately evaluated for this purpose. Moreover, 5α-reductase inhibitors have a strong potential for producing birth defects in male babies and this limits their use in women. However, 5α-reductase inhibitors are frequently used to treat hirsutism, excessive facial/body hair in women and can be combined with birth control pills to prevent pregnancy. There is no evidence as of 2010 to support the use of cimetidine or ketoconazole in the treatment of acne.
Hormonal treatments for acne such as combined birth control pills and antiandrogens may be considered first-line therapy for acne under many circumstances, including desired contraception, known or suspected hyperandrogenism, acne during adulthood, acne that flares premenstrually, and when symptoms of significant sebum production (seborrhea) are co-present. Hormone therapy is effective for acne both in women with hyperandrogenism and in women with normal androgen levels.
Azelaic acid
Azelaic acid is effective for mild to moderate acne when applied topically at a 15–20% concentration. Treatment twice daily for six months is necessary, and is as effective as topical benzoyl peroxide 5%, isotretinoin 0.05%, and erythromycin 2%. Azelaic acid is an effective acne treatment due to its ability to reduce skin cell accumulation in the follicle and its antibacterial and anti-inflammation, anti-inflammatory properties. It has a slight skin-lightening effect due to its ability to inhibit melanin synthesis. Therefore, it is useful in treating individuals with acne who are also affected by post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Azelaic acid may cause skin irritation. It is less effective and more expensive than retinoids. Azelaic acid also led to worse treatment response when compared to benzoyl peroxide. When compared to tretinoin, azelaic acid makes little or no treatment response.Salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is a topically applied beta-hydroxy acid that Bacteriostatic agent, stops bacteria from reproducing and has keratolytic properties. It is less effective than retinoid therapy. Salicylic acid opens obstructed skin pores and promotes the shedding of epithelial skin cells. Xerosis, Dry skin is the most commonly seen side effect with topical application, though hyperpigmentation, darkening of the skin can occur in individuals with darker skin types.Other medications
Topical and oral preparations ofnicotinamide
Niacinamide or Nicotinamide (NAM) is a form of vitamin B3 found in food and used as a dietary supplement and medication. As a supplement, it is used by mouth to prevent and treat pellagra (niacin deficiency). While nicotinic acid (niacin) may ...
(the amide form of Niacin (nutrient), vitamin B3) are alternative medical treatments. Nicotinamide reportedly improves acne due to its anti-inflammatory properties, its ability to suppress sebum production, and its wound healing properties. Topical and oral preparations of zinc are suggested treatments for acne; evidence to support their use for this purpose is limited. Zinc's capacities to reduce inflammation and sebum production as well as inhibit ''C. acnes'' growth are its proposed mechanisms for improving acne. Antihistamines may improve symptoms among those already taking isotretinoin due to their anti-inflammatory properties and their ability to suppress sebum production.
Hydroquinone lightens the skin when applied topically by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for converting the amino acid tyrosine to the skin pigment melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
, and is used to treat acne-associated post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. By interfering with the production of melanin in the epidermis, hydroquinone leads to less hyperpigmentation as darkened skin cells are naturally shed over time. Improvement in skin hyperpigmentation is typically seen within six months when used twice daily. Hydroquinone is ineffective for hyperpigmentation affecting deeper layers of skin such as the dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided i ...
. The use of a sunscreen
Sunscreen, also known as sunblock or sun cream, is a photoprotective topical product for the skin that mainly absorbs, or to a much lesser extent reflects, some of the sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation and thus helps protect against sunburn and ...
with SPF 15 or higher in the morning with reapplication every two hours is recommended when using hydroquinone. Its application only to affected areas lowers the risk of lightening the color of normal skin but can lead to a temporary ring of lightened skin around the hyperpigmented area. Hydroquinone is generally well-tolerated; side effects are typically mild (e.g., skin irritation) and occur with the use of a higher than the recommended 4% concentration. Most preparations contain the preservative sodium metabisulfite, which has been linked to rare cases of allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis and severe asthma exacerbations in susceptible people. In extremely rare cases, the frequent and improper application of high-dose hydroquinone has been associated with a systemic condition known as exogenous ochronosis (skin discoloration and connective tissue damage from the accumulation of homogentisic acid).
Combination therapy
Combination therapy—using medications of different classes together, each with a different mechanism of action—has been demonstrated to be a more effective approach to acne treatment than monotherapy. The use of topical benzoyl peroxide and antibiotics together is more effective than antibiotics alone. Similarly, using a topical retinoid with an antibiotic clears acne lesions faster than the use of antibiotics alone. Frequently used combinations include the following: antibiotic and benzoyl peroxide, antibiotic and topical retinoid, or topical retinoid and benzoyl peroxide. Dermatologists generally prefer combining benzoyl peroxide with a retinoid over the combination of a topical antibiotic with a retinoid. Both regimens are effective, but benzoyl peroxide does not lead to antibiotic resistance.Pregnancy
Although sebaceous gland activity in the skin increases during the late stages of pregnancy, pregnancy has not been reliably associated with worsened acne severity. In general, topically applied medications are considered the first-line approach to acne treatment during pregnancy, as they have little systemic absorption and are therefore unlikely to harm a developing fetus. Highly recommended therapies include topically applied benzoyl peroxide (pregnancy category C) and azelaic acid (category B). Salicylic acid carries a category C safety rating due to higher systemic absorption (9–25%), and an association between the use of anti-inflammatory medications in the third trimester and adverse effects to the developing fetus including oligohydramnios, too little amniotic fluid in the uterus and early closure of the babies' ductus arteriosus blood vessel. Prolonged use of salicylic acid over significant areas of the skin or under occlusive dressing, occlusive (sealed) dressings is not recommended as these methods increase systemic absorption and the potential for fetal harm. Tretinoin (category C) and adapalene (category C) are very poorly absorbed, but certain studies have suggested teratogenic effects in the first trimester. The data examining the association between maternal topical retinoid exposure in the first trimester of pregnancy and adverse pregnancy outcomes is limited. A systematic review of observational studies concluded that such exposure does not appear to increase the risk of major congenital malformations, birth defects, Spontaneous abortion, miscarriages, stillbirths, premature births, or low birth weight. Similarly, in studies examining the effects of topical retinoids during pregnancy, fetal harm has not been seen in the second and third trimesters. Nevertheless, since rare harms from topical retinoids are not ruled out, they are not recommended for use during pregnancy due to persistent safety concerns. Retinoids contraindicated for use during pregnancy include the topical retinoid tazarotene, and oral retinoids isotretinoin and acitretin (all category X). Spironolactone is relatively contraindicated for use during pregnancy due to its antiandrogen effects. Finasteride is not recommended as it is highly teratogenic. Topical antibiotics deemed safe during pregnancy include clindamycin, erythromycin, and metronidazole (all category B), due to negligible systemic absorption. Nadifloxacin and dapsone (category C) are other topical antibiotics that may be used to treat acne in pregnant women but have received less study. No adverse fetal events have been reported from the topical use of dapsone. If retinoids are used there is a high risk of abnormalities occurring in the developing fetus; women of childbearing age are therefore required to use effective birth control if retinoids are used to treat acne. Oral antibiotics deemed safe for pregnancy (all category B) include azithromycin, cephalosporins, and penicillins. Tetracyclines (category D) are contraindicated during pregnancy as they are known to deposit in developing fetal teeth, resulting in yellow discoloration and enamel hypoplasia, thinned tooth enamel. Their use during pregnancy has been associated with the development of acute fatty liver of pregnancy and is further avoided for this reason.Procedures
Limited evidence supports comedo extraction, but it is an option for comedones that do not improve with standard treatment. Another procedure for immediate relief is the injection of a corticosteroid into an inflamed acne comedo. Electrocautery and electrofulguration are effective alternative treatments for comedones. Light therapy is a treatment method that involves delivering certain specific wavelengths of light to an area of skin affected by acne. Both regular and laser light have been used. The evidence for light therapy as a treatment for acne is weak and inconclusive. Various light therapies appear to provide a short-term benefit, but data for long-term outcomes, and outcomes in those with severe acne, are sparse; it may have a role for individuals whose acne has been resistant to topical medications. A 2016 meta-analysis was unable to conclude whether light therapies were more beneficial than placebo or no treatment, nor the duration of benefit. When regular light is used immediately following the application of a photosensitizer, sensitizing substance to the skin such as aminolevulinic acid or methyl aminolevulinate, the treatment is referred to as photodynamic therapy (PDT). PDT has the most supporting evidence of all light therapy modalities. PDT treats acne by using various forms of light (e.g., blue light or red light) that preferentially target the pilosebaceous unit. Once the light activates the sensitizing substance, this generates free radicals and reactive oxygen species in the skin, which purposefully damage the sebaceous glands and kill ''C. acnes'' bacteria. Many different types of nonablative lasers (i.e., lasers that do not vaporize the top layer of the skin but rather induce a physiologic response in the skin from the light) have been used to treat acne, including those that use infrared wavelengths of light. Ablative lasers (such as Carbon dioxide laser, CO2 and fractional types) have also been used to treat active acne and its scars. When ablative lasers are used, the treatment is often referred to as laser resurfacing because, as mentioned previously, the entire upper layers of the skin are vaporized. Ablative lasers are associated with higher rates of adverse effects compared with non-ablative lasers, with examples being post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, persistent facial redness, and persistent pain. Physiologically, certain wavelengths of light, used with or without accompanying topical chemicals, are thought to kill bacteria and decrease the size and activity of the glands that produce sebum. Disadvantages of light therapy can include its cost, the need for multiple visits, the time required to complete the procedure(s), and pain associated with some of the treatment modalities. Typical side effects include desquamation, skin peeling, temporary reddening of the skin, swelling, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Dermabrasion is an effective therapeutic procedure for reducing the appearance of superficial atrophic scars of the boxcar and rolling varieties. Ice-pick scars do not respond well to treatment with dermabrasion due to their depth. The procedure is painful and has many potential side effects such as skin sensitivity to sunlight, erythema, redness, and Hypopigmentation, decreased pigmentation of the skin. Dermabrasion has fallen out of favor with the introduction of laser resurfacing. Unlike dermabrasion, there is no evidence that microdermabrasion is an effective treatment for acne. Dermal or subcutaneous Injectable filler, fillers are substances injected into the skin to improve the appearance of acne scars. Fillers are used to increase naturalcollagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole ...
production in the skin and to increase skin volume and decrease the depth of acne scars. Examples of fillers used for this purpose include hyaluronic acid; poly(methyl methacrylate) microspheres with collagen; human and bovine collagen derivatives, and fat harvested from the person's own body (autologous fat transfer).
Microneedling is a procedure in which an instrument with multiple rows of tiny needles is rolled over the skin to elicit a wound healing response and stimulate collagen production to reduce the appearance of atrophic acne scars in people with darker skin color. Notable adverse effects of microneedling include post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and tram track scarring (described as discrete slightly raised scars in a linear distribution similar to a tram track). The latter is thought to be primarily attributable to improper technique by the practitioner, including the use of excessive pressure or inappropriately large needles.
Subcision is useful for the treatment of superficial atrophic acne scars and involves the use of a small needle to loosen the fibrotic adhesions that result in the depressed appearance of the scar.
Chemical peels can be used to reduce the appearance of acne scars. Mild peels include those using glycolic acid, lactic acid, salicylic acid, Jessner's solution, or a lower concentration (20%) of trichloroacetic acid. These peels only affect the epidermis, epidermal layer of the skin and can be useful in the treatment of superficial acne scars as well as skin pigmentation changes from inflammatory acne. Higher concentrations of trichloroacetic acid (30–40%) are considered to be medium-strength peels and affect the skin as deep as the Dermis#Stratum papillare, papillary dermis. Formulations of trichloroacetic acid concentrated to 50% or more are considered to be deep chemical peels. Medium-strength and deep-strength chemical peels are more effective for deeper atrophic scars but are more likely to cause side effects such as skin pigmentation changes, infection, and Milium (dermatology), small white superficial cysts known as milia.
Alternative medicine
Researchers are investigating complementary therapies as treatment for people with acne. Evidence-based medicine#Assessing the quality of evidence, Low-quality evidence suggests topical application of tea tree oil or bee venom may reduce the total number of skin lesions in those with acne. Tea tree oil appears to be approximately as effective as benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid but is associated with allergic contact dermatitis. Proposed mechanisms for tea tree oil's anti-acne effects include antibacterial action against ''C. acnes'' and anti-inflammatory properties. Numerous other plant-derived therapies have demonstrated positive effects against acne (e.g., basil oil; oligosaccharides from seaweed; however, few well-done studies have examined their use for this purpose. There is a lack of high-quality evidence for the use of acupuncture, Herbalism, herbal medicine, or cupping therapy for acne.Self-care
Many over-the-counter treatments in many forms are available, which are often known as cosmeceuticals. Certain types of makeup may be useful to mask acne. In those with oily skin, a water-based product is often preferred.Prognosis
Acne usually improves around the age of 20 but may persist into adulthood. Permanent physical scarring may occur. Rare complications from acne or its treatment include the formation of pyogenic granulomas, osteoma cutis, and acne with facial edema. Early and aggressive treatment of acne is advocated by some in the medical community to reduce the chances of these poor outcomes.Mental health impact
There is good evidence to support the idea that acne and associated scarring negatively affect a person's psychological state, worsen mood, lower self-esteem, and are associated with a higher risk of anxiety disorders, depression (mood), depression, and Suicidal ideation, suicidal thoughts. Misperceptions about acne's causative and aggravating factors are common, and people with acne often blame themselves, and others often blame those with acne for their condition. Such blame can worsen the affected person's sense of self-esteem. Until the 20th century, even among dermatologists, the list of causes was believed to include excessive sexual thoughts and masturbation. Dermatology's association with sexually transmitted infections, especially syphilis, contributed to the stigma. Another psychological complication of acne vulgaris is acne excoriée, which occurs when a person persistently picks and scratches pimples, irrespective of the severity of their acne. This can lead to significant scarring, changes in the affected person's skin pigmentation, and a cyclic worsening of the affected person's anxiety about their appearance.Epidemiology
Globally, acne affects approximately 650 million people, or about 9.4% of the population, as of 2010. It affects nearly 90% of people in Western societies during their teenage years, but can occur before adolescence and may persist into adulthood. While acne that first develops between the ages of 21 and 25 is uncommon, it affects 54% of women and 40% of men older than 25 years of age and has a lifetime prevalence of 85%. About 20% of those affected have moderate or severe cases. It is slightly more common in females than males (9.8% versus 9.0%). In those over 40 years old, 1% of males and 5% of females still have problems. Rates appear to be lower in rural societies. While some research has found it affects people of all ethnic groups, acne may not occur in the non-Westernized peoples of Papua New Guinea and Paraguay. Acne affects 40–50 million people in the United States (16%) and approximately 3–5 million in Australia (23%). Severe acne tends to be more common in people of Caucasian or Amerindian descent than in people of African descent.History
Historical records indicate Pharaoh, Pharaohs had acne, which may be the earliest known reference to the disease. Sulfur's usefulness as a topical remedy for acne dates back to at least the reign of Cleopatra (69–30 BCE). The sixth-century Greece, Greek physician Aëtius of Amida reportedly coined the term "" (,) or "", which seems to be a reference to facial skin lesions that occur during "the 'wikt:acme, acme' of life" (puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. ...
).
In the 16th century, the French physician and botanist François Boissier de Sauvages de Lacroix provided one of the earlier descriptions of acne. He used the term "psydracia achne" to describe small, red, and hard Tubercle (anatomy), tubercles that altered a person's facial appearance during adolescence and were neither itchy nor painful.
The recognition and characterization of acne progressed in 1776 when Josef Plenck (an Austrian physician) published a book that proposed the novel concept of classifying skin diseases by their elementary (initial) lesions. In 1808 the England, English dermatologist Robert Willan refined Plenck's work by providing the first detailed descriptions of several skin disorders using morphologic terminology that remains in use today. Thomas Bateman (physician), Thomas Bateman continued and expanded on Robert Willan's work as his student and provided the first descriptions and illustrations of acne accepted as accurate by modern dermatologists. Erasmus Wilson, in 1842, was the first to make the distinction between acne vulgaris and rosacea. The first professional medical monograph dedicated entirely to acne was written by Lucius Duncan Bulkley and published in New York in 1885.
Scientists initially hypothesized that acne represented a disease of the skin's hair follicle, and occurred due to blockage of the pore by sebum. During the 1880s, they observed bacteria by microscopy in skin samples from people with acne. Investigators believed the bacteria caused comedones, sebum production, and ultimately acne. During the mid-twentieth century, dermatologists realized that no single hypothesized factor (sebum, bacteria, or excess keratin) fully accounted for the disease in its entirety. This led to the current understanding that acne could be explained by a sequence of related events, beginning with blockage of the skin follicle by excessive dead skin cells, followed by bacterial invasion of the hair follicle pore, changes in sebum production, and inflammation.
The approach to acne treatment underwent significant changes during the twentieth century. Retinoids became a medical treatment for acne in 1943. Benzoyl peroxide was first proposed as a treatment in 1958 and remains a staple of acne treatment. The introduction of oral tetracycline antibiotics (such as minocycline) modified acne treatment in the 1950s. These reinforced the idea amongst dermatologists that bacterial growth on the skin plays an important role in causing acne. Subsequently, in the 1970s, tretinoin
Tretinoin, also known as all-''trans'' retinoic acid (ATRA), is a medication used for the treatment of acne and acute promyelocytic leukemia. For acne, it is applied to the skin as a cream, gel or ointment. For leukemia, it is taken by mouth ...
(original trade name Retin A) was found to be an effective treatment. The development of oral isotretinoin
Isotretinoin, also known as 13-''cis''-retinoic acid and sold under the brand name Accutane among others, is a medication primarily used to treat severe acne. It is also used to prevent certain skin cancers ( squamous-cell carcinoma), and in t ...
(sold as Accutane and Roaccutane) followed in 1980. After its introduction in the United States, scientists identified isotretinoin as a medication highly likely to cause birth defects if taken during pregnancy. In the United States, more than 2,000 women became pregnant while taking isotretinoin between 1982 and 2003, with most pregnancies ending in abortion or miscarriage. Approximately 160 babies were born with birth defects due to maternal use of isotretinoin during pregnancy.
Treatment of acne with topical crushed dry ice, known as cryoslush, was first described in 1907 but is no longer performed commonly. Before 1960, the use of X-rays was also a common treatment.
Society and culture
The costs and social impact of acne are substantial. In the United States, acne vulgaris is responsible for more than 5 million physician, doctor visits and costs over billion each year in Variable cost, direct costs. Similarly, acne vulgaris is responsible for 3.5 million doctor visits each year in the United Kingdom. Sales for the top ten leading acne treatment brands in the US in 2015 amounted to $352million. Acne vulgaris and its resultant scars are associated with significant social and academic difficulties that can last into adulthood. During the Great Depression, dermatologists discovered that young men with acne had difficulty obtaining jobs. Until the 1930s, many people viewed acne as a trivial problem among middle-class girls because, unlike smallpox and tuberculosis, no one died from it, and a feminine problem, because boys were much less likely to seek medical assistance for it. During World War II, some soldiers in tropical climates developed such severe and widespread tropical acne on their bodies that they were declared medically Selective Service System#Classifications, unfit for duty.Research
Efforts to better understand the mechanisms of sebum production are underway. This research aims to develop medications that target and interfere with the hormones that are known to increase sebum production (e.g., IGF-1 and alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone). Other sebum-lowering medications such as topical antiandrogens, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor modulators, and inhibitors of the stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 enzyme are also a focus of research efforts. Particles that release nitric oxide into the skin to decrease skin inflammation caused by ''C. acnes'' and theimmune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
have shown promise for improving acne in early clinical trials. Another avenue of early-stage research has focused on how to best use laser and light therapy to selectively destroy sebum-producing glands in the skin's hair follicles to reduce sebum production and improve acne appearance.
The use of antimicrobial peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for a ...
against ''C. acnes'' is under investigation as a treatment for acne to overcoming antibiotic resistance. In 2007, scientists reported the first genome DNA sequencing, sequencing of a ''C. acnes'' bacteriophage (PA6). The authors proposed applying this research toward the development of phage therapy, bacteriophage therapy as an acne treatment to overcome the problems associated with long-term antibiotic use, such as bacterial resistance. Oral and topical probiotics are under evaluation as treatments for acne. Probiotics may have therapeutic effects for those affected by acne due to their ability to decrease skin inflammation and improve skin moisture by increasing the skin's ceramide content. As of 2014, knowledge of the effects of probiotics on acne in humans was limited.
Decreased levels of retinoic acid in the skin may contribute to comedo formation. Researchers are investigating methods to increase the skin's production of retinoic acid to address this deficiency. A vaccine against inflammatory acne has shown promising results in mice and humans. Some have voiced concerns about creating a vaccine designed to neutralize a stable community of normal skin bacteria that is known to protect the skin from colonization by more harmful microorganisms.
Other animals
Acne can occur on Feline acne, cats, dogs, and horses.References
Further reading
* * *External links
Acne Support
Expert, impartial advice on acne by the British Association of Dermatologists, BAD. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Acne Vulgaris Acneiform eruptions Cutaneous conditions Dermatology task force articles Puberty Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate