Ankylopollexia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ankylopollexia is an
 Ankylopollexians varied greatly in size over the course of their evolution.. Jurassic genus ''Camptosaurus'' was small, no more than in length and half a tonne in weight. The largest known ankylopollexian, dating to the late
Ankylopollexians varied greatly in size over the course of their evolution.. Jurassic genus ''Camptosaurus'' was small, no more than in length and half a tonne in weight. The largest known ankylopollexian, dating to the late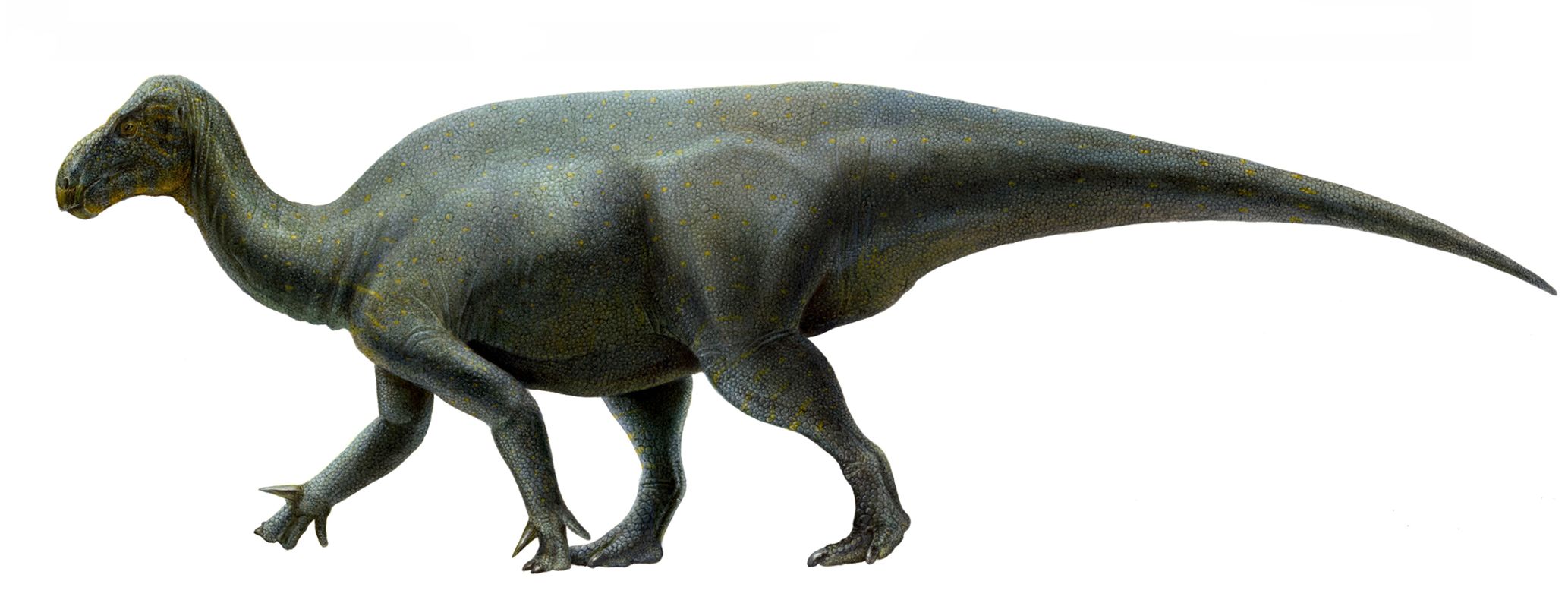  Primitive ankylopollexians tended to be smaller as compared to the larger, more derived
Primitive ankylopollexians tended to be smaller as compared to the larger, more derived
 About 157 million years ago, Ankylopollexia and
About 157 million years ago, Ankylopollexia and
 The
The 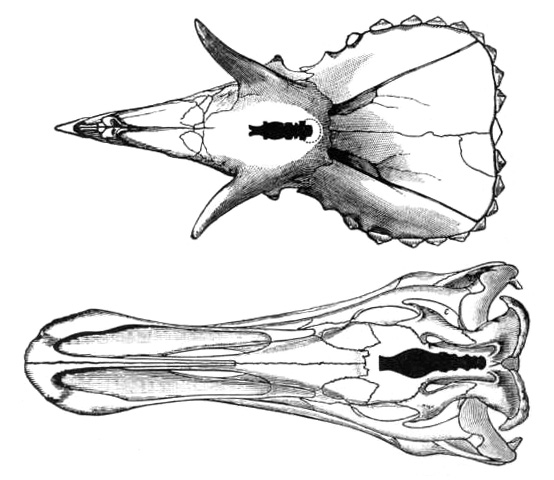
 The advent of
The advent of
 Ankylopollexians would in the Cretaceous become one of the most successful groups on the planet, being both widespread and numerous in nature. Around this time, ankylopollexians spread to
Ankylopollexians would in the Cretaceous become one of the most successful groups on the planet, being both widespread and numerous in nature. Around this time, ankylopollexians spread to
extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
of ornithischian dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
that lived from the Late Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third Epoch (geology), epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time scale, geologic time from 161.5 ± 1.0 to 143.1 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic stratum, strata.Owen ...
to the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre ...
. It is a derived clade of iguanodontian ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (). They represent one of the most successful groups of herbivorous dinosaurs during the Cretaceous. The most primitive members of the group were bipedal and relatively sm ...
s and contains the subgroup Styracosterna. The name stems from the Greek word, “ankylos”, mistakenly taken to mean stiff, fused (in fact the adjective means bent or curved; used of fingers, it can mean hooked), and the Latin word, “pollex”, meaning thumb. Originally described in 1986 by Sereno, a most likely synapomorphic feature of a conical thumb spine defines the clade.Sereno, P.C. (1986). "Phylogeny of the bird-hipped dinosaurs (order Ornithischia)". National Geographic Research 2 (2): 234–56
First appearing around 156 million years ago, in the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
, Ankylopollexia became an extremely successful and widespread clade during the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
, and were found around the world. The group died out at the end of the Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian ( ) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age (uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage) of the Late Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or Upper Cretaceous series (s ...
. They grew to be quite large, comparable to some carnivorous dinosaurs and they were universally herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat n ...
.
Size
Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campa ...
age (around 70 million years ago), belonged to the hadrosaurid family, and is named ''Shantungosaurus
''Shantungosaurus'' (meaning "''Shandong Lizard''") is a genus of very large saurolophine hadrosaurid dinosaur found in the Late Cretaceous Wangshi Group of the Shandong Peninsula in China, containing a single species, ''Shantungosaurus gigante ...
''. It was around to in length and weighed, for the largest individuals, up to .
 Primitive ankylopollexians tended to be smaller as compared to the larger, more derived
Primitive ankylopollexians tended to be smaller as compared to the larger, more derived hadrosaur
Hadrosaurids (), also hadrosaurs or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod fami ...
s. There are, however, exceptions to this trend. A single track from a large ornithopod, likely a relative of ''Camptosaurus'', was reported from the Lourinhã Formation
The Lourinhã Formation () is a fossil-rich geological formation in western Portugal, named for the municipality of Lourinhã. The formation is mostly Late Jurassic in age (Kimmeridgian/Tithonian), with the top of the formation extending into the ...
, dating to the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
. The corresponding animal had an estimated hip height of around , much larger than the contemporary relative ''Draconyx
''Draconyx'' (meaning "dragon claw") is a genus of dinosaur from the Late Jurassic. It was an Ornithopoda, ornithopod which lived in what is now Portugal and was a herbivore. It was found in the Lourinhã Formation in 1991, and described by Oct� ...
''. The primitive styracosternan '' Iguanacolossus'' was named for its distinct robustness and large size, likely around in length. Regarding hadrosaurs, one of the more basal members of Hadrosauroidea
Hadrosauroidea is a clade or superfamily of ornithischian dinosaurs that includes the "duck-billed" dinosaurs, or Hadrosauridae, and all dinosaurs more closely related to them than to ''Iguanodon''. Their remains have been recovered in Asia, Euro ...
, the Chinese genus '' Bolong'', is estimated to have been around . Another exception of this trend is ''Tethyshadros
''Tethyshadros'' ("Tethys Ocean, Tethyan hadrosauroid") is a genus of Hadrosauroidea, hadrosauroid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Campanian) Calcare di Aurisina (previously thought to come from the younger Liburnia Formation) of Trieste, Ita ...
'', a more derived genus of Hadrosauroidea. Estimated to have weighed , ''Tethyshadros'' have been found only on certain islands in Italy. Its diminutive size is explained by insular dwarfism
Insular dwarfism, a form of phyletic dwarfism, is the process and condition of large animals evolving or having a reduced body size when their population's range is limited to a small environment, primarily islands. This natural process is disti ...
. In addition a 44 cm scapula belonging to an ankylopollexian has been found in the Lourinhã Formation the length of the scapula indicates an animal similar in size to Camptosaurus.
Classification
 About 157 million years ago, Ankylopollexia and
About 157 million years ago, Ankylopollexia and Dryosauridae
Dryosauridae was a family of primitive iguanodonts, first proposed by Milner & Norman in 1984. They are known from Middle Jurassic to Early Cretaceous rocks of Africa, Europe, and North America.
Dryosauridae was first proposed in 1984 by Britis ...
are believed to have split into separate evolutionary branches.Norman, David B.; Weishampel, David B. (1990). "Iguanodontidae and related ornithopods". In Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.). The Dinosauria. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 510–533. . Originally named and described in 1986 by Paul Sereno, Ankylopollexia would receive a phylogenetic definition in a later paper by Sereno in 2005. In the 1986 paper, the groups Camptosauridae and Styracosterna were used to define the clade, but in the 2005 paper, a phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
definition was given: the last common ancestor of the species ''Camptosaurus dispar'' and ''Parasaurolophus walkeri'' and all its descendants. Ankylopollexia would receive a formal ''PhyloCode
The ''International Code of Phylogenetic Nomenclature'', known as the ''PhyloCode'' for short, is a formal set of rules governing phylogenetic nomenclature. Its current version is specifically designed to regulate the naming of clades, leaving the ...
'' definition as "the smallest clade containing '' Camptosaurus dispar'' and ''Iguanodon bernissartensis
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species found worldwide have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous, Taxonomy (bi ...
''". This clade contains the two subclades Camptosauridae and Styracosterna, which are both defined using ''Camptosaurus dispar'' and ''Iguanodon bernissartensis'', creating a node-stem triplet with Ankylopollexia.
The cladogram below follows the phylogenetic analysis of Bertozzo ''et al.'' (2017).
Palaeobiology
Brain
 The
The neurobiology
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, ...
of ankylopollexians has been studied as far back as 1871, when a well preserved cranium (specimen NHMUK R2501) discovered in September 1869 from the Wealden Group
The Wealden Group, occasionally also referred to as the Wealden Supergroup, is a group (stratigraphy), group (a sequence of rock strata) in the lithostratigraphy of southern England. The Wealden group consists of wiktionary:paralic, paralic to c ...
on the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight (Help:IPA/English, /waɪt/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''WYTE'') is an island off the south coast of England which, together with its surrounding uninhabited islets and Skerry, skerries, is also a ceremonial county. T ...
and tentatively referred to the genus ''Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning 'iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species found worldwide have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous, Taxonomy (bi ...
'' was described by John Hulke. He noted that due to the lesser correlation of the shape of the brain and wall of cranial cavity in reptiles, any deduction of the shape of the brain of the animal would be approximate. The referral of this skull was reinforced in a later study, published in 1897. It was here inquired that the brain of the dinosaur may have been more closely associated to the cavity than that of modern reptiles, and so an endocast
An endocast is the internal cast of a hollow object, often referring to the cranial vault in the study of brain development in humans and other organisms. Endocasts can be artificially made for examining the properties of a hollow, inaccessible ...
was created and studied. This was not the first endocast of an ankylopolloxian brain, for in 1893, the skull of a ''Claosaurus annectens
''Edmontosaurus annectens'' (meaning "connected lizard from Edmonton"), often colloquially and historically known as ''Anatosaurus'' (meaning "duck lizard"), is a species of flat-headed saurolophine hadrosaurid dinosaur from the late Maastrichtia ...
'' (today referred to the genus ''Edmontosaurus
''Edmontosaurus'' ( ) (meaning "lizard from Edmonton"), with the second species often colloquially and historically known as ''Anatosaurus'' or ''Anatotitan'' (meaning "duck lizard" and "giant duck"), is a genus of hadrosaurid (duck-billed) din ...
'') was used by Othniel Charles Marsh
Othniel Charles Marsh (October 29, 1831 – March 18, 1899) was an American professor of paleontology. A prolific fossil collector, Marsh was one of the preeminent paleontologists of the nineteenth century. Among his legacies are the discovery or ...
to create a cast of the brain cavity. Some basics remarks were made, including the small size of the organ, but interpreting minute features of the organ was noted to be difficult. The 1897 paper noted the similarity of the two endocasts.
Hadrosaurs
Hadrosaurids (), also hadrosaurs or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod fami ...
have been noted as having the most complex brains among ankylopollexians, and indeed among ornithischian dinosaurs as a whole. The brains of a large variety of taxa have been studied. John Ostrom, would, in 1961, provide what was then the most extensive and detailed review and work on hadrosaur neuro-anatomy. This area of hadrosaur study was in its infancy at this point, and only the species known today as ''Edmontosaurus annectens'', ''Edmontosaurus regalis'', and ''Gryposaurus notabilis'' (at that time thought to be a synonym of its relative ''Kritosaurus
''Kritosaurus'' is an incompletely known genus of hadrosaurid (duck-billed) dinosaur. It lived about 74.5-66 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous of North America. The name means "separated lizard" (referring to the arrangement of the cheek ...
'') had specimens suitable at the time to be examined (''Lambeosaurus'' was listed as having a briefly described braincase, but this was a mistake originating in Lull and Wright (1942)). Ostrom supported the view that the brains of hadrosaurs and other dinosaurs would've likely only filled a portion of the cranial cavity, therefore hindering the ability to learn from endocasts, but noted they were still useful. He noted, similar to Marsh, noted the small predicted size of the organ, but also that it was significantly developed. A number of similarities to the brains of modern reptiles were noted.

James Hopson
James Allen Hopson (born 1935) is an American paleontologist and professor (now retired) at the University of Chicago. His work has focused on the evolution of the synapsids (a group of amniotes that includes the mammals), and has been focused on ...
investigated the encephalization quotient
Encephalization quotient (EQ), encephalization level (EL), or just encephalization is a relative brain size measure that is defined as the ratio between observed and predicted brain mass for an animal of a given size, based on nonlinear regre ...
s (EQs) of various dinosaurs in 1977 study. Three ornithopods for which brain endocasts had previously been produced – ''Camptosaurus
''Camptosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of plant-eating, beaked ornithischian dinosaurs of the Late Jurassic Period (geology), period of western North America and possibly also Europe. The name means 'flexible lizard' (Ancient Greek, Greek (') meaning ...
'', ''Iguanodon'', and ''Anatosaurus'' (now known as ''Edmontosaurus annectens'') – were investigated. It was found that they had relatively high EQs compared to many other dinosaurs (ranging from 0.8 to 1.5), comparable to that of carnosauria
Carnosauria is an extinct group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs that lived during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.
While Carnosauria was historically considered largely synonymous with Allosauroidea, some recent studies have revived Ca ...
n theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
s and of modern crocodilian
Crocodilia () is an Order (biology), order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorp ...
s, but far lower than that of coelurosauria
Coelurosauria (; from Greek, meaning "hollow-tailed lizards") is the clade containing all theropod dinosaurs more closely related to birds than to carnosaurs.
Coelurosauria is a subgroup of theropod dinosaurs that includes compsognathids, tyra ...
n theropods. The latter two genera, which lived later than ''Camptosaurus'', had somewhat higher EQs than the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
taxon, which, being at the lower end, was more comparable to the ceratopsian
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Asia and Europe, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Late Ju ...
genus ''Protoceratops
''Protoceratops'' (; ) is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 75 to 71 million years ago. The genus ''Protoceratops'' includes two species: ''P. andrewsi'' and the larger ''P. hellenik ...
''. Reasonings suggested for their comparably high intelligence were the need for acute senses in the lack of defensive weapons, and more complex intraspecific behaviours as indicated by their acoustic and visual display structures.
In a first for any terrestrial fossil vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
, Brasier ''et al.'' (2017) reported mineralized soft tissues from the brain of an iguanodontian dinosaur, from the Valanginian
In the geologic timescale, the Valanginian is an age or stage of the Early or Lower Cretaceous. It spans between 137.05 ± 0.2 Ma and 132.6 ± 0.2 Ma (million years ago). The Valanginian Stage succeeds the Berriasian Stage of the Lower Cretac ...
age (around 133 million years ago) Upper Tunbridge Wells Formation at Bexhill, Sussex
Sussex (Help:IPA/English, /ˈsʌsɪks/; from the Old English ''Sūþseaxe''; lit. 'South Saxons'; 'Sussex') is an area within South East England that was historically a kingdom of Sussex, kingdom and, later, a Historic counties of England, ...
. Fragmentary ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (). They represent one of the most successful groups of herbivorous dinosaurs during the Cretaceous. The most primitive members of the group were bipedal and relatively sm ...
remains were associated with the fossil, and though assigning the specimen to any one taxon with certainty wasn't possible, '' Barilium'' or ''Hypselospinus
''Hypselospinus'' is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur which was first described as a species of ''Iguanodon'' (''I. fittoni'') by Richard Lydekker in 1889, the specific name (zoology), specific name honouring William Henry Fitton.
History and n ...
'' were put forward as likely candidates. The specimen compared well to endocasts of similar taxa, such as one from a ''Mantellisaurus
''Mantellisaurus'' is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur that lived in the Barremian and early Aptian ages of the Early Cretaceous Period of Europe. Its remains are known from Belgium (Bernissart), England, Spain and Germany. The type species, ty ...
'' on display at the Oxford University Museum of Natural History
The Oxford University Museum of Natural History (OUMNH) is a museum displaying many of the University of Oxford's natural history specimens, located on Parks Road in Oxford, England. It also contains a lecture theatre which is used by the univers ...
. Detailed observations were made with the use of a scanning electron microscope
A scanning electron microscope (SEM) is a type of electron microscope that produces images of a sample by scanning the surface with a focused beam of electrons. The electrons interact with atoms in the sample, producing various signals that ...
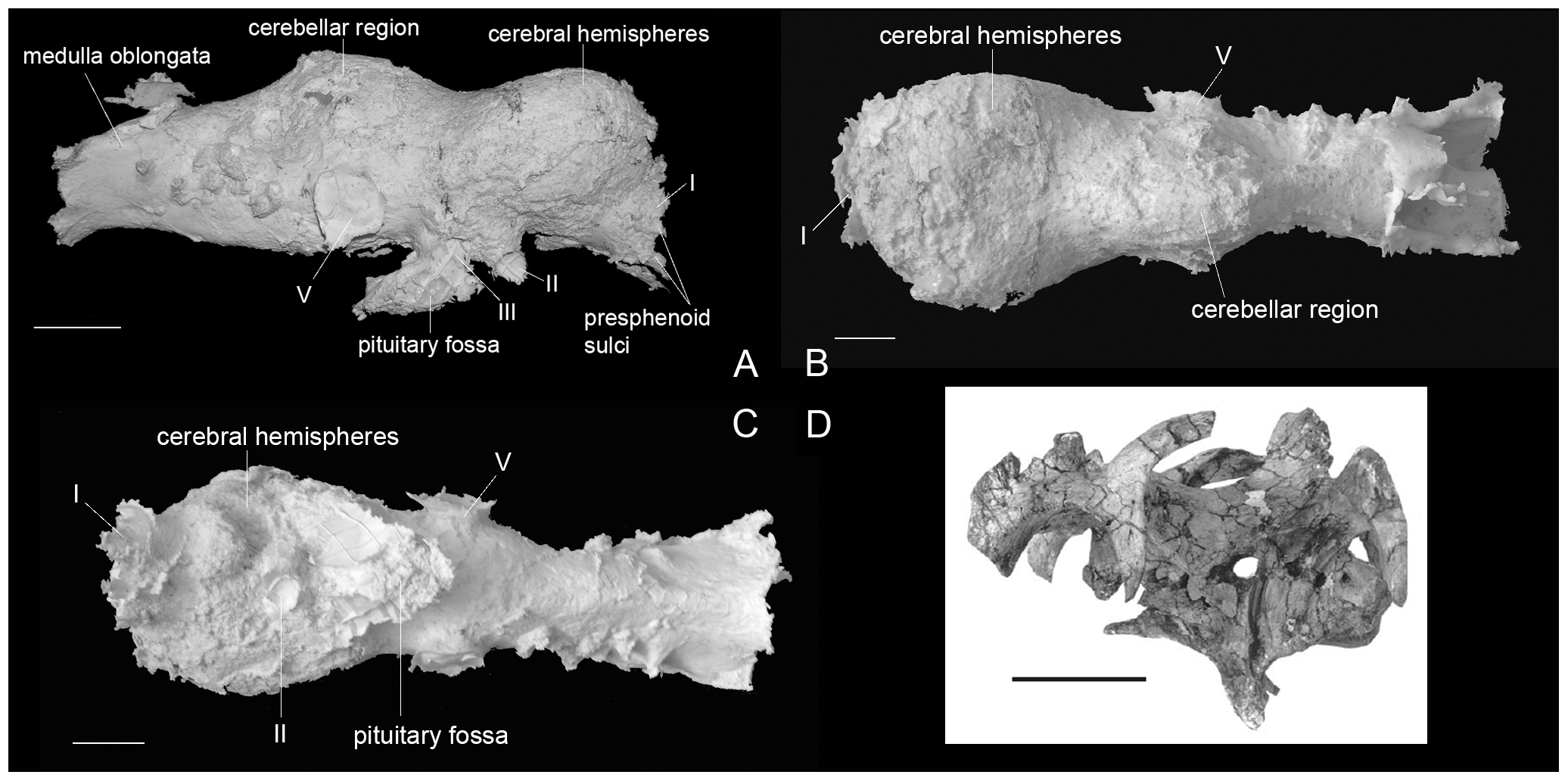
. Only some parts of the brain were preserved; the cerebellar
The cerebellum (: cerebella or cerebellums; Latin for 'little brain') is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as it or e ...
and cerebral expansions were best preserved, whereas the olfactory lobes and medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involun ...
were missing or nearly so. The neural tissues seemed to be very tightly packed, indicating an EC closer to five (with hadrosaurs having even higher ECs), nearly matching that of the most intelligent non-avian theropods. Though it was noted this was in-line with their complex behaviour, as had been noted by Hopson, it was cautioned the dense packing may have been an artifact of preservation, and the original lower estimates were considered more accurate. Some of the complex behaviours ascribed can be seen to some extent in modern crocodilians, who fall near the original numbers.
 The advent of
The advent of CT scanning
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
for use in palaeontology has allowed for more widespread application of this without the need for specimen destruction. Modern research using these methods has focused largely on hadrosaurs. In a 2009 study by palaeontologist David C. Evans and colleagues, the brains of various lambeosaurine hadrosaur genera were scanned and compared to each other, related taxa, and previous predictions. Contra the early works, Evans' studies indicate that only some regions of the hadrosaur brain were loosely correlated to the brain wall. As with previous studies, EQ values were investigated; even the lowest end of the determined EQ range was still higher than that of modern reptiles and most non-maniraptoran
Maniraptora is a clade of coelurosaurian dinosaurs which includes the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs that were more closely related to them than to '' Ornithomimus velox''. It contains the major subgroups Avialae, Dromaeosauridae, Troodontidae ...
dinosaurs, though fell well short of maniraptorans themselves. The size of the cerebral hemispheres
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres ...
was, for the first time, remarked upon, being far larger than in other ornithischians and all large saurischian
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithis ...
dinosaurs; maniraptorans ''Conchoraptor
''Conchoraptor'' (meaning "conch plunderer") is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous epoch, about 70 million years ago. It is known from the Barun Goyot and Nemegt Formation, Nemegt formations of Mongolia ...
'' and ''Archaeopteryx
''Archaeopteryx'' (; ), sometimes referred to by its German name, "" ( ''Primeval Bird'') is a genus of bird-like dinosaurs. The name derives from the ancient Greek (''archaîos''), meaning "ancient", and (''ptéryx''), meaning "feather" ...
'' had very similar proportions. This lends further support to the idea of complex behaviours and relatively high intelligence, for non-avian dinosaurs, in hadrosaurids. Lambeosaurine ''Amurosaurus
''Amurosaurus'' (; "Amur lizard") is a genus of lambeosaurinae, lambeosaurine hadrosaurid dinosaur found in the latest Cretaceous period (66 million years ago)Godefroit, P., Lauters, P., Van Itterbeeck, J., Bolotsky, Y. and Bolotsky, I.Y. (2011) ...
'' was the subject of a 2013 paper once again looking into a cranial endocast. A once again high EQ range was found, higher than that of living reptiles, sauropod
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
s and other ornithischians, but different EQ estimates for theropods were cited, placing the hadrosaur numbers significantly below the majority of theropods. Additionally, the relative cerebral volume was only 30% in ''Amurosaurus'', significantly lower than in ''Hypacrosaurus'', closer to that of theropods like ''Tyrannosaurus'', though still distinctly larger than previously estimated numbers for more primitive iguanodonts. This demonstrated a previously unrecognized level of variation in neuro-anatomy within Hadrosauridae.
Palaeobiogeography
 Ankylopollexians would in the Cretaceous become one of the most successful groups on the planet, being both widespread and numerous in nature. Around this time, ankylopollexians spread to
Ankylopollexians would in the Cretaceous become one of the most successful groups on the planet, being both widespread and numerous in nature. Around this time, ankylopollexians spread to Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
and Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. An early example is the Chinese genus '' Bayannurosaurus'', from the Berriasian
In the geological timescale, the Berriasian is an age/ stage of the Early/Lower Cretaceous. It is the oldest subdivision in the entire Cretaceous. It has been taken to span the time between 143.1 ±0.6 Ma and 137.05 ± 0.2 (million years ago) ...
. The oldest genus, found in Wyoming
Wyoming ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States, Western United States. It borders Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho t ...
, is '' Camptosaurus dispar'', which dates to around the Callovian
In the geologic timescale, the Callovian is an age and stage in the Middle Jurassic, lasting between 165.3 ± 1.1 Ma (million years ago) and 161.5 ± 1.0 Ma. It is the last stage of the Middle Jurassic, following the Bathonian and preceding the ...
- Oxfordian, about 156-157 million years ago.Carpenter, K. and Wilson, Y. (2008). "A new species of Camptosaurus (Ornithopoda: Dinosauria) from the Morrison Formation (Upper Jurassic) of Dinosaur National Monument, Utah, and a biomechanical analysis of its forelimb". Annals of the Carnegie Museum 76: 227–263. doi:10.2992/0097-4463(2008)76 27:ansoco.0.co;2.
References
External links
* {{Taxonbar, from=Q2490737 Ankylopollexia Dinosaur clades