Altius Space Machines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Altius Space Machines is a subsidiary company of Voyager Space Holdings (Jan 2020), based in Broomfield, CO dedicated to engineering the future in Aerospace.
Core Capabilities
Patent number: US 2019/0241286A1
OneWeb YouTube Video
 An electropermanent magnets (EPM) Is an Altius Space Machines patented technology, which offer numerous benefits over existing mechanical or magnetic interfaces. EPMs are solid-state switchable magnets, with no moving parts and can be put into an unlimited number of form factors
An electropermanent magnets (EPM) Is an Altius Space Machines patented technology, which offer numerous benefits over existing mechanical or magnetic interfaces. EPMs are solid-state switchable magnets, with no moving parts and can be put into an unlimited number of form factors
Patent number: 10984936
Combines the best characteristics of both varieties to provide a desired magnetic field that:
Patent Pending: 20210210267


Altius' Magnetic Tool Changer uses a solid-state switchable EPM magnetic latch and acts as a robotic end-effector. The robotic side connects to a tool side that can have a number of different tools (robotic or traditional). If the tool side is robotic, the tool changer can provide power and data to the tool and use it as if it were hard-wired.
 Altius was selected under NASA's SBIR to develop the Experimental Swarm Construction Hardware EPM based Robotic interface (ESCHER) for NASA's In-Space Assembly (ISA) initiative of modular satellites and space facilities.
NASA Applications
Altius was selected under NASA's SBIR to develop the Experimental Swarm Construction Hardware EPM based Robotic interface (ESCHER) for NASA's In-Space Assembly (ISA) initiative of modular satellites and space facilities.
NASA Applications
 Features:
Features:
 Altius has developed an Electromechanically driven propellant transfer valve for the transfer of fluid or gas.
Contains a paired Active and Passive Assembly for a tolerant fluid coupling.
*Active Assembly mass: <1.2 kg
*Passive Assembly mass: <0.3 kg
*MAWP: 725 PSI
*Total Stroke: 1.75"
*Tolerant of mechanical misalignment and thermal gradients
Altius has developed an Electromechanically driven propellant transfer valve for the transfer of fluid or gas.
Contains a paired Active and Passive Assembly for a tolerant fluid coupling.
*Active Assembly mass: <1.2 kg
*Passive Assembly mass: <0.3 kg
*MAWP: 725 PSI
*Total Stroke: 1.75"
*Tolerant of mechanical misalignment and thermal gradients
- Ideation, Conceptual Design, and Research and Development, Flight Hardware Manufacturing
- System and Architecture Level Ideation and Design
- Electropermanent Magnet (EPM)
- Electrical/Mechanical/Robotics Systems
- Cryogenic Fluid Systems
- Space Environmental Testing Lab (TVAC, Vibe, HALT/HASS)
History
2010–2012
In 2010, Altius Space Machines, with support from theSRI International
SRI International (SRI) is an American nonprofit organization, nonprofit scientific research, scientific research institute and organization headquartered in Menlo Park, California. The trustees of Stanford University established SRI in 1946 as ...
invented the "Sticky Boom" Electroadhesive Boom-Rendezvous system to solve several of the key challenges associated with rendezvous and capture of the Orbiting Sample Canister (OSC) for a Mars Sample Return (MSR) mission. This system significantly improves on previously proposed sample canister capture systems, by providing the following key features:
- High inherent safety — Contact and capture event takes place at a significant distance from the orbiter
- Electromechanical steering for the last few meters of the OS rendezvous and capture process – Reduces rendezvous propellant consumption
- High tolerance for positioning and velocity errors between orbiter and target – Reduces requirements for precision control of orbiter during the capture maneuver.
- Very low mass and volume compared to other solutions
- The same system can capture the OS and transfer it to an Earth Entry Vehicle using the same hardware.
- Provides a simple means of reliable, non-mechanical contact and proximity detection.
- Low-risk solution—booms are based on systems with extensive flight experience, the capture device has seen extensive testing in a terrestrial environment as well as successful preliminary microgravity dynamic testing aboard a parabolic aircraft.
- Small enough for affordable near-term testing in LEO using CubeSat or other rideshare opportunities.
NewSpace Business Plan Competition
Private spaceflight is spaceflight or the development of spaceflight technology that is conducted and paid for by an entity other than a government agency.
In the early decades of the Space Age, the government space agencies of the Soviet Un ...
in Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo Count ...
, sponsored by the Space Frontier Foundation
The Space Frontier Foundation is an American space advocacy nonprofit corporation organized to promote the interests of increased involvement of the private sector, in collaboration with government, in the exploration and development of space. ...
.
Altius won a contract with DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military.
Originally known as the Ad ...
in July 2012 to build a composite extensible robotic
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics integrate ...
boom arm
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between t ...
for the DARPA Phoenix
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military.
Originally known as the Ad ...
project.
They also began work in 2012 developing Gecko-adhesive grippers, as part of work to build a ''Gecko Gripper Touch-to-Grasp tool'' that incorporated JPL
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States.
Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA a ...
’s "synthetic Gecko adhesive technology that mimics the ability of Gecko lizards to adhere to walls." The work leveraged previous work done by Altius on uncooperative capture mechanisms using electroadhesion.
2013–2015
In 2014, Altius began work on a MagnetoShellaerocapture
Aerocapture is an orbital transfer maneuver in which a spacecraft uses
aerodynamic drag force from a single pass through a planetary
atmosphere to decelerate and achieve orbit insertion.
Aerocapture uses a planet's or moon's atmosphere to accom ...
and aerobraking
Aerobraking is a spaceflight maneuver that reduces the high point of an elliptical orbit ( apoapsis) by flying the vehicle through the atmosphere at the low point of the orbit ( periapsis). The resulting drag slows the spacecraft. Aerobraking ...
technology for cubesat
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSat ...
s. Called ''MIDAS'', Multi-Purpose Interplanetary Deployable Aerocapture System, the 6U CubeSats will be designed to be used on an interplanetary mission such as to Mars, Venus, or Jupiter's moon Europa
Other work includes the "Kraken Asteroid Boulder Retrieval System." In late 2014, Altius expects to test prototypes of grasping arms and non-force-closure grip
Grip(s) or The Grip may refer to:
Common uses
* Grip (job), a job in the film industry
* Grip strength, a measure of hand strength
Music
* Grip (percussion), a method for holding a drum stick or mallet
* ''The Grip'', a 1977 album by Arthur Bl ...
per concepts for capturing a boulder
In geology, a boulder (or rarely bowlder) is a rock fragment with size greater than in diameter. Smaller pieces are called cobbles and pebbles. While a boulder may be small enough to move or roll manually, others are extremely massive.
In ...
off the surface of an asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the Solar System#Inner solar system, inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic o ...
. The study is funded by NASA as part of their broader Asteroid Redirect Mission
The Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM), also known as the Asteroid Retrieval and Utilization (ARU) mission and the Asteroid Initiative, was a space mission proposed by NASA in 2013; the mission was later cancelled. The Asteroid Retrieval Roboti ...
(ARM) project and is intended to mature system concepts and key technologies while assessing the feasibility of potential commercial partnerships for ARM.
In 2015 Altius won a contract to build lightweight robotic manipulators, that utilize rollable composite STEM booms to provide a prismatic extension/retraction DOF, as robot arms for Assistive Free-Flyers (AFFs) on the International Space Station. These Low-Inertia STEM Arm (LISA) manipulators can provide comparable or better manipulation capabilities to AFFs than traditional robotic manipulators, but with less mass, lower inertia, better stowability, and the ability to reach into hard-to-access locations.:
2016–2018
2019-Present
Product Line
DogTag™
The DogTag™ is a universal grapple fixture that supports a wide variety of capture methods. :Patent number: US 2019/0241286A1
- Mechanical Grasping
- Snare Capture
- Magnetic Capture
- Gecko Adhesion
- Electrostatic Adhesion
- Chemical Adhesion
- Harpoon Capture
OneWeb YouTube Video
Electropermanent Magnets (EPMs)
 An electropermanent magnets (EPM) Is an Altius Space Machines patented technology, which offer numerous benefits over existing mechanical or magnetic interfaces. EPMs are solid-state switchable magnets, with no moving parts and can be put into an unlimited number of form factors
An electropermanent magnets (EPM) Is an Altius Space Machines patented technology, which offer numerous benefits over existing mechanical or magnetic interfaces. EPMs are solid-state switchable magnets, with no moving parts and can be put into an unlimited number of form factorsPatent number: 10984936
Combines the best characteristics of both varieties to provide a desired magnetic field that:
- Very strong grip – 500 kPa already demonstrated (72.5 psi), theoretically capable of up to 1 MPa (145 psi)
- No power to maintain state, only to change state
- Solid-state, no moving parts
- Simple command and control
- Available in dual-mode (Distance Attraction/Surface Grip/Off) or single-mode (On/Off)
- Magnetic field is tightly constrained and does not create any significant magnetic flux beyond the passive-interface
Dual-Mode EPM
Altius is currently working to develop the Dual-Mode EPM. This EPM will have a "Long-Range Mode" (LRM) and a "Short-Range Mode" (SRM). The LRM will exert meaningful force at a distance of 5 cm, exert slight force at 10–20 cm, and Grip force at contact sufficient to prevent "bouncing off". SRM achieves grip pressure = 200 kPAPatent Pending: 20210210267
EPM Based Products
Altius has developed many products that contain EPM Technology and continues to invent new and innovative products to meet the needs of On-Orbit servicing.= MagTag™
= Altius has developed a MagTag Modular Interface which allows for a new paradigm in spacecraft design, construction, and servicing: an EPM latched electrical and/or fluid connection interface.- Robust: EPMs offer a strong (1 kN) magnetic connection with no moving parts
- Lightweight & Low-profile: <500g total, each interface half can fit within a 10 x 10 x 5 cm envelope
- Latching: EPMs only require power (<20J) to change gripping states from on-to-off and will maintain the latch without active power
- Highly-Capable: The baseline design supports 600W of transferred power at 28V, and over 1Gbit/s data transfer rates
- Launch Lock Capable: MagTags are strong enough to support multi-kg payloads during launch
- Scalable: Arrays of MagTags on a pallet can support a variety of modules and sub-modules for installation
= Magnetic Tool Changer
=

Altius' Magnetic Tool Changer uses a solid-state switchable EPM magnetic latch and acts as a robotic end-effector. The robotic side connects to a tool side that can have a number of different tools (robotic or traditional). If the tool side is robotic, the tool changer can provide power and data to the tool and use it as if it were hard-wired.
- Dust-Tolerant Hermetic Design: Designed without any exposed moving electrical or mechanical parts on either side of the interface.
- High Reliability: Has no moving parts, dramatically increasing the reliability over traditional mechanical tool changers.
- Low Actuation Power: Solid-state switchable magnet design has low peak power consumption (<5W if desired), only consuming power when the magnet is switching from on to off.
- Lightweight/Compact: By eliminating the need for complex mechanical latching systems, the proposed tool changer can be dramatically lighter than traditional mechanical tool changers.
- Tight Reach Capability: The compact EPM tool changer enables the insertion of sampling tools or sensors into much tighter geometric areas than would be possible with a turret or mechanical tool changer design.
- Power and Data Transfer: The Tool Changer is capable of wireless power (inductive) and data transfer >100 watts and up to 870 Mbit/s. Data is transferred usin
Keyssa
technology.
= In-Space Docking & Assembly
== ESCHER (example)
= Altius was selected under NASA's SBIR to develop the Experimental Swarm Construction Hardware EPM based Robotic interface (ESCHER) for NASA's In-Space Assembly (ISA) initiative of modular satellites and space facilities.
NASA Applications
Altius was selected under NASA's SBIR to develop the Experimental Swarm Construction Hardware EPM based Robotic interface (ESCHER) for NASA's In-Space Assembly (ISA) initiative of modular satellites and space facilities.
NASA Applications
- In Space Assembly (ISA) of modular satellites and space facilities
- Rapid assembly/disassembly structures enabling multi-robot missions for collaborative planetary exploration
- Universal interface for swarm assemble-able orbital and planetary structures
- Payload quick swap interface for hosted and replaceable payloads
- UAV interface for docking, recharging, and payload manipulation.
- Universal interface for robotic assembly/disassembly terrestrial structures in remote, harsh environments
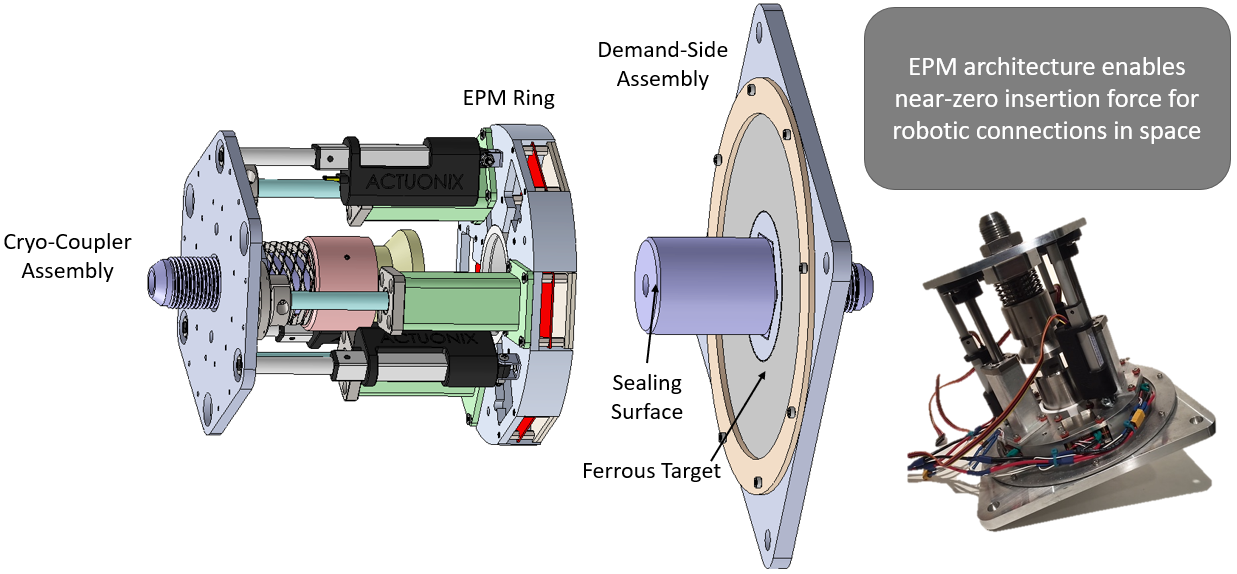
= Cryogenic Fluid Connector for In-Space Refueling
= Features:
Features:
- Designed to re-use existing match-plate valve stems on launch vehicles
- Zero mating force connection using solid-state electro-permanent magnets (EPMs)
- Mating and blowoff forces reacted locally by a dedicated draw-down mechanism consisting of a linear servo array
- Dual poppet for dry disconnect
- Self aligning
- Avg. Helium Leak Rate @ 50psi: 0.00001 cc/sec
- Proof tested to 100psi hydrostatically
- Flow coefficient (water): 4.9-5.3
- Magnetic latch tested up to 1000N (force sensor limit)
- Maximum latching force of 2135 N
Cryo-Coupler v2
Space-Rated Propellant Transfer Valve (PTV)
 Altius has developed an Electromechanically driven propellant transfer valve for the transfer of fluid or gas.
Contains a paired Active and Passive Assembly for a tolerant fluid coupling.
*Active Assembly mass: <1.2 kg
*Passive Assembly mass: <0.3 kg
*MAWP: 725 PSI
*Total Stroke: 1.75"
*Tolerant of mechanical misalignment and thermal gradients
Altius has developed an Electromechanically driven propellant transfer valve for the transfer of fluid or gas.
Contains a paired Active and Passive Assembly for a tolerant fluid coupling.
*Active Assembly mass: <1.2 kg
*Passive Assembly mass: <0.3 kg
*MAWP: 725 PSI
*Total Stroke: 1.75"
*Tolerant of mechanical misalignment and thermal gradients
References
{{coord, 39.9223199589016, -105.1025781309834, region:US_type:landmark, display=title Aerospace companies of the United States