In
software testing
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations.
Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the Quality (business), quality of software and the risk of its failure to a User (computin ...
, test automation is the use of
software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
separate from the software being tested to control the execution of tests and the comparison of actual outcomes with predicted outcomes. Test automation can automate some repetitive but necessary tasks in a formalized testing process already in place, or perform additional testing that would be difficult to do manually. Test automation is critical for
continuous delivery
Continuous delivery (CD) is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time. It aims at building, testing, and releasing software with greater speed ...
and
continuous testing
Continuous testing is the process of executing automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to obtain immediate feedback on the business risks associated with a software release candidate. .
General approaches
There are many approaches to test automation, however below are the general approaches used widely:
*
Graphical user interface testing
In software engineering, graphical user interface testing is the process of software testing, testing a product's graphical user interface (GUI) to ensure it meets its specifications. This is normally done through the use of a variety of test ca ...
. A testing framework that generates
user interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine fro ...
events such as keystrokes and mouse clicks, and observes the changes that result in the user interface, to validate that the observable behavior of the program is correct.
*
API driven testing. A testing framework that uses a programming interface to the application to validate the behaviour under test. Typically API driven testing bypasses application user interface altogether. It can also be testing
public (usually) interfaces to classes, modules or libraries are tested with a variety of input arguments to validate that the results that are returned are correct.
Other approaches
Model-based testing
One way to generate test cases automatically is
model-based testing
Model-based testing is an application of model-based design for designing and optionally also executing artifacts to perform software testing or system testing. Models can be used to represent the desired behavior of a system under test (SUT), or ...
through use of a model of the system for test case generation, but research continues into a variety of alternative methodologies for doing so. In some cases, the model-based approach enables non-technical users to create automated business test cases in plain English so that no programming of any kind is needed in order to configure them for multiple operating systems, browsers, and smart devices.
Regression testing
Some
software testing
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations.
Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the Quality (business), quality of software and the risk of its failure to a User (computin ...
tasks (such as extensive low-level interface
regression testing
Regression testing (rarely, ''non-regression testing'') is re-running functional and non-functional tests to ensure that previously developed and tested software still performs as expected after a change. If not, that would be called a '' regr ...
) can be laborious and time-consuming to do manually. In addition, a manual approach might not always be effective in finding certain classes of defects. Test automation offers a possibility to perform these types of testing effectively.
Once automated tests have been developed, they can be run quickly and repeatedly many times. This can be a cost-effective method for regression testing of software products that have a long maintenance life. Even minor patches over the lifetime of the application can cause existing features to break which were working at an earlier point in time.
API testing
API testing is also being widely used by software testers as it enables them to verify requirements independent of their GUI implementation, commonly to test them earlier in development, and to make sure the test itself adheres to clean code principles, especially the
single responsibility principle. It involves directly testing
API
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build ...
s as part of
integration testing, to determine if they meet expectations for functionality, reliability, performance, and security.
[Testing APIs protects applications and reputations](_blank)
by Amy Reichert, SearchSoftwareQuality March 2015 Since APIs lack a
GUI, API testing is performed at the
message layer.
[All About API Testing: An Interview with Jonathan Cooper](_blank)
by Cameron Philipp-Edmonds, Stickyminds August 19, 2014 API testing is considered critical when an API serves as the primary interface to
application logic.
Graphical user interface (GUI) testing
Many test automation tools provide record and playback features that allow users to interactively record user actions and replay them back any number of times, comparing actual results to those expected. The advantage of this approach is that it requires little or no
software development
Software development is the process of designing and Implementation, implementing a software solution to Computer user satisfaction, satisfy a User (computing), user. The process is more encompassing than Computer programming, programming, wri ...
. This approach can be applied to any application that has a
graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
. However, reliance on these features poses major reliability and maintainability problems. Relabelling a button or moving it to another part of the window may require the test to be re-recorded. Record and playback also often adds irrelevant activities or incorrectly records some activities.
A variation on this type of tool is for testing of web sites. Here, the "interface" is the web page. However, such a framework utilizes entirely different techniques because it is rendering
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets ( ...
and listening to
DOM Events instead of operating system events.
Headless browsers or solutions based on
Selenium Web Driver are normally used for this purpose.
[Headless Testing with PhantomJS;http://phantomjs.org/headless-testing.html]
Another variation of this type of test automation tool is for testing mobile applications. This is very useful given the number of different sizes, resolutions, and operating systems used on mobile phones. For this variation, a framework is used in order to instantiate actions on the mobile device and to gather results of the actions.
Another variation is script-less test automation that does not use record and playback, but instead builds a model of the application and then enables the tester to create test cases by simply inserting test parameters and conditions, which requires no scripting skills.
Methodologies
Test-driven development
Test automation, mostly using unit testing, is a key feature of
extreme programming
Extreme programming (XP) is a software development methodology intended to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements. As a type of agile software development,"Human Centred Technology Workshop 2006 ", 2006, ...
and
agile software development
Agile software development is an umbrella term for approaches to software development, developing software that reflect the values and principles agreed upon by ''The Agile Alliance'', a group of 17 software practitioners, in 2001. As documented ...
, where it is known as
test-driven development
Test-driven development (TDD) is a way of writing source code, code that involves writing an test automation, automated unit testing, unit-level test case that fails, then writing just enough code to make the test pass, then refactoring both the ...
(TDD) or test-first development. Unit tests can be written to define the functionality ''before'' the code is written. However, these unit tests evolve and are extended as coding progresses, issues are discovered and the code is subjected to refactoring.
Only when all the tests for all the demanded features pass is the code considered complete. Proponents argue that it produces software that is both more reliable and less costly than code that is tested by manual exploration. It is considered more reliable because the code coverage is better, and because it is run constantly during development rather than once at the end of a
waterfall
A waterfall is any point in a river or stream where water flows over a vertical drop or a series of steep drops. Waterfalls also occur where meltwater drops over the edge
of a tabular iceberg or ice shelf.
Waterfalls can be formed in seve ...
development cycle. The developer discovers defects immediately upon making a change, when it is least expensive to fix. Finally,
code refactoring
In computer programming and software design, code refactoring is the process of restructuring existing source code—changing the '' factoring''—without changing its external behavior. Refactoring is intended to improve the design, structure, ...
is safer when unit testing is used; transforming the code into a simpler form with less
code duplication, but equivalent behavior, is much less likely to introduce new defects when the refactored code is covered by unit tests.
Continuous testing
Continuous testing
Continuous testing is the process of executing automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to obtain immediate feedback on the business risks associated with a software release candidate. is the process of executing automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to obtain immediate feedback on the business risks associated with a software release candidate.
[Part of the Pipeline: Why Continuous Testing Is Essential](_blank)
by Adam Auerbach, TechWell Insights August 2015[The Relationship between Risk and Continuous Testing: An Interview with Wayne Ariola](_blank)
by Cameron Philipp-Edmonds, Stickyminds December 2015 For Continuous Testing, the scope of testing extends from validating bottom-up requirements or user stories to assessing the system requirements associated with overarching business goals.
[DevOps: Are You Pushing Bugs to Clients Faster](_blank)
by Wayne Ariola and Cynthia Dunlop, PNSQC October 2015
Considerations
Factors to consider for the decision to implement test automation
What to automate, when to automate, or even whether one really needs automation are crucial decisions which the testing (or development) team must make. A multi-vocal literature review of 52 practitioner and 26 academic sources found that five main factors to consider in test automation decision are: 1) System Under Test (SUT), 2) the types and numbers of tests, 3) test-tool, 4) human and organizational topics, and 5) cross-cutting factors. The most frequent individual factors identified in the study were: need for regression testing, economic factors, and maturity of SUT.
Plateau effect
While the reusability of automated tests is valued by software development companies, this property can also be viewed as a disadvantage. It leads to the so-called
"Pesticide Paradox", where repeatedly executed scripts stop detecting errors that go beyond their frameworks. In such cases,
manual testing
:''Compare with Test automation''.
Manual testing is the process of manually Software testing, testing software for defects. It requires a tester to play the role of an end user where by they use most of the application's features to ensure corre ...
may be a better investment. This ambiguity once again leads to the conclusion that the decision on test automation should be made individually, keeping in mind project requirements and peculiarities.
What to test
Testing tools can help automate tasks such as product installation, test data creation, GUI interaction, problem detection (consider parsing or polling agents equipped with
test oracle
In software testing, a test oracle (or just oracle) is a provider of information that describes correct output based on the input of a test case. Testing with an oracle involves comparing actual results of the system under test (SUT) with the ex ...
s), defect logging, etc., without necessarily automating tests in an end-to-end fashion.
One must keep satisfying popular requirements when thinking of test automation:
*
Platform and
OS independence
* Data driven capability (Input Data, Output Data,
Metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
* Descriptive ...
)
* Customization Reporting (DB
Data Base Access,
Crystal Reports
Crystal Reports is a business intelligence application marketed to small- and medium-sized businesses by SAP.
History
Terry Cunningham and the Cunningham Group originated the software in 1984. Crystal Services Inc. marketed the product (origina ...
)
* Easy debugging and logging
*
Version control
Version control (also known as revision control, source control, and source code management) is the software engineering practice of controlling, organizing, and tracking different versions in history of computer files; primarily source code t ...
friendly – minimal binary files
* Extensible & Customization (Open
API
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build ...
s to be able to integrate with other tools)
* Common Driver (For example, in the Java development ecosystem, that means
Ant
Ants are Eusociality, eusocial insects of the Family (biology), family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the Taxonomy (biology), order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from Vespoidea, vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cre ...
or
Maven and the popular
IDEs). This enables tests to integrate with the developers'
workflows
Workflow is a generic term for orchestrated and repeatable patterns of activity, enabled by the systematic organization of resources into processes that transform materials, provide services, or process information. It can be depicted as a sequen ...
.
* Support unattended test runs for integration with build processes and batch runs.
Continuous integration
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice of integrating source code changes frequently and ensuring that the integrated codebase is in a workable state.
Typically, developers Merge (version control), merge changes to an Branching (revisio ...
servers require this.
* Email Notifications like
bounce messages
* Support distributed execution environment (distributed
test bed)
* Distributed application support (distributed
SUT)
Roles
Test automation tools
Test automation tools can be expensive and are usually employed in combination with manual testing. Test automation can be made cost-effective in the long term, especially when used repeatedly in
regression testing
Regression testing (rarely, ''non-regression testing'') is re-running functional and non-functional tests to ensure that previously developed and tested software still performs as expected after a change. If not, that would be called a '' regr ...
. A good candidate for test automation is a test case for common flow of an application, as it is required to be executed (regression testing) every time an enhancement is made in the application. Test automation reduces the effort associated with manual testing. Manual effort is needed to develop and maintain automated checks, as well as reviewing test results.
Test engineer
In automated testing, the
test engineer or
software quality assurance
Software quality assurance (SQA) is a means and practice of monitoring all software engineering processes, methods, and work products to ensure compliance against defined standards. It may include ensuring conformance to standards or models, suc ...
person must have software coding ability since the test cases are written in the form of source code which when run produce output according to the
assertions that are a part of it. Some test automation tools allow for test authoring to be done by keywords instead of coding, which do not require programming.
Testing at different levels
A strategy to decide the amount of tests to automate is the test automation pyramid. This strategy suggests to write three types of tests with different granularity. The higher the level, less is the amount of tests to write.
Unit, service, and user interface levels

* As a solid foundation,
unit testing
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior.
Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the Integration ...
provides robustness to the software products. Testing individual parts of the code makes it easy to write and run the tests. Developers write unit tests as a part of each story and integrate them with CI.
* The service layer refers to testing the services of an application separately from its user interface, these services are anything that the application does in response to some input or set of inputs.
* At the top level we have
UI testing which has fewer tests due to the different attributes that make it more complex to run, for example the fragility of the tests, where a small change in the user interface can break a lot of tests and adds maintenance effort.
Unit, integration, and end-to-end levels
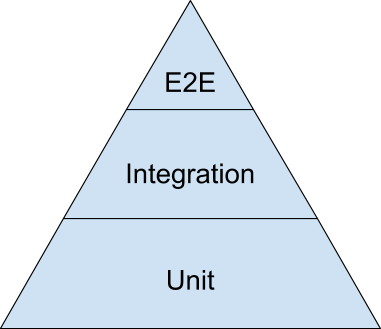
One conception of the testing pyramid contains unit, integration, and end-to-end unit tests. According to
Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
's testing blog, unit tests should make up the majority of your testing strategy, with fewer integration tests and only a small amount of end-to-end tests.
* Unit tests: These are tests that test individual components or units of code in isolation. They are fast, reliable, and isolate failures to small units of code.
* Integration tests: These tests check how different units of code work together. Although individual units may function properly on their own, integration tests ensure that they operate together coherently.
* End-to-end tests: These test the system as a whole, simulating real-world usage scenarios. They are the slowest and most complex tests.
Framework approach in automation
A test automation framework is an integrated system that sets the rules of automation of a specific product. This system integrates the function libraries, test data sources, object details and various reusable modules. These components act as small building blocks which need to be assembled to represent a business process. The framework provides the basis of test automation and simplifies the automation effort.
The main advantage of a
framework of assumptions, concepts and tools that provide support for automated software testing is the low cost for
maintenance
The technical meaning of maintenance involves functional checks, servicing, repairing or replacing of necessary devices, equipment, machinery, building infrastructure and supporting utilities in industrial, business, and residential installa ...
. If there is change to any
test case
In software engineering, a test case is a specification of the inputs, execution conditions, testing procedure, and expected results that define a single test to be executed to achieve a particular software testing objective, such as to exercise ...
then only the test case file needs to be updated and the
driver Script and
startup script
In Unix-based computer operating systems, init (short for ''initialization'') is the first process started during booting of the operating system. Init is a daemon process that continues running until the system is shut down. It is the direc ...
will remain the same. Ideally, there is no need to update the scripts in case of changes to the application.
Choosing the right framework/scripting technique helps in maintaining lower costs. The costs associated with test scripting are due to development and maintenance efforts. The approach of scripting used during test automation has effect on costs.
Various framework/scripting techniques are generally used:
# Linear (procedural code, possibly generated by tools like those that use record and playback)
# Structured (uses control structures - typically ‘if-else’, ‘switch’, ‘for’, ‘while’ conditions/ statements)
#
Data-driven
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous value (semiotics), values that convey information, describing the quantity, qualitative property, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols t ...
(data is persisted outside of tests in a database, spreadsheet, or other mechanism)
#
Keyword-driven
# Hybrid (two or more of the patterns above are used)
# Agile automation framework
The Testing framework is responsible for:
# defining the format in which to express expectations
# creating a mechanism to hook into or drive the application under test
# executing the tests
# reporting results
Unit testing frameworks
A growing trend in software development is the use of
unit testing
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior.
Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the Integration ...
frameworks such as the
xUnit frameworks (for example,
JUnit
JUnit is a test automation framework for the Java programming language. JUnit is often used for unit testing, and is one of the xUnit frameworks.
JUnit is linked as a JAR at compile-time. The latest version of the framework, JUnit 5, resides ...
and
NUnit) that allow the execution of unit tests to determine whether various sections of the
code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communicati ...
are acting as expected under various circumstances.
Test case
In software engineering, a test case is a specification of the inputs, execution conditions, testing procedure, and expected results that define a single test to be executed to achieve a particular software testing objective, such as to exercise ...
s describe tests that need to be run on the program to verify that the program runs as expected.
Test automation interface
Test automation interfaces are platforms that provide a single
workspace for incorporating multiple testing tools and frameworks for
System/Integration testing of application under test. The goal of Test Automation Interface is to simplify the process of mapping tests to business criteria without coding coming in the way of the process. Test automation interface are expected to improve the efficiency and flexibility of maintaining test scripts.

Test Automation Interface consists of the following core modules:
* Interface Engine
* Interface Environment
* Object Repository
Interface engine
Interface engines are built on top of Interface Environment. Interface engine consists of a
parser
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is a process of analyzing a string of symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar by breaking it into parts. The term '' ...
and a test runner. The parser is present to parse the object files coming from the object repository into the test specific scripting language. The test runner executes the test scripts using a
test harness.
Object repository
Object repositories are a collection of UI/Application object data recorded by the testing tool while exploring the application under test.
Defining boundaries between automation framework and a testing tool
Tools are specifically designed to target some particular test environment, such as Windows and web automation tools, etc. Tools serve as a driving agent for an automation process. However, an automation framework is not a tool to perform a specific task, but rather infrastructure that provides the solution where different tools can do their job in a unified manner. This provides a common platform for the automation engineer.
There are various types of frameworks. They are categorized on the basis of the automation component they leverage. These are:
#
Data-driven testing
#
Modularity-driven testing
#
Keyword-driven testing
#
Hybrid testing
#
Model-based testing
Model-based testing is an application of model-based design for designing and optionally also executing artifacts to perform software testing or system testing. Models can be used to represent the desired behavior of a system under test (SUT), or ...
# Code-driven testing
#
Behavior driven development
Data-driven testing
Modularity-driven testing
Keyword-driven testing
Hybrid testing
Model-based testing
Behavior driven development
See also
*
Comparison of GUI testing tools
*
List of web testing tools
*
Continuous testing
Continuous testing is the process of executing automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to obtain immediate feedback on the business risks associated with a software release candidate.
*
Fuzzing
In programming and software development, fuzzing or fuzz testing is an automated software testing technique that involves providing invalid, unexpected, or random data as inputs to a computer program. The program is then monitored for exceptio ...
*
Headless browser
*
Software testing
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations.
Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the Quality (business), quality of software and the risk of its failure to a User (computin ...
*
System testing
System testing, a.k.a. end-to-end (E2E) testing, is testing conducted on a complete software system.
System testing describes testing at the system level to contrast to testing at the system integration, integration or unit level.
System t ...
*
Unit test
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior.
Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the integration ...
References
General references
*
*
*
* Roman Savenkov: ''How to Become a Software Tester.'' Roman Savenkov Consulting, 2008,
*
*
* Hayes, Linda G., "Automated Testing Handbook", Software Testing Institute, 2nd Edition, March 2004
* Kaner, Cem,
Architectures of Test Automation", August 2000
{{DEFAULTSORT:Test Automation
Automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
Automation software
 * As a solid foundation,
* As a solid foundation,  One conception of the testing pyramid contains unit, integration, and end-to-end unit tests. According to
One conception of the testing pyramid contains unit, integration, and end-to-end unit tests. According to  Test Automation Interface consists of the following core modules:
* Interface Engine
* Interface Environment
* Object Repository
Test Automation Interface consists of the following core modules:
* Interface Engine
* Interface Environment
* Object Repository