Angular Cheilitis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Angular cheilitis (AC) is
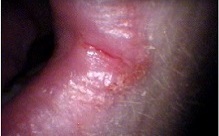 A fairly mild case of angular cheilitis extending onto the facial skin in a young person (affected area is within the black oval).
Angular cheilitis is a fairly non specific term which describes the presence of an inflammatory lesion in a particular anatomic site (i.e. the corner of the mouth). As there are different possible causes and contributing factors from one person to the next, the appearance of the lesion is somewhat variable. The lesions are more commonly symmetrically present on both sides of the mouth, but sometimes only one side may be affected. In some cases, the lesion may be confined to the mucosa of the lips, and in other cases the lesion may extend past the
A fairly mild case of angular cheilitis extending onto the facial skin in a young person (affected area is within the black oval).
Angular cheilitis is a fairly non specific term which describes the presence of an inflammatory lesion in a particular anatomic site (i.e. the corner of the mouth). As there are different possible causes and contributing factors from one person to the next, the appearance of the lesion is somewhat variable. The lesions are more commonly symmetrically present on both sides of the mouth, but sometimes only one side may be affected. In some cases, the lesion may be confined to the mucosa of the lips, and in other cases the lesion may extend past the
 Allergic reactions may account for about 25–34% of cases of generalized cheilitis (i.e., inflammation not confined to the angles of the mouth). It is unknown how frequently allergic reactions are responsible for cases of angular cheilitis, but any substance capable of causing generalized allergic cheilitis may present involving the corners of the mouth alone.
Examples of potential
Allergic reactions may account for about 25–34% of cases of generalized cheilitis (i.e., inflammation not confined to the angles of the mouth). It is unknown how frequently allergic reactions are responsible for cases of angular cheilitis, but any substance capable of causing generalized allergic cheilitis may present involving the corners of the mouth alone.
Examples of potential
inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of one or both corners of the mouth
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and animal communication#Auditory, vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also t ...
. Often the corners are red with skin breakdown and crusting. It can also be itchy or painful. The condition can last for days to years. Angular cheilitis is a type of cheilitis (inflammation of the lips).
Angular cheilitis can be caused by infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
, irritation, or allergies
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
. Infections include by fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
such as '' Candida albicans'' and bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
such as '' Staph. aureus''. Irritants include poorly fitting dentures
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth, supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable ( removable partial denture or comp ...
, licking the lips or drooling, mouth breathing resulting in a dry mouth, sun exposure, overclosure of the mouth, smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
, and minor trauma. Allergies may include substances like toothpaste, makeup, and food. Often a number of factors are involved. Other factors may include poor nutrition or poor immune function. Diagnosis may be helped by testing for infections and patch testing for allergies.
Treatment for angular cheilitis is typically based on the underlying causes along with the use of a barrier cream
A barrier cream is a Topical medication, topical formulation used in industrial applications and as a cosmetic to place a physical barrier between the skin and contaminants that may irritate the skin (contact dermatitis or occupational dermatitis ...
. Frequently an antifungal
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as ...
and antibacterial cream is also tried. Angular cheilitis is a fairly common problem, with estimates that it affects 0.7% of the population. It occurs most often in people in their 30s to 60s, and is also relatively common in children. In the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreeme ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, vitamin B12, and other vitamin deficiencies are a common cause.
Signs and symptoms
 A fairly mild case of angular cheilitis extending onto the facial skin in a young person (affected area is within the black oval).
Angular cheilitis is a fairly non specific term which describes the presence of an inflammatory lesion in a particular anatomic site (i.e. the corner of the mouth). As there are different possible causes and contributing factors from one person to the next, the appearance of the lesion is somewhat variable. The lesions are more commonly symmetrically present on both sides of the mouth, but sometimes only one side may be affected. In some cases, the lesion may be confined to the mucosa of the lips, and in other cases the lesion may extend past the
A fairly mild case of angular cheilitis extending onto the facial skin in a young person (affected area is within the black oval).
Angular cheilitis is a fairly non specific term which describes the presence of an inflammatory lesion in a particular anatomic site (i.e. the corner of the mouth). As there are different possible causes and contributing factors from one person to the next, the appearance of the lesion is somewhat variable. The lesions are more commonly symmetrically present on both sides of the mouth, but sometimes only one side may be affected. In some cases, the lesion may be confined to the mucosa of the lips, and in other cases the lesion may extend past the vermilion border
The vermilion border (sometimes spelled vermillion border), also called margin or zone, is the normally sharp demarcation between the lip and the adjacent normal skin. It represents the change in the epidermis from highly keratinized external ski ...
(the edge where the lining on the lips becomes the skin on the face) onto the facial skin. Initially, the corners of the mouth develop a gray-white thickening and adjacent erythema
Erythema (, ) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology inc ...
(redness). Later, the usual appearance is a roughly triangular area of erythema, edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. S ...
(swelling) and breakdown of skin at either corner of the mouth. The mucosa of the lip may become fissured (cracked), crusted, ulcerated or atrophied. There is not usually any bleeding. Where the skin is involved, there may be radiating rhagades (linear fissures) from the corner of the mouth. Infrequently, the dermatitis
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
(which may resemble eczema
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
) can extend from the corner of the mouth to the skin of the cheek or chin. If ''Staphylococcus aureus'' is involved, the lesion may show golden yellow crusts. In chronic angular cheilitis, there may be suppuration ( pus formation), exfoliation (scaling) and formation of granulation tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size ...
.
Sometimes contributing factors can be readily seen, such as loss of lower face height from poorly made or worn dentures, which results in mandibular overclosure ("collapse of jaws"). If there is a nutritional deficiency underlying the condition, various other signs and symptoms such as glossitis (swollen tongue) may be present. In people with angular cheilitis who wear dentures, often there may be erythematous mucosa underneath the denture (normally the upper denture), an appearance consistent with denture-related stomatitis. Typically the lesions give symptoms of soreness, pain, pruritus (itching) or burning or a raw feeling.
Causes
Angular cheilitis is thought to be a multifactorial disorder of infectious origin, with many local and systemic predisposing factors. The sores in angular cheilitis are often infected withfungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
(yeasts), bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, or a combination thereof; this may represent a secondary, opportunistic infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection that occurs most commonly in individuals with an immunodeficiency disorder and acts more severe on those with a weakened immune system. These types of infections are considered serious and can be caused b ...
by these pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s. Some studies have linked the initial onset of angular cheilitis with nutritional deficiencies, especially of the B (B2-riboflavin) vitamin and iron (which causes iron deficiency anemia), which in turn may be evidence of malnutrition or malabsorption. Angular cheilitis can be a manifestation of contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a type of acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by exposure to chemical or physical agents. Symptoms of contact dermatitis can include itchy or dry skin, a red rash, bumps, blisters, or swelling. These rashes ...
, which is considered in two groups; irritational and allergic.
Infection
The involved organisms are: * Candida species alone (usually '' Candida albicans''), which accounts for about 20% of cases, * Bacterial species, either: ** ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'' alone, which accounts for about 20% of cases,
** β-hemolytic streptococci alone. These types of bacteria have been detected in between 8–15% of cases of angular cheilitis, but less commonly are they present in isolation,
* Or a combination of the above organisms, (a polymicrobial infection) with about 60% of cases involving both ''C. albicans'' and ''S. aureus''.
Candida can be detected in 93% of angular cheilitis lesions. This organism is found in the mouths of about 40% of healthy individuals, and it is considered by some to be normal commensal component of the oral microbiota. However, Candida shows dimorphism, namely a yeast form which is thought to be relatively harmless and a pathogenic
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
The term ...
hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one o ...
l form which is associated with invasion of host tissues. Potassium hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula K OH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Along with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), KOH is a prototypical strong base. It has many industrial and niche applications, most of which utili ...
preparation is recommended by some to help distinguish between the harmless and the pathogenic forms, and thereby highlight which cases of angular cheilitis are truly caused by Candida. The mouth may act as a reservoir of Candida that reinfects the sores at the corners of the mouth and prevents the sores from healing.
A lesion caused by recurrence of a latent herpes simplex
Herpes simplex, often known simply as herpes, is a viral disease, viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Herpes infections are categorized by the area of the body that is infected. The two major types of herpes are Cold sore, ora ...
infection can occur in the corner of the mouth. This is herpes labialis (a cold sore), and is sometimes termed "angular herpes simplex". A cold sore at the corner of the mouth behaves similarly to elsewhere on the lips, and follows a pattern of vesicle (blister) formation followed by rupture leaving a crusted sore which resolves in about 7–10 days, and recurs in the same spot periodically, especially during periods of stress. Rather than utilizing antifungal creams, angular herpes simplex is treated in the same way as a cold sore, with topical antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials ...
s such as aciclovir.
Irritation contact dermatitis
22% of cases of angular cheilitis are due to irritants.Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which ...
contains digestive enzyme
Digestive enzymes take part in the chemical process of digestion, which follows the mechanical process of digestion. Food consists of macromolecules of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats that need to be broken down chemically by digestive enzymes ...
s, which may have a degree of digestive action on tissues if they are left in contact. The corner of the mouth is normally exposed to saliva more than any other part of the lips. Reduced lower facial height (vertical dimension or facial support) is usually caused by edentulism (tooth loss), or wearing worn down, old dentures or ones which are not designed optimally. This results in overclosure of the mandible (collapse of the jaws), which extenuates the angular
skin folds at the corners of the mouth, in effect creating an intertriginous skin crease. The tendency of saliva to pool in these areas is increased, constantly wetting the area, which may cause tissue maceration and favors the development of a yeast infection. As such, angular cheilitis is more commonly seen in edentulous people (people without any teeth). It is by contrast uncommon in persons who retain their natural teeth. Angular cheilitis is also commonly seen in denture wearers. Angular cheilitis is present in about 30% of people with denture-related stomatitis. It is thought that reduced vertical dimension of the lower face may be a contributing factor in up to 11% of elderly persons with angular cheilitis and in up to 18% of denture wearers who have angular cheilitis. Reduced vertical dimension can also be caused by tooth migration, wearing orthodontic appliances, and elastic tissue damage caused by ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of th ...
exposure and smoking.
Habits or conditions that keep the corners of the mouth moist might include chronic lip licking, thumb sucking (or sucking on other objects such as pens, pipes, lollipops), dental cleaning (e.g. flossing), chewing gum, hypersalivation, drooling and mouth breathing. Some consider habitual lip licking or picking to be a form of nervous tic, and do not consider this to be true angular cheilitis, instead calling it ''perlèche'' (derived from the French word ''pourlècher'' meaning "to lick one's lips"), or " factitious cheilitis" is applied to this habit. The term "cheilocandidiasis" describes exfoliative (flaking) lesions of the lips and the skin around the lips, and is caused by a superficial candidal infection due to chronic lip licking. Less severe cases occur during cold, dry weather, and is a form of chapped lips. Individuals may lick their lips in an attempt to provide a temporary moment of relief, only serving to worsen the condition.
The sunscreen in some types of lip balm degrades over time into an irritant. Using expired lipbalm can initiate mild angular cheilitis, and when the person applies more lipbalm to alleviate the cracking, it only aggravates it. Because of the delayed onset of contact dermatitis and the recovery period lasting days to weeks, people typically do not make the connection between the causative agent and the symptoms.
Nutritional deficiencies
Several different nutritional deficiency states ofvitamin
Vitamins are Organic compound, organic molecules (or a set of closely related molecules called vitamer, vitamers) that are essential to an organism in small quantities for proper metabolism, metabolic function. Nutrient#Essential nutrients, ...
s or mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s have been linked to angular cheilitis. It is thought that in about 25% of people with AC, iron deficiency
Iron deficiency, or sideropenia, is the state in which a body lacks enough iron to supply its needs. Iron is present in all cells in the human body and has several vital functions, such as carrying oxygen to the tissues from the lungs as a key ...
or deficiency of B vitamins
B vitamins are a class of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in Cell (biology), cell metabolism and synthesis of red blood cells. They are a chemically diverse class of compounds.
Dietary supplements containing all eight are referr ...
are involved. Nutritional deficiencies may be a more common cause of AC in Third World
The term Third World arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, the Southern Cone, NATO, Western European countries and oth ...
countries. Chronic iron deficiency may also cause koilonychia (spoon shaped deformity of the fingernails) and glossitis (inflammation of the tongue). It is not completely understood how iron deficiency causes AC, but it is known that it causes a degree of immunocompromise (decreased efficiency of the immune system) which may in turn allow an opportunistic infection of candida. Vitamin B2 deficiency (ariboflavinosis) may also cause AC, and other conditions such as redness of mucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ...
s, magenta colored glossitis (pink inflammation of the tongue). Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 is one of the B vitamins, and is an essential nutrient for humans. The term essential nutrient refers to a group of six chemically similar compounds, i.e., "vitamers", which can be interconverted in biological systems. Its active f ...
deficiency may also cause AC, along with glossitis, and skin changes similar to seborrhoeic dermatitis
Seborrhoeic dermatitis (also spelled seborrheic dermatitis in American English) is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include flaky, scaly, greasy, and occasionally itchy and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are ...
around the eyes, nose and mouth. Vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have fe ...
is sometimes responsible for AC, and commonly occurs together with folate deficiency (a lack of folic acid
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
), which also causes glossitis and megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of macrocytic anemia. An anemia is a red blood cell defect that can lead to an undersupply of oxygen. Megaloblastic anemia results from inhibition of DNA replication, DNA synthesis during red blood cell production. ...
. Vitamin B3
Vitamin B3, colloquially referred to as niacin, is a vitamin family that includes three forms, or vitamers: nicotinic acid (niacin), nicotinamide (niacinamide), and nicotinamide riboside. All three forms of vitamin B3 are converted within th ...
deficiency (pellagra
Pellagra is a disease caused by a lack of the vitamin niacin (vitamin B3). Symptoms include inflamed skin, diarrhea, dementia, and sores in the mouth. Areas of the skin exposed to friction and radiation are typically affected first. Over tim ...
) is another possible cause, and in which other association conditions such as dermatitis
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
, diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
, dementia
Dementia is a syndrome associated with many neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by a general decline in cognitive abilities that affects a person's ability to perform activities of daily living, everyday activities. This typically invo ...
and glossitis can occur. Biotin
Biotin (also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. ...
(vitamin B7) deficiency has also been reported to cause AC, along with hair loss
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring ...
(alopecia) and dry eyes. Zinc deficiency
Zinc deficiency is defined either as insufficient body levels of zinc to meet the needs of the body, or as a zinc blood level below the normal range. However, since a decrease in blood concentration is only detectable after long-term or severe ...
is known to cause AC. Other symptoms may include diarrhea, alopecia
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scarring ...
and dermatitis
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
. Acrodermatitis enteropathica is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder causing impaired absorption of zinc, and is associated with AC.
In general, these nutritional disorders may be caused by malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
, such as may occur in alcoholism
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World He ...
or in poorly considered diets, or by malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a varie ...
secondary to gastrointestinal disorders (e.g. Coeliac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spelt ...
or chronic pancreatitis) or gastrointestinal surgeries (e.g. pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is a disease where not enough red blood cells are produced due to a deficiency of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Those affected often have a gradual onset. The most common initial symptoms are Fatigue, feeling tired and weak. Other ...
caused by ileal resection in Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
).
Systemic disorders
Some systemic disorders are involved in angular cheilitis by virtue of their association with malabsorption and the creation of nutritional deficiencies described above. Such examples include people withanorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa (AN), often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by Calorie restriction, food restriction, body image disturbance, fear of gaining weight, and an overpowering desire to be thin.
Individuals wit ...
. Other disorders may cause lip enlargement (e.g. orofacial granulomatosis), which alters the local anatomy and extenuates the skin folds at the corners of the mouth. More still may be involved because they affect the immune system, allowing normally harmless organisms like Candida to become pathogenic and cause an infection. Xerostomia (dry mouth) is thought to account for about 5% of cases of AC. Xerostomia itself has many possible causes, but commonly the cause may be side effects of medications, or conditions such as Sjögren's syndrome. Conversely, conditions which cause drooling or sialorrhoea (excessive salivation) can cause angular cheilitis by creating a constant wet environment in the corners of the mouth. About 25% of people with Down syndrome appear to have AC. This is due to relative macroglossia, an apparently large tongue in a small mouth, which may constantly stick out of the mouth causing maceration of the corners of the mouth with saliva. Inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine ...
s (such as Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
or ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is one of the two types of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), with the other type being Crohn's disease. It is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary sympto ...
) can be associated with angular cheilitis. In Crohn's, it is likely the result of malabsorption and immunosuppressive therapy which gives rise to the sores at the corner of the mouth. Glucagonomas are rare pancreatic endocrine tumors which secrete glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a Glucagon (medic ...
, and cause a syndrome of dermatitis, glucose intolerance, weight loss and anemia. AC is a common feature of glucagonoma syndrome. Infrequently, angular cheilitis may be one of the manifestations of chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, and sometimes cases of oropharyngeal or esophageal candidiasis may accompany angular cheilitis. Angular cheilitis may be present in human immunodeficiency virus infection, neutropenia, or diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
. Angular cheilitis is more common in people with eczema
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
because their skin is more sensitive to irritants. Other conditions possibly associated include plasma cell gingivitis, Melkersson–Rosenthal syndrome
Melkersson–Rosenthal syndrome is a rare neurological disorder characterized by recurring facial paralysis, swelling of the face and lips (usually the upper lip: cheilitis granulomatosis) and the development of folds and furrows in the tongue ( ...
, or sideropenic dysphagia (also called Plummer–Vinson syndrome or Paterson–Brown–Kelly syndrome).
Drugs
Several drugs may cause AC as a side effect, by various mechanisms, such as creating drug-induced xerostomia. Various examples includeisotretinoin
Isotretinoin, also known as 13-''cis''-retinoic acid and sold under the brand name Accutane among others, is a medication used to treat skin diseases like harlequin-type ichthyosis, and lamellar ichthyosis, and severe cystic acne or moderat ...
, indinavir, and sorafenib. Isotretinoin (Accutane), an analog of vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is an essential nutrient. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinyl esters, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most not ...
, is a medication which dries the skin. Less commonly, angular cheilitis is associated with primary hypervitaminosis A, which can occur when large amounts of liver (including cod liver oil and other fish oils) are regularly consumed or as a result from an excess intake of vitamin A in the form of vitamin supplements. Recreational drug users may develop AC. Examples include cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
, methamphetamine
Methamphetamine (contracted from ) is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is mainly used as a recreational drug use, recreational or Performance-enhancing substance, performance-enhancing drug and less commonly as a secon ...
, heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a morphinan opioid substance synthesized from the Opium, dried latex of the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy; it is mainly used as a recreational drug for its eupho ...
, and hallucinogen
Hallucinogens, also known as psychedelics, entheogens, or historically as psychotomimetics, are a large and diverse class of psychoactive drugs that can produce altered states of consciousness characterized by major alterations in thought, mo ...
s.
Allergic contact dermatitis
 Allergic reactions may account for about 25–34% of cases of generalized cheilitis (i.e., inflammation not confined to the angles of the mouth). It is unknown how frequently allergic reactions are responsible for cases of angular cheilitis, but any substance capable of causing generalized allergic cheilitis may present involving the corners of the mouth alone.
Examples of potential
Allergic reactions may account for about 25–34% of cases of generalized cheilitis (i.e., inflammation not confined to the angles of the mouth). It is unknown how frequently allergic reactions are responsible for cases of angular cheilitis, but any substance capable of causing generalized allergic cheilitis may present involving the corners of the mouth alone.
Examples of potential allergen
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
s include substances that may be present in some types of lipstick, toothpaste, acne products, cosmetics, chewing gum, mouthwash, foods, dental appliances, and materials from dentures or mercury containing amalgam fillings. It is usually impossible to tell the difference between irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis without a patch test
A patch test is a diagnostic method used to determine which specific substances cause allergic inflammation of a patient's skin.
Patch testing helps identify which substances may be causing a delayed-type allergic reaction in a patient and ...
.
Loss of lower facial height
Severe tooth wear or ill fitting dentures may cause wrinkling at the corners of the lip that creates a favorable environment for the condition. This can be corrected with onlays or crowns on the worn teeth to restore height or new dentures with "taller" teeth. The loss of vertical dimension has been associated with angular cheilitis in older individuals with an increase in facial laxity.Diagnosis
Angular cheilitis is normally a diagnosis made clinically. If the sore is unilateral, rather than bilateral, this suggests a local factor (''e.g.'', trauma) or a split syphiliticpapule
A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the skin lesion, skin. It may have a rounded, pointed or flat top, and may have a umbilication, dip. It can appear with a Peduncle (anatomy), stalk, be thread-like or look warty. It can be soft or firm a ...
. Angular cheilitis caused by mandibular overclosure, drooling, and other irritants is usually bilateral.
The lesions are normally swabbed to detect if Candida or pathogenic
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
The term ...
bacterial species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
may be present. Persons with angular cheilitis who wear dentures often also will have their denture swabbed in addition. A complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC) or full haemogram (FHG), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blo ...
(full blood count) may be indicated, including assessment of the levels of iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, ferritin
Ferritin is a universal intracellular and extracellular protein that stores iron and releases it in a controlled fashion. The protein is produced by almost all living organisms, including archaea, bacteria, algae, higher plants, and animals. ...
, vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino a ...
(and possibly other B vitamins
B vitamins are a class of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in Cell (biology), cell metabolism and synthesis of red blood cells. They are a chemically diverse class of compounds.
Dietary supplements containing all eight are referr ...
), and folate
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing and ...
.
Classification
Angular cheilitis could be considered to be a type of cheilitis or stomatitis. Where Candida species are involved, angular cheilitis is classed as a type of oral candidiasis, specifically a primary (group I) Candida-associated lesion. This form angular cheilitis which is caused by Candida is sometimes termed "Candida-associated angular cheilitis", or less commonly, "monilial perlèche". Angular cheilitis can also be classified as acute (sudden, short-lived appearance of the condition) or chronic (lasts a long time or keeps returning), orrefractory
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compound ...
(the condition persists despite attempts to treat it).
Management
There are four aspects to the treatment of angular cheilitis. Firstly, potential reservoirs of infection inside the mouth are identified and treated. Oral candidiasis, especially denture-related stomatitis is often found to be present where there is angular cheilitis, and if it is not treated, the sores at the corners of the mouth may often recur. This involves having dentures properly fitted and disinfected. Commercial preparations are marketed for this purpose, although dentures may be left in dilute (1:10 concentration) householdbleach
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color from (i.e. to whiten) fabric or fiber (in a process called bleaching) or to disinfect after cleaning. It often refers specifically t ...
overnight, but only if they are entirely plastic and do not contain any metal parts, and with rinsing under clean water before use. Improved denture hygiene is often required thereafter, including not wearing the denture during sleep and cleaning it daily.
Secondly, there may be a need to increase the vertical dimension of the lower face to prevent overclosure of the mouth and formation of deep skin folds. This may require the construction of a new denture with an adjusted bite. Rarely, in cases resistant to normal treatments, surgical procedures such as collagen injections (or other facial fillers such as autologous fat or crosslinked hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid (; abbreviated HA; conjugate base hyaluronate), also called hyaluronan, is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminog ...
) are used in an attempt to restore the normal facial contour. Other measures which seek to reverse the local factors that may be contributing to the condition include improving oral hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's oral cavity clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and adopting good hygiene habits. It is important that oral hygiene be carr ...
, stopping smoking or other tobacco habits and use of a barrier cream (e.g. zinc oxide
Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the Chemical formula, formula . It is a white powder which is insoluble in water. ZnO is used as an additive in numerous materials and products including cosmetics, Zinc metabolism, food supplements, rubbe ...
paste) at night.
Thirdly, treatment of the infection and inflammation of the lesions themselves is addressed. This is usually with topical antifungal medication, such as clotrimazole
Clotrimazole, sold under the brand name Lotrimin, among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, diaper rash, tinea versicolor, and types of ringworm including athlete's foot and jock itc ...
, amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococ ...
, ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, sold under the brand name Nizoral, among others, is an antiandrogen, antifungal drug, antifungal, and antiglucocorticoid medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. Applied to the skin it is used for fungal skin inf ...
, or nystatin
Nystatin, sold under the brand name Mycostatin among others, is an antifungal medication. It is used to treat ''Candida (fungus), Candida'' infections of the skin including diaper rash, Candidiasis, thrush, esophageal candidiasis, and vaginal ...
cream. Some antifungal creams are combined with corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s such as hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone is the name for the hormone cortisol when supplied as a medication. It is a corticosteroid and works as an anti-inflammatory and by immune suppression. Uses include conditions such as adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenogenit ...
or triamcinolone to reduce inflammation, and certain antifungals such as miconazole also have some antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
action. Diiodohydroxyquinoline is another topical therapy for angular cheilitis. If ''Staphylococcus aureus'' infection is demonstrated by microbiological culture to be responsible (or suspected), the treatment may be changed to fusidic acid cream, an antibiotic which is effective against this type of bacteria. Aside from fusidic acid, neomycin
Neomycin, also known as framycetin, is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against Gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against ...
, mupirocin, metronidazole
Metronidazole, sold under the brand name Flagyl and Metrogyl among others, is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal medication. It is used either alone or with other antibiotics to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, endocarditis, and bacterial vagino ...
, and chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine is a disinfectant and antiseptic which is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to disinfect surgical instruments. It is also used for cleaning wounds, preventing dental plaque, treating yeast infections of the mouth, and ...
are alternative options in this scenario.
Finally, if the condition appears resistant to treatment, investigations for underlying causes such as anemia or nutrient deficiencies or HIV infection. Identification of the underlying cause is essential for treating chronic cases. The lesions may resolve when the underlying disease is treated, e.g. with a course of oral iron or vitamin B supplements. Patch test
A patch test is a diagnostic method used to determine which specific substances cause allergic inflammation of a patient's skin.
Patch testing helps identify which substances may be causing a delayed-type allergic reaction in a patient and ...
ing is recommended by some in cases which are resistant to treatment and where allergic contact dermatitis is suspected.
Prognosis
Most cases of angular cheilitis respond quickly when antifungal treatment is used. In more long standing cases, the severity of the condition often follows a relapsing and remitting course over time. The condition can be difficult to treat and can be prolonged.Epidemiology
AC is a relatively common condition, accounting for between 0.7 – 3.8% of oral mucosal lesions in adults and between 0.2 – 15.1% in children, though overall it occurs most commonly in adults in the third to sixth decades of life. It occurs worldwide, and both males and females are affected. Angular cheilitis is the most common presentation of fungal and bacterial infections of the lips.Etymology
The term ''angular cheilitis'' comes from theAncient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
, meaning 'lip', and ''-itis'', referring to inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
.
References
External links
{{Oral pathology Lip disorders Conditions of the mucous membranes Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate