Art of the United Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Art of the United Kingdom refers to all forms of visual art in or associated with the
The Art of the United Kingdom refers to all forms of visual art in or associated with the
 The oldest surviving British art includes
The oldest surviving British art includes
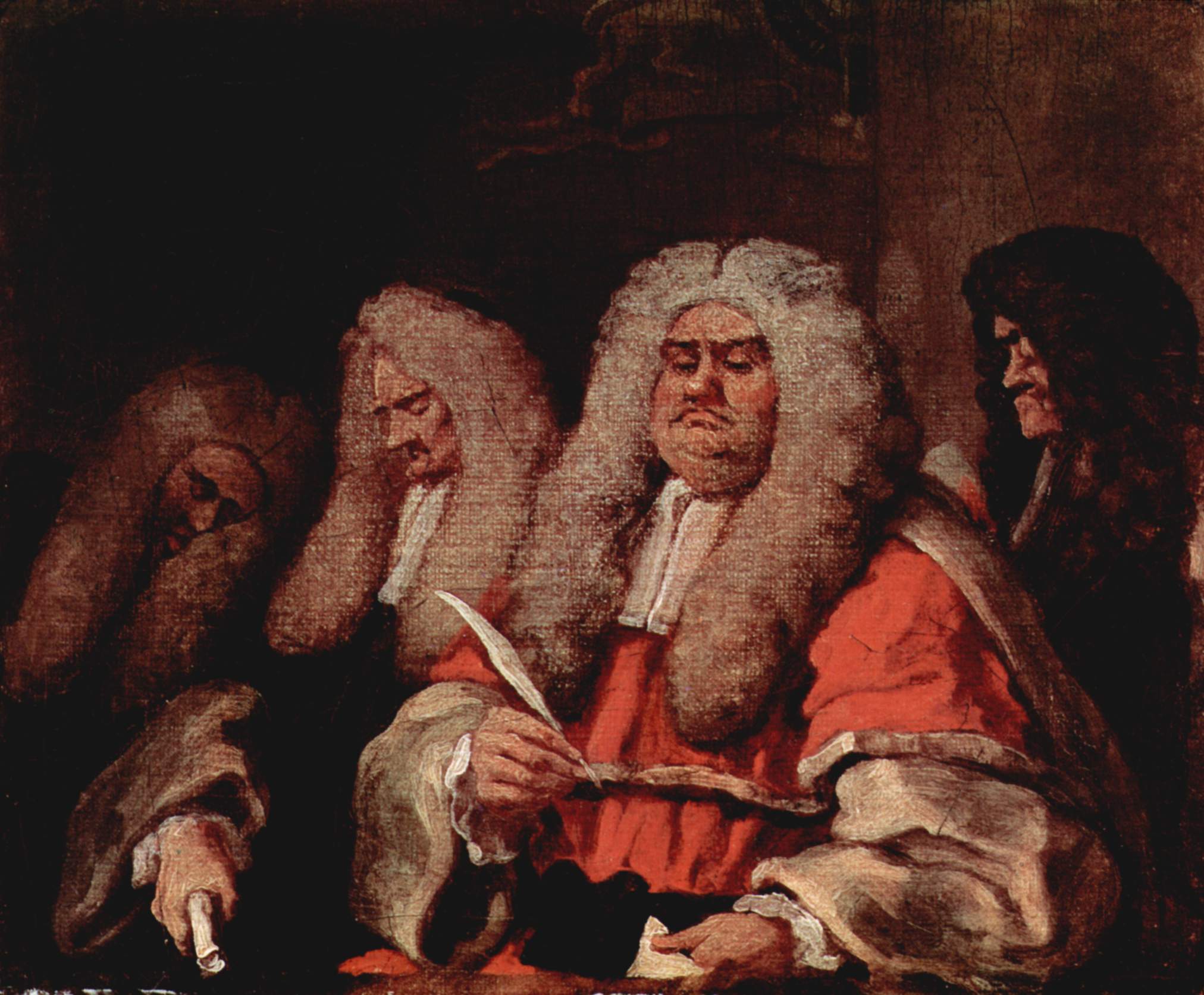 The so-called
The so-called  There was a recognition that, even more than the rest of Europe given the lack of British artists, the training of artists needed to be extended beyond the workshop of established masters, and various attempts were made to set up academies, starting with Kneller in 1711, with the help of Pellegrini, in Great Queen Street. The academy was taken over by Thornhill in 1716, but seems to have become inactive by the time
There was a recognition that, even more than the rest of Europe given the lack of British artists, the training of artists needed to be extended beyond the workshop of established masters, and various attempts were made to set up academies, starting with Kneller in 1711, with the help of Pellegrini, in Great Queen Street. The academy was taken over by Thornhill in 1716, but seems to have become inactive by the time
File:SirJohnRushout4thBt.jpg,
The

 Paintings recording scenes from the theatre were another subgenre, painted by the German
Paintings recording scenes from the theatre were another subgenre, painted by the German
File:Self-portrait c.1747-9 by Joshua Reynolds (2).jpg,
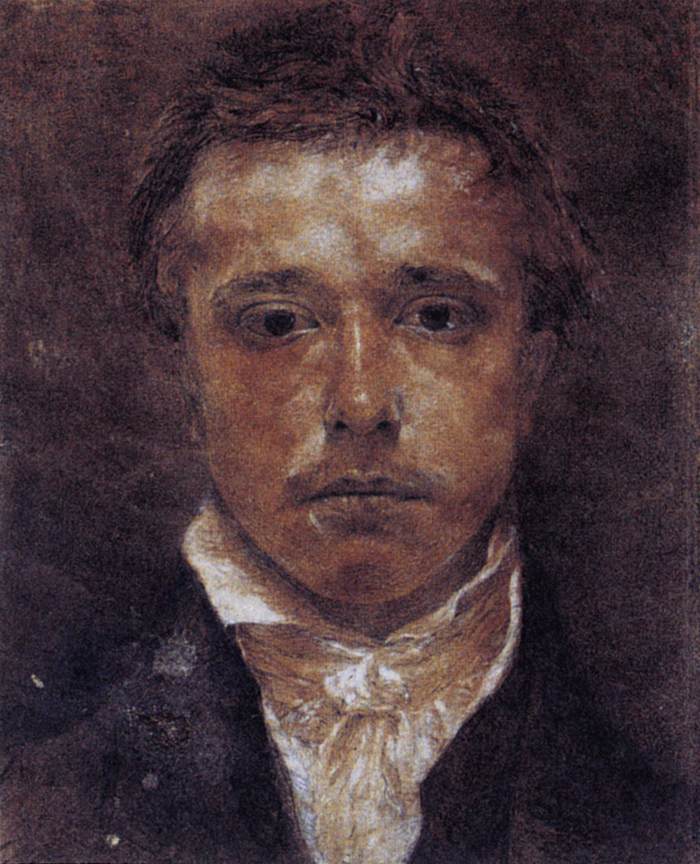 The late 18th century and the early 19th century characterized by the
The late 18th century and the early 19th century characterized by the
File:Pinkie detailed.jpg,
 The
The  British history was a very common subject, with the Middle Ages, Elizabeth I,
British history was a very common subject, with the Middle Ages, Elizabeth I,  Victorian painting developed the Hogarthian social subject, packed with moralizing detail, and the tradition of illustrating scenes from literature, into a range of types of genre painting, many with only a few figures, others large and crowded scenes like Frith's best-known works. Holman Hunt's '' The Awakening Conscience'' (1853) and Augustus Egg's set of '' Past and Present'' (1858) are of the first type, both dealing with "fallen women", a perennial Victorian concern. As Peter Conrad points out, these were paintings designed to be read like novels, whose meaning emerged after the viewer had done the work of deciphering it. Other "anecdotal" scenes were lighter in mood, tending towards being captionless ''
Victorian painting developed the Hogarthian social subject, packed with moralizing detail, and the tradition of illustrating scenes from literature, into a range of types of genre painting, many with only a few figures, others large and crowded scenes like Frith's best-known works. Holman Hunt's '' The Awakening Conscience'' (1853) and Augustus Egg's set of '' Past and Present'' (1858) are of the first type, both dealing with "fallen women", a perennial Victorian concern. As Peter Conrad points out, these were paintings designed to be read like novels, whose meaning emerged after the viewer had done the work of deciphering it. Other "anecdotal" scenes were lighter in mood, tending towards being captionless '' Larger paintings concerned with the social conditions of the poor tended to concentrate on rural scenes, so that the misery of the human figures was at least offset by a landscape. Painters of these included Frederick Walker,
Larger paintings concerned with the social conditions of the poor tended to concentrate on rural scenes, so that the misery of the human figures was at least offset by a landscape. Painters of these included Frederick Walker,  Scottish art was now regaining an adequate home market, allowing it to develop a distinctive character, of which the " Glasgow Boys" were one expression, straddling
Scottish art was now regaining an adequate home market, allowing it to develop a distinctive character, of which the " Glasgow Boys" were one expression, straddling

 The Art of the United Kingdom refers to all forms of visual art in or associated with the
The Art of the United Kingdom refers to all forms of visual art in or associated with the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
since the formation of the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, w ...
in 1707 and encompasses English art
English art is the body of visual arts made in England. England has Europe's earliest and northernmost ice-age cave art. Prehistoric art in England largely corresponds with art made elsewhere in contemporary Britain, but early medieval Anglo-Sa ...
, Scottish art
Scottish art is the body of visual art made in what is now Scotland, or about Scottish subjects, since prehistoric times. It forms a distinctive tradition within European art, but the political union with England has led its partial subsumation ...
, Welsh art and Irish art, and forms part of Western art history. During the 18th century, Britain began to reclaim the leading place England had previously played in European art during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, being especially strong in portraiture and landscape art
Landscape painting, also known as landscape art, is the depiction of natural scenery such as mountains
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although de ...
.
Increased British prosperity at the time led to a greatly increased production of both fine art
In European academic traditions, fine art is developed primarily for aesthetics or creative expression, distinguishing it from decorative art or applied art, which also has to serve some practical function, such as pottery or most metalwor ...
and the decorative arts
]
The decorative arts are arts or crafts whose object is the design and manufacture of objects that are both beautiful and functional. It includes most of the arts making objects for the interiors of buildings, and interior design, but not usua ...
, the latter often being exported. The Romanticism, Romantic period resulted from very diverse talents, including the painters William Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual art of the Romantic Age. ...
, J. M. W. Turner
Joseph Mallord William Turner (23 April 177519 December 1851), known in his time as William Turner, was an English Romantic painter, printmaker and watercolourist. He is known for his expressive colouring, imaginative landscapes and turbulen ...
, John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedham Vale, the ...
and Samuel Palmer. The Victorian period saw a great diversity of art, and a far bigger quantity created than before. Much Victorian art is now out of critical favour, with interest concentrated on the Pre-Raphaelites and the innovative movements at the end of the 18th century.
The training of artists, which had long been neglected, began to improve in the 18th century through private and government initiatives, and greatly expanded in the 19th century. Public exhibitions and the later opening of museums brought art to a wider public, especially in London. In the 19th century publicly displayed religious art once again became popular after a virtual absence since the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
, and, as in other countries, movements such as the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood (later known as the Pre-Raphaelites) was a group of English painters, poets, and art critics, founded in 1848 by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, William Michael Rossetti, Jam ...
and the Glasgow School
The Glasgow School was a circle of influential artists and designers that began to coalesce in Glasgow, Scotland in the 1870s, and flourished from the 1890s to around 1910. Representative groups included The Four (also known as the Spook School ...
contended with established Academic art
Academic art, or academicism or academism, is a style of painting and sculpture produced under the influence of European academies of art. Specifically, academic art is the art and artists influenced by the standards of the French Académie ...
.
The British contribution to early Modernist art was relatively small, but since World War II British artists have made a considerable impact on Contemporary art
Contemporary art is the art of today, produced in the second half of the 20th century or in the 21st century. Contemporary artists work in a globally influenced, culturally diverse, and technologically advancing world. Their art is a dynamic co ...
, especially with figurative work, and Britain remains a key centre of an increasingly globalized art world.
Background
 The oldest surviving British art includes
The oldest surviving British art includes Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connecting ...
from around 2600 BC, and tin and gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
works of art produced by the Beaker people
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the European Bronze Age. Arising from ...
from around 2150 BC. The La Tène style of Celtic art
Celtic art is associated with the peoples known as Celts; those who spoke the Celtic languages in Europe from pre-history through to the modern period, as well as the art of ancient peoples whose language is uncertain, but have cultural and styli ...
reached the British Isles rather late, no earlier than about 400 BC, and developed a particular "Insular Celtic" style seen in objects such as the Battersea Shield
The Battersea Shield is one of the most significant pieces of ancient Celtic art found in Britain. It is a sheet bronze covering of a (now vanished) wooden shield decorated in La Tène style. The shield is on display in the British Museum, ...
, and a number of bronze mirror-backs decorated with intricate patterns of curves, spirals and trumpet-shapes. Only in the British Isles can Celtic decorative style be seen to have survived throughout the Roman period, as shown in objects like the Staffordshire Moorlands Pan
The Staffordshire Moorlands Pan, sometimes known as the Ilam Pan, is a 2nd-century AD enamelled bronze ''trulla'' with an inscription relating to the forts of Hadrian's Wall. It was found in June 2003 in Ilam parish, Staffordshire, by met ...
and the resurgence of Celtic motifs, now blended with Germanic interlace and Mediterranean elements, in Christian Insular art
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, was produced in the post-Roman era of Great Britain and Ireland. The term derives from ''insula'', the Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland shared a largely common style dif ...
. This had a brief but spectacular flowering in all the countries that now form the United Kingdom in the 7th and 8th centuries, in works such as the Book of Kells
The Book of Kells ( la, Codex Cenannensis; ga, Leabhar Cheanannais; Dublin, Trinity College Library, MS A. I. 8 sometimes known as the Book of Columba) is an illuminated manuscript Gospel book in Latin, containing the four Gospels of the ...
and Book of Lindisfarne. The Insular style was influential across Northern Europe, and especially so in later Anglo-Saxon art
Anglo-Saxon art covers art produced within the Anglo-Saxon period of English history, beginning with the Migration period style that the Anglo-Saxons brought with them from the continent in the 5th century, and ending in 1066 with the Norman ...
, although this received new Continental influences.
The English contribution to Romanesque art
Romanesque art is the art of Europe from approximately 1000 AD to the rise of the Gothic style in the 12th century, or later depending on region. The preceding period is known as the Pre-Romanesque period. The term was invented by 19th-centur ...
and Gothic art
Gothic art was a style of medieval art that developed in Northern France out of Romanesque art in the 12th century AD, led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, and much of Northern, Southern ...
was considerable, especially in illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is often supplemented with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers, liturgical services and psalms, th ...
s and monumental sculpture for churches, though the other countries were now essentially provincial, and in the 15th century Britain struggled to keep up with developments in painting on the Continent. A few examples of top-quality English painting on walls or panel from before 1500 have survived, including the Westminster Retable, The Wilton Diptych
The Wilton Diptych () is a small portable diptych of two hinged panels, painted on both sides, now in the National Gallery, London. It is an extremely rare survival of a late medieval religious panel painting from England.
The diptych was pain ...
and some survivals from paintings in Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
and the Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north bank ...
.
The Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
s of England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
and Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
were especially destructive of existing religious art, and the production of new work virtually ceased. The Artists of the Tudor Court were mostly imported from Europe, setting a pattern that would continue until the 18th century. The portraiture of Elizabeth I
The portraiture of Elizabeth I spans the evolution of English royal portraits in the early modern period (1400/1500-1800), depicting Queen Elizabeth I of England and Ireland (1533–1603), from the earliest representations of simple likenesses ...
ignored contemporary European Renaissance models to create iconic images that border on naive art. The portraitists Hans Holbein and Anthony van Dyck were the most distinguished and influential of a large number of artists who spent extended periods in Britain, generally eclipsing local talents like Nicolas Hilliard, the painter of portrait miniature
A portrait miniature is a miniature portrait painting, usually executed in gouache, Watercolor painting, watercolor, or Vitreous enamel, enamel. Portrait miniatures developed out of the techniques of the miniatures in illuminated manuscripts, an ...
s, Robert Peake the elder, William Larkin, William Dobson, and John Michael Wright, a Scot who mostly worked in London.
Landscape painting was as yet little developed in Britain at the time of the Union, but a tradition of marine art had been established by the father
A father is the male parent of a child. Besides the paternal bonds of a father to his children, the father may have a parental, legal, and social relationship with the child that carries with it certain rights and obligations. An adoptive fathe ...
and son both called Willem van de Velde, who had been the leading Dutch maritime painters until they moved to London in 1673, in the middle of the Third Anglo-Dutch War
The Third Anglo-Dutch War ( nl, Derde Engels-Nederlandse Oorlog), 27 March 1672 to 19 February 1674, was a naval conflict between the Dutch Republic and England, in alliance with France. It is considered a subsidiary of the wider 1672 to 1678 ...
.
Early 18th century
 The so-called
The so-called Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union ( gd, Achd an Aonaidh) were two Act of Parliament, Acts of Parliament: the Union with Scotland Act 1706 passed by the Parliament of England, and the Union with England Act 1707 passed by the Parliament of Scotland. They put ...
came in the middle of the long period of domination in London of Sir Godfrey Kneller, a German portraitist who had eventually succeeded as principal court painter the Dutch Sir Peter Lely
Sir Peter Lely (14 September 1618 – 7 December 1680) was a painter of Dutch origin whose career was nearly all spent in England, where he became the dominant portrait painter to the court.
Life
Lely was born Pieter van der Faes to Dutch ...
, whose style he had adopted for his enormous and formulaic output, of greatly varying quality, which was itself repeated by an army of lesser painters. His counterpart in Edinburgh, Sir John Baptist Medina, born in Brussels to Spanish parents, had died just before the Union took place, and was one of the last batch of Scottish knights to be created. Medina had first worked in London, but in mid-career moved to the less competitive environment of Edinburgh, where he dominated portraiture of the Scottish elite. However, after the Union the movement was to be all in the other direction, and Scottish aristocrats resigned themselves to paying more to have their portraits painted in London, even if by Scottish painters such as Medina's pupil William Aikman, who moved down in 1723, or Allan Ramsay Allan Ramsay may refer to:
*Allan Ramsay (poet) or Allan Ramsay the Elder (1686–1758), Scottish poet
*Allan Ramsay (artist) or Allan Ramsay the Younger (1713–1784), Scottish portrait painter
*Allan Ramsay (diplomat) (1937–2022), British diplom ...
.
There was an alternative, more direct, tradition in British portraiture to that of Lely and Kneller, tracing back to William Dobson and the German or Dutch Gerard Soest, who trained John Riley, to whom only a few works are firmly attributed and who in turn trained Jonathan Richardson
Jonathan Richardson (12 January 1667 – 28 May 1745), sometimes called "the Elder" to distinguish him from his son (Jonathan Richardson the Younger), was an English artist, collector of drawings and writer on art, working almost entirely as a ...
, a fine artist who trained Thomas Hudson who trained Joshua Reynolds and Joseph Wright of Derby. Richardson also trained the most notable Irish portraitist of the period, Charles Jervas who enjoyed social and financial success in London despite his clear limitations as an artist.
An exception to the dominance of the " lower genres" of painting was Sir James Thornhill
Sir James Thornhill (25 July 1675 or 1676 – 4 May 1734) was an English painter of historical subjects working in the Italian baroque tradition. He was responsible for some large-scale schemes of murals, including the " Painted Hall" at the ...
(1675/76–1734) who was the first and last significant English painter of huge Baroque allegorical decorative schemes, and the first native painter to be knighted. His best-known work is at Greenwich Hospital, Blenheim Palace and the cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome.
The word derives, via Italian, fr ...
of Saint Paul's Cathedral, London. His drawings show a taste for strongly drawn realism in the direction his son-in-law William Hogarth
William Hogarth (; 10 November 1697 – 26 October 1764) was an English painter, engraver, pictorial satirist, social critic, editorial cartoonist and occasional writer on art. His work ranges from realistic portraiture to comic strip-lik ...
was to pursue, but this is largely overridden in the finished works, and for Greenwich he took to heart his careful list of "Objections that will arise from the plain representation of the King's landing as it was in fact and in the modern way and dress" and painted a conventional Baroque glorification. Like Hogarth, he played the nationalist card in promoting himself, and eventually beat Sebastiano Ricci
Sebastiano Ricci (1 August 165915 May 1734) was an Italian painter of the late Baroque school of Venice. About the same age as Piazzetta, and an elder contemporary of Tiepolo, he represents a late version of the vigorous and luminous Corton ...
to enough commissions that in 1716 he and his team retreated to France, Giovanni Antonio Pellegrini having already left in 1713. Once the other leading foreign painters of allegoric schemes, Antonio Verrio and Louis Laguerre
Louis Laguerre (1663 – 20 April 1721) was a French decorative painter mainly working in England.
Born in Versailles in 1663 and trained at the Paris Academy under Charles Le Brun, he came to England in 1683, where he first worked with Anton ...
, had died in 1707 and 1721 respectively, Thornhill had the field to himself, although by the end of his life commissions for grand schemes had dried up from changes in taste.
From 1714 the new Hanoverian dynasty conducted a far less ostentatious court, and largely withdrew from patronage of the arts, other than the necessary portraits. Fortunately, the booming British economy was able to supply aristocratic and mercantile wealth to replace the court, above all in London.
William Hogarth
William Hogarth (; 10 November 1697 – 26 October 1764) was an English painter, engraver, pictorial satirist, social critic, editorial cartoonist and occasional writer on art. His work ranges from realistic portraiture to comic strip-lik ...
was a great presence in the second quarter of the century, whose art was successful in achieving a particular English character, with vividly moralistic scenes of contemporary life, full of both satire and pathos, attuned to the tastes and prejudices of the Protestant middle-class, who bought the engraved
Engraving is the practice of incising a design onto a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or glass are engraved, or may provide an in ...
versions of his paintings in huge numbers. Other subjects were only issued as prints, and Hogarth was both the first significant British printmaker, and still the best known. Many works were series of four or more scenes, of which the best known are: '' A Harlot's Progress'' and '' A Rake's Progress'' from the 1730s and '' Marriage à-la-mode'' from the mid-1740s. In fact, although he only once briefly left England and his own propaganda asserted his Englishness and often attacked the Old Master
In art history, "Old Master" (or "old master")Old Masters De ...
s, his background in printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed techni ...
, more closely aware of Continental art than most British painting, and apparently his ability to quickly absorb lessons from other painters, meant that he was more aware of, and made more use of, Continental art than most of his contemporaries.
Like many later painters Hogarth wanted above all to achieve success at history painting
History painting is a genre in painting defined by its subject matter rather than any artistic style or specific period. History paintings depict a moment in a narrative story, most often (but not exclusively) Greek and Roman mythology and Bible ...
in the Grand Manner
Grand Manner refers to an idealized aesthetic style derived from classicism and the art of the High Renaissance. In the eighteenth century, British artists and connoisseurs used the term to describe paintings that incorporated visual metaphors i ...
, but his few attempts were not successful and are now little regarded. His portraits were mostly of middle-class sitters shown with an apparent realism that reflected both sympathy and flattery, and included some in the fashionable form of the conversation piece, recently introduced from France by Philippe Mercier, which was to remain a favourite in Britain, taken up by artists such as Francis Hayman
Francis Hayman (1708 – 2 February 1776) was an English painter and illustrator who became one of the founding members of the Royal Academy in 1768, and later its first librarian.
Life and works
Born in Exeter, Devon, Hayman begun his arti ...
, though usually abandoned once an artist could get good single figure commissions.
 There was a recognition that, even more than the rest of Europe given the lack of British artists, the training of artists needed to be extended beyond the workshop of established masters, and various attempts were made to set up academies, starting with Kneller in 1711, with the help of Pellegrini, in Great Queen Street. The academy was taken over by Thornhill in 1716, but seems to have become inactive by the time
There was a recognition that, even more than the rest of Europe given the lack of British artists, the training of artists needed to be extended beyond the workshop of established masters, and various attempts were made to set up academies, starting with Kneller in 1711, with the help of Pellegrini, in Great Queen Street. The academy was taken over by Thornhill in 1716, but seems to have become inactive by the time John Vanderbank
John Vanderbank (9 September 1694 – 23 December 1739)Waterhouse, Ellis. ''Painting in Britain 1530–1790'' (Penguin Books, 1957). was a leading English portrait painter who enjoyed a high reputation during the last decade of King George I ...
and Louis Chéron set up their own academy in 1720. This did not last long, and in 1724/5 Thornhill tried again in his own house, with little success. Hogarth inherited the equipment for this, and used it to start the St. Martin's Lane Academy
The St Martin's Lane Academy, a precursor of the Royal Academy, was organised in 1735 by William Hogarth, from the circle of artists and designers who gathered at Slaughter's Coffee House at the upper end of St Martin's Lane, London. The artist ...
in 1735, which was the most enduring, eventually being absorbed by the Royal Academy
The Royal Academy of Arts (RA) is an art institution based in Burlington House on Piccadilly in London. Founded in 1768, it has a unique position as an independent, privately funded institution led by eminent artists and architects. Its purp ...
in 1768. Hogarth also helped solve the problem of a lack of exhibition venues in London, arranging for shows at the Foundling Hospital
The Foundling Hospital in London, England, was founded in 1739 by the philanthropic sea captain Thomas Coram. It was a children's home established for the "education and maintenance of exposed and deserted young children." The word " hospita ...
from 1746.
The Scottish portraitist Allan Ramsay Allan Ramsay may refer to:
*Allan Ramsay (poet) or Allan Ramsay the Elder (1686–1758), Scottish poet
*Allan Ramsay (artist) or Allan Ramsay the Younger (1713–1784), Scottish portrait painter
*Allan Ramsay (diplomat) (1937–2022), British diplom ...
worked in Edinburgh before moving to London by 1739. He made visits of three years to Italy at the beginning and end of his career, and anticipated Joshua Reynolds in bringing a more relaxed version of "Grand Manner" to British portraiture, combined with very sensitive handling in his best work, which is generally agreed to have been of female sitters. His main London rival in the mid-century, until Reynolds made his reputation, was Reynold's master, the stodgy Thomas Hudson.
John Wootton
John Wootton (c.1686– 13 November 1764)Deuchar, S. (2003). "Wootton, John". Grove Art Online. was an English painter of sporting subjects, battle scenes and landscapes, and illustrator.
Life
Born in Snitterfield, Warwickshire (near Stratf ...
, active from about 1714 to his death in 1765, was the leading sporting painter of his day, based in the capital of English horse racing at Newmarket, and producing large numbers of portraits of horses and also battle scenes and conversation pieces with a hunting
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products ( fur/ hide, bone/ tusks, horn/ a ...
or riding setting. He had begun life as a page to the family of the Dukes of Beaufort, who in the 1720s sent him to Rome, where he acquired a classicising landscape style based on that of Gaspard Dughet
Gaspard Dughet (15 June 1615 – 25 May 1675), also known as Gaspard Poussin, was a French painter born in Rome.
Life
Dughet was born in Rome, the son of a French pastry-cook
and his Italian wife. He has always generally been considered as a Fr ...
and Claude, which he used in some pure landscape paintings, as well as views of country houses and equine subjects. This introduced an alternative to the various Dutch and Flemish artists who had previously set the prevailing landscape style in Britain, and through intermediary artists such as George Lambert George Lambert may refer to:
Politicians
*George Lambert, 1st Viscount Lambert (1866–1958), British MP and peer
*George Lambert, 2nd Viscount Lambert (1909–1989), his son, also a British MP and peer
* George Lambert (Australian politician) ( ...
, the first British painter to base a career on landscape subjects, was to greatly influence other British artists such as Gainsborough. Samuel Scott was the best of the native marine and townscape artists, though in the latter specialization he could not match the visiting Canaletto
Giovanni Antonio Canal (18 October 1697 – 19 April 1768), commonly known as Canaletto (), was an Italian painter from the Republic of Venice, considered an important member of the 18th-century Venetian school.
Painter of city views or ...
, who was in England from nine years from 1746, and whose Venetian views were a favourite souvenir of the Grand Tour
The Grand Tour was the principally 17th- to early 19th-century custom of a traditional trip through Europe, with Italy as a key destination, undertaken by upper-class young European men of sufficient means and rank (typically accompanied by a tu ...
.
Sir John Rushout, 4th Baronet
Sir John Rushout, 4th Baronet (6 February 16852 February 1775), of Northwick Park, Worcestershire was a British Whig politician who sat in the House of Commons for 55 years from 1713 to 1768. He was a supporter of Pulteney in opposition to Walp ...
, by Godfrey Kneller, 1716
File:William Hogarth 047.jpg, William Hogarth
William Hogarth (; 10 November 1697 – 26 October 1764) was an English painter, engraver, pictorial satirist, social critic, editorial cartoonist and occasional writer on art. His work ranges from realistic portraiture to comic strip-lik ...
, '' The Graham Children'', 1742
File:Marriage A-la-Mode 2, The Tête à Tête - William Hogarth.jpg, William Hogarth
William Hogarth (; 10 November 1697 – 26 October 1764) was an English painter, engraver, pictorial satirist, social critic, editorial cartoonist and occasional writer on art. His work ranges from realistic portraiture to comic strip-lik ...
, '' Marriage A-la-Mode (Hogarth)'', c. 1743-45
File:Lost Portrait of Charles Edward Stuart.jpg, Allan Ramsay Allan Ramsay may refer to:
*Allan Ramsay (poet) or Allan Ramsay the Elder (1686–1758), Scottish poet
*Allan Ramsay (artist) or Allan Ramsay the Younger (1713–1784), Scottish portrait painter
*Allan Ramsay (diplomat) (1937–2022), British diplom ...
, '' Portrait of Charles Stuart'', 1745
File:John Byng.jpg, Thomas Hudson, ''Portrait of John Byng
Admiral John Byng (baptised 29 October 1704 – 14 March 1757) was a British Royal Navy officer who was court-martialled and executed by firing squad. After joining the navy at the age of thirteen, he participated at the Battle of Cape Pass ...
'', 1749
File:William Hogarth 032.jpg, William Hogarth
William Hogarth (; 10 November 1697 – 26 October 1764) was an English painter, engraver, pictorial satirist, social critic, editorial cartoonist and occasional writer on art. His work ranges from realistic portraiture to comic strip-lik ...
, '' Humours of an Election'' 1755
antiquary
An antiquarian or antiquary () is an aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient artifacts, archaeological and historic sit ...
and engraver George Vertue was a figure in the London art scene for most of the period, and his copious notebooks were adapted and published in the 1760s by Horace Walpole
Horatio Walpole (), 4th Earl of Orford (24 September 1717 – 2 March 1797), better known as Horace Walpole, was an English writer, art historian, man of letters, antiquarian, and Whig politician.
He had Strawberry Hill House built in Twi ...
as ''Some Anecdotes of Painting in England'', which remains a principal source for the period.
From his arrival in London in 1720, the Flemish sculptor John Michael Rysbrack was the leader in his field until the arrival in 1730 of Louis-François Roubiliac
Louis-François Roubiliac (or Roubilliac, or Roubillac) (31 August 1702 – 11 January 1762) was a French sculptor who worked in England. One of the four most prominent sculptors in London working in the rococo style, he was described by Margar ...
who had a Rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, ...
style which was highly effective in busts and small figures, though by the following decade he was also commissioned for larger works. He also produced models for the Chelsea porcelain factory founded in 1743, a private enterprise which sought to compete with Continental factories mostly established by rulers. Roubiliac's style formed that of the leading native sculptor Sir Henry Cheere, and his brother John who specialized in statues for gardens.
The strong London silversmithing trade was dominated by the descendants of Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bez ...
refugees like Paul de Lamerie
Paul de Lamerie (9 April 1688 – 1 August 1751) was a London-based silversmith. The Victoria and Albert Museum describes him as the "greatest silversmith working in England in the 18th century". He was being referred to as the ‘King’s silv ...
, Paul Crespin, Nicholas Sprimont
Nicholas is a male given name and a surname.
The Eastern Orthodox Church, the Roman Catholic Church, and the Anglican Churches celebrate Saint Nicholas every year on December 6, which is the name day for "Nicholas". In Greece, the name and it ...
, and the Courtauld family, as well as Georges Wickes. Orders were received from as far away as the courts of Russia and Portugal, though English styles were still led by Paris. The manufacture of silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
at Spitalfields
Spitalfields is a district in the East End of London and within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The area is formed around Commercial Street (on the A1202 London Inner Ring Road) and includes the locale around Brick Lane, Christ Church ...
in London was also a traditional Huguenot business, but from the late 1720s silk design was dominated by the surprising figure of Anna Maria Garthwaite
Anna Maria Garthwaite (b. Harston, Leicestershire, c. 14 March 1688 – October 1763) was an English textile designer known for creating vivid floral designs for silk fabrics hand-woven in Spitalfields, London, in the mid-18th century. Garthw ...
, a parson's daughter from Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire (abbreviated Lincs.) is a county in the East Midlands of England, with a long coastline on the North Sea to the east. It borders Norfolk to the south-east, Cambridgeshire to the south, Rutland to the south-west, Leicestershir ...
who emerged at the age of 40 as a designer of largely floral patterns in Rococo styles.
Unlike in France and Germany, the English adoption of the Rococo style was patchy rather than whole-hearted, and there was resistance to it on nationalist grounds, led by Richard Boyle, 3rd Earl of Burlington
Richard Boyle, 3rd Earl of Burlington and 4th Earl of Cork, (25 April 1694 – 4 December 1753) was a British architect and noble often called the "Apollo of the Arts" and the "Architect Earl". The son of the 2nd Earl of Burlington and 3rd Ea ...
and William Kent
William Kent (c. 1685 – 12 April 1748) was an English architect, landscape architect, painter and furniture designer of the early 18th century. He began his career as a painter, and became Principal Painter in Ordinary or court painter, bu ...
, who promoted styles in interior design and furniture to match the Palladianism
Palladian architecture is a European architectural style derived from the work of the Venetian architect Andrea Palladio (1508–1580). What is today recognised as Palladian architecture evolved from his concepts of symmetry, perspective and ...
of the architecture they produced together, also beginning the influential British tradition of the landscape garden
The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden (french: Jardin à l'anglaise, it, Giardino all'inglese, german: Englischer Landschaftsgarten, pt, Jardim inglês, es, Jardín inglés), is a sty ...
, according to Nikolaus Pevsner
Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 – 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, '' The Buildings of England'' ...
"the most influential of all English innovations in art". The French-born engraver Hubert-François Gravelot, in London from 1732 to 1745, was a key figure in importing Rococo taste in book illustrations and ornament prints for craftsmen to follow.
Late 18th century
In the modern popular mind, English art from about 1750–1790 — today referred to as the "classical age" of English painting — was dominated bySir Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter, specialising in portraits. John Russell said he was one of the major European painters of the 18th century. He promoted the "Grand Style" in painting which depende ...
(1723–1792), George Stubbs
George Stubbs (25 August 1724 – 10 July 1806) was an English painter, best known for his paintings of horses. Self-trained, Stubbs learnt his skills independently from other great artists of the 18th century such as Reynolds or Gainsborou ...
(1724–1806), Thomas Gainsborough
Thomas Gainsborough (14 May 1727 (baptised) – 2 August 1788) was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists of ...
(1727–1788) and Joseph Wright of Derby
Joseph Wright (3 September 1734 – 29 August 1797), styled Joseph Wright of Derby, was an English landscape and portrait painter. He has been acclaimed as "the first professional painter to express the spirit of the Industrial Revolution".
Wr ...
(1734–1797). At the time Reynolds was considered the dominant figure, Gainsborough was very highly reputed, but Stubbs was seen as a mere painter of animals and viewed as far a less significant figure than many other painters that are today little-known or forgotten. The period saw continued rising prosperity for Britain and British artists: "By the 1780s English painters were among the wealthiest men in the country, their names familiar to newspaper readers, their quarrels and cabals the talk of the town, their subjects known to everyone from the displays in the print-shop windows", according to Gerald Reitlinger
Gerald Roberts Reitlinger (born 1900 in London, United Kingdom – died 1978 in St Leonards-on-Sea, United Kingdom) was an art historian, especially of Asian ceramics, and a scholar of historical changes in taste in art and their reflection in ...
.
Reynolds returned from a long visit to Italy in 1753, and very quickly established a reputation as the most fashionable London portraitist, and before long as a formidable figure in society;, the public leader of the arts in Britain. He had studied both classical and modern Italian art, and his compositions discreetly re-use models seen on his travels. He could convey a wide range of moods and emotions, whether heroic military men or very young women, and often to unite background and figure in a dramatic way.
The Society for the encouragement of Arts, Manufactures & Commerce
The Royal Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce (RSA), also known as the Royal Society of Arts, is a London-based organisation committed to finding practical solutions to social challenges. The RSA acronym is used m ...
had been founded in 1754, principally to provide a location for exhibitions. In 1761 Reynolds was a leader in founding the rival Society of Artists of Great Britain, where the artists had more control. This continued until 1791, despite the founding of the Royal Academy of Arts
The Royal Academy of Arts (RA) is an art institution based in Burlington House on Piccadilly in London. Founded in 1768, it has a unique position as an independent, privately funded institution led by eminent artists and architects. Its purp ...
in 1768, which immediately became both the most important exhibiting organization and the most important school in London. Reynolds was its first President, holding the office until his death in 1792. His published ''Discourses'', first delivered to the students, were regarded as the first major writing on art in English, and set out the aspiration for a style to match the classical grandeur of classical sculpture and High Renaissance
In art history, the High Renaissance was a short period of the most exceptional artistic production in the Italian states, particularly Rome, capital of the Papal States, and in Florence, during the Italian Renaissance. Most art historians stat ...
painting.
After the Academy was established, Reynolds' portraits became more overly classicizing, and often more distant, until in the late 1770s he returned to a more intimate style, perhaps influenced by the success of Thomas Gainsborough
Thomas Gainsborough (14 May 1727 (baptised) – 2 August 1788) was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists of ...
, who only settled in London in 1773, after working in Ipswich
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England, of which it is the county town. The town is located in East Anglia about away from the mouth of the River Orwell and the North Sea. Ipswich is both on the Great Eastern Main Line r ...
and then Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
. While Reynolds' practice of aristocratic portraits seem exactly matched to his talents, Gainsborough, if not forced to follow the market for his work, might well have developed as a pure landscape painter, or a portraitist in the informal style of many of his portraits of his family. He continued to paint pure landscapes, largely for pleasure until his later years; full recognition of his landscapes came only in the 20th century. His main influences were French in his portraits and Dutch in his landscapes, rather than Italian, and he is famous for the brilliant light touch of his brushwork. George Romney also became prominent in about 1770 and was active until 1799, though with a falling-off in his last years. His portraits are mostly characterful but flattering images of dignified society figures, but he developed an obsession with the flighty young Emma Hamilton from 1781, painting her about sixty times in more extravagant poses. His work was especially sought-after by American collectors in the early 20th century and many are now in American museums. By the end of the period this generation had been succeeded by younger portraitists including John Hoppner, Sir William Beechey and the young Gilbert Stuart, who only realized his mature style after he returned to America.
The Welsh painter Richard Wilson returned to London from seven years in Italy in 1757, and over the next two decades developed a "sublime" landscape style adapting the Franco-Italian tradition of Claude and Gaspard Dughet to British subjects. Though much admired, like those of Gainsborough his landscapes were hard to sell, and he sometimes resorted, as Reynolds complained, to the common strategem of turning them into history painting
History painting is a genre in painting defined by its subject matter rather than any artistic style or specific period. History paintings depict a moment in a narrative story, most often (but not exclusively) Greek and Roman mythology and Bible ...
s by adding a few small figures, which doubled their price to about £80. He continued to paint scenes set in Italy, as well as England and Wales, and his death in 1782 came just as large numbers of artists began to travel to Wales, and later the Lake District and Scotland in search of mountainous views, both for oil paintings and watercolour
Watercolor (American English) or watercolour (British English; see spelling differences), also ''aquarelle'' (; from Italian diminutive of Latin ''aqua'' "water"), is a painting method”Watercolor may be as old as art itself, going back to t ...
s which were now starting their long period of popularity in Britain, both with professionals and amateurs. Paul Sandby
Paul Sandby (1731 – 7 November 1809) was an English map-maker turned landscape painter in watercolours, who, along with his older brother Thomas, became one of the founding members of the Royal Academy in 1768.
Life and work
Sandby wa ...
, Francis Towne, John Warwick Smith
John "Warwick" Smith (26 July 1749 – 22 March 1831) was a British watercolour landscape painter and illustrator.
Life and work
Smith was born at Irthington, near Carlisle, Cumberland, the son of a gardener to the Gilpin family, and ...
, and John Robert Cozens were among the leading specialist painters and the clergyman and amateur artist William Gilpin was an important writer who stimulated the popularity of amateur painting of the picturesque
Picturesque is an aesthetic ideal introduced into English cultural debate in 1782 by William Gilpin in ''Observations on the River Wye, and Several Parts of South Wales, etc. Relative Chiefly to Picturesque Beauty; made in the Summer of the Year ...
, while the works of Alexander Cozens
Alexander Cozens (1717–1786) was a British landscape painter in watercolours, born in Russia, in Saint Petersburg. He taught drawing and wrote treatises on the subject, evolving a method in which imaginative drawings of landscapes could be w ...
recommended forming random ink blots into landscape compositions—even Constable tried this technique.

History painting
History painting is a genre in painting defined by its subject matter rather than any artistic style or specific period. History paintings depict a moment in a narrative story, most often (but not exclusively) Greek and Roman mythology and Bible ...
in the grand manner continued to be the most prestigious form of art, though not the easiest to sell, and Reynolds made several attempts at it, as unsuccessful as Hogarth's. The unheroic nature of modern dress was seen as a major obstacle in the depiction of contemporary scenes, and the Scottish gentleman-artist and art dealer Gavin Hamilton Gavin Hamilton may refer to:
* Gavin Hamilton (archbishop of St Andrews) (died 1571), archbishop of St Andrews
* Gavin Hamilton (bishop of Galloway) (1561–1612), bishop of Galloway
* Gavin Hamilton (artist) (1723–1798), Scottish artist
* Gavin ...
preferred classical scenes as well as painting some based on his Eastern travels, where his European figures by-passed the problem by wearing Arab dress. He spent most of his adult life based in Rome and had at least as much influence on Neo-Classicism
Neoclassicism (also spelled Neo-classicism) was a Western cultural movement in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiquity. Neoclassicism was ...
in Europe as in Britain. The Irishman James Barry was an influence on Blake but had a difficult career, and spent years on his cycle ''The Progress of Human Culture'' in the Great Room of the Royal Society of Arts
The Royal Society for the Encouragement of Arts, Manufactures and Commerce (RSA), also known as the Royal Society of Arts, is a London-based organisation committed to finding practical solutions to social challenges. The RSA acronym is used m ...
. The most successful history painters, who were not afraid of buttons and wigs, were both Americans settled in London: Benjamin West
Benjamin West, (October 10, 1738 – March 11, 1820) was a British-American artist who painted famous historical scenes such as '' The Death of Nelson'', '' The Death of General Wolfe'', the '' Treaty of Paris'', and '' Benjamin Franklin Drawin ...
and John Singleton Copley
John Singleton Copley (July 3, 1738 – September 9, 1815) was an Anglo-American painter, active in both colonial America and England. He was probably born in Boston, Massachusetts, to Richard and Mary Singleton Copley, both Anglo-Irish. Afte ...
, though one of his most successful works ''Watson and the Shark
''Watson and the Shark'' is an oil painting by the American painter John Singleton Copley, depicting the rescue of the English boy Brook Watson from a shark attack in Havana, Cuba. Copley, then living in London, painted three versions. The 17 ...
'' (1778) was able to mostly avoid them, showing a rescue from drowning. Smaller scale subjects from literature were also popular, pioneered by Francis Hayman
Francis Hayman (1708 – 2 February 1776) was an English painter and illustrator who became one of the founding members of the Royal Academy in 1768, and later its first librarian.
Life and works
Born in Exeter, Devon, Hayman begun his arti ...
, one of the first to paint scenes from Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
, and Joseph Highmore
Joseph Highmore (13 June 1692 – 3 March 1780) was an English painter of portraits, conversation pieces and history subjects, illustrator and author. After retiring from his career as a painter at the age of 70, he published art historica ...
, with a series illustrating the novel '' Pamela''. At the end of the period the Boydell Shakespeare Gallery was an ambitious project for paintings, and prints after them, illustrating "the Bard", as he had now become, while exposing the limitations of contemporary English history painting. Joseph Wright of Derby
Joseph Wright (3 September 1734 – 29 August 1797), styled Joseph Wright of Derby, was an English landscape and portrait painter. He has been acclaimed as "the first professional painter to express the spirit of the Industrial Revolution".
Wr ...
was mainly a portrait painter who also was one of the first artists to depict the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, as well as developing a cross between the conversation piece and history painting in works like ''An Experiment on a Bird in the Air Pump
''An Experiment on a Bird in the Air Pump'' is a 1768 oil-on-canvas painting by Joseph Wright of Derby, one of a number of candlelit scenes that Wright painted during the 1760s. The painting departed from convention of the time by depicting a ...
'' (1768) and ''A Philosopher Lecturing on the Orrery
''A Philosopher Lecturing on the Orrery'', or the full title, ''A Philosopher giving that Lecture on the Orrery in which a lamp is put in place of the Sun'', is a 1766 painting by Joseph Wright of Derby depicting a lecturer giving a demonstrati ...
'' (c. 1766), which like many of his works are lit only by candlelight, giving a strong chiaroscuro
Chiaroscuro ( , ; ), in art, is the use of strong contrast (vision), contrasts between light and dark, usually bold contrasts affecting a whole composition. It is also a technical term used by artists and art historians for the use of contrasts ...
effect.
 Paintings recording scenes from the theatre were another subgenre, painted by the German
Paintings recording scenes from the theatre were another subgenre, painted by the German Johann Zoffany
Johan Joseph Zoffany (born Johannes Josephus Zaufallij; 13 March 1733 – 11 November 1810) was a German neoclassical painter who was active mainly in England, Italy and India. His works appear in many prominent British collections, includin ...
among others. Zoffany painted portraits and conversation pieces, who also spent over two years in India, painting the English nabobs and local scenes, and the expanding British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading post ...
played an increasing role in British art. Training in art was considered a useful skill in the military for sketch maps and plans, and many British officers made the first Western images, often in watercolour, of scenes and places around the world. In India, the Company style
Company style, also known as Company painting or Patna painting (Hindi: ''kampani kalam'') is a term for a hybrid Indo-European style of paintings made in India by Indian artists, many of whom worked for European patrons in the East India Company ...
developed as a hybrid form between Western and Indian art
Indian art consists of a variety of art forms, including painting, sculpture, pottery, and textile arts such as woven silk. Geographically, it spans the entire Indian subcontinent, including what is now India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, N ...
, produced by Indians for a British market.
Thomas Rowlandson
Thomas Rowlandson (; 13 July 175721 April 1827) was an English artist and caricaturist of the Georgian Era, noted for his political satire and social observation. A prolific artist and printmaker, Rowlandson produced both individual social an ...
produced watercolours and prints satirizing British life, but mostly avoided politics. The master of the political caricature
A caricature is a rendered image showing the features of its subject in a simplified or exaggerated way through sketching, pencil strokes, or other artistic drawings (compare to: cartoon). Caricatures can be either insulting or complimentary, a ...
, sold individually by print shops (often acting as publishers also), either hand-coloured or plain, was James Gillray
James Gillray (13 August 1756Gillray, James and Draper Hill (1966). ''Fashionable contrasts''. Phaidon. p. 8.Baptism register for Fetter Lane (Moravian) confirms birth as 13 August 1756, baptism 17 August 1756 1June 1815) was a British caricatu ...
. The emphasis on portrait-painting in British art was not entirely due to the vanity of the sitters. There was a large collector's market for portrait prints, mostly reproductions of paintings, which were often mounted in albums. From the mid-century there was a great growth in the expensive but more effective reproductions in mezzotint
Mezzotint is a monochrome printmaking process of the '' intaglio'' family. It was the first printing process that yielded half-tones without using line- or dot-based techniques like hatching, cross-hatching or stipple. Mezzotint achieves tona ...
, of portraits and other paintings, with special demand from collectors for early proof states "before letter" (that is, before the inscriptions were added), which the printmakers obligingly printed off in growing numbers.
This period marked one of the high points in British decorative arts. Around the mid-century many porcelain
Porcelain () is a ceramic material made by heating substances, generally including materials such as kaolinite, in a kiln to temperatures between . The strength and translucence of porcelain, relative to other types of pottery, arises main ...
factories opened, including Bow in London, and in the provinces Lowestoft
Lowestoft ( ) is a coastal town and civil parish in the East Suffolk district of Suffolk, England.OS Explorer Map OL40: The Broads: (1:25 000) : . As the most easterly UK settlement, it is north-east of London, north-east of Ipswich and so ...
, Worcester, Royal Crown Derby
The Royal Crown Derby Porcelain Company is the oldest or second oldest remaining English porcelain manufacturer, based in Derby, England (disputed by Royal Worcester, who claim 1751 as their year of establishment). The company, particularly kno ...
, Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its E ...
, and Wedgwood
Wedgwood is an English fine china, porcelain and luxury accessories manufacturer that was founded on 1 May 1759 by the potter and entrepreneur Josiah Wedgwood and was first incorporated in 1895 as Josiah Wedgwood and Sons Ltd. It was rap ...
, with Spode following in 1767. Most were started as small concerns, with some lasting only a few decades while others still survive today. By the end of the period British porcelain services were being commissioned by foreign royalty and the British manufacturers were especially adept at pursuing the rapidly expanding international middle-class market, developing bone china
Bone china is a type of ceramic that is composed of bone ash, feldspathic material, and kaolin. It has been defined as "ware with a translucent body" containing a minimum of 30% of phosphate derived from animal bone and calculated calcium phos ...
and transfer-print
Transfer printing is a method of decorating pottery or other materials using an engraved copper or steel plate from which a monochrome print on paper is taken which is then transferred by pressing onto the ceramic piece.John Fleming (art histori ...
ed wares as well as hand-painted true porcelain.
The three leading furniture makers, Thomas Chippendale
Thomas Chippendale (1718–1779) was a cabinet-maker in London, designing furniture in the mid-Georgian, English Rococo, and Neoclassical styles. In 1754 he published a book of his designs in a trade catalogue titled ''The Gentleman and Cab ...
(1718–1779), Thomas Sheraton
Thomas Sheraton (1751 – 22 October 1806) was a furniture designer, one of the "big three" English furniture makers of the 18th century, along with Thomas Chippendale and George Hepplewhite. Sheraton gave his name to a style of furniture charac ...
(1751–1806) and George Hepplewhite
George Hepplewhite (1727? – 21 June 1786) was a cabinetmaker. He is regarded as having been one of the "big three" English furniture makers of the 18th century, along with Thomas Sheraton and Thomas Chippendale. There are no pieces of furnit ...
(1727?–1786) had varied styles and have achieved the lasting fame they have mainly as the authors of pattern books used by other makers in Britain and abroad. In fact it is far from clear if the last two named ever ran actual workshops, though Chippendale certainly was successful in this and in what we now call interior design; unlike France Britain had abandoned its guild
A guild ( ) is an association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area. The earliest types of guild formed as organizations of tradesmen belonging to a professional association. They sometimes ...
system, and Chippendale was able to employ specialists in all the crafts needed to complete a redecoration. During the period Rococo and Chinoiserie
(, ; loanword from French ''chinoiserie'', from ''chinois'', "Chinese"; ) is the European interpretation and imitation of Chinese and other East Asian artistic traditions, especially in the decorative arts, garden design, architecture, literatu ...
gave way to Neo-Classicism
Neoclassicism (also spelled Neo-classicism) was a Western cultural movement in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiquity. Neoclassicism was ...
, with the Scottish architect and interior designer Robert Adam
Robert Adam (3 July 17283 March 1792) was a British neoclassical architect, interior designer and furniture designer. He was the son of William Adam (1689–1748), Scotland's foremost architect of the time, and trained under him. With his ...
(1728–1792) leading the new style.
Sir Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter, specialising in portraits. John Russell said he was one of the major European painters of the 18th century. He promoted the "Grand Style" in painting which depende ...
, ''Self-portrait, aged about 24'' c. 1747-9
File:Cornard_Wood.png, Thomas Gainsborough
Thomas Gainsborough (14 May 1727 (baptised) – 2 August 1788) was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists of ...
, '' Cornard Wood, near Sudbury, Suffolk'', 1748
File:Whistlejacket_by_George_Stubbs_edit.jpg, George Stubbs
George Stubbs (25 August 1724 – 10 July 1806) was an English painter, best known for his paintings of horses. Self-trained, Stubbs learnt his skills independently from other great artists of the 18th century such as Reynolds or Gainsborou ...
, '' Whistlejacket'', c. 1762
File:Wright of Derby, The Orrery.jpg, Joseph Wright of Derby
Joseph Wright (3 September 1734 – 29 August 1797), styled Joseph Wright of Derby, was an English landscape and portrait painter. He has been acclaimed as "the first professional painter to express the spirit of the Industrial Revolution".
Wr ...
, ''A Philosopher Lecturing on the Orrery
''A Philosopher Lecturing on the Orrery'', or the full title, ''A Philosopher giving that Lecture on the Orrery in which a lamp is put in place of the Sun'', is a 1766 painting by Joseph Wright of Derby depicting a lecturer giving a demonstrati ...
'', c. 1766
File:The Kongouro from New Holland (Kangaroo) NMM ZBA5754 (cropped).jpg, George Stubbs
George Stubbs (25 August 1724 – 10 July 1806) was an English painter, best known for his paintings of horses. Self-trained, Stubbs learnt his skills independently from other great artists of the 18th century such as Reynolds or Gainsborou ...
, '' The Kongouro from New Holland'', 1772
File:Thomas_Gainsborough_-_The_Honourable_Mrs_Graham_(1757_-_1792)_-_Google_Art_Project.jpg, Thomas Gainsborough
Thomas Gainsborough (14 May 1727 (baptised) – 2 August 1788) was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists of ...
, '' Portrait of Mrs Mary Graham'', 1777
File:Sir Joshua Reynolds - The Ladies Waldegrave - Google Art Project.jpg, Sir Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter, specialising in portraits. John Russell said he was one of the major European painters of the 18th century. He promoted the "Grand Style" in painting which depende ...
, ''The Ladies Waldegrave
''The Ladies Waldegrave'' is a group portrait by Joshua Reynolds from 1780–81, now in the Scottish National Gallery, who acquired it in 1952. It shows the three daughters of James Waldegrave, 2nd Earl Waldegrave, and Maria Walpole – from ...
'', 1780–81
File:Thomas Gainsborough - Mr and Mrs William Hallett ('The Morning Walk') - WGA8418.jpg, Thomas Gainsborough
Thomas Gainsborough (14 May 1727 (baptised) – 2 August 1788) was an English portrait and landscape painter, draughtsman, and printmaker. Along with his rival Sir Joshua Reynolds, he is considered one of the most important British artists of ...
, '' The Morning Walk'', 1785
File:The Age of Innocence - Reynolds.jpg, Sir Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter, specialising in portraits. John Russell said he was one of the major European painters of the 18th century. He promoted the "Grand Style" in painting which depende ...
, ''The Age of Innocence
''The Age of Innocence'' is a 1920 novel by American author Edith Wharton. It was her twelfth novel, and was initially serialized in 1920 in four parts, in the magazine '' Pictorial Review''. Later that year, it was released as a book by D. Ap ...
'', 1785–88
19th century and the Romantics
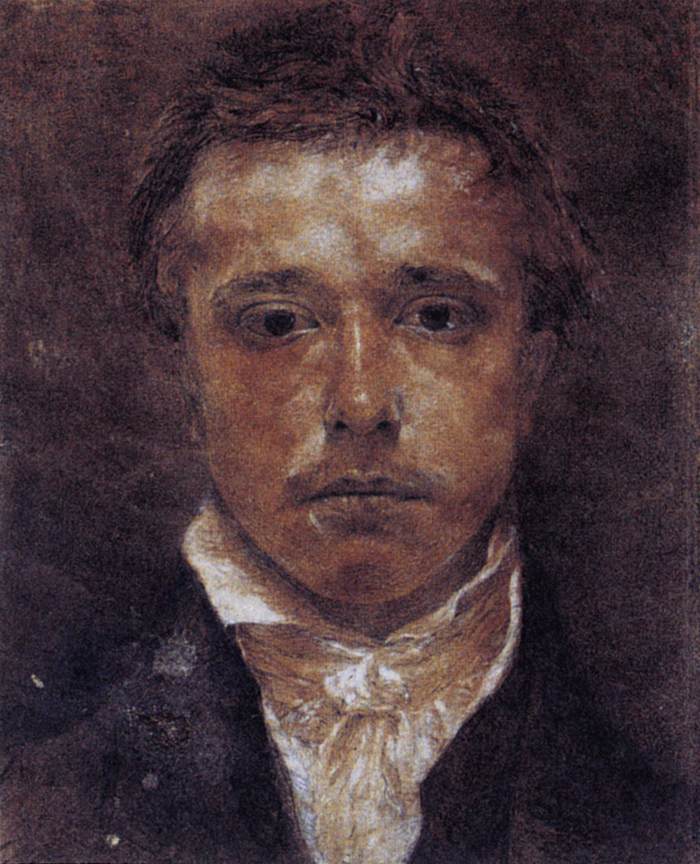 The late 18th century and the early 19th century characterized by the
The late 18th century and the early 19th century characterized by the Romantic movement
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
in British art includes Joseph Wright of Derby
Joseph Wright (3 September 1734 – 29 August 1797), styled Joseph Wright of Derby, was an English landscape and portrait painter. He has been acclaimed as "the first professional painter to express the spirit of the Industrial Revolution".
Wr ...
, James Ward, Samuel Palmer, Richard Parkes Bonington
Richard Parkes Bonington (25 October 1802 – 23 September 1828) was an English Romantic landscape painter, who moved to France at the age of 14 and can also be considered as a French artist, and an intermediary bringing aspects of English styl ...
, John Martin John Martin may refer to:
Business
*John Martin (businessman) (1820–1905), American lumberman and flour miller
*John Charles Martin (fl. 1913–1931), American newspaper publisher
*John Martin (publisher) (born 1930), American founder of Black ...
and was perhaps the most radical period in British art, also producing William Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual art of the Romantic Age. ...
(1757–1827), John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedham Vale, the ...
(1776–1837) and J.M.W. Turner (1775–1851), the later two being arguably the most internationally influential of all British artists. Turner's style, based on the Italianate tradition although he never saw Italy until in his forties, passed through considerable changes before his final wild, almost abstract, landscapes that explored the effects of light, and were a profound influence on the Impressionists
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passa ...
and other later movements. Constable normally painted pure landscapes with at most a few genre figures, in a style based on Northern European traditions, but, like Turner, his "six-footers" were intended to make as striking an impact as any history painting. They were carefully prepared using studies and full-size oil sketches, whereas Turner was notorious for finishing his exhibition pieces when they were already hanging for show, freely adjusting them to dominate the surrounding works in the tightly-packed hangs of the day.
Blake's visionary style was a minority taste in his lifetime, but influenced the younger group of " Ancients" of Samuel Palmer, John Linnell, Edward Calvert and George Richmond, who gathered in the country at Shoreham, Kent in the 1820s, producing intense and lyrical pastoral idylls in conditions of some poverty. They went on to more conventional artistic careers and Palmer's early work was entirely forgotten until the early 20th century. Blake and Palmer became a significant influence on modernist artists of the 20th century seen (among others) in the painting of British artists such as Dora Carrington, Paul Nash and Graham Sutherland. Blake also had an enormous influence on the beat poet
The Beat Generation was a literary subculture movement started by a group of authors whose work explored and influenced American culture and politics in the post-war era. The bulk of their work was published and popularized by Silent Generation ...
s of the 1950s and the counterculture of the 1960s
The counterculture of the 1960s was an anti-establishment cultural phenomenon that developed throughout much of the Western world in the 1960s and has been ongoing to the present day. The aggregate movement gained momentum as the civil rights mo ...
.
Thomas Lawrence
Sir Thomas Lawrence (13 April 1769 – 7 January 1830) was an English portrait painter and the fourth president of the Royal Academy. A child prodigy, he was born in Bristol and began drawing in Devizes, where his father was an innkeeper at t ...
was already a leading portraitist by the start of the 20th century, and able to give a Romantic dash to his portraits of high society, and the leaders of Europe gathered at the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
after the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
. Henry Raeburn was the most significant portraitist since the Union to remain based in Edinburgh throughout his career, an indication of increasing Scottish prosperity. But David Wilkie took the traditional road south, achieving great success with subjects of country life and hybrid genre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other ...
and history scenes such as '' The Chelsea Pensioners reading the Waterloo Dispatch'' (1822).
John Flaxman
John Flaxman (6 July 1755 – 7 December 1826) was a British sculptor
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dim ...
was the most thorough-going neo-classical English artist. Beginning as a sculptor, he became best known for his many spare "outline drawings" of classical scenes, often illustrating literature, which were reproduced as prints. These imitated the effects of the classical-style reliefs he also produced. The German-Swiss Henry Fuseli
Henry Fuseli ( ; German: Johann Heinrich Füssli ; 7 February 1741 – 17 April 1825) was a Swiss painter, draughtsman and writer on art who spent much of his life in Britain. Many of his works, such as '' The Nightmare'', deal with supernatu ...
also produced work in a linear graphic style, but his narrative scenes, often from English literature, were intensely Romantic and highly dramatic.
Thomas Lawrence
Sir Thomas Lawrence (13 April 1769 – 7 January 1830) was an English portrait painter and the fourth president of the Royal Academy. A child prodigy, he was born in Bristol and began drawing in Devizes, where his father was an innkeeper at t ...
, '' Sarah Barrett Moulton: Pinkie'', 1794
File:Newton-WilliamBlake.jpg, William Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual art of the Romantic Age. ...
, '' Newton'', 1805
File:John Constable - Wivenhoe Park, Essex - Google Art Project.jpg, John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedham Vale, the ...
, '' Wivenhoe Park, Essex'', 1816
File:The White Horse by John Constable - Google Art Project.jpg, John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedham Vale, the ...
, ''The White Horse'', 1819
File:David Wilkie Chelsea Pensioners Reading the Waterloo Dispatch.jpg, David Wilkie, '' Chelsea Pensioners reading the Waterloo Dispatch'', 1822
File:Constable Salisbury meadows.jpg, John Constable
John Constable (; 11 June 1776 – 31 March 1837) was an English landscape painter in the Romantic tradition. Born in Suffolk, he is known principally for revolutionising the genre of landscape painting with his pictures of Dedham Vale, the ...
, ''Salisbury Cathedral from the Meadows
''Salisbury Cathedral from the Meadows'' was painted by John Constable in 1831, three years after the death of his wife, Maria. It is currently on display in London, at Tate Britain, in the Clore gallery. He later added nine lines from ''The Sea ...
'', 1831
File:Slave-ship.jpg, J. M. W. Turner
Joseph Mallord William Turner (23 April 177519 December 1851), known in his time as William Turner, was an English Romantic painter, printmaker and watercolourist. He is known for his expressive colouring, imaginative landscapes and turbulen ...
, '' The Slave Ship'', 1840
File:Blue Rigi painting.jpg, J. M. W. Turner
Joseph Mallord William Turner (23 April 177519 December 1851), known in his time as William Turner, was an English Romantic painter, printmaker and watercolourist. He is known for his expressive colouring, imaginative landscapes and turbulen ...
, ''The Rigi
In 1842, British artist J. M. W. Turner painted three watercolours of the Rigi, a mountain in the Alps in Central Switzerland, which he had visited the previous summer. Widely regarded as some of his finest works, the watercolours capture the ...
'', 1842
File:Turner - Rain, Steam and Speed - National Gallery file.jpg, J. M. W. Turner
Joseph Mallord William Turner (23 April 177519 December 1851), known in his time as William Turner, was an English Romantic painter, printmaker and watercolourist. He is known for his expressive colouring, imaginative landscapes and turbulen ...
, '' Rain, Steam and Speed – The Great Western Railway'', 1844
Victorian art
 The
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood (later known as the Pre-Raphaelites) was a group of English painters, poets, and art critics, founded in 1848 by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, William Michael Rossetti, Jam ...
(PRB) achieved considerable influence after its foundation in 1848 with paintings that concentrated on religious, literary, and genre
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other ...
subjects executed in a colourful and minutely detailed style, rejecting the loose painterly brushwork of the tradition represented by "Sir Sloshua" Reynolds. PRB artists included John Everett Millais
Sir John Everett Millais, 1st Baronet, ( , ; 8 June 1829 – 13 August 1896) was an English painter and illustrator who was one of the founders of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. He was a child prodigy who, aged eleven, became the youngest s ...
, William Holman Hunt
William Holman Hunt (2 April 1827 – 7 September 1910) was an English painter and one of the founders of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. His paintings were notable for their great attention to detail, vivid colour, and elaborate symbolism. ...
, Dante Gabriel Rossetti
Gabriel Charles Dante Rossetti (12 May 1828 – 9 April 1882), generally known as Dante Gabriel Rossetti (), was an English poet, illustrator, painter, translator and member of the Rossetti family. He founded the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhoo ...
, and Ford Madox Brown
Ford Madox Brown (16 April 1821 – 6 October 1893) was a British painter of moral and historical subjects, notable for his distinctively graphic and often William Hogarth, Hogarthian version of the Pre-Raphaelite style. Arguably, his mos ...
(never officially a member), and figures such as Edward Burne-Jones
Sir Edward Coley Burne-Jones, 1st Baronet, (; 28 August, 183317 June, 1898) was a British painter and designer associated with the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood which included Dante Gabriel Rossetti, John Millais, Ford Madox Brown and Holman ...
and John William Waterhouse
John William Waterhouse (6 April 184910 February 1917) was an English painter known for working first in the Academic style and for then embracing the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood's style and subject matter. His artworks were known for their dep ...
were later much influenced by aspects of their ideas, as was the designer William Morris
William Morris (24 March 1834 – 3 October 1896) was a British textile designer, poet, artist, novelist, architectural conservationist, printer, translator and socialist activist associated with the British Arts and Crafts Movement. He ...
. Morris advocated a return to hand-craftsmanship in the decorative arts over the industrial manufacture that was rapidly being applied to all crafts. His efforts to make beautiful objects affordable (or even free) for everyone led to his wallpaper and tile designs defining the Victorian
Victorian or Victorians may refer to:
19th century
* Victorian era, British history during Queen Victoria's 19th-century reign
** Victorian architecture
** Victorian house
** Victorian decorative arts
** Victorian fashion
** Victorian literature ...
aesthetic and instigating the Arts and Crafts movement.
The Pre-Raphaelites, like Turner, were supported by the authoritative art critic John Ruskin
John Ruskin (8 February 1819 20 January 1900) was an English writer, philosopher, art critic and polymath of the Victorian era. He wrote on subjects as varied as geology, architecture, myth, ornithology, literature, education, botany and po ...
, himself a fine amateur artist. For all their technical innovation, they were both traditional and Victorian in their adherence to the history painting
History painting is a genre in painting defined by its subject matter rather than any artistic style or specific period. History paintings depict a moment in a narrative story, most often (but not exclusively) Greek and Roman mythology and Bible ...
as the highest form of art, and their subject matter was thoroughly in tune with Victorian taste, and indeed "everything that the publishers of steel engravings welcomed", enabling them to merge easily into the mainstream in their later careers.
While the Pre-Raphaelites had a turbulent and divided reception, the most popular and expensive painters of the period included Edwin Landseer
Sir Edwin Henry Landseer (7 March 1802 – 1 October 1873) was an English painter and sculptor, well known for his paintings of animals – particularly horses, dogs, and stags. However, his best-known works are the lion sculptures at the bas ...
, who specialized in sentimental animal subjects, which were favourites of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
and Prince Albert
Prince Albert most commonly refers to:
*Albert, Prince Consort (1819–1861), consort of Queen Victoria
*Albert II, Prince of Monaco (born 1958), present head of state of Monaco
Prince Albert may also refer to:
Royalty
* Albert I of Belgium ...
. In the later part of the century artists could earn large sums from selling the reproduction rights of their paintings to print publishers, and works of Landseer, especially his '' Monarch of the Glen'' (1851), a portrait of a Highland stag, were among the most popular. Like Millais' ''Bubbles
Bubble, Bubbles or The Bubble may refer to:
Common uses
* Bubble (physics), a globule of one substance in another, usually gas in a liquid
** Soap bubble
* Economic bubble, a situation where asset prices are much higher than underlying fundame ...
'' (1886) it was used on packaging and advertisements for decades, for brands of whisky and soap respectively.
During the late Victorian era in Britain the academic paintings, some enormously large, of Lord Leighton and the Dutch-born Lawrence Alma-Tadema
Sir Lawrence Alma-Tadema, (; born Lourens Alma Tadema ; 8 January 1836 – 25 June 1912) was a Dutch painter who later settled in the United Kingdom becoming the last officially recognised denizen in 1873. Born in Dronryp, the Netherlands, ...
were enormously popular, both often featuring lightly clad beauties in exotic or classical settings, while the allegorical works of G. F. Watts matched the Victorian sense of high purpose. The classical ladies of Edward Poynter
Sir Edward John Poynter, 1st Baronet (20 March 183626 July 1919) was an English painter, designer, and draughtsman, who served as President of the Royal Academy.
Life
Poynter was the son of architect Ambrose Poynter. He was born in Paris, ...
and Albert Moore wore more clothes and met with rather less success. William Powell Frith
William Powell Frith (9 January 1819 – 2 November 1909) was an English painter specialising in genre subjects and panoramic narrative works of life in the Victorian era. He was elected to the Royal Academy in 1853, presenting ''The Sleep ...
painted highly detailed scenes of social life, typically including all classes of society, that include comic and moral elements and have an acknowledged debt to Hogarth, though tellingly different from his work.
For all such artists the Royal Academy Summer Exhibition
The Summer Exhibition is an open art exhibition held annually by the Royal Academy in Burlington House, Piccadilly in central London, England, during the months of June, July, and August. The exhibition includes paintings, prints, drawings, sc ...
was an essential platform, reviewed at huge length in the press, which often alternated ridicule and extravagant praise in discussing works. The ultimate, and very rare, accolade was when a rail had to be put in front of a painting to protect it from the eager crowd; up to 1874 this had only happened to Wilkie's '' Chelsea Pensioners'', Frith's ''The Derby Day
''The Derby Day'' is a large oil painting showing a panoramic view of The Derby, painted by William Powell Frith over 15 months from 1856 to 1858. It has been described by Christie's as Frith's "undisputed masterpiece" and also "arguably the ...
'' and '' Salon d'Or, Homburg'' and Luke Filde's '' The Casual Ward'' (see below). A great number of artists laboured year after year in the hope of a hit there, often working in manners to which their talent was not really suited, a trope exemplified by the suicide in 1846 of Benjamin Haydon
Benjamin Robert Haydon (; 26 January 178622 June 1846) was a British painter who specialised in grand historical pictures, although he also painted a few contemporary subjects and portraits. His commercial success was damaged by his often tactles ...
, a friend of Keats and Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian er ...
and a better writer than painter, leaving his blood splashed over his unfinished ''King Alfred and the First British Jury''.
 British history was a very common subject, with the Middle Ages, Elizabeth I,
British history was a very common subject, with the Middle Ages, Elizabeth I, Mary, Queen of Scots
Mary, Queen of Scots (8 December 1542 – 8 February 1587), also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567.
The only surviving legitimate child of James V of S ...
and the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians ("Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of Kingdom of England, England's governanc ...
especially popular sources for subjects. Many painters mentioned elsewhere painted historical subjects, including Millais ('' The Boyhood of Raleigh'' and many others), Ford Madox Brown (''Cromwell on his Farm
''Cromwell on his Farm'' (1874) is a painting by Ford Madox Brown which depicts Oliver Cromwell observing a bonfire on his farm and thinking of a passage in the Book of Psalms: "Lord, how long wilt thou hide thyself - forever? And shall thy wrat ...
''), David Wilkie, Watts and Frith, and West, Bonington and Turner in earlier decades. The London-based Irishman Daniel Maclise
Daniel Maclise (25 January 180625 April 1870) was an Irish history painter, literary and portrait painter, and illustrator, who worked for most of his life in London, England.
Early life
Maclise was born in Cork, Ireland, the son of Alex ...
and Charles West Cope painted scenes for the new Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north bank ...
. Lady Jane Grey was, like Mary Queen of Scots, a female whose sufferings attracted many painters, though none quite matched '' The Execution of Lady Jane Grey'', one of many British historical subjects by the Frenchman Paul Delaroche. Painters prided themselves on the increasing accuracy of their period settings in terms of costume and objects, studying the collections of the new Victoria and Albert Museum
The Victoria and Albert Museum (often abbreviated as the V&A) in London is the world's largest museum of applied arts, decorative arts and design, housing a permanent collection of over 2.27 million objects. It was founded in 1852 and ...
and books, and scorning the breezy approximations of earlier generations of artists.
Punch
Punch commonly refers to:
* Punch (combat), a strike made using the hand closed into a fist
* Punch (drink), a wide assortment of drinks, non-alcoholic or alcoholic, generally containing fruit or fruit juice
Punch may also refer to:
Places
* Pun ...
'' cartoons.
Towards the end of the 19th century the problem picture
A problem picture is a genre of art popular in late Victorian painting, characterised by the deliberately ambiguous depiction of a key moment in a narrative that can be interpreted in several different ways, or which portrays an unresolved dilemma. ...
left the details of the narrative action deliberately ambiguous, inviting the viewer to speculate on it using the evidence in front of them, but not supplying a final answer (artists learned to smile enigmatically when asked). This sometimes provoked discussion on sensitive social issues, typically involving women, that might have been hard to raise directly. They were enormously popular; newspapers ran competitions for readers to supply the meaning of the painting.
Many artists participated in the revival of original artistic printmaking
Printmaking is the process of creating artworks by printing, normally on paper, but also on fabric, wood, metal, and other surfaces. "Traditional printmaking" normally covers only the process of creating prints using a hand processed techni ...
usually known as the etching revival, although prints in many other techniques were also made. This began in the 1850s and continued until the fallout from the 1929 Wall Street Crash brought about a collapse in the very high prices that the most fashionable artists had been achieving.
British Orientalism
In art history, literature and cultural studies, Orientalism is the imitation or depiction of aspects in the Eastern world. These depictions are usually done by writers, designers, and artists from the Western world. In particular, Orientalist ...
, though not as common as in France at the same period, had many specialists, including John Frederick Lewis, who lived for nine years in Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo met ...
, David Roberts, a Scot who made lithographs of his travels in the Middle East and Italy, the nonsense writer Edward Lear
Edward Lear (12 May 1812 – 29 January 1888) was an English artist, illustrator, musician, author and poet, who is known mostly for his literary nonsense in poetry and prose and especially his limericks, a form he popularised.
His principal a ...
, a continual traveller who reached as far as Ceylon
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
, and Richard Dadd. Holman Hunt also travelled to Palestine to obtain authentic settings for his Biblical pictures. The Frenchman James Tissot
Jacques Joseph Tissot (; 15 October 1836 – 8 August 1902), anglicized as James Tissot (), was a French painter and illustrator. He was a successful painter of fashionable, modern scenes and society life in Paris before moving to London in 1871 ...
, who fled to London after the fall of the Paris Commune
The Paris Commune (french: Commune de Paris, ) was a revolutionary government that seized power in Paris, the capital of France, from 18 March to 28 May 1871.
During the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71, the French National Guard had defende ...
, divided his time between scenes of high society social events and a huge series of Biblical illustrations, made in watercolour for reproductive publication. Frederick Goodall specialized in scenes of Ancient Egypt.
 Larger paintings concerned with the social conditions of the poor tended to concentrate on rural scenes, so that the misery of the human figures was at least offset by a landscape. Painters of these included Frederick Walker,
Larger paintings concerned with the social conditions of the poor tended to concentrate on rural scenes, so that the misery of the human figures was at least offset by a landscape. Painters of these included Frederick Walker, Luke Fildes
__NOTOC__
Sir Samuel Luke Fildes (3 October 1843 – 28 February 1927) was a British painter and illustrator born in Liverpool and trained at the South Kensington and Royal Academy Schools. He was the grandson of the political activist Ma ...
(although he made his name in 1874 with '' Applicants for Admission to a Casual Ward''- see above), Frank Holl, George Clausen
Sir George Clausen (18 April 1852 – 22 November 1944) was a British artist working in oil and watercolour, etching, mezzotint, dry point and occasionally lithographs. He was knighted in 1927.
Biography
George Clausen was born at 8 William S ...
, and the German Hubert von Herkomer
Sir Hubert von Herkomer (born as Hubert Herkomer; 26 May 1849 – 31 March 1914) was a Bavarian-born British painter, pioneering film-director, and composer. Though a very successful portrait artist, especially of men, he is mainly remembered fo ...
.
William Bell Scott
William Bell Scott (1811–1890) was a Scottish artist in oils and watercolour and occasionally printmaking. He was also a poet and art teacher, and his posthumously published reminiscences give a chatty and often vivid picture of life in the ...
, a friend of the Rossettis, painted historical scenes and other types of work, but was also one of the few artists to depict scenes from heavy industry. His memoirs are a useful source for the period, and he was one of several artists to be employed for a period in the greatly expanded system of government art schools, which were driven by the administrator Henry Cole
Sir Henry Cole FRSA (15 July 1808 – 18 April 1882) was a British civil servant and inventor who facilitated many innovations in commerce and education in the 19th century in the United Kingdom. Cole is credited with devising the concept of ...
(the inventor of the Christmas card
A Christmas card is a greeting card sent as part of the traditional celebration of Christmas in order to convey between people a range of sentiments related to Christmastide and the Christmas and holiday season, holiday season. Christmas cards ...
) and employed Richard Redgrave, Edward Poynter
Sir Edward John Poynter, 1st Baronet (20 March 183626 July 1919) was an English painter, designer, and draughtsman, who served as President of the Royal Academy.
Life
Poynter was the son of architect Ambrose Poynter. He was born in Paris, ...
, Richard Burchett, the Scottish designer Christopher Dresser and many others. Burchett was headmaster of the "South Kensington Schools", now the Royal College of Art
The Royal College of Art (RCA) is a public research university in London, United Kingdom, with campuses in South Kensington, Battersea and White City. It is the only entirely postgraduate art and design university in the United Kingdom. It of ...
, which gradually replaced the Royal Academy School as the leading British art school, though around the start of the 20th century the Slade School of Fine Art
The UCL Slade School of Fine Art (informally The Slade) is the art school of University College London (UCL) and is based in London, England. It has been ranked as the UK's top art and design educational institution. The school is organised as ...
produced many of the forward-looking artists.
The Royal Academy was initially by no means as conservative and restrictive as the Paris Salon
The Salon (french: Salon), or rarely Paris Salon (French: ''Salon de Paris'' ), beginning in 1667 was the official art exhibition of the Académie des Beaux-Arts in Paris. Between 1748 and 1890 it was arguably the greatest annual or biennial art ...
, and the Pre-Raphaelites had most of their submissions for exhibition accepted, although like everyone else they complained about the positions their paintings were given. They were especially welcomed at the Liverpool Academy of Arts, one of the largest regional exhibiting organizations; the Royal Scottish Academy
The Royal Scottish Academy (RSA) is the country’s national academy of art. It promotes contemporary Scottish art.
The Academy was founded in 1826 by eleven artists meeting in Edinburgh. Originally named the Scottish Academy, it became the ...
was founded in 1826 and opened its grand new building in the 1850s. There were alternative London locations like the British Institution
The British Institution (in full, the British Institution for Promoting the Fine Arts in the United Kingdom; founded 1805, disbanded 1867) was a private 19th-century society in London formed to exhibit the works of living and dead artists; it w ...
, and as the conservatism of the Royal Academy gradually increased, despite the efforts of Lord Leighton when President, new spaces opened, notably the Grosvenor Gallery in Bond Street
Bond Street in the West End of London links Piccadilly in the south to Oxford Street in the north. Since the 18th century the street has housed many prestigious and upmarket fashion retailers. The southern section is Old Bond Street and the l ...
, from 1877, which became the home of the Aesthetic Movement. The New English Art Club exhibited from 1885 many artists with Impressionist tendencies, initially using the Egyptian Hall, opposite the Royal Academy, which also hosted many exhibitions of foreign art. The American portrait painter John Singer Sargent
John Singer Sargent (; January 12, 1856 – April 14, 1925) was an American expatriate artist, considered the "leading portrait painter of his generation" for his evocations of Edwardian-era luxury. He created roughly 900 oil paintings and mor ...
(1856–1925), spent most of his working career in Europe and he maintained his studio in London (where he died) from 1886 to 1907.
Alfred Sisley
Alfred Sisley (; ; 30 October 1839 – 29 January 1899) was an Impressionist landscape painter who was born and spent most of his life in France, but retained British citizenship. He was the most consistent of the Impressionists in his dedicatio ...
, who was French by birth but had British nationality, painted in France as one of the Impressionists
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passa ...
; Walter Sickert and Philip Wilson Steer at the start of their careers were also strongly influenced, but despite the dealer Paul Durand-Ruel bringing many exhibitions to London, the movement made little impact in England until decades later. Some members of the Newlyn School
The Newlyn School was an art colony of artists based in or near Newlyn, a fishing village adjacent to Penzance, on the south coast of Cornwall, from the 1880s until the early twentieth century. The establishment of the Newlyn School was remini ...
of landscapes and genre scenes adopted a quasi-Impressionist technique while others used realist or more traditional levels of finish.
The late 19th century also saw the Decadent movement
The Decadent movement (Fr. ''décadence'', “decay”) was a late-19th-century artistic and literary movement, centered in Western Europe, that followed an aesthetic ideology of excess and artificiality.
The Decadent movement first flourished ...
in France and the British Aesthetic movement
Aestheticism (also the Aesthetic movement) was an art movement in the late 19th century which privileged the aesthetic value of literature, music and the arts over their socio-political functions. According to Aestheticism, art should be pro ...
. The British-based American painter James Abbott McNeill Whistler
James Abbott McNeill Whistler (; July 10, 1834July 17, 1903) was an American painter active during the American Gilded Age and based primarily in the United Kingdom. He eschewed sentimentality and moral allusion in painting and was a leading pr ...
, Aubrey Beardsley
Aubrey Vincent Beardsley (21 August 187216 March 1898) was an English illustrator and author. His black ink drawings were influenced by Japanese woodcuts, and depicted the grotesque, the decadent, and the erotic. He was a leading figure in the ...
, and the former Pre-Raphaelites
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood (later known as the Pre-Raphaelites) was a group of English painters, poets, and art critics, founded in 1848 by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, William Michael Rossetti, Jam ...
Dante Gabriel Rossetti
Gabriel Charles Dante Rossetti (12 May 1828 – 9 April 1882), generally known as Dante Gabriel Rossetti (), was an English poet, illustrator, painter, translator and member of the Rossetti family. He founded the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhoo ...
, and Edward Burne-Jones
Sir Edward Coley Burne-Jones, 1st Baronet, (; 28 August, 183317 June, 1898) was a British painter and designer associated with the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood which included Dante Gabriel Rossetti, John Millais, Ford Madox Brown and Holman ...
are associated with those movements, with late Burne-Jones and Beardsley both being admired abroad and representing the nearest British approach to European Symbolism
Symbolism or symbolist may refer to:
Arts
* Symbolism (arts), a 19th-century movement rejecting Realism
** Symbolist movement in Romania, symbolist literature and visual arts in Romania during the late 19th and early 20th centuries
** Russian sym ...
. In 1877 James McNeill Whistler sued the art critic
An art critic is a person who is specialized in analyzing, interpreting, and evaluating art. Their written critiques or reviews contribute to art criticism and they are published in newspapers, magazines, books, exhibition brochures, and catalogu ...
John Ruskin
John Ruskin (8 February 1819 20 January 1900) was an English writer, philosopher, art critic and polymath of the Victorian era. He wrote on subjects as varied as geology, architecture, myth, ornithology, literature, education, botany and po ...
for libel after the critic condemned his painting ''Nocturne in Black and Gold: The Falling Rocket''. Ruskin accused Whistler of "ask ngtwo hundred guineas for throwing a pot of paint in the public's face." The jury reached a verdict in favor of Whistler but awarded him only a single farthing in nominal damages, and the court costs were split. The cost of the case, together with huge debts from building his residence ("The White House" in Tite Street, Chelsea, designed with E. W. Godwin, 1877–8), bankrupted Whistler by May 1879, resulting in an auction of his work, collections, and house. Stansky notes the irony that the Fine Art Society of London, which had organized a collection to pay for Ruskin's legal costs, supported him in etching "the stones of Venice" (and in exhibiting the series in 1883) which helped recoup Whistler's costs.
 Scottish art was now regaining an adequate home market, allowing it to develop a distinctive character, of which the " Glasgow Boys" were one expression, straddling
Scottish art was now regaining an adequate home market, allowing it to develop a distinctive character, of which the " Glasgow Boys" were one expression, straddling Impressionism
Impressionism was a 19th-century art movement characterized by relatively small, thin, yet visible brush strokes, open composition, emphasis on accurate depiction of light in its changing qualities (often accentuating the effects of the passa ...
in painting, and Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Moder ...
, Japonism
''Japonisme'' is a French term that refers to the popularity and influence of Japanese art and design among a number of Western European artists in the nineteenth century following the forced reopening of foreign trade with Japan in 1858. Japo ...
and the Celtic Revival
The Celtic Revival (also referred to as the Celtic Twilight) is a variety of movements and trends in the 19th, 20th and 21st centuries that see a renewed interest in aspects of Celtic culture. Artists and writers drew on the traditions of Gae ...
in design, with the architect and designer Charles Rennie Mackintosh now their best-known member. Painters included Thomas Millie Dow, George Henry, Joseph Crawhall and James Guthrie.
New printing technology brought a great