Newcastle University (legally the University of Newcastle upon Tyne) is a
public
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociology, sociological concept of the ''Öf ...
research university
A research university or a research-intensive university is a university that is committed to research as a central part of its mission. They are "the key sites of Knowledge production modes, knowledge production", along with "intergenerational ...
based in
Newcastle upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne, or simply Newcastle ( , Received Pronunciation, RP: ), is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. It is England's northernmost metropolitan borough, located o ...
,
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
. It has overseas campuses in Singapore and Malaysia. The university is a
red brick university
A redbrick university (or red-brick university) normally refers to one of the nine civic universities originally founded as university colleges in the major industrial cities of England in the second half of the 19th century.
However, wi ...
and a member of the
Russell Group
The Russell Group is a self-selected association of twenty-four public research universities in the United Kingdom. The group is headquartered in Cambridge and was established in 1994 to represent its members' interests, principally to governme ...
, an association of research-intensive UK universities.
The university's history began with the School of Medicine and Surgery (later the College of Medicine), established in Newcastle in 1834, and the
College of Physical Science (later renamed Armstrong College), founded in 1871. These two colleges came to form the larger division of the federal
University of Durham
Durham University (legally the University of Durham) is a collegiate public research university in Durham, England, founded by an Act of Parliament in 1832 and incorporated by royal charter in 1837. It was the first recognised university to ...
, with the
Durham Colleges forming the other. The Newcastle colleges merged to form King's College in 1937. In 1963, following an Act of Parliament, King's College became the University of Newcastle upon Tyne.
The university is subdivided into three faculties: the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences; the Faculty of Medical Sciences; and the Faculty of Science, Agriculture and Engineering. The university offers over 200 full-time undergraduate degree programmes and over 300 postgraduate taught and research programmes across a range of disciplines. The annual income of the institution for 2023–24 was £619.8 million of which £126.1 million was from research grants and contracts, with an expenditure of £475 million.
History
The establishment of a university in
Newcastle upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne, or simply Newcastle ( , Received Pronunciation, RP: ), is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. It is England's northernmost metropolitan borough, located o ...
was first proposed in 1831 by
Thomas Greenhow in a lecture to the
Literary and Philosophical Society
The Literary and Philosophical Society of Newcastle upon Tyne (or the ''Lit & Phil'' as it is popularly known) is a historical library in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, and the largest Subscription library, independent library outside London. The ...
. In 1832 a group of local medics – physicians George Fife (teaching ''materia medica'' and therapeutics) and Samuel Knott (teaching theory and practice of medicine), and surgeons
John Fife (teaching surgery), Alexander Fraser (teaching anatomy and physiology) and Henry Glassford Potter (teaching chemistry) – started offering medical lectures in Bell's Court to supplement the apprenticeship system (a fourth surgeon, Duncan McAllum, is mentioned by some sources among the founders, but was not included in the prospectus). The first session started on 1 October 1832 with eight or nine students, including
John Snow
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology and early germ theory, in part because of hi ...
, then apprenticed to a local surgeon-apothecary, the opening lecture being delivered by John Fife. In 1834 the lectures and practical demonstrations moved to the Hall of the Company of Barber Surgeons to accommodate the growing number of students, and the School of Medicine and Surgery was formally established on 1 October 1834.
On 25 June 1851, following a dispute among the teaching staff, the school was formally dissolved and the lecturers split into two rival institutions. The majority formed the Newcastle College of Medicine, and the others established themselves as the Newcastle upon Tyne College of Medicine and Practical Science with competing lecture courses. In July 1851 the majority college was recognised by the
Society of Apothecaries
The Worshipful Society of Apothecaries of London is one of the livery companies of the City of London. It is one of the largest livery companies (with over 1,600 members in 2012) and ranks 58th in their order of precedence.
The society is a me ...
and in October by the
Royal College of Surgeons of England
The Royal College of Surgeons of England (RCS England) is an independent professional body and registered charity that promotes and advances standards of surgery, surgical care for patients, and regulates surgery and dentistry in England and Wa ...
and in January 1852 was approved by the
University of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a collegiate university, federal Public university, public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The ...
to submit its students for London medical degree examinations. Later in 1852, the majority college was formally linked to the
University of Durham
Durham University (legally the University of Durham) is a collegiate public research university in Durham, England, founded by an Act of Parliament in 1832 and incorporated by royal charter in 1837. It was the first recognised university to ...
, becoming the "Newcastle-upon-Tyne College of Medicine in connection with the University of Durham". The college awarded its first 'Licence in Medicine' (LicMed) under the auspices of the University of Durham in 1856, with external examiners from Oxford and London, becoming the first medical examining body in the United Kingdom to institute practical examinations alongside written and ''viva voce'' examinations. The two colleges amalgamated in 1857, with the first session of the unified college opening on 3 October that year. In 1861 the degree of Master of Surgery was introduced, allowing for the double qualification of Licence of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery, along with the degrees of Bachelor of Medicine and Doctor of Medicine, both of which required residence in Durham. In 1870 the college was brought into closer connection with the university, becoming the "Durham University College of Medicine" with the Reader in Medicine becoming the Professor of Medicine, the college gaining a representative on the university's senate, and residence at the college henceforth counting as residence in the university towards degrees in medicine and surgery, removing the need for students to spend a period of residence in Durham before they could receive the higher degrees.
Attempts to realise a place for the teaching of sciences in the city were finally met with the foundation of the
College of Physical Science in 1871. The college offered instruction in mathematics, physics, chemistry and geology to meet the growing needs of the mining industry, becoming the "Durham College of Physical Science" in 1883 and then renamed after
William George Armstrong
William Armstrong, 1st Baron Armstrong, (26 November 1810 – 27 December 1900) was an English engineer and industrialist who founded the Armstrong Whitworth manufacturing concern on Tyneside. He was also an eminent scientist, inventor and phi ...
as ''Armstrong College'' in 1904. Both of these institutions were part of the University of Durham, which became a federal university under the Durham University Act 1908 with two divisions in Durham and Newcastle. By 1908, the Newcastle division was teaching a full range of subjects in the Faculties of Medicine, Arts, and Science, which also included agriculture and engineering.
Throughout the early 20th century, the medical and science colleges outpaced the growth of their Durham counterparts. Following tensions between the two Newcastle colleges in the early 1930s, a
Royal Commission
A royal commission is a major ad-hoc formal public inquiry into a defined issue in some monarchies. They have been held in the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, Norway, Malaysia, Mauritius and Saudi Arabia. In republics an equi ...
in 1934 recommended the merger of the two colleges to form "King's College, Durham"; that was effected by the Durham University Act 1937. Further growth of both division of the federal university led to tensions within the structure and a feeling that it was too large to manage as a single body. On 1 August 1963 the Universities of Durham and Newcastle upon Tyne Act 1963 separated the two thus creating the "University of Newcastle upon Tyne". As the successor of King's College, Durham, the university at its founding in 1963, adopted the
coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon f ...
originally granted to the Council of King's College in 1937.
Above the
portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cu ...
of the Students' Union building are bas-relief carvings of the arms and mottoes of the University of Durham, Armstrong College and Durham University College of Medicine, the predecessor parts of Newcastle University. While a Latin motto, (''mind moves matter'') appears in the Students' Union building, the university itself does not have an official motto.
In 1967, Newcastle became the only British university to confer an honorary degree on
Martin Luther King
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister, civil rights activist and political philosopher who was a leader of the civil rights movement from 1955 until his a ...
.
The university established a branch campus in London in 2015, in partnership with
INTO University Partnerships
INTO University Partnerships is a British for-profit pathway education provider focused on the provision of foundation courses for international students.
History and ownership
INTO University Partnerships was founded in 2005 by Andrew Colin, ...
, at INTO's existing London campus. The London campus was closed in 2021.
In 2024, Newcastle University had a drop in income of £35 million, referred to as a crisis by the local branch of the
Universities and Colleges Union (UCU). The university had already made £15 million of savings in its budget for the year, but this left a deficit of £20 million. As a result, academic promotions were cancelled and the university announced a voluntary redundancy scheme. The UCU held a consultative ballot of members on possible strike action related to the cuts in November 2024.
Campus and location
United Kingdom

The university occupies a campus site close to
Haymarket in central Newcastle upon Tyne. It is located to the northwest of the city centre between the open spaces of
Leazes Park and the
Town Moor; the university medical school and
Royal Victoria Infirmary
The Royal Victoria Infirmary (RVI) is a 673-bed tertiary referral hospital and research centre in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, with strong links to Newcastle University.
The hospital is part of the Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation T ...
are adjacent to the west.
The Armstrong building is the oldest building on the campus and is the site of the original Armstrong College. The building was constructed in three stages; the north east wing was completed first at a cost of £18,000 and opened by
Princess Louise Princess Louise may refer to:
People
* Louise of Denmark (disambiguation), various princesses
* Louise of Prussia (disambiguation), various princesses
* Louise of Saxe-Meiningen (disambiguation), various princesses
* Princess Louise of Schleswig-H ...
on 5 November 1888. The south-east wing, which includes the Jubilee Tower, and south-west wings were opened in 1894. The Jubilee Tower was built with surplus funds raised from an Exhibition to mark
Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
's
Jubilee
A jubilee is often used to refer to the celebration of a particular anniversary of an event, usually denoting the 25th, 40th, 50th, 60th, and the 70th anniversary. The term comes from the Hebrew Bible (see, "Old Testament"), initially concerning ...
in 1887. The north-west front, forming the main entrance, was completed in 1906 and features two stone figures to represent science and the arts. Much of the later construction work was financed by Sir Isaac
Lowthian Bell, the
metallurgist
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
and former
Lord Mayor
Lord mayor is a title of a mayor of what is usually a major city in a Commonwealth realm, with special recognition bestowed by the sovereign. However, the title or an equivalent is present in other countries, including forms such as "high mayor". A ...
of Newcastle, after whom the main tower is named. In 1906 it was opened by
King Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910.
The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria and ...
.
The building contains the ''King's Hall'', which serves as the university's chief hall for ceremonial purposes where
Congregation
Congregation may refer to:
Religion
*Church (congregation), a religious organization that meets in a particular location
*Congregation (Roman Curia), an administrative body of the Catholic Church
*Religious congregation, a type of religious instit ...
ceremonies are held. It can contain 500 seats. King Edward VII gave permission to call the Great Hall, King's Hall.
During the
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the building was requisitioned by the
War Office
The War Office has referred to several British government organisations throughout history, all relating to the army. It was a department of the British Government responsible for the administration of the British Army between 1857 and 1964, at ...
to create the first Northern General Hospital, a facility for the
Royal Army Medical Corps
The Royal Army Medical Corps (RAMC) was a specialist corps in the British Army which provided medical services to all Army personnel and their families, in war and in peace.
On 15 November 2024, the corps was amalgamated with the Royal Army De ...
to treat military casualties. Graduation photographs are often taken in the University Quadrangle, next to the Armstrong building. In 1949 the Quadrangle was turned into a formal garden in memory of members of Newcastle University who gave their lives in the two World Wars. In 2017, a statue of
Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr. (born Michael King Jr.; January 15, 1929 – April 4, 1968) was an American Baptist minister, civil and political rights, civil rights activist and political philosopher who was a leader of the civil rights move ...
was erected in the inner courtyard of the Armstrong Building, to celebrate the 50th anniversary of his honorary degree from the university.
The Bruce Building is a former brewery, constructed between 1896 and 1900 on the site of the Hotspur Hotel, and designed by the architect
Joseph Oswald as the new premises of
Newcastle Breweries Limited. The university occupied the building from the 1950s, but, having been empty for some time, the building was refurbished in 2016 to become residential and office space.
The Devonshire Building, opened in 2004, incorporates in an energy efficient design. It uses
photovoltaic cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect. s to help to power motorised shades that control the temperature of the building and
geothermal heating
Geothermal heating is the direct use of geothermal energy for some heating applications. Humans have taken advantage of geothermal heat this way since the Paleolithic era. Approximately seventy countries made direct use of a total of 270 PJ o ...
coils. Its architects won awards in the Hadrian awards and the
RICS
The Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS) is a global professional body for those working in the Built Environment, Construction, Land, Property and Real Estate. The RICS was founded in London in 1868. It works at a cross-governmental ...
Building of the Year Award 2004. The university won a
Green Gown Award for its construction.

Plans for additions and improvements to the campus were made public in March 2008 and completed in 2010 at a cost of £200 million. They included a redevelopment of the south-east (Haymarket) façade with a five-storey King's Gate administration building as well as new student accommodation. Two additional buildings for the school of medicine were also built.
September 2012 saw the completion of the new buildings and facilities for
INTO Newcastle University on the university campus. The main building provides 18 new teaching rooms, a Learning Resource Centre, a lecture theatre, science lab, administrative and academic offices and restaurant.
The Philip Robinson Library is the main university library and is named after a bookseller in the city and benefactor to the library. The Walton Library specialises in services for the Faculty of Medical Sciences in the Medical School. It is named after
Lord Walton of Detchant, former Dean of the Faculty of Medicine and Professor of Neurology. The library has a relationship with the Northern region of the
NHS
The National Health Service (NHS) is the term for the publicly funded health care, publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom: the National Health Service (England), NHS Scotland, NHS Wales, and Health and Social Care (Northern ...
allowing their staff to use the library for research and study. The Law Library specialises in resources relating to law, and the Marjorie Robinson Library Rooms offers additional study spaces and computers. Together, these house over one million books and 500,000 electronic resources. Some schools within the university, such as the School of Modern Languages, also have their own smaller libraries with smaller highly specialised collections.
In addition to the city centre campus there are buildings such as the
Dove Marine Laboratory
The Dove Marine Laboratory is a research and teaching laboratory which forms part of the School of Marine Science and Technology within Newcastle University in the United Kingdom.
History
The original Laboratory was established in October 189 ...
located on
Cullercoats
Cullercoats is a coastal settlement in the metropolitan borough of North Tyneside, Tyne and Wear, England. Historically in Northumberland, it has now been absorbed into the wider Tyneside conurbation, sitting between Tynemouth to the south and W ...
Bay, and Cockle Park Farm in
Northumberland
Northumberland ( ) is a ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in North East England, on the Anglo-Scottish border, border with Scotland. It is bordered by the North Sea to the east, Tyne and Wear and County Durham to the south, Cumb ...
.
International
In September 2008, the university's first overseas branch was opened in Singapore, a Marine International campus called, NUMI Singapore. This later expanded beyond marine subjects and became Newcastle University Singapore, largely through becoming an Overseas University Partner of
Singapore Institute of Technology
The Singapore Institute of Technology (SIT or Singaporetech) is a public autonomous university in Singapore. The university offers industry-focused, applied degree programmes; it confers its own degree programmes as well as specialised degree ...
.
In 2011, the university's Medical School opened an international branch campus in
Iskandar Puteri
Iskandar Puteri (formerly known as Nusajaya) is a Cities of Malaysia, city and the administrative capital of the state of Johor, Malaysia. It is situated along the Straits of Johor at the southern end of the Malay Peninsula and the southernmos ...
,
Johor
Johor, also spelled Johore,'' is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia in the south of the Malay Peninsula. It borders with Pahang, Malacca and Negeri Sembilan to the north. Johor has maritime borders with Singapore ...
,
Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
, namely Newcastle University Medicine Malaysia.
Student accommodation
Newcastle University has many catered and non-catered
halls of residence
A dormitory (originated from the Latin word ''dormitorium'', often abbreviated to dorm), also known as a hall of residence, a residence hall (often abbreviated to halls), or a hostel, is a building primarily providing sleeping and residential qu ...
available to first-year students, located around the city of Newcastle. Popular Newcastle areas for private student houses and flats off campus include
Jesmond
Jesmond ( ) is a suburb of Newcastle upon Tyne, Tyne and Wear, England, situated north of the city centre and to the east of the Town Moor. Jesmond is considered to be one of the most affluent suburbs of Newcastle upon Tyne, with higher aver ...
,
Heaton,
Sandyford
Sandyford () is a suburb of Dublin, located in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Ireland.
Sandyford Business District makes up much of the suburb and encompasses 4 business parks: Sandyford Business Park, Stillorgan Business Park, Central Park and S ...
,
Shieldfield,
South Shields
South Shields () is a coastal town in South Tyneside, Tyne and Wear, England; it is on the south bank of the mouth of the River Tyne. The town was once known in Roman Britain, Roman times as ''Arbeia'' and as ''Caer Urfa'' by the Early Middle Ag ...
and
Spital Tongues.
Henderson Hall Henderson may refer to:
People
*Henderson (surname), description of the surname, and a list of people with the surname
* Clan Henderson, a Scottish clan
Places Argentina
* Henderson, Buenos Aires
Australia
* Henderson, Western Australia
Canada
...
was used as a hall of residence until a fire destroyed it in 2023.
St Mary's College in
Fenham, one of the halls of residence, was formerly St Mary's College of Education, a teacher training college.
Organisation and governance
The current
Chancellor
Chancellor () is a title of various official positions in the governments of many countries. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the (lattice work screens) of a basilica (court hall), which separa ...
is the British poet and artist
Imtiaz Dharker. She assumed the position of Chancellor on 1 January 2020.
The vice-chancellor is
Chris Day, a hepatologist and former pro-vice-chancellor of the Faculty of Medical Sciences.
The university has an enrolment of some 16,000 undergraduate and 5,600 postgraduate students. Teaching and research are delivered in 19 academic schools, 13 research institutes and 38 research centres, spread across three Faculties: the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences; the Faculty of Medical Sciences; and the Faculty of Science, Agriculture and Engineering. The university offers around 175 full-time undergraduate degree programmes in a wide range of subject areas spanning arts, sciences, engineering and medicine, together with approximately 340 postgraduate taught and research programmes across a range of disciplines.
It holds a series of public lectures called 'Insights' each year in the Curtis Auditorium in the Herschel Building. Many of the university's partnerships with companies, like
Red Hat
Red Hat, Inc. (formerly Red Hat Software, Inc.) is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North ...
, are housed in the Herschel Annex.
Chancellors and vice-chancellors
Chancellors
*
Hugh Percy, 10th Duke of Northumberland (1963–1988)
*
Matthew White Ridley, 4th Viscount Ridley
Matthew White Ridley, 4th Viscount Ridley (29 July 1925 – 22 March 2012) was a British nobleman. He was Lord Steward of the Household from 1989 to 2001.
Background, education and military service
Ridley was the son of Matthew White Ridley, 3rd ...
(1988–1999)
*
Chris Patten
Christopher Francis Patten, Baron Patten of Barnes (; born 12 May 1944), is a British politician who was the Chairman of the Conservative Party from 1990 to 1992, and the 28th and last Governor of Hong Kong from 1992 to 1997. He was made a lif ...
(1999–2009)
*
Liam Donaldson
Sir Liam Joseph Donaldson (born 3 May 1949) is a British physician. He was formerly the Chief Medical Officer for England, being the 15th occupant of the post since it was established in 1855. As such, he was principal advisor to the United Ki ...
(2009–2019)
*
Imtiaz Dharker (2020–)
Vice-chancellors
*
Charles Bosanquet (1963–1968)
*
Henry Miller
Henry Valentine Miller (December 26, 1891 – June 7, 1980) was an American novelist, short story writer and essayist. He broke with existing literary forms and developed a new type of semi-autobiographical novel that blended character study, so ...
(1968–1976)
*
Ewan Stafford Page (1976–1978, acting)
*
Laurence Martin (1978–1990)
*Duncan Murchison (1991, acting)
*
James Wright (1992–2000)
*
Christopher Edwards (2001–2007)
*
Chris Brink (2007–2016)
*
Chris Day (2017–present)
Civic responsibility
The university describes itself as a civic university, with a role to play in society by bringing its research to bear on issues faced by communities (local, national or international).
In 2012, the university opened the Newcastle Institute for Social Renewal to address issues of social and economic change, representing the research-led academic schools across the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences and the Business School.
Mark Shucksmith was Director of the Newcastle Institute for Social Renewal (NISR) at Newcastle University, where he is also Professor of Planning.
In 2006, the university was granted
fair trade status and from January 2007 it became a
smoke-free campus.
The university has also been actively involved with several of the region's museums for many years. The
Great North Museum: Hancock originally opened in 1884 and is often a venue for the university's events programme.
Faculties, schools and institutes
Teaching schools within the university are based within three faculties. Each faculty is led by a Provost/Pro-vice-chancellor and a team of Deans with specific responsibilities. The university also has research institutes based within each faculty.
Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences
= Schools
=
*School of Architecture, Planning and Landscape
* School of Arts and Cultures
*
Newcastle University Business School (including the former Faculty of Economics and Social Sciences)
* School of Education, Communication and Language Sciences
* School of English Literature, Language and Linguistics
* School of Geography, Politics and Sociology
* School of History, Classics and Archaeology
*
Newcastle Law School
*
School of Modern Languages
* School X
=Institutes
=
*Institute of Creative Arts Practice
*Humanities Research Institute
*Institute of Social Science
Faculty of Medical Sciences
= Schools
=
* School of Biomedical, Nutritional and Sport Sciences
*
School of Dental Sciences
*
School of Medical Education
* School of Pharmacy
* School of Psychology
* Centre for Bacterial Cell Biology (CBCB)
=Institutes
=
*Biosciences Institute
*Population Health Sciences Institute
*Translational and Clinical Research Institute
Faculty of Science, Agriculture and Engineering
= Schools
=
* School of Computing
* School of Engineering
* School of Mathematics, Statistics and Physics
* School of Natural and Environmental Sciences
=Institutes
=
*Agri-Food Research and Innovation
*Digital Institute
Economics Department
As early as the 1900/1 academic year, there was teaching in
economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
(
political economy
Political or comparative economy is a branch of political science and economics studying economic systems (e.g. Marketplace, markets and national economies) and their governance by political systems (e.g. law, institutions, and government). Wi ...
, as it was then known) at Newcastle, making Economics the oldest department in what would only much later become the Business School. The Economics Department is currently headed by the
Sir David Dale Chair. Among the eminent economists having served in the Department (both as holders of the Sir David Dale Chair) are
Harry Mainwaring Hallsworth and
Stanley Dennison.
Business School
Like its peers in the north of England, such as the business schools of
University of Bradford
The University of Bradford is a public research university located in the city of Bradford, West Yorkshire, England. A plate glass university, it received its royal charter in 1966, making it the 40th university to be created in Britain, but ...
and
Manchester Metropolitan University
Manchester Metropolitan University is located in the centre of Manchester, England. The university has 40,000 students and over 4,000 members of staff. It is home to four faculties (Arts and Humanities, Business and Law, Health and Education ...
, Newcastle University Business School is a
triple accredited business school, with accreditation by the three major accreditation bodies:
AACSB
The Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB) is an American professional and accreditation organization. It was founded as the American Assembly of Collegiate Schools of Business in 1916 to provide accreditation to business ...
,
AMBA and
EQUIS
The EFMD Quality Improvement System (EQUIS) is a business school accreditation managed by Brussels based EFMD. It provides accreditation for higher education institutions of management and business administration and is run by the European Fou ...
.
In 2002, Newcastle University Business School established the Business Accounting and Finance or 'Flying Start' degree in association with the
ICAEW
The Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales (ICAEW) is a professional membership organisation that promotes, develops and supports chartered accountants and students around the world. As of December 2024, it has over 210,000 memb ...
and
PricewaterhouseCoopers
PricewaterhouseCoopers, also known as PwC, is a multinational professional services network based in London, United Kingdom.
It is the second-largest professional services network in the world and is one of the Big Four accounting firms, alon ...
.
The course offers an accelerated route towards the
ACA Chartered Accountancy qualification and is the Business School's Flagship programme.
In 2011 the business school opened their new building built on the former
Scottish and Newcastle brewery site next to
St James' Park
St James' Park is a Association football, football stadium in Newcastle upon Tyne, England. It is the home of Newcastle United F.C., Newcastle United. With a seating capacity of 52,305, it is the List of football stadiums in England, 8th la ...
. This building was officially opened on 19 March 2012 by
Lord Burns.
The business school operated a central London campus from 2014 to 2021, in partnership with
INTO University Partnerships
INTO University Partnerships is a British for-profit pathway education provider focused on the provision of foundation courses for international students.
History and ownership
INTO University Partnerships was founded in 2005 by Andrew Colin, ...
until 2020.
Medical School
The
BMC Medicine journal reported in 2008 that medical graduates from
Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
,
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 Unit ...
and Newcastle performed better in postgraduate tests than any other medical school in the UK.
In 2008 the Medical School announced that they were expanding their campus to
Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
.
[
The ]Royal Victoria Infirmary
The Royal Victoria Infirmary (RVI) is a 673-bed tertiary referral hospital and research centre in Newcastle upon Tyne, England, with strong links to Newcastle University.
The hospital is part of the Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation T ...
has always had close links with the Faculty of Medical Sciences as a major teaching hospital.
School of Modern Languages
The School of Modern Languages consists of five sections: East Asian (which includes Japanese and Chinese); French; German; Spanish, Portuguese & Latin American Studies; and Translating & Interpreting Studies. Six languages are taught from beginner's level to full degree level ‒ Chinese, Japanese, French, German, Spanish and Portuguese ‒ and beginner's courses in Catalan, Dutch, Italian and Quechua are also available. Beyond the learning of the languages themselves, Newcastle also places a great deal of emphasis on study and experience of the cultures of the countries where the languages taught are spoken. The School of Modern Languages hosts North East England
North East England, commonly referred to simply as the North East within England, is one of nine official regions of England. It consists of County DurhamNorthumberland, , Northumberland, Tyne and Wear and part of northern North Yorkshire. ...
's only branches of two internationally important institutes: the Camões Institute, a language institute for Portuguese, and the Confucius Institute
Confucius Institutes (CI; ) are public educational and cultural promotion programs of the state of China. The stated aim of the program is to promote Chinese language and culture, support local Chinese teaching internationally, and facilita ...
, a language and cultural institute for Chinese.
The teaching of modern foreign languages at Newcastle predates the creation of Newcastle University itself, as in 1911 Armstrong College in Newcastle installed Albert George Latham, its first professor of modern languages.
The School of Modern Languages at Newcastle is the lead institution in the North East Routes into Languages ConsortiumDurham University
Durham University (legally the University of Durham) is a collegiate university, collegiate public university, public research university in Durham, England, founded by an Act of Parliament (UK), Act of Parliament in 1832 and incorporated by r ...
, Northumbria University
Northumbria University (legally the University of Northumbria at Newcastle) is a Public research university, public research university located in Newcastle upon Tyne, North East England, North East of England. It has been a university since 199 ...
, the University of Sunderland
The University of Sunderland is a public research university located in Sunderland in the North East of England. Its predecessor, Sunderland Technical College, was established as a municipal training college in 1901. It gained university status ...
, the Teesside University
Teesside University is a public university with its main campus in Middlesbrough, North Yorkshire in North East England. It was officially opened as ''Constantine Technical College'' in 1930, before becoming a polytechnic in 1969, and finally g ...
and a network of schools, undertakes work activities of discovery of languages for the 9 to 13 years pupils.
Newcastle Law School
Newcastle Law School is the longest established law school in the north-east of England when law was taught at the university's predecessor college before it became independent from Durham University.[
The Law School occupies four specially adapted late-Victorian town houses. The Staff Offices, the Alumni Lecture Theatre and seminar rooms as well as the Law Library are all located within the School buildings.]
School of Computing
The School of Computing was ranked in the Times Higher Education world Top 100. Research areas include Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) and ubiquitous computing, secure and resilient systems, synthetic biology, scalable computing (high performance systems, data science, machine learning and data visualization), and advanced modelling. The school led the formation of the National Innovation Centre for Data. Innovative teaching in the School was recognised in 2017 with the award of a National Teaching Fellowship.
Cavitation tunnel
 Newcastle University has the second largest
Newcastle University has the second largest cavitation tunnel
A water tunnel is an experimental facility used for testing the Fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic behavior of submerged bodies in flowing water. It functions similar to a recirculating wind tunnel, but uses water as the working fluid, and related phe ...
in the UK. Founded in 1950, and based in the Marine Science and Technology Department, the Emerson Cavitation Tunnel is used as a test basin for propellers, water turbines, underwater coatings and interaction of propellers with ice. The Emerson Cavitation Tunnel was recently relocated to a new facility in Blyth.
Museums and galleries
The university is associated with a number of the region's museums and galleries, including the Great North Museum
The Great North Museum: Hancock is a museum of natural history and ancient civilisations in Newcastle upon Tyne, England.
The museum was established in 1884 and was formerly known as the Hancock Museum. In 2006 it merged with Newcastle Unive ...
project, which is primarily based at the world-renowned Hancock Museum
The Great North Museum: Hancock is a museum of natural history and ancient civilisations in Newcastle upon Tyne, England.
The museum was established in 1884 and was formerly known as the Hancock Museum. In 2006 it merged with Newcastle Unive ...
. The Great North Museum: Hancock also contains the collections from two of the university's former museums, the Shefton Museum and the Museum of Antiquities, both now closed. The university's Hatton Gallery is also a part of the Great North Museum project, and remains within the Fine Art Building.
Finances
In the financial year ending 31 July 2024, Newcastle had a total income of £619.8 million (2022/23 – £592.4 million) and total expenditure of £475 million (2022/23 – £558 million).
Academic profile
Reputation and rankings
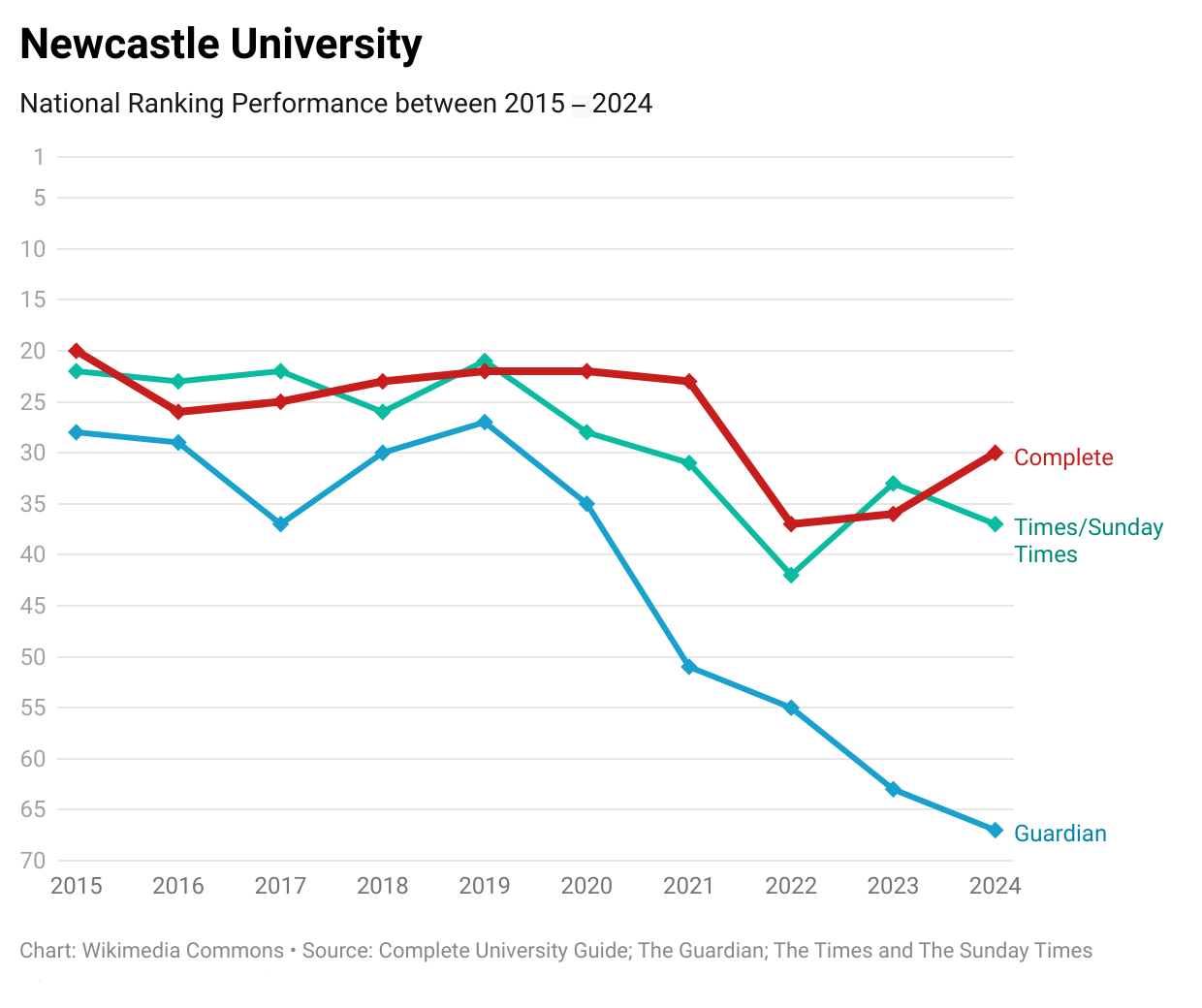 The university is a member of the
The university is a member of the Russell Group
The Russell Group is a self-selected association of twenty-four public research universities in the United Kingdom. The group is headquartered in Cambridge and was established in 1994 to represent its members' interests, principally to governme ...
of the UK's research-intensive universities. It is ranked in the top 200 of most world rankings, and in the top 40 of most UK rankings. it is ranked 110th globally by QS,Leiden
Leiden ( ; ; in English language, English and Archaism, archaic Dutch language, Dutch also Leyden) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Provinces of the Nethe ...
, 139th by Times Higher Education
''Times Higher Education'' (''THE''), formerly ''The Times Higher Education Supplement'' (''The THES''), is a British magazine reporting specifically on news and issues related to higher education.
Ownership
TPG Capital acquired TSL Education ...
Academic Ranking of World Universities
The ''Academic Ranking of World Universities'' (''ARWU''), also known as the Shanghai Ranking, is one of the annual publications of world university rankings. The league table was originally compiled and issued by Shanghai Jiao Tong Universi ...
.
Admissions
In terms of average UCAS
The Universities and Colleges Admissions Service (UCAS ) is a charity and private limited company based in Cheltenham, England, which provides educational support services. Formed on 27 July 1993 by the merger of the former university admis ...
points of entrants, Newcastle ranked joint 19th in Britain in 2014. In 2015, the university gave offers of admission to 92.1% of its applicants, the highest amongst the Russell Group
The Russell Group is a self-selected association of twenty-four public research universities in the United Kingdom. The group is headquartered in Cambridge and was established in 1994 to represent its members' interests, principally to governme ...
.
25.1% of Newcastle's undergraduates are privately educated, the thirteenth highest proportion amongst mainstream British universities. In the 2016–17 academic year, the university had a domicile breakdown of 74:5:21 of UK:EU:non-EU students respectively with a female to male ratio of 51:49.
Research
 Newcastle is a member of the
Newcastle is a member of the Russell Group
The Russell Group is a self-selected association of twenty-four public research universities in the United Kingdom. The group is headquartered in Cambridge and was established in 1994 to represent its members' interests, principally to governme ...
of 24 research-intensive universities. In the 2021 Research Excellence Framework
The Research Excellence Framework (REF) is a research impact evaluation of British Higher Education Institutions (HEIs). It is the successor to the Research Assessment Exercise and it was first used in 2014 to assess the period 2008–2013. REF is ...
(REF), which assesses the quality of research in UK higher education institutions, Newcastle is ranked joint 33rd by GPA (along with the University of Strathclyde
The University of Strathclyde () is a public research university located in Glasgow, Scotland. Founded in 1796 as the Andersonian Institute, it is Glasgow's second-oldest university, having received its royal charter in 1964 as the first techn ...
and the University of Sussex
The University of Sussex is a public university, public research university, research university located in Falmer, East Sussex, England. It lies mostly within the city boundaries of Brighton and Hove. Its large campus site is surrounded by the ...
) and 15th for research power (the grade point average score of a university, multiplied by the full-time equivalent number of researchers submitted).
Student life
Students' union
 Newcastle University Students' Union (NUSU), known as the Union Society until a 2012 rebranding, includes student-run sports clubs and societies.
The Union building was built in 1924 following a generous gift from an anonymous donor, who is now believed to have been Sir Cecil Cochrane, a major benefactor to the university. It is built in the neo- Jacobean style and was designed by the local architect Robert Burns Dick. It was opened on 22 October 1925 by the Rt. Hon.
Newcastle University Students' Union (NUSU), known as the Union Society until a 2012 rebranding, includes student-run sports clubs and societies.
The Union building was built in 1924 following a generous gift from an anonymous donor, who is now believed to have been Sir Cecil Cochrane, a major benefactor to the university. It is built in the neo- Jacobean style and was designed by the local architect Robert Burns Dick. It was opened on 22 October 1925 by the Rt. Hon. Lord Eustace Percy
Eustace Sutherland Campbell Percy, 1st Baron Percy of Newcastle (21 March 1887 – 3 April 1958), styled Lord Eustace Percy between 1899 and 1953, was a British diplomat, Conservative politician, public servant, and aristocrat from the Percy ...
, who later served as Rector of King's College from 1937 to 1952. It is a Grade II listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
. In 2010, the university donated £8 million towards a redevelopment project for the Union Building.
The Students' Union is run by seven paid sabbatical officers, including a Welfare and Equality Officer, and ten part-time unpaid officer positions. The former leader of the Liberal Democrats Tim Farron
Timothy James Farron (born 27 May 1970) is a British politician who served as Leader of the Liberal Democrats from 2015 to 2017. He has been the Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) for Westmorland and Lonsdale since ...
was President of NUSU in 1991–1992. The Students' Union also employs around 300 people in ancillary roles including bar staff and entertainment organisers.
''The Courier'' is a weekly student newspaper
A student publication is a media outlet such as a newspaper, magazine, television show, or radio station Graduate student journal, produced by students at an educational institution. These publications typically cover local and school-related new ...
. Established in 1948, the current weekly readership is around 12,000, most of whom are students at the university. ''The Courier'' has won ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in Manchester in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'' and changed its name in 1959, followed by a move to London. Along with its sister paper, ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardi ...
s ''Student Publication of the Year'' award twice in a row, in 2012 and 2013. It is published every Monday during term time.
Newcastle Student Radio is a student radio station based in the university. It produces shows on music, news, talk and sport and aims to cater for a wide range of musical tastes.
NUTV, known as TCTV from 2010 to 2017, is student television channel, first established in 2007. It produces live and on-demand content with coverage of events, as well as student-made programmes and shows.
Student exchange
Newcastle University has signed over 100 agreements with foreign universities allowing for student exchange to take place reciprocally.
Sport
Newcastle is one of the leading universities for sport in the UK and is consistently ranked within the top 12 out of 152 higher education institutions in the British Universities and Colleges Sport (BUCS) rankings. More than 50 student-led sports clubs are supported through a team of professional staff and a network of indoor and outdoor sports facilities based over four sites. The university have a strong rugby history and were the winners of the Northumberland Senior Cup in 1965.
The university enjoys a friendly sporting rivalry with local universities. The Stan Calvert Cup was held between 1994 and 2018 by major sports teams from Newcastle and Northumbria University
Northumbria University (legally the University of Northumbria at Newcastle) is a Public research university, public research university located in Newcastle upon Tyne, North East England, North East of England. It has been a university since 199 ...
. The Boat Race of the North
The Boat Race of the North is an annual rowing event between the boat clubs of Durham and Newcastle universities in England. The event is usually staged on the River Tyne in Newcastle, although the 2018 race was held on the River Wear i ...
has also taken place between the rowing
Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically a ...
clubs of Newcastle and Durham University
Durham University (legally the University of Durham) is a collegiate university, collegiate public university, public research university in Durham, England, founded by an Act of Parliament (UK), Act of Parliament in 1832 and incorporated by r ...
.
Newcastle University F.C. compete in men's senior football in the Northern League Division Two.
The university's Cochrane Park sports facility was a training venue for the teams playing football games at St James' Park
St James' Park is a Association football, football stadium in Newcastle upon Tyne, England. It is the home of Newcastle United F.C., Newcastle United. With a seating capacity of 52,305, it is the List of football stadiums in England, 8th la ...
for the 2012 London Olympics
The 2012 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XXX Olympiad and also known as London 2012, were an international multi-sport event held from 27 July to 12 August 2012 in London, England, United Kingdom. The first event, the ...
.
Notable people
See also
*Armorial of UK universities
The armorial of British universities is the collection of coats of arms of universities in the United Kingdom. Modern arms of universities began appearing in England around the middle of the 15th century, with University of Oxford, Oxford's being ...
* List of Newcastle University people
*List of modern universities in Europe (1801–1945)
The list of modern universities in Europe (1801–1940) contains all University, universities that were founded in Europe after the French Revolution and before the end of World War II. Universities are regarded as comprising all institutions ...
*List of universities in the United Kingdom
This is a list of universities in the United Kingdom (alphabetical by substantive name). Below that are lists of university colleges and other recognised bodies (institutions with degree awarding powers), followed by a list of defunct institution ...
*Rankings of universities in the United Kingdom
Three national rankings of universities in the United Kingdom are published annually by the ''Complete University Guide'' and ''The Guardian'', as well as a collaborative list by ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times''. Rankings have also been pro ...
*Universities in the United Kingdom
Universities in the United Kingdom have generally been instituted by royal charter, papal bull, Act of Parliament, or an instrument of government under the Further and Higher Education Act 1992 or the Higher Education and Research Act 2017. Deg ...
References
External links
Newcastle University – ncl.ac.uk
{{authority control
Buildings and structures in Newcastle upon Tyne
Russell Group
Universities and colleges established in 1834
Exempt charities
1834 establishments in England
Tourist attractions in Newcastle upon Tyne
Universities UK
 The university occupies a campus site close to Haymarket in central Newcastle upon Tyne. It is located to the northwest of the city centre between the open spaces of Leazes Park and the Town Moor; the university medical school and
The university occupies a campus site close to Haymarket in central Newcastle upon Tyne. It is located to the northwest of the city centre between the open spaces of Leazes Park and the Town Moor; the university medical school and  Plans for additions and improvements to the campus were made public in March 2008 and completed in 2010 at a cost of £200 million. They included a redevelopment of the south-east (Haymarket) façade with a five-storey King's Gate administration building as well as new student accommodation. Two additional buildings for the school of medicine were also built.
September 2012 saw the completion of the new buildings and facilities for INTO Newcastle University on the university campus. The main building provides 18 new teaching rooms, a Learning Resource Centre, a lecture theatre, science lab, administrative and academic offices and restaurant.
The Philip Robinson Library is the main university library and is named after a bookseller in the city and benefactor to the library. The Walton Library specialises in services for the Faculty of Medical Sciences in the Medical School. It is named after Lord Walton of Detchant, former Dean of the Faculty of Medicine and Professor of Neurology. The library has a relationship with the Northern region of the
Plans for additions and improvements to the campus were made public in March 2008 and completed in 2010 at a cost of £200 million. They included a redevelopment of the south-east (Haymarket) façade with a five-storey King's Gate administration building as well as new student accommodation. Two additional buildings for the school of medicine were also built.
September 2012 saw the completion of the new buildings and facilities for INTO Newcastle University on the university campus. The main building provides 18 new teaching rooms, a Learning Resource Centre, a lecture theatre, science lab, administrative and academic offices and restaurant.
The Philip Robinson Library is the main university library and is named after a bookseller in the city and benefactor to the library. The Walton Library specialises in services for the Faculty of Medical Sciences in the Medical School. It is named after Lord Walton of Detchant, former Dean of the Faculty of Medicine and Professor of Neurology. The library has a relationship with the Northern region of the  Newcastle University has the second largest
Newcastle University has the second largest  The university is a member of the
The university is a member of the  Newcastle is a member of the
Newcastle is a member of the  Newcastle University Students' Union (NUSU), known as the Union Society until a 2012 rebranding, includes student-run sports clubs and societies.
The Union building was built in 1924 following a generous gift from an anonymous donor, who is now believed to have been Sir Cecil Cochrane, a major benefactor to the university. It is built in the neo- Jacobean style and was designed by the local architect Robert Burns Dick. It was opened on 22 October 1925 by the Rt. Hon.
Newcastle University Students' Union (NUSU), known as the Union Society until a 2012 rebranding, includes student-run sports clubs and societies.
The Union building was built in 1924 following a generous gift from an anonymous donor, who is now believed to have been Sir Cecil Cochrane, a major benefactor to the university. It is built in the neo- Jacobean style and was designed by the local architect Robert Burns Dick. It was opened on 22 October 1925 by the Rt. Hon.