Asexual reproduction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Asexual reproduction is a type of
 Some cells divide by budding (for example baker's yeast), resulting in a "mother" and a "daughter" cell that is initially smaller than the parent. Budding is also known on a multicellular level; an animal example is the hydra, which reproduces by budding. The buds grow into fully matured individuals which eventually break away from the parent organism.
Internal budding is a process of asexual reproduction, favoured by parasites such as '' Toxoplasma gondii''. It involves an unusual process in which two (''endodyogeny'') or more (''endopolygeny'') daughter cells are produced inside a mother cell, which is then consumed by the offspring prior to their separation.
Also, budding (external or internal) occurs in some worms like '' Taenia'' or '' Echinococcus''; these worms produce cysts and then produce (invaginated or evaginated) protoscolex with budding.
Some cells divide by budding (for example baker's yeast), resulting in a "mother" and a "daughter" cell that is initially smaller than the parent. Budding is also known on a multicellular level; an animal example is the hydra, which reproduces by budding. The buds grow into fully matured individuals which eventually break away from the parent organism.
Internal budding is a process of asexual reproduction, favoured by parasites such as '' Toxoplasma gondii''. It involves an unusual process in which two (''endodyogeny'') or more (''endopolygeny'') daughter cells are produced inside a mother cell, which is then consumed by the offspring prior to their separation.
Also, budding (external or internal) occurs in some worms like '' Taenia'' or '' Echinococcus''; these worms produce cysts and then produce (invaginated or evaginated) protoscolex with budding.
 Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction found in plants where new individuals are formed without the production of seeds or spores and thus without syngamy or meiosis. Examples of vegetative reproduction include the formation of miniaturized plants called plantlets on specialized leaves, for example in kalanchoe ('' Bryophyllum daigremontianum'') and many produce new plants from
Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction found in plants where new individuals are formed without the production of seeds or spores and thus without syngamy or meiosis. Examples of vegetative reproduction include the formation of miniaturized plants called plantlets on specialized leaves, for example in kalanchoe ('' Bryophyllum daigremontianum'') and many produce new plants from
 Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction where a new organism grows from a fragment of the parent. Each fragment develops into a mature, fully grown individual. Fragmentation is seen in many organisms. Animals that reproduce asexually include planarians, many annelid worms including polychaetes and some oligochaetes, turbellarians and
Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction where a new organism grows from a fragment of the parent. Each fragment develops into a mature, fully grown individual. Fragmentation is seen in many organisms. Animals that reproduce asexually include planarians, many annelid worms including polychaetes and some oligochaetes, turbellarians and
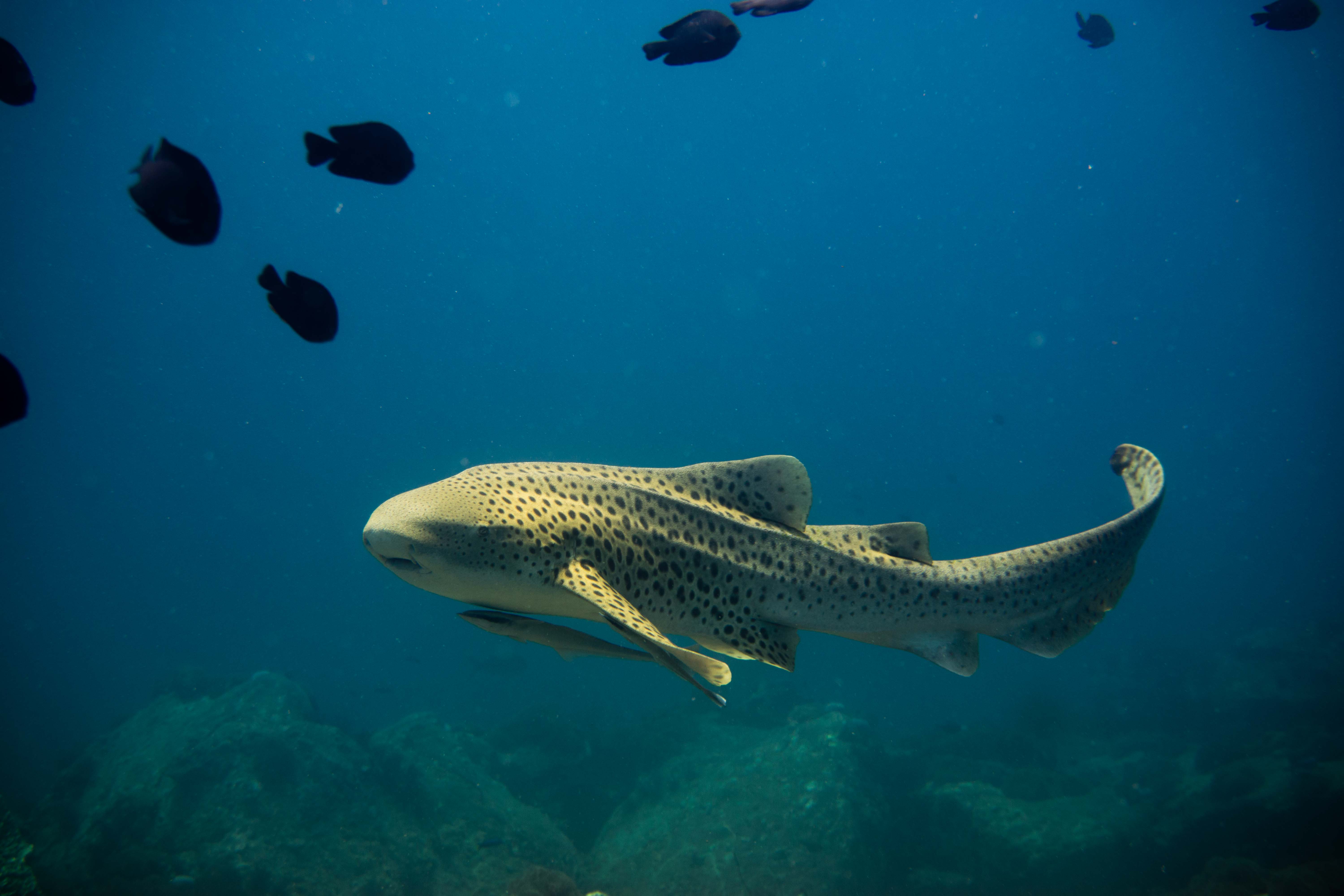 In facultative parthenogenesis, females can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Because of the many advantages of sexual reproduction, most facultative parthenotes only reproduce asexually when forced to. This typically occurs in instances when finding a mate becomes difficult. For example, female zebra sharks will reproduce asexually if they are unable to find a mate in their ocean habitats.
Parthenogenesis was previously believed to rarely occur in vertebrates, and only be possible in very small animals. However, it has been discovered in many more species in recent years. Today, the largest species that has been documented reproducing parthenogenically is the Komodo dragon at 10 feet long and over 300 pounds.
In facultative parthenogenesis, females can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Because of the many advantages of sexual reproduction, most facultative parthenotes only reproduce asexually when forced to. This typically occurs in instances when finding a mate becomes difficult. For example, female zebra sharks will reproduce asexually if they are unable to find a mate in their ocean habitats.
Parthenogenesis was previously believed to rarely occur in vertebrates, and only be possible in very small animals. However, it has been discovered in many more species in recent years. Today, the largest species that has been documented reproducing parthenogenically is the Komodo dragon at 10 feet long and over 300 pounds.
 Heterogony is a form of facultative parthenogenesis where females alternate between sexual and asexual reproduction at regular intervals (see Alternation between sexual and asexual reproduction).
Heterogony is a form of facultative parthenogenesis where females alternate between sexual and asexual reproduction at regular intervals (see Alternation between sexual and asexual reproduction).
 In obligate parthenogenesis, females only reproduce asexually. One example of this is the desert grassland whiptail lizard, a hybrid of two other species. Typically hybrids are infertile but through parthenogenesis this species has been able to develop stable populations.
Gynogenesis is a form of obligate parthenogenesis where a sperm cell is used to initiate reproduction. However, the sperm's genes never get incorporated into the egg cell. The best known example of this is the Amazon molly. Because they are obligate parthenotes, there are no males in their species so they depend on males from a closely related species (the Sailfin molly) for sperm.
In obligate parthenogenesis, females only reproduce asexually. One example of this is the desert grassland whiptail lizard, a hybrid of two other species. Typically hybrids are infertile but through parthenogenesis this species has been able to develop stable populations.
Gynogenesis is a form of obligate parthenogenesis where a sperm cell is used to initiate reproduction. However, the sperm's genes never get incorporated into the egg cell. The best known example of this is the Amazon molly. Because they are obligate parthenotes, there are no males in their species so they depend on males from a closely related species (the Sailfin molly) for sperm.
 Some species can alternate between sexual and asexual strategies, an ability known as '' heterogamy'', depending on many conditions. Alternation is observed in several
Some species can alternate between sexual and asexual strategies, an ability known as '' heterogamy'', depending on many conditions. Alternation is observed in several
Inheritance of asexual reproduction by a single recessive locus has also been found in the
Asexual reproduction
{{DEFAULTSORT:Asexual Reproduction
reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual ...
that does not involve the fusion of gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s inherit the full set of genes of their single parent and thus the newly created individual is genetically and physically similar to the parent or an exact clone of the parent. Asexual reproduction is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms such as archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
and bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
. Many eukaryotic
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
organisms including plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s, animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s, and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
can also reproduce asexually. In vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
, the most common form of asexual reproduction is parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek + ) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which the embryo develops directly from an egg without need for fertilization. In animals, parthenogenesis means the development of an embryo from an unfertiliz ...
, which is typically used as an alternative to sexual reproduction in times when reproductive opportunities are limited. Some monitor lizards, including Komodo dragons, can reproduce asexually.
While all prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s reproduce without the formation and fusion of gametes, mechanisms for lateral gene transfer such as conjugation
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to:
Linguistics
*Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form
*Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language
Mathematics
*Complex conjugation, the change o ...
, transformation and transduction can be likened to sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
in the sense of genetic recombination
Genetic recombination (also known as genetic reshuffling) is the exchange of genetic material between different organisms which leads to production of offspring with combinations of traits that differ from those found in either parent. In eukaryot ...
in meiosis.
Types of asexual reproduction
Fission
Prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Gree ...
s (Archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
and Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
) reproduce asexually through binary fission
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical o ...
, in which the parent organism divides in two to produce two genetically identical daughter organisms. Eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s (such as protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s and unicellular fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
) may reproduce in a functionally similar manner by mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
; most of these are also capable of sexual reproduction.
Multiple fission at the cellular level occurs in many protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s, e.g. sporozoans and algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) is an informal term for any organisms of a large and diverse group of photosynthesis, photosynthetic organisms that are not plants, and includes species from multiple distinct clades. Such organisms range from unicellular ...
. The nucleus of the parent cell divides several times by mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
, producing several nuclei. The cytoplasm then separates, creating multiple daughter cells.
In apicomplexans, multiple fission, or schizogony appears either as merogony, sporogony or gametogony. Merogony results in merozoites, which are multiple daughter cells, that originate within the same cell membrane, sporogony results in sporozoite
Apicomplexans, a group of intracellular parasites, have life cycle stages that allow them to survive the wide variety of environments they are exposed to during their complex life cycle. Each stage in the life cycle of an apicomplexan organis ...
s, and gametogony results in microgamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s.
Budding
 Some cells divide by budding (for example baker's yeast), resulting in a "mother" and a "daughter" cell that is initially smaller than the parent. Budding is also known on a multicellular level; an animal example is the hydra, which reproduces by budding. The buds grow into fully matured individuals which eventually break away from the parent organism.
Internal budding is a process of asexual reproduction, favoured by parasites such as '' Toxoplasma gondii''. It involves an unusual process in which two (''endodyogeny'') or more (''endopolygeny'') daughter cells are produced inside a mother cell, which is then consumed by the offspring prior to their separation.
Also, budding (external or internal) occurs in some worms like '' Taenia'' or '' Echinococcus''; these worms produce cysts and then produce (invaginated or evaginated) protoscolex with budding.
Some cells divide by budding (for example baker's yeast), resulting in a "mother" and a "daughter" cell that is initially smaller than the parent. Budding is also known on a multicellular level; an animal example is the hydra, which reproduces by budding. The buds grow into fully matured individuals which eventually break away from the parent organism.
Internal budding is a process of asexual reproduction, favoured by parasites such as '' Toxoplasma gondii''. It involves an unusual process in which two (''endodyogeny'') or more (''endopolygeny'') daughter cells are produced inside a mother cell, which is then consumed by the offspring prior to their separation.
Also, budding (external or internal) occurs in some worms like '' Taenia'' or '' Echinococcus''; these worms produce cysts and then produce (invaginated or evaginated) protoscolex with budding.
Vegetative propagation
 Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction found in plants where new individuals are formed without the production of seeds or spores and thus without syngamy or meiosis. Examples of vegetative reproduction include the formation of miniaturized plants called plantlets on specialized leaves, for example in kalanchoe ('' Bryophyllum daigremontianum'') and many produce new plants from
Vegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction found in plants where new individuals are formed without the production of seeds or spores and thus without syngamy or meiosis. Examples of vegetative reproduction include the formation of miniaturized plants called plantlets on specialized leaves, for example in kalanchoe ('' Bryophyllum daigremontianum'') and many produce new plants from rhizome
In botany and dendrology, a rhizome ( ) is a modified subterranean plant stem that sends out roots and Shoot (botany), shoots from its Node (botany), nodes. Rhizomes are also called creeping rootstalks or just rootstalks. Rhizomes develop from ...
s or stolon
In biology, a stolon ( from Latin ''wikt:stolo, stolō'', genitive ''stolōnis'' – "branch"), also known as a runner, is a horizontal connection between parts of an organism. It may be part of the organism, or of its skeleton. Typically, animal ...
(for example in strawberry
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown Hybrid (biology), hybrid plant cultivated worldwide for its fruit. The genus ''Fragaria'', the strawberries, is in the rose family, Rosaceae. The fruit ...
). Some plants reproduce by forming bulbs or tuber
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure that plants use as storage organs for nutrients, derived from stems or roots. Tubers help plants perennate (survive winter or dry months), provide energy and nutrients, and are a means of asexual reproduc ...
s, for example tulip bulbs and '' Dahlia'' tubers. In these examples, all the individuals are clones, and the clonal population may cover a large area.
Spore formation
Many multicellular organisms producespore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
s during their biological life cycle in a process called ''sporogenesis''. Exceptions are animals and some protists, which undergo ''meiosis'' immediately followed by fertilization. Plants and many algae on the other hand undergo ''sporic meiosis'' where meiosis leads to the formation of haploid spores rather than gametes. These spores grow into multicellular individuals called gametophytes, without a fertilization event. These haploid individuals produce gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s through mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
. Meiosis and gamete formation therefore occur in separate multicellular generations or "phases" of the life cycle, referred to as alternation of generations. Since sexual reproduction is often more narrowly defined as the fusion of gametes (fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give ...
), spore formation in plant sporophyte
A sporophyte () is one of the two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular organism, multicellular phases in the biological life cycle, life cycles of plants and algae. It is a diploid multicellular organism which produces asexual Spo ...
s and algae might be considered a form of asexual reproduction (agamogenesis) despite being the result of meiosis and undergoing a reduction in ploidy. However, both events (spore formation and fertilization) are necessary to complete sexual reproduction in the plant life cycle.
Fungi and some algae can also utilize true asexual spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
formation, which involves mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
giving rise to reproductive cells called mitospores that develop into a new organism after dispersal. This method of reproduction is found for example in conidial fungi and the red algae
Red algae, or Rhodophyta (, ; ), make up one of the oldest groups of eukaryotic algae. The Rhodophyta comprises one of the largest Phylum, phyla of algae, containing over 7,000 recognized species within over 900 Genus, genera amidst ongoing taxon ...
''Polysiphonia'', and involves sporogenesis without meiosis. Thus the chromosome number of the spore cell is the same as that of the parent producing the spores. However, mitotic sporogenesis is an exception and most spores, such as those of plants and many algae, are produced by meiosis.
Fragmentation
 Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction where a new organism grows from a fragment of the parent. Each fragment develops into a mature, fully grown individual. Fragmentation is seen in many organisms. Animals that reproduce asexually include planarians, many annelid worms including polychaetes and some oligochaetes, turbellarians and
Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction where a new organism grows from a fragment of the parent. Each fragment develops into a mature, fully grown individual. Fragmentation is seen in many organisms. Animals that reproduce asexually include planarians, many annelid worms including polychaetes and some oligochaetes, turbellarians and sea stars
A sea is a large body of salt water. There are particular seas and the sea. The sea commonly refers to the ocean, the interconnected body of seawaters that spans most of Earth. Particular seas are either marginal seas, second-order section ...
. Many fungi and plants reproduce asexually. Some plants have specialized structures for reproduction via fragmentation, such as '' gemmae'' in mosses and liverworts
Liverworts are a group of non-vascular plant, non-vascular embryophyte, land plants forming the division Marchantiophyta (). They may also be referred to as hepatics. Like mosses and hornworts, they have a gametophyte-dominant life cycle, in wh ...
. Most lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), m ...
s, which are a symbiotic union of a fungus and photosynthetic
Photosynthesis ( ) is a Biological system, system of biological processes by which Photoautotrophism, photosynthetic organisms, such as most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, convert light energy, typically from sunlight, into the chemical ener ...
algae or cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
, reproduce through fragmentation to ensure that new individuals contain both symbionts. These fragments can take the form of ''soredia'', dust-like particles consisting of fungal hyphae wrapped around photobiont cells.
Clonal Fragmentation in multicellular or colonial organisms is a form of asexual reproduction or cloning where an organism is split into fragments. Each of these fragments develop into mature, fully grown individuals that are clones of the original organism. In echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as ...
s, this method of reproduction is usually known as ''fissiparity''. Due to many environmental and epigenetic differences, clones originating from the same ancestor might actually be genetically and epigenetically different.
Agamogenesis
Agamogenesis is any form of reproduction that does not involve any union of gametes. Examples areparthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek + ) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which the embryo develops directly from an egg without need for fertilization. In animals, parthenogenesis means the development of an embryo from an unfertiliz ...
and apomixis.
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis is a form of agamogenesis in which an unfertilized egg develops into a new individual. It has been documented in over 2,000 species. Parthenogenesis occurs in the wild in manyinvertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s (e.g. water fleas, rotifer
The rotifers (, from Latin 'wheel' and 'bearing'), sometimes called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic Coelom#Pseudocoelomates, pseudocoelomate animals.
They were first describ ...
s, aphids, stick insects, some ants, bees and parasitic wasps) and vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s (mostly reptiles, amphibians, and fish). It has also been documented in domestic birds and in genetically altered lab mice. Plants can engage in parthenogenesis as well through a process called apomixis. However this process is considered by many to not be an independent reproduction method, but instead a breakdown of the mechanisms behind sexual reproduction. Parthenogenetic organisms can be split into two main categories: facultative and obligate.
= Facultative parthenogenesis
= In facultative parthenogenesis, females can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Because of the many advantages of sexual reproduction, most facultative parthenotes only reproduce asexually when forced to. This typically occurs in instances when finding a mate becomes difficult. For example, female zebra sharks will reproduce asexually if they are unable to find a mate in their ocean habitats.
Parthenogenesis was previously believed to rarely occur in vertebrates, and only be possible in very small animals. However, it has been discovered in many more species in recent years. Today, the largest species that has been documented reproducing parthenogenically is the Komodo dragon at 10 feet long and over 300 pounds.
In facultative parthenogenesis, females can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Because of the many advantages of sexual reproduction, most facultative parthenotes only reproduce asexually when forced to. This typically occurs in instances when finding a mate becomes difficult. For example, female zebra sharks will reproduce asexually if they are unable to find a mate in their ocean habitats.
Parthenogenesis was previously believed to rarely occur in vertebrates, and only be possible in very small animals. However, it has been discovered in many more species in recent years. Today, the largest species that has been documented reproducing parthenogenically is the Komodo dragon at 10 feet long and over 300 pounds.
 Heterogony is a form of facultative parthenogenesis where females alternate between sexual and asexual reproduction at regular intervals (see Alternation between sexual and asexual reproduction).
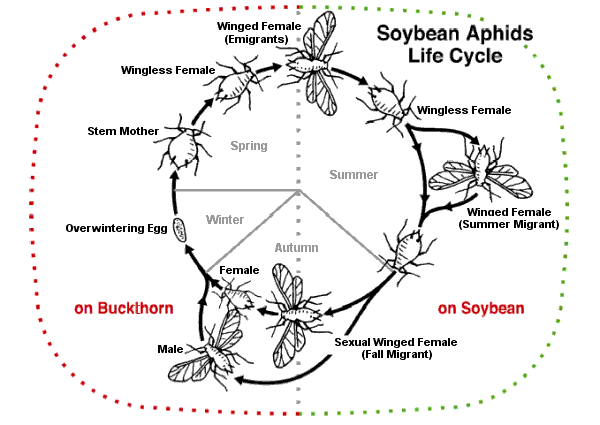
Heterogony is a form of facultative parthenogenesis where females alternate between sexual and asexual reproduction at regular intervals (see Alternation between sexual and asexual reproduction). Aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects in the Taxonomic rank, family Aphididae. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white Eriosomatinae, woolly ...
s are one group of organism that engages in this type of reproduction. They use asexual reproduction to reproduce quickly and create winged offspring that can colonize new plants and reproduce sexually in the fall to lay eggs for the next season. However, some aphid species are obligate parthenotes.
= Obligate parthenogenesis
= In obligate parthenogenesis, females only reproduce asexually. One example of this is the desert grassland whiptail lizard, a hybrid of two other species. Typically hybrids are infertile but through parthenogenesis this species has been able to develop stable populations.
Gynogenesis is a form of obligate parthenogenesis where a sperm cell is used to initiate reproduction. However, the sperm's genes never get incorporated into the egg cell. The best known example of this is the Amazon molly. Because they are obligate parthenotes, there are no males in their species so they depend on males from a closely related species (the Sailfin molly) for sperm.
In obligate parthenogenesis, females only reproduce asexually. One example of this is the desert grassland whiptail lizard, a hybrid of two other species. Typically hybrids are infertile but through parthenogenesis this species has been able to develop stable populations.
Gynogenesis is a form of obligate parthenogenesis where a sperm cell is used to initiate reproduction. However, the sperm's genes never get incorporated into the egg cell. The best known example of this is the Amazon molly. Because they are obligate parthenotes, there are no males in their species so they depend on males from a closely related species (the Sailfin molly) for sperm.
Apomixis and nucellar embryony
Apomixis in plants is the formation of a newsporophyte
A sporophyte () is one of the two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular organism, multicellular phases in the biological life cycle, life cycles of plants and algae. It is a diploid multicellular organism which produces asexual Spo ...
without fertilization. It is important in ferns and in flowering plants, but is very rare in other seed plants. In flowering plants, the term "apomixis" is now most often used for agamospermy, the formation of seeds without fertilization, but was once used to include vegetative reproduction
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is a form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or specializ ...
. An example of an apomictic plant would be the triploid European dandelion. Apomixis mainly occurs in two forms: In gametophytic apomixis, the embryo arises from an unfertilized egg within a diploid embryo sac that was formed without completing meiosis. In nucellar embryony, the embryo is formed from the diploid nucellus tissue surrounding the embryo sac. Nucellar embryony occurs in some citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the family Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, mandarins, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes.
''Citrus'' is nativ ...
seeds. Male apomixis can occur in rare cases, such as in the Saharan Cypress '' Cupressus dupreziana'', where the genetic material of the embryo is derived entirely from pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
.
Androgenesis
Androgenesis occurs when azygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
is produced with only paternal nuclear genes. During standard sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
, one female and one male parent each produce haploid gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s (such as a sperm or egg cell, each containing only a single set of chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s), which recombine to create offspring with genetic material from both parents. However, in androgenesis, there is no recombination of maternal and paternal chromosomes, and only the paternal chromosomes are passed down to the offspring (the inverse of this is gynogenesis, where only the maternal chromosomes are inherited, which is more common than androgenesis). The offspring produced in androgenesis will still have maternally inherited mitochondria, as is the case with most sexually reproducing species.
Androgenesis occurs in nature in many invertebrates (for example, clams, stick insects, some ants, bees, flies and parasitic wasps) and vertebrates (mainly amphibians and fish). The androgenesis
Androgenesis is a system of asexual reproduction that requires the presence of eggs and occurs when a zygote is produced with only paternal nuclear genes. During standard sexual reproduction, one female parent and one male parent each produce h ...
has also been seen in genetically modified laboratory mice.
One of two things can occur to produce offspring with exclusively paternal genetic material: the maternal nuclear genome can be eliminated from the zygote, or the female can produce an egg with no nucleus, resulting in an embryo developing with only the genome of the male gamete.
Male apomixis
Other type of androgenesis is the male apomixis or paternal apomixis is a reproductive process in which a plant develops from a sperm cell (male gamete) without the participation of a female cell (ovum). In this process, the zygote is formed solely with genetic material from the father, resulting in offspring genetically identical to the male organism. This has been noted in many plants like ''Nicotiana
''Nicotiana'' () is a genus of herbaceous plants and shrubs in the Family (biology), family Solanaceae, that is Native plant, indigenous to the Americas, Australia, Southwestern Africa and the South Pacific. Various ''Nicotiana'' species, common ...
'', ''Capsicum frutescens
''Capsicum frutescens'' is a wild chili pepper having plant genetics, genetic proximity to the cultivated pepper ''Capsicum chinense'' native to Central America, Central and South America. Pepper cultivars of ''C. frutescens'' can be annual or sh ...
'', '' Cicer arietinum'', '' Poa arachnifera'', '' Solanum verrucosum'', '' Phaeophyceae'', '' Pripsacum dactyloides'', ''Zea mays
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
'', and occurs as the regular reproductive method in '' Cupressus dupreziana''. This contrasts with the more common apomixis, where development occurs without fertilization, but with genetic material only from the mother.
There are also clonal species that reproduce through vegetative reproduction
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is a form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or specializ ...
like '' Lomatia tasmanica'' and ''Pando'', where the genetic material is exclusively male.
Other species where androgenesis
Androgenesis is a system of asexual reproduction that requires the presence of eggs and occurs when a zygote is produced with only paternal nuclear genes. During standard sexual reproduction, one female parent and one male parent each produce h ...
has been observed naturally are the stick insects '' Bacillus rossius and Bassillus Grandii'', the little fire ant '' Wasmannia auropunctata'', '' Vollenhovia emeryi'', '' Paratrechina longicornis'', occasionally in '' Apis mellifera'', the '' Hypseleotris'' carp gudgeons, the parasitoid '' Venturia canescens'', and occasionally in fruit flies ''Drosophila melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (an insect of the Order (biology), order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly", "pomace fly" ...
'' carrying a specific mutant allele. It has also been induced in many crops and fish via irradiation of an egg cell to destroy the maternal nuclear genome.
Obligate androgenesis
Obligate androgenesis is the process in which males are capable of producing both eggs and sperm, however, the eggs have no genetic contribution and the offspring come only from the sperm, which allows these individuals to self-fertilize and produce clonal offspring without the need for females. They are also capable of interbreeding with sexual and other androgenetic lineages in a phenomenon known as "egg parasitism." This method of reproduction has been found in several species of the clam genus '' Corbicula'', many plants like, '' Cupressus dupreziana'', '' Lomatia tasmanica'', '' Pando'' and recently in the fish '' Squalius alburnoides''. Other species whereandrogenesis
Androgenesis is a system of asexual reproduction that requires the presence of eggs and occurs when a zygote is produced with only paternal nuclear genes. During standard sexual reproduction, one female parent and one male parent each produce h ...
has been observed naturally are the stick insects '' Bacillus rossius and Bassillus Grandii'', the little fire ant '' Wasmannia auropunctata'', '' Vollenhovia emeryi'', '' Paratrechina longicornis'', occasionally in '' Apis mellifera'', the '' Hypseleotris'' carp gudgeons, the parasitoid '' Venturia canescens'', and occasionally in fruit flies ''Drosophila melanogaster
''Drosophila melanogaster'' is a species of fly (an insect of the Order (biology), order Diptera) in the family Drosophilidae. The species is often referred to as the fruit fly or lesser fruit fly, or less commonly the "vinegar fly", "pomace fly" ...
'' carrying a specific mutant allele. It has also been induced in many crops and fish via irradiation of an egg cell to destroy the maternal nuclear genome.
Alternation between sexual and asexual reproduction
 Some species can alternate between sexual and asexual strategies, an ability known as '' heterogamy'', depending on many conditions. Alternation is observed in several
Some species can alternate between sexual and asexual strategies, an ability known as '' heterogamy'', depending on many conditions. Alternation is observed in several rotifer
The rotifers (, from Latin 'wheel' and 'bearing'), sometimes called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic Coelom#Pseudocoelomates, pseudocoelomate animals.
They were first describ ...
species (cyclical parthenogenesis e.g. in Brachionus species) and a few types of insects.
One example of this is aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects in the Taxonomic rank, family Aphididae. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white Eriosomatinae, woolly ...
s which can engage in heterogony. In this system, females are born pregnant and produce only female offspring. This cycle allows them to reproduce very quickly. However, most species reproduce sexually once a year. This switch is triggered by environmental changes in the fall and causes females to develop eggs instead of embryos. This dynamic reproductive cycle allows them to produce specialized offspring with polyphenism, a type of polymorphism where different phenotypes have evolved to carry out specific tasks.
The cape bee ''Apis mellifera'' subsp. ''capensis'' can reproduce asexually through a process called thelytoky. The freshwater crustacean '' Daphnia'' reproduces by parthenogenesis in the spring to rapidly populate ponds, then switches to sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
as the intensity of competition and predation increases. Monogonont rotifer
The rotifers (, from Latin 'wheel' and 'bearing'), sometimes called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic Coelom#Pseudocoelomates, pseudocoelomate animals.
They were first describ ...
s of the genus '' Brachionus'' reproduce via cyclical parthenogenesis: at low population densities females produce asexually and at higher densities a chemical cue accumulates and induces the transition to sexual reproduction. Many protists and fungi alternate between sexual and asexual reproduction. A few species of amphibians, reptiles, and birds have a similar ability.
The slime mold '' Dictyostelium'' undergoes binary fission (mitosis) as single-celled amoebae under favorable conditions. However, when conditions turn unfavorable, the cells aggregate and follow one of two different developmental pathways, depending on conditions. In the social pathway, they form a multi-cellular slug which then forms a fruiting body with asexually generated spores. In the sexual pathway, two cells fuse to form a giant cell that develops into a large cyst. When this macrocyst germinates, it releases hundreds of amoebic cells that are the product of meiotic recombination between the original two cells.
The hyphae of the common mold ('' Rhizopus'') are capable of producing both mitotic as well as meiotic spores. Many algae similarly switch between sexual and asexual reproduction. A number of plants use both sexual and asexual means to produce new plants, some species alter their primary modes of reproduction from sexual to asexual under varying environmental conditions.
Inheritance in asexual species
In therotifer
The rotifers (, from Latin 'wheel' and 'bearing'), sometimes called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic Coelom#Pseudocoelomates, pseudocoelomate animals.
They were first describ ...
'' Brachionus calyciflorus'' asexual reproduction (obligate parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis (; from the Greek + ) is a natural form of asexual reproduction in which the embryo develops directly from an egg without need for fertilization. In animals, parthenogenesis means the development of an embryo from an unfertiliz ...
) can be inherited by a recessive allele, which leads to loss of sexual reproduction in homozygous offspring.Inheritance of asexual reproduction by a single recessive locus has also been found in the
parasitoid wasp
Parasitoid wasps are a large group of hymenopteran Superfamily (zoology), superfamilies, with all but the wood wasps (Orussoidea) being in the wasp-waisted Apocrita. As parasitoids, they lay their eggs on or in the bodies of other arthropods, ...
''Lysiphlebus fabarum''.
Examples in animals
Asexual reproduction is found in nearly half of the animal phyla. Parthenogenesis occurs in the hammerhead shark and the blacktip shark. In both cases, the sharks had reached sexual maturity in captivity in the absence of males, and in both cases the offspring were shown to be genetically identical to the mothers. The New Mexico whiptail is another example. Some reptiles use theZW sex-determination system
The ZW sex-determination system is a chromosomal system that determines the sex of offspring in birds, some fish and crustaceans such as the giant river prawn, some insects (including butterflies and moths), the schistosome family of flatwor ...
, which produces either males (with ZZ sex chromosomes) or females (with ZW or WW sex chromosomes). Until 2010, it was thought that the ZW chromosome system used by reptiles was incapable of producing viable WW offspring, but a (ZW) female boa constrictor was discovered to have produced viable female offspring with WW chromosomes. The female boa could have chosen any number of male partners (and had successfully in the past) but on this occasion she reproduced asexually, creating 22 female babies with WW sex-chromosomes.
Polyembryony is a widespread form of asexual reproduction in animals, whereby the fertilized egg or a later stage of embryonic development splits to form genetically identical clones. Within animals, this phenomenon has been best studied in the parasitic Hymenoptera. In the nine-banded armadillos, this process is obligatory and usually gives rise to genetically identical quadruplets. In other mammals, monozygotic twinning has no apparent genetic basis, though its occurrence is common. There are at least 10 million identical human twins and triplets in the world today.
Bdelloid rotifer
The rotifers (, from Latin 'wheel' and 'bearing'), sometimes called wheel animals or wheel animalcules, make up a phylum (Rotifera ) of microscopic and near-microscopic Coelom#Pseudocoelomates, pseudocoelomate animals.
They were first describ ...
s reproduce exclusively asexually, and all individuals in the class Bdelloidea are females. Asexuality evolved in these animals millions of years ago and has persisted since. There is evidence to suggest that asexual reproduction has allowed the animals to evolve new proteins through the Meselson effect that have allowed them to survive better in periods of dehydration. Bdelloid rotifers are extraordinarily resistant to damage from ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
due to the same DNA-preserving adaptations used to survive dormancy. These adaptations include an extremely efficient mechanism for repairing DNA double-strand breaks. This repair mechanism was studied in two Bdelloidea species, ''Adineta vaga'', and ''Philodina roseola''. and appears to involve mitotic recombination between homologous DNA regions within each species.
Molecular evidence strongly suggests that several species of the stick insect genus '' Timema'' have used only asexual (parthenogenetic) reproduction for millions of years, the longest period known for any insect. Similar findings suggest that the mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as eac ...
species '' Oppiella nova'' may have reproduced entirely asexually for millions of years.
In the grass thrips genus ''Aptinothrips
''Aptinothrips'' is a genus of insects belonging to the family Thripidae.
The species of this genus are found in Europe, Australia and Northern America.
Species:
* '' Aptinothrips elegans'' Priesner, 1924
* '' Aptinothrips karnyi'' John, 19 ...
'' there have been several transitions to asexuality, likely due to different causes.
Adaptive significance of asexual reproduction
A complete lack ofsexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
is relatively rare among multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s, particularly animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s. It is not entirely understood why the ability to reproduce sexually is so common among them. Current hypotheses suggest that asexual reproduction may have short term benefits when rapid population growth is important or in stable environments, while sexual reproduction offers a net advantage by allowing more rapid generation of genetic diversity, allowing adaptation to changing environments. Developmental constraints may underlie why few animals have relinquished sexual reproduction completely in their life-cycles. Almost all asexual modes of reproduction maintain meiosis either in a modified form or as an alternative pathway. Facultatively apomictic plants increase frequencies of sexuality relative to apomixis after abiotic stress. Another constraint on switching from sexual to asexual reproduction would be the concomitant loss of meiosis and the protective recombinational repair of DNA damage afforded as one function of meiosis.Avise, J. (2008) Clonality: The Genetics, Ecology and Evolution of Sexual Abstinence in Vertebrate Animals. See pp. 22–25. Oxford University Press.
See also
* Alternation of generations *Self-fertilization
Autogamy or self-fertilization refers to the Cell fusion, fusion of two gametes that come from one individual. Autogamy is predominantly observed in the form of self-pollination, a Reproduction, reproductive mechanism employed by many flowering pl ...
* Bacterial conjugation
* Biological life cycle
* Biological reproduction, also simply reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual ...
* Cloning
Cloning is the process of producing individual organisms with identical genomes, either by natural or artificial means. In nature, some organisms produce clones through asexual reproduction; this reproduction of an organism by itself without ...
* Hermaphrodite
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic.
The individuals of many ...
* Plant reproduction
* Sex
References
Further reading
* * *External links
Asexual reproduction
{{DEFAULTSORT:Asexual Reproduction