Air Defense Command on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Aerospace Defense Command was a major
 Air Defense Command was activated on 21 March 1946 with the former CAF Fourth Air Force, the inactive Tenth Air Force, and the tbd's Fourteenth Air Force. Second Air Force was reactivated and added on 6 June 1946. In December 1946 the "Development of Radar Equipment for Detecting and Countering Missiles of the German A-4 type" was planned, part of the
Air Defense Command was activated on 21 March 1946 with the former CAF Fourth Air Force, the inactive Tenth Air Force, and the tbd's Fourteenth Air Force. Second Air Force was reactivated and added on 6 June 1946. In December 1946 the "Development of Radar Equipment for Detecting and Countering Missiles of the German A-4 type" was planned, part of the
 The
The
/ref> The F-86D was not ideal, however; its afterburner consumed a great deal of fuel in getting it to altitude, and the pilot was overburdened by cockpit tasks. The F-89D was modified to accept The North American F-108 Rapier was the first proposed successor to the F-106. It was to be capable of Mach 3 performance and was intended to serve as a long-range interceptor that could destroy attacking Soviet bombers over the poles before they could get near US territory. It was also to serve as the escort fighter for the XB-70 Valkyrie Mach-3 strategic bomber, also to be built by North American. The Air Force expected that the first F-108A would be ready for service by early 1963. An order for no less than 480 F-108s was anticipated.
However, by mid-1959, the Air Force was already beginning to experience some doubts about the high cost of the Rapier program. The primary strategic threat from the Soviet Union was now perceived to be its battery of intercontinental ballistic missiles instead of its force of long-range bombers. Against intercontinental ballistic missiles, the F-108A interceptor would be completely useless. In addition, the Air Force was increasingly of the opinion that unmanned intercontinental ballistic missiles could accomplish the mission of the B-70 Valkyrie/F-108 Rapier combination much more effectively and at far lower cost. Consequently, the F-108A project was cancelled in its entirety on 23 September 1959, before any prototypes could be built.
The North American F-108 Rapier was the first proposed successor to the F-106. It was to be capable of Mach 3 performance and was intended to serve as a long-range interceptor that could destroy attacking Soviet bombers over the poles before they could get near US territory. It was also to serve as the escort fighter for the XB-70 Valkyrie Mach-3 strategic bomber, also to be built by North American. The Air Force expected that the first F-108A would be ready for service by early 1963. An order for no less than 480 F-108s was anticipated.
However, by mid-1959, the Air Force was already beginning to experience some doubts about the high cost of the Rapier program. The primary strategic threat from the Soviet Union was now perceived to be its battery of intercontinental ballistic missiles instead of its force of long-range bombers. Against intercontinental ballistic missiles, the F-108A interceptor would be completely useless. In addition, the Air Force was increasingly of the opinion that unmanned intercontinental ballistic missiles could accomplish the mission of the B-70 Valkyrie/F-108 Rapier combination much more effectively and at far lower cost. Consequently, the F-108A project was cancelled in its entirety on 23 September 1959, before any prototypes could be built.
 In 1968, ADCOM began the phaseout of the F-101 and F-102 interceptors from active duty units, with both types mostly being transferred to the Air National Guard. The F-101 would remain in a limited role on active duty until 1982, serving in such roles as towed target carrier aircraft and simulated enemy radar contacts for Airborne Weapons Controller students training for duties aboard the E-3 Sentry AWACS. The F-102 would see service until the mid-1980s as the PQM-102 aerial target drone. The F-106 Delta Dart was the primary air defense interceptor aircraft for the US Air Force during the 1970s and early 1980s. It was also the last dedicated interceptor in U.S. Air Force service to date. It was gradually retired during the 1980s, though the QF-106 drone conversions of the aircraft were used until 1998 as aerial targets under the FSAT program.
In 1968, ADCOM began the phaseout of the F-101 and F-102 interceptors from active duty units, with both types mostly being transferred to the Air National Guard. The F-101 would remain in a limited role on active duty until 1982, serving in such roles as towed target carrier aircraft and simulated enemy radar contacts for Airborne Weapons Controller students training for duties aboard the E-3 Sentry AWACS. The F-102 would see service until the mid-1980s as the PQM-102 aerial target drone. The F-106 Delta Dart was the primary air defense interceptor aircraft for the US Air Force during the 1970s and early 1980s. It was also the last dedicated interceptor in U.S. Air Force service to date. It was gradually retired during the 1980s, though the QF-106 drone conversions of the aircraft were used until 1998 as aerial targets under the FSAT program.
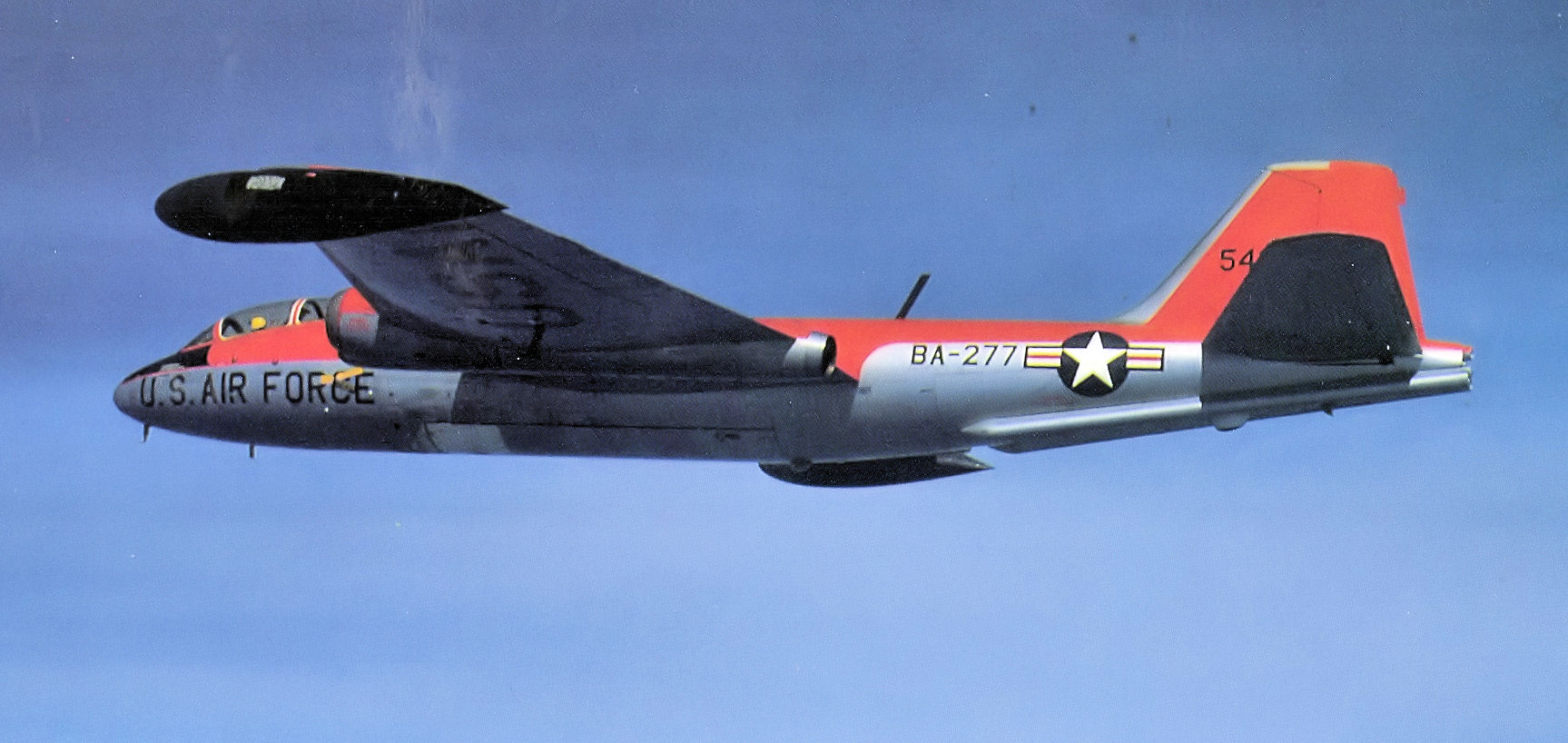 B-57E Canberra dedicated
B-57E Canberra dedicated 
 "Faker", or simulated target aircraft flew mock penetrations into air defense sectors to exercise GDI stations, Air Defense Direction Centers, and interceptor squadrons. Initially using modified B-25 Mitchell and
"Faker", or simulated target aircraft flew mock penetrations into air defense sectors to exercise GDI stations, Air Defense Direction Centers, and interceptor squadrons. Initially using modified B-25 Mitchell and 
 In early 1977 strong Congressional pressure to reduce management "overhead", and the personal conviction of the USAF Chief of Staff that substantial savings could be realized without a reduction in operational capability, moved the final "reorganization" of ADCOM to center stage. Two years of planning followed, but by late 1979 the Air Force was ready to carry it through. It was conducted in two phases:
On 1 October 1979 ADCOM atmospheric defense resources (interceptors, warning radars, and associated bases and personnel) were transferred to Tactical Air Command. They were placed under Air Defense, Tactical Air Command (ADTAC), compatible to a
In early 1977 strong Congressional pressure to reduce management "overhead", and the personal conviction of the USAF Chief of Staff that substantial savings could be realized without a reduction in operational capability, moved the final "reorganization" of ADCOM to center stage. Two years of planning followed, but by late 1979 the Air Force was ready to carry it through. It was conducted in two phases:
On 1 October 1979 ADCOM atmospheric defense resources (interceptors, warning radars, and associated bases and personnel) were transferred to Tactical Air Command. They were placed under Air Defense, Tactical Air Command (ADTAC), compatible to a
command
Command may refer to:
Computing
* Command (computing), a statement in a computer language
* command (Unix), a Unix command
* COMMAND.COM, the default operating system shell and command-line interpreter for DOS
* Command key, a modifier key on A ...
of the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
, responsible for air defense of the continental United States. It was activated in 1968 and disbanded in 1980. Its predecessor, Air Defense Command, was established in 1946, briefly inactivated in 1950, reactivated in 1951, and then redesignated ''Aerospace'' rather than ''Air'' in 1968. Its mission was to provide air defense of the Continental United States (CONUS). It directly controlled all active measures, and was tasked to coordinate all passive means of air defense.
Air defense during World War II
Continental United States air defense forces duringWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
were initially under the command of the four air districts – Northeast Air District, Northwest Air District, Southeast Air District, and Southwest Air District. The air districts were established on 16 January 1941, before the Pearl Harbor attack. The four air districts also handled USAAF combat training with the Army Ground Forces
The Army Ground Forces were one of the three autonomous components of the Army of the United States during World War II, the others being the Army Air Forces and Army Service Forces. Throughout their existence, Army Ground Forces were the la ...
and "organization and training of bomber, fighter and other units and crews for assignments overseas". The air districts were redesignated on 26 March 1941 as the First Air Force, Second Air Force, Third Air Force, and Fourth Air Force
The Fourth Air Force (4 AF) is a numbered air force of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC). It is headquartered at March Air Reserve Base, California.
4 AF directs the activities and supervises the training of more than 30,000 Air Force Reserv ...
. The First and Fourth Air Forces, through their interceptor commands, managed the civilian Aircraft Warning Service on the East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and West
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance langu ...
coasts, respectively.
The USAAF's Aircraft Warning Corps provided air defense warning with information centers that networked an area's " Army Radar Stations" which communicated radar tracks by telephone. The AWC information centers also integrated visual reports processed by Ground Observer Corps filter centers. AWC information centers notified air defense command posts of the " 4 continental air forces" for deploying interceptor aircraft which used command guidance
Command guidance is a type of missile guidance in which a ground station or aircraft relay signals to a guided missile via radio control or through a wire connecting the missile to the launcher and tell the missile where to steer to intercept its ...
for ground-controlled interception
Ground-controlled interception (GCI) is an air defence tactic whereby one or more radar stations or other observational stations are linked to a command communications centre which guides interceptor aircraft to an airborne target. This tactic wa ...
. The USAAF inactivated the aircraft warning network in April 1944.
Continental Air Forces
Continental Air Forces (CAF) was activated on 12 December 1944, including the four Air Forces, to bring the continental air defense task under one command. AAF Regulation 20-1, dated 15 September 1945, specified the post-war CAF mission. For aircraft warning, in 1945 CAF had recommended "research and development be undertaken on radar and allied equipment for an air defense system orthe future threat", e.g., a "radar ithrange of 1,000 miles, o detectat an altitude of 200 miles, and at a speed of 1,000 miles per hour". HQ AAF responded that "until the kind of defense needed to counter future attacks could be determined, AC&W planning would have to be restricted to the use of available radar sets". CAF's January 1946 ''Radar Defense Report for Continental United States'' recommended military characteristics for a post-war Air Defense System "based upon such advanced equipment", and the HQ AAF Plans reminded "the command that radar defense planning had to be based on the available equipment." Reorganization of Continental Air Forces began in 1945, when ground radar and interceptor plans were prepared for the transfer at CAF HQ in the expectation that 'it would become Air Defense Command.' CAF installations that were transferred to ADC included Mitchel Field (21 March 1946), Hamilton Army Airfield (21 March 1946), Myrtle Beach Army Air Field (27 March 1946), Shaw Field (1 April 1946), McChord Field (1 August 1946), Grandview Army Air Field (1 January 1952), Seymour Johnson Field (1 April 1956), and Tyndall Field (1 July 1957).Air Defense Command 1946
Signal Corps
A signal corps is a military branch, responsible for military communications (''signals''). Many countries maintain a signal corps, which is typically subordinate to a country's army.
Military communication usually consists of radio, telephone, ...
' Project 414A. The Distant Early Warning Line was "first conceived—and rejected—in 1946".
A 1947 proposal for 411 radar stations and 18 control centers costing $600 million was the Project Supremacy plan for a postwar Radar Fence that was rejected by Air Defense Command since "no provision was made in it for the Alaska to Greenland net with flanks guarded by aircraft and picket ships equiredfor 3 to 6 hours of warning time", and "Congress failed to act on legislation required to support the proposed system". (In the spring and summer of 1947, 3 ADC AC&W plans had gone unfunded.) By 1948 there were only 5 AC&W stations, including the Twin Lights station in NJ that opened in June and Montauk NY "Air Warning Station #3 (5 July)--cf.
The abbreviation cf. (short for either Latin or , both meaning 'compare') is generally used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. However some sources offer differing or even contr ...
SAC radar stations, e.g., at Dallas
Dallas () is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of Texas metropolitan areas, most populous metropolitan area in Texas and the Metropolitan statistical area, fourth-most ...
& Denver
Denver ( ) is a List of municipalities in Colorado#Consolidated city and county, consolidated city and county, the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Colorado, most populous city of the U.S. state of ...
Bomb Plots.
ADC became a subordinate operational command of Continental Air Command on 1 December 1948 and on 27 June 1950, United States air defense systems began 24-hour operations two days after the start of the Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was s ...
. By the time ADC was inactivated on 1 July 1950, ADC had deployed the Lashup Radar Network with existing radars at 43 sites. In addition, 36 Air National Guard fighter units were called to active duty for the mission.
Reformation 1951
ADC was reinstated as a major command on 1 January 1951 at Mitchel Air Force Base, New York. A rudimentary command centre was established that year from a former hallway/latrine area. The headquarters was moved to Ent Air Force Base in Colorado Springs on 8 January 1951. It received 21 former ConAC active-duty fighter squadrons (37 additional Air National Guard fighter squadrons if called to active duty). ADC was also assigned the 25th, 26th 27th and 28th Air Divisions (Defense) ADC completed the Priority Permanent System network for Aircraft Warning and Control (ground-controlled interception
Ground-controlled interception (GCI) is an air defence tactic whereby one or more radar stations or other observational stations are linked to a command communications centre which guides interceptor aircraft to an airborne target. This tactic wa ...
) in 1952. Gaps were filled by additional Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is a Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government agency within the United States Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Transportation that regulates civil aviation in t ...
(FAA) radar stations and the Ground Observation Corps
The Ground Observer Corps (GOC), sometimes erroneously referred to as the Ground ''Observation'' Corps, was the name of two American civil defense organizations during the middle 20th century.
World War II organization
The first Ground Observer ...
(disbanded 1959). In May 1954, ADC moved their initial, rudimentary command center into a "much improved 15,000-square-foot concrete block" building with "main battle control center".
During the mid-1950s, planners devised the idea of extending the wall of powerful land-based radar seaward with Airborne early warning and control
An airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) system is an airborne radar early warning system designed to detect aircraft, ships, vehicles, missiles and other incoming projectiles at long ranges, as well as performing command and control of the ...
units. This was done by equipping two wings of Lockheed RC-121 Warning Star aircraft, the 551st Airborne Early Warning and Control Wing, based at Otis Air Force Base, Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, and the 552nd AEWCW, based at McClellan Air Force Base
McClellan Air Force Base (1935–2001) is a former United States Air Force base in California, located in the North Highlands, California, North Highlands area of Sacramento County, California, Sacramento County, northeast of Sacramento, Califo ...
, California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, one wing stationed on each coast. The RC-121s, EC-121s and Texas Towers, it was believed, would contribute to extending contiguous east-coast radar coverage some 300 to 500 miles seaward. In terms of the air threat of the 1950s, this meant a gain of at least 30 extra minutes warning time of an oncoming bomber attack. ADC's Operation Tail Wind on 11–12 July tested its augmentation plan that required Air Training Command interceptors participate in an air defense emergency. A total of seven ATC bases actively participated in the exercise, deploying aircraft and aircrews and supporting the ADC radar net. As the USAF prepared to deploy the Tactical Air Command
Tactical Air Command (TAC) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. It was a List of Major Commands of the United States Air Force, Major Command of the United States Air Force, established on 21 March 1946 and headquartered at Lang ...
E-3 Sentry in the later 1970s, active-duty units were phased out EC-121 operations by the end of 1975. All remaining EC-121s were transferred to the Air Force Reserve
The Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC) is a major command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force, with its headquarters at Robins Air Force Base, Georgia. It is the federal Air Reserve Component (ARC) of the U.S. Air Force, consisting of commis ...
, which formed the 79th AEWCS at Homestead Air Force Base, Florida in early 1976. The active duty force continued to provide personnel to operate the EC-121s on a 24-hour basis, assigning Detachment 1, 20th Air Defense Squadron to Homestead AFB as associate active duty crews to fly the Reserve-owned aircraft. Besides monitoring Cuban waters, these last Warning Stars also operated from NAS Keflavik, Iceland. Final EC-121 operations ended in September 1978.
Air and Aerospace Defense Command
United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
activated Air Defense Command (ADC) in 1946, with a Numbered Air Force
A Numbered Air Force (NAF) is a type of organization in the United States Air Force that is subordinate to a List of Major Commands of the United States Air Force, major command (MAJCOM) and has assigned to it operational units such as wings, squ ...
of the former Continental Air Forces, from which it took its mission of air warning and air defense. In September 1947, it became part of the newly established United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
. The command become a subordinate organization of Continental Air Command (ConAC) on 1 December 1948. ConAC gradually assumed direct charge of ADC air defense components, and ADC inactivated on 1 July 1950. But five months later, on 10 November 1950, Generals Vandenberg and Twining notified General Ennis C. Whitehead that "the Air Force had approved activation of a separate Air Defense Command CONAC">Continental_Air_Command.html" ;"title="rom Continental Air Command">CONACwith headquarters on Ent Air Force Base">Ent." The new command's mission was to be to stop a handful of conventionally armed piston engine-powered bombers on a one-way mission. The command was formally reactivated on 1 January 1951.
With advances in Soviet bombers, ADC completed improved radar networks and manned interceptors in the 1950s. At the end of the decade it computerized Air Defense Direction Centers to allow air defense controllers to more quickly review integrated military air defense warning (MADW) data and dispatch defenses (e.g., surface-to-air missiles in 1959). ADC began missile warning and space surveillance missions in 1960 and 1961, and established a temporary missile warning network for the 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis () in Cuba, or the Caribbean Crisis (), was a 13-day confrontation between the governments of the United States and the Soviet Union, when American deployments of Nuclear weapons d ...
. In 1968 it was redesignated Aerospace Defense Command (ADCOM).
In 1975, ADCOM became a specified command and the United States' executive agent in the North American Air Defense Command—the single CINCNORAD/CINCAD commanded both. ADCOM's last surface-to-air missiles were taken off alert in 1972, and the Federal Aviation Administration
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is a Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government agency within the United States Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Transportation that regulates civil aviation in t ...
took over many of ADCOM's SAGE radar stations
The SAGE radar stations of Air Defense Command (Aerospace Defense Command after 1968) were the military installations operated by List of United States Air Force aircraft control and warning squadrons, USAF squadrons using the first automated air d ...
.
Tactical Air Command and ADTAC
On 1 October 1979 ADCOM interceptors/bases and remaining air warning radar stations transferred toTactical Air Command
Tactical Air Command (TAC) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. It was a List of Major Commands of the United States Air Force, Major Command of the United States Air Force, established on 21 March 1946 and headquartered at Lang ...
(TAC), with these "atmospheric" units assigned to Air Defense, Tactical Air Command (ADTAC). ADCOM's missile warning and space surveillance installations transferred in 1979 to the Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile compon ...
's Directorate of Space and Missile Warning Systems (SAC/SX),) and the North American Aerospace Defense Command
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ; , CDAAN), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a Combined operations, combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air ...
's Air Force Element, NORAD/ADCOM (AFENA), which was redesignated the Aerospace Defense Center. The command was inactivated on 31 March 1980.
With the disestablishment of TAC and SAC in 1992, the Aerospace Defense Center, the ADCOM specified command organizations, along with SAC's missile warning and space surveillance installations. became part of Air Force Space Command
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere ...
(AFSPC). Air Force Space Command activated its headquarters in the same Chidlaw Building where ADCOM had been inactivated.
Chronology of major events
*27 March 1946: The United States Army Air Force activates the Air Defense Command at Mitchel Field, New York *1 December 1948: Air Defense Command became a component of Continental Air Command *1 July 1950: Air Defense Command inactivated because the Continental Air Command gradually assumed full charge of United States air defense *1 January 1951: Air Defense Command reestablished at Mitchel AFB *8 January 1951: Air Defense Command headquarters moved to Ent Air Force Base, Colorado * 1 October 1953: The 4701st Airborne Early Warning and Control Squadron, the first AEW&C system, was activated at McClellan AFB, California. *15 April 1957: Air Defense Command assigned operational control of the DEW Line and all atmospheric defense units of the inactivated Northeast Air Command. *12 September 1957: NORAD is established at Ent AFB with Canadian Air Defense Command air defense units and United States Continental Air Defense Command air defense units *1 December 1958: SAGE Combat Center No 1 at Hancock Field, New York became operational *1 January 1959: The first BOMARC squadron, the 46th Air Defense Missile Squadron was activated at McGuire AFB, New Jersey. *30 September 1960: ADC's BMEWS Central Computer and Display Facility at Ent AFB achieved initial operational capability, providing missile warning to SAC andThe Pentagon
The Pentagon is the headquarters building of the United States Department of Defense, in Arlington County, Virginia, across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C. The building was constructed on an accelerated schedule during World War II. As ...
*1 July 1961: ADC took over the Laredo and Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger, more populous island of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, the country. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is the southernmost island in ...
missile and space vehicle tracking stations
*15 January 1968: Air Defense Command is redesignated as Aerospace Defense Command (ADCOM)
*1 July 1975: Aerospace Defense Command designated a "Specified Command" taking over Continental Air Defense Command roles and responsibilities
*1 October 1975: Alaskan ADCOM Region established, Aerospace Defense Command assumes control of missile warning and space surveillance forces of Alaskan Air Command
*29 May 1979: The USAF made a public announcement of its plans to reorganize its aerospace defense forces. Consequently, the USAF inactivated ADCOM as a major command and reassigned its resources to other commands.
*31 March 1980: Aerospace Defense Command inactivated at the Chidlaw Building in Colorado Springs, Colorado.
Interceptor Aircraft
ADC had four day-type fighter squadrons (FDS) in 1946. The ADC interceptor force grew to ninety-three (93) active Air Force fighter interceptor squadrons, seventy-six (76)Air National Guard
The Air National Guard (ANG), also known as the Air Guard, is a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States Air Force, as well as the air militia (United States), militia of each U.S. ...
fighter interceptor squadrons, several U.S. Navy fighter squadrons, USAF and USN airborne early warning squadrons, radar squadrons, training squadrons, and numerous support units that have played important roles in our nation's defense.
The first ADC interceptor, the P-61 Black Widow, did not have the capabilities to engage the Soviet Tu-4 bomber. Its successor, the F-82 Twin Mustang, was even more disappointing. It took a long time to get into production and did not perform well in inclement weather.
The early jet fighters, such as the F-80 Shooting Star and F-84 Thunderjet, lacked all-weather capability and were deemed useless for air defense purposes. Much hope was placed on two jet-powered interceptors, the XP-87 Blackhawk and the XP-89 Scorpion. (Designations changed to XF-87 and XF-89.) They, in turn, also proved to be inadequate: the XF-87 was cancelled and the Scorpion underwent extensive redesign.
The first-generation jets gave way to all-weather dedicated interceptor jets. The F-94 Starfire was pressed into service as an "interim" interceptor, and North American in 1949 pushed an interceptor version of the Sabre, the F-86D. Despite the demands its complexity made upon a single pilot, the F-86D was backed by senior Air Force officials. Some 2,504 would be built and it would in time be the most numerous interceptor in the Air Defense Command fleet, with more than 1,000 in service by the end of 1955Baugher – North American F-86D Sabre/ref> The F-86D was not ideal, however; its afterburner consumed a great deal of fuel in getting it to altitude, and the pilot was overburdened by cockpit tasks. The F-89D was modified to accept
AIM-4 Falcon
The Hughes AIM-4 Falcon was the first operational guided air-to-air missile of the United States Air Force. Development began in 1946; the weapon was first tested in 1949. The missile entered service with the USAF in 1956.
Produced in both heat- ...
guided missiles (F-89H) and AIR-2 Genie atomic warhead rockets (F-89J) as armament. The F-86D was modified (F-86L) to include an FDDL SAGE data link that permitted automatic ground control. The F-86L and F-89H became available in 1956, and the F-89J in 1957.
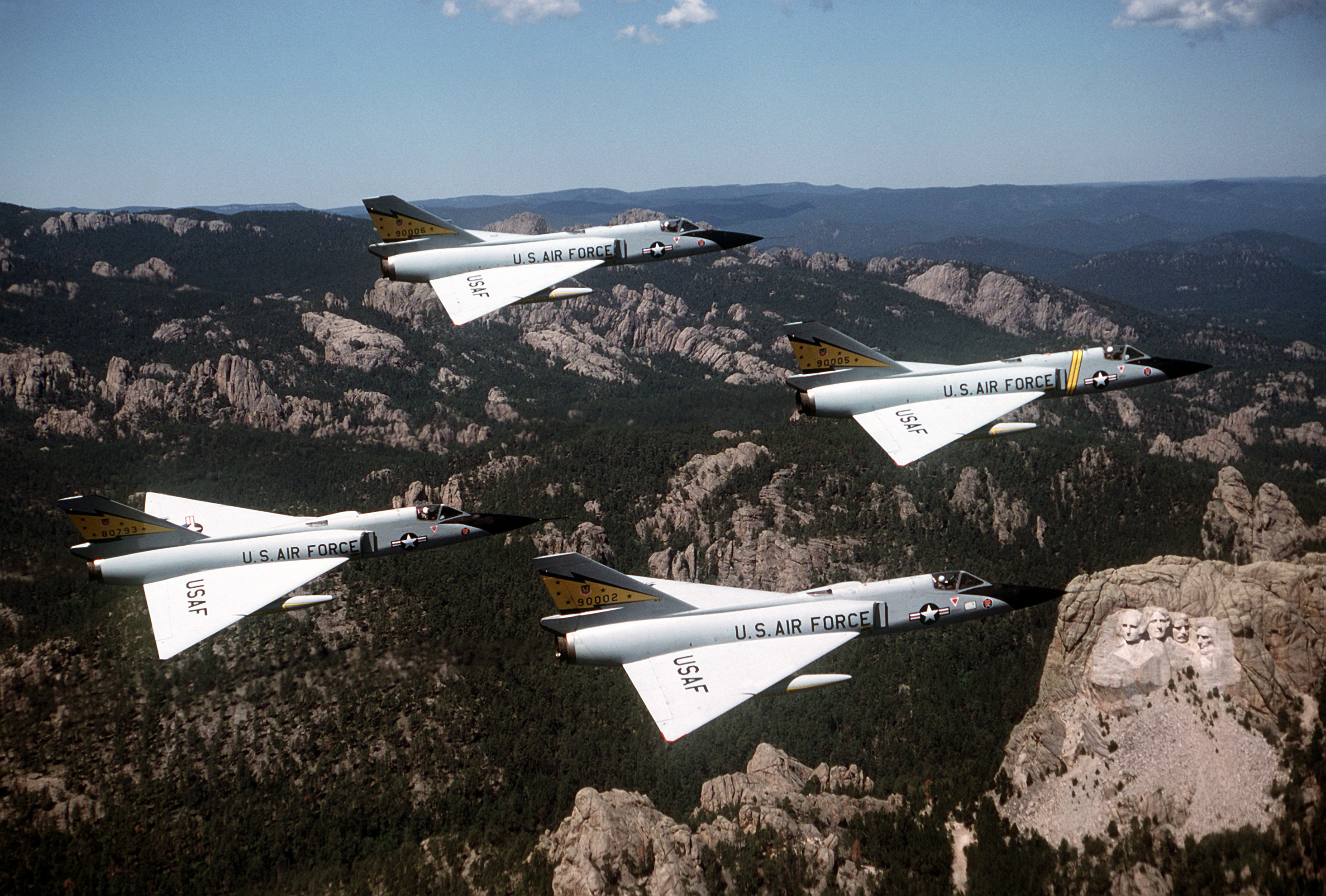
The first of the Century Series supersonic interceptors was the F-102A Delta Dagger in 1956, followed by the F-104A Starfighter in 1958. The F-101B Voodoo and F-106 Delta Dart were first received by ADC during the first half of 1959. By 1960, the ADC interceptor force was composed of the F-101, F-104, F-106, and the F-102.USAF Aerospace Defense Command publication, The Interceptor, January 1979 (Volume 21, Number 1).
 The North American F-108 Rapier was the first proposed successor to the F-106. It was to be capable of Mach 3 performance and was intended to serve as a long-range interceptor that could destroy attacking Soviet bombers over the poles before they could get near US territory. It was also to serve as the escort fighter for the XB-70 Valkyrie Mach-3 strategic bomber, also to be built by North American. The Air Force expected that the first F-108A would be ready for service by early 1963. An order for no less than 480 F-108s was anticipated.
However, by mid-1959, the Air Force was already beginning to experience some doubts about the high cost of the Rapier program. The primary strategic threat from the Soviet Union was now perceived to be its battery of intercontinental ballistic missiles instead of its force of long-range bombers. Against intercontinental ballistic missiles, the F-108A interceptor would be completely useless. In addition, the Air Force was increasingly of the opinion that unmanned intercontinental ballistic missiles could accomplish the mission of the B-70 Valkyrie/F-108 Rapier combination much more effectively and at far lower cost. Consequently, the F-108A project was cancelled in its entirety on 23 September 1959, before any prototypes could be built.
The North American F-108 Rapier was the first proposed successor to the F-106. It was to be capable of Mach 3 performance and was intended to serve as a long-range interceptor that could destroy attacking Soviet bombers over the poles before they could get near US territory. It was also to serve as the escort fighter for the XB-70 Valkyrie Mach-3 strategic bomber, also to be built by North American. The Air Force expected that the first F-108A would be ready for service by early 1963. An order for no less than 480 F-108s was anticipated.
However, by mid-1959, the Air Force was already beginning to experience some doubts about the high cost of the Rapier program. The primary strategic threat from the Soviet Union was now perceived to be its battery of intercontinental ballistic missiles instead of its force of long-range bombers. Against intercontinental ballistic missiles, the F-108A interceptor would be completely useless. In addition, the Air Force was increasingly of the opinion that unmanned intercontinental ballistic missiles could accomplish the mission of the B-70 Valkyrie/F-108 Rapier combination much more effectively and at far lower cost. Consequently, the F-108A project was cancelled in its entirety on 23 September 1959, before any prototypes could be built.
 In 1968, ADCOM began the phaseout of the F-101 and F-102 interceptors from active duty units, with both types mostly being transferred to the Air National Guard. The F-101 would remain in a limited role on active duty until 1982, serving in such roles as towed target carrier aircraft and simulated enemy radar contacts for Airborne Weapons Controller students training for duties aboard the E-3 Sentry AWACS. The F-102 would see service until the mid-1980s as the PQM-102 aerial target drone. The F-106 Delta Dart was the primary air defense interceptor aircraft for the US Air Force during the 1970s and early 1980s. It was also the last dedicated interceptor in U.S. Air Force service to date. It was gradually retired during the 1980s, though the QF-106 drone conversions of the aircraft were used until 1998 as aerial targets under the FSAT program.
In 1968, ADCOM began the phaseout of the F-101 and F-102 interceptors from active duty units, with both types mostly being transferred to the Air National Guard. The F-101 would remain in a limited role on active duty until 1982, serving in such roles as towed target carrier aircraft and simulated enemy radar contacts for Airborne Weapons Controller students training for duties aboard the E-3 Sentry AWACS. The F-102 would see service until the mid-1980s as the PQM-102 aerial target drone. The F-106 Delta Dart was the primary air defense interceptor aircraft for the US Air Force during the 1970s and early 1980s. It was also the last dedicated interceptor in U.S. Air Force service to date. It was gradually retired during the 1980s, though the QF-106 drone conversions of the aircraft were used until 1998 as aerial targets under the FSAT program.
Interceptor gunnery training
 B-57E Canberra dedicated
B-57E Canberra dedicated Air Defense Command
Aerospace Defense Command was a major command (military formation), command of the United States Air Force, responsible for air defense of the continental United States. It was activated in 1968 and disbanded in 1980. Its predecessor, Air De ...
target towing aircraft were used for training of F-86D Sabre, F-94C Starfire, and F-89D Scorpion interceptors firing 2.75-inch Mk 4/Mk 40 Folding-Fin Aerial Rockets. Due to the nature of air-to-air weapon training requiring a large amount of air space, only a few locations were available for practice ranges. ADC assigned these aircraft to bases close to these large, restricted areas, and fighter-interceptor squadrons deployed to these bases for this type of "hot fire" training which took place in these ranges.
The gunnery schools were located at Yuma AFB, Arizona ( 17th Tow Target Squadron (TTS)), and later moved to MacDill AFB
MacDill Air Force Base (MacDill AFB) is an active United States Air Force installation located 4 miles (6.4 km) south-southwest of downtown Tampa, Florida.
The "host wing" for MacDill AFB is the 6th Air Refueling Wing (6 ARW), assig ...
, Florida where the training continued over the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
. With the move to Florida, the 3d TTS was formed at George AFB, California which performed training over the Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert (; ; ) is a desert in the rain shadow of the southern Sierra Nevada mountains and Transverse Ranges in the Southwestern United States. Named for the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous Mohave people, it is located pr ...
in Southern California. Additional units were located at Biggs AFB, near El Paso, Texas (1st TTS) and the 4756th TTS was located at Tyndall AFB, Florida to support the Fighter Weapons Center located there. ADC also supported overseas training at Johnson AB, Japan (the 6th Tow Target Squadron). From Johnson AB, B-57Es deployed to Clark AB, Philippines; Andersen AFB, Guam, Naha AB, Okinawa and Itazuke AB, Misawa AB and Yokota AB, all in Japan for training of the interceptor squadrons assigned to those bases. The 6th TTS was inactivated by late 1957 and the Canberra trainers were designated a flight of the 8th Bombardment Squadron at Johnson AB. In Europe, USAFE supported a squadron of B-57E gunnery trainers at Wheelus AB, Libya where European-based interceptors deployed for "live firing" over the vast desert range there.
To provide challenges for interceptors, The B-57Es towed styrofoam, bomb-shaped radar reflectant targets. These could be towed at higher altitudes than the high-drag 45' banners but hits could still be scored on them. By 1960, the rocket firing interceptors were giving way to F-102 Delta Dagger interceptors firing heat-seeking AIM-4 Falcon
The Hughes AIM-4 Falcon was the first operational guided air-to-air missile of the United States Air Force. Development began in 1946; the weapon was first tested in 1949. The missile entered service with the USAF in 1956.
Produced in both heat- ...
air-to-air missiles. This made the target towing mission of the B-57E obsolete, and the B-57Es were adapted to electronic countermeasures and faker target aircraft (EB-57E) (see below).
In order to cover combat losses in the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
caused by two major ground explosions, twelve B-57Es were reconfigured as combat-capable B-57Bs at the Martin factory in late 1965 and were deployed to Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
for combat bombardment operations. Six other B-57Es were converted to RB-57E "Patricia Lynn" tactical reconnaissance aircraft in 1966 during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
, operating from Tan Son Nhut Air Base until 1971.

Interceptor Missiles (IMs)
The Bomarc Missile Program delivered the first CIM-10 Bomarc supersonicsurface-to-air missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground or the sea to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-ai ...
to ADC during September 1959 at Fort Dix's BOMARC Base No. 1 near the missile launch control center on McGuire AFB (groundbreaking for McGuire's Air Defense Direction Center to house the IBM AN/FSQ-7 Combat Direction Central for Bomarc ground-controlled interception
Ground-controlled interception (GCI) is an air defence tactic whereby one or more radar stations or other observational stations are linked to a command communications centre which guides interceptor aircraft to an airborne target. This tactic wa ...
had been in 1957.) To ensure probability of kill before bombers could drop their weapons, the AN/FSQ-7 used the Automatic Target and Battery Evaluation
Automatic may refer to:
Music Bands
* Automatic (Australian band), Australian rock band
* Automatic (American band), American rock band
* The Automatic, a Welsh alternative rock band
Albums
* ''Automatic'' (Jack Bruce album), a 1983 el ...
(ATABE) to determine which bombers/formations to assign to which manned interceptor base (e.g., using nuclear air-to-air missiles), which to assign to Bomarcs (e.g., with W-40 nuclear warheads) and if available, which to assign to the region's Nike Army Air Defense Command Post
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
(that also had ATABE software for efficiently coordinating fire from multiple Hercules missile batteries.) Bomarc missiles bases were along the east and west coasts of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
and the central areas of the continent (e.g., Suffolk County Missile Annex was on Long Island, New York
Long Island is a densely populated continental island in southeastern New York (state), New York state, extending into the Atlantic Ocean. It constitutes a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land are ...
.) The supersonic Bomarc missiles were the first long-range anti-aircraft missiles in the world, and the longer range BOMARC B models required less time after erected until they could be launched.Gibson, James (2000), Nuclear Weapons of the United States: An Illustrated History, Schiffer Publishing, Ltd .
Defense Systems Evaluation
 "Faker", or simulated target aircraft flew mock penetrations into air defense sectors to exercise GDI stations, Air Defense Direction Centers, and interceptor squadrons. Initially using modified B-25 Mitchell and
"Faker", or simulated target aircraft flew mock penetrations into air defense sectors to exercise GDI stations, Air Defense Direction Centers, and interceptor squadrons. Initially using modified B-25 Mitchell and B-29 Superfortress
The Boeing B-29 Superfortress is a retired American four-engined Propeller (aeronautics), propeller-driven heavy bomber, designed by Boeing and flown primarily by the United States during World War II and the Korean War. Named in allusion to ...
bombers, the aircraft would fly attack profile missions at unexpected, random times and attempt to evade coverage by flying at low altitudes and randomly flying in different directions to confuse interceptors. The aircraft were modified to carry electronic countermeasures (ECM) gear to attempt to confuse radar operators. In 1957, the propeller-driven aircraft were phased out and replaced by Martin B-57 medium bombers which were being phased out of Tactical Air Command. Initially RB-57As from reconnaissance units were modified to have their former camera bays refitted to carry out the latest ECM systems to confuse the defenders. Wing racks, originally designed for bombs, now carried chaff dispensers and the navigator position was replaced with an Electronic Warfare Officer (EWO). The modified B-57s were designated as EB-57 (E for special electronic installation).Mikesh, Robert C. Martin B-57 Canberra: The Complete Record.Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing Ltd., 1995. .
Considerable realism would be generated into these simulated aggressor attack missions being flown by the B-57 crews. Often several EB-57s were used to form separate tracks and provide a coordinated jamming attack to complicate the testing. When inside the range of the GCI radar, and in anticipation of interception, chaff was dispensed to confuse the defense force and electronic pulses to jam radar signals were turned on. It was up to the defending interceptors and GCI stations to sort out the correct interception.
Units operating these specially equipped aircraft were designated Defense Systems Evaluation Squadrons (DSES). The 4713th Defense Systems Evaluation Squadron was stationed for training in the Northeast. The 4713th also deployed frequently to USAFE in West Germany for training of NATO forces. The other was the 4677th Defense Systems Evaluation Squadron, which concentrated on Fighter Interceptor Squadron training for units in the Western United States. In 1974, the 4713th DSES was inactivated and its EB-57s were divided between two Air National Guard units and the 4677th DSES was redesignated as the 17th Defense Systems Evaluation Squadron
The 17th Defense Systems Evaluation Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 24th Air Division of Aerospace Defense Command at Malmstrom AFB, Montana. It was inactivated on 13 July 1979.
The squadron ( ...
. This unit was inactivated in July 1979 and was the last to fly B-57s in the active duty USAF. It shared the Defense Systems Evaluation mission with the Kansas and Vermont Air National Guard. Defense Systems Evaluation operations were also carried out by the 6091st Reconnaissance Squadron, Yokota AB, Japan; later the 556th Reconnaissance Squadron and moved to Kadena AB, Okinawa. EB-57s were also deployed to Alaskan Air Command, Elmendorf AFB, Alaska, frequently.
The 134th Defense Systems Evaluation Squadron, Vermont Air National Guard, retired its last EB-57 in 1983, and the operational use of the B-57 Canberra ended. ADC supported 4-story SAGE blockhouses were hardened for overpressures of . NORAD sector direction center (NSDCs) also had air defense artillery
The Air Defense Artillery Branch is the Anti-aircraft warfare, air defense branch of the United States Army, specializing in the use of anti-aircraft weapons (such as surface-to-air missiles) to conduct anti-aircraft warfare operations. In the ...
director (ADAD) consoles nd an ArmyADA battle staff officer." The sector direction centers automatically communicated crosstelling of "SAGE reference track data" to/from adjacent sectors' DCs and to 10 Project Nike Missile Master Army Air Defense Command Post
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
s.

Continental defense
From 1 September 1954 until 1975, ADC was a component of the unified Continental Air Defense Command (CONAD) along with the Army's ARAACOM (1957 ARADCOM) and until 1965, the Navy's NAVFORCONAD. The USAF as the executive CONAD agent initially used ADC's: *General Benjamin Chidlaw as CINCONAD, *headquarters staff and ADC HQ building for the unified command staff, and *new blockhouse for the unified command center ADC'a Permanent System radar stations were used for CONAD target data, along with Navy picket ships ( Atlantic and Pacific Barrier until 1965) and Army Project Nike "target acquisition radars". A CONAD reorganization that started in 1956 created a separate multi-service CONAD headquarters staff (with an Air Force Element), separated command of ADC from CINCONAD, and in 1957 added Alaskan Air Command and Northeast Air Command components to ADC Former NEAC installations in the smaller "Canadian Northeast Area" were transferred to the Canadian Air Defence Command. (e.g., the Hall Beach DEW Line station constructed 1955–1957--cf.
The abbreviation cf. (short for either Latin or , both meaning 'compare') is generally used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. However some sources offer differing or even contr ...
Canada's Hopedale stations of the 1954 Pinetree Line and 1957 Mid-Canada Line.)
64th Air Division personnel were assigned to main stations of the 1957 DEW Line and annually inspected auxiliary/intermediate DEW stations maintained by the "DEW M&O Contractor." On 1 March 1957 CONAD reduced the number of ADC interceptor squadrons on alert for the Air Defense Identification Zone. "At the end of 1957, ADC operated 182 radar stations…32 had been added during the last half of the year as low-altitude, unmanned gap-filler radars. The total consisted of 47 gap-filler stations, 75 Permanent System radars, 39 semimobile radars, 19 Pinetree stations,…1 Lashup eraradar and a single Texas Tower". After the NORAD agreement was signed on 12 May 1958, ADC became a NORAD component.
;SAGE: The Semi-Automatic Ground Environment
The Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) was a system of mainframe computer, large computers and associated computer network, networking equipment that coordinated data from many radar sites and processed it to produce a single unified image ...
(SAGE) for radar operators was installed at ADC's general surveillance stations by deploying Burroughs AN/FST-2 Coordinate Data Transmitting Set electronics. Implementation of the SAGE Geographic Reorganization Plan of 25 July 1958 activated new ADC military installations, e.g., GATR stations for vectoring manned interceptors as well as BOMARC missile launch complexes with nearby GAT Facilities. On 20 December 1958 NORAD approved the "USAF ADC Plan" which included 10 Super Combat Centers (SCCs) in underground bunkers to replace 5 above-ground Combat Centers remaining to be built. Modification of FAA radars to the ARSR-1A configuration (Amplitron, "antenna gear box modification", etc.) were to be complete by November 1960 (e.g., at the Fort Heath radar station) and all 3 Texas Towers were in-service by April 1959 with ADC detachments/radars on offshore platforms near the New England coast, and the Continental Air Defense Integration North schedule for gap-filler radars included those for "P-20F, London, Ontario
London is a city in southwestern Ontario, Canada, along the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor. The city had a population of 422,324 according to the 2021 Canadian census. London is at the confluence of the Thames River (Ontario), Thames River and N ...
; C-4-C, Brampton, Ontario
Brampton is a city in the Canadian Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Ontario, and the regional seat of the Regional Municipality of Peel. It is part of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) and is a List of municipalities in Ontario#L ...
; C-5-C, Mt Carleton, New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
; and C-6-D, Les Etroits. Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
"—in the spring of 1959, ADC requested the Air Defense Systems Integration Division to study accelerating the scheduled 1962 deployment of those 4 sites." After the planned SCCs were cancelled in 1960, the SAGE System was augmented by the " pre-SAGE semiautomatic intercept system" for Backup Interceptor Control as at North Bend AFS in February 1962 ( BUIC II first at North Truro AFS in 1966.)
By 30 June 1958, the planned ADC anti-ICBM processing facility to coordinate the ABM missile fire was considered "the heart of the entire lannedballistic missile defense system (conceived to have Nike Zeus
Nike Zeus was an anti-ballistic missile (ABM) system developed by the United States Army during the late 1950s and early 1960s that was designed to destroy incoming Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile warheads before they could hit their ...
and Wizard missiles.) On 19 October 1959, HQ USAF assigned ADC the "planning responsibility" for eventual operations of the Missile Defense Alarm System to detect ICBM launches with infrared sensors on space vehicles.
Missile warning and space surveillance
ADC's BMEWS Central Computer and Display Facility was built as an austere network center (instead of for coordinating anti-ICBM fire) which "at midnight on 30 September I960…achieved initial operational capability" (IOC). On 1 July 1961 for space surveillance, ADC took over the Laredo Test Site and the Trinidad Air Station fromRome Air Development Center
Rome Laboratory (Rome Air Development Center until 1991) is a U.S. Air Force research laboratory for " command, control, and communications" research and development and is responsible for planning and executing the USAF science and technology pr ...
. The " 1st Aero" cadre at the Hanscom AFB NSSCC moved 496L System operations in July 1961 to Ent's " SPADATS Center" in the annex of building P4. Operational BMEWS control of the Thule Site J RCA AN/FPS-50 Radar Sets transferred from RCA to ADC on 5 January 1962 ( the 12MWS activated in 1967.) By 30 June 1962, integration of ADC's BMEWS CC&DF and the SPADATS Center was completed at Ent AFB, and the Air Forces Iceland transferred from Military Air Transport Service
The Military Air Transport Service (MATS) is an inactive United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense Unified Command. Activated on 1 June 1948, MATS was a consolidation of the United States Navy's Naval Air Transport Service (NA ...
to ADC on 1 July 1962.
The 9th ADD established the temporary 1962 " Cuban Missile Early Warning System" for the missile crisis. Responsibility for a USAFSS squadron's AN/FPS-17 radar station in Turkey for missile test monitoring transferred to ADC on 1 July 1963, the same date the site's AN/FPS-79 achieved IOC.NORAD Historical Summary, January–July 1963. By January 1963, ADC's Detachment 3 of the 9th Aerospace Defense Division (9th ADD) was providing space surveillance data from the Moorestown BMEWS station "to a Spacetrack Analysis Center at Colorado Springs." On 31 December 1965, Forward Scatter Over-the-Horizon network data from the 440L Data Reduction Center was being received by ADC for missile warning, and a NORAD plan for 1 April 1966 was for ADC to "reorganize its remaining 26th, 28th, 29th, and 73d Air Divisions into four air forces."NORAD Historical Summary, July–December 1965.
The 1966 20th Surveillance Squadron began ADC's phased array
In antenna (radio), antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled Antenna array, array of antennas which creates a radio beam, beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point ...
operations with the Eglin AFB Site C-6 Project Space Track
Project Space Track was a research and development project of the US Air Force, to create a tracking system for all artificial satellites of the Earth and space probes, domestic and foreign.
Project Space Track was started in 1957 at the Air For ...
radar (the Eglin phased array's IOC was in 1969, and the North Dakota CMEWS "began passing" PARCS phased array data to NORAD in 1977 after being "modified for the ADCOM mission".
After claiming in March 1958 that "the Army's ZEUS did not have the growth potential to handle possible enemy evasion decoy and countermeasure tactics", the USAF similarly identified by early 1959 that its planned Wizard missile was "not cost effective" against ICBM warheads. (cited by Leonard p. 113)—the Army Zeus deployed successors against ICBMs (SAFEGUARD System, 1975–6) and space vehicles ( Johnston Atoll, 1962–75). After tests of the 1959 High Virgo (at Explorer 5), 1959 Bold Orion ( Explorer 6), and 1963 Project 505 (Nike Zeus
Nike Zeus was an anti-ballistic missile (ABM) system developed by the United States Army during the late 1950s and early 1960s that was designed to destroy incoming Soviet intercontinental ballistic missile warheads before they could hit their ...
) anti-satellite tests (the latter's nuclear burst destroyed a satellite), the Air Force Systems Command
The Air Force Systems Command (AFSC) is an inactive United States Air Force Major Command. It was established in April 1951, being split off from Air Materiel Command. The mission of AFSC was Research and Development for new weapons systems.
AFS ...
ASM-135 ASAT
The ASM-135 ASAT is an air-launched anti-satellite multistage missile that was developed by Ling-Temco-Vought's LTV Aerospace division. The ASM-135 was carried exclusively by United States Air Force (USAF) F-15 Eagle fighter aircraft. The pro ...
collided with a satellite in 1984.
Consolidated C3
ADC's Consolidated Command. Control and Communications Program, FY 1965–1972 was an outgrowth of a 196x "ADC-NORAD PAGE Study" for replacing SAGE/BUIC with a Primary Automated Ground Environment (PAGE) . The program with a Joint DOD/FAA National Airspace System (NAS) resulted with DOD/FAA agreements for a common aircraft surveillance system, with the FAA "to automate its new National Airspace System (NAS) centers". ADC estimated its portion "would cost about $6 million, with annual operating, maintenance, and communication costs about $3.5 million" ("the first BUIC III was set to begin in April 1967 at Z-50, Saratoga Springs".) As the space mission grew the command changed its name, effective 15 January 1968, to Aerospace Defense Command, or ADCOM. Under ADCOM, emphasis went to systems for ballistic missile detection and warning and space surveillance, and the atmospheric detection and warning system, which had been in an almost continuous state of expansion and improvement since the 1950s, went into decline. BOMARC, for example, was dropped from the weapons inventory, and the F-101 and F-102 passed from the regular Air Force inventory into the National Guard. To save funds and manpower, drastic reductions were made in the number of long range radar stations, the number of interceptor squadrons, and in the organizational structure. By 1968 the DOD was making plans to phase down the current air defense system and transition to a new system which included an Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS), Over-the-Horizon Backscatter (OTH-B) radar, and an improved F-106 interceptor aircraft. The changing emphasis in the threat away from the manned bomber and to the ballistic missile brought reorganization and reduction in aerospace defense resources and personnel and almost continuous turmoil in the management structure. The headquarters of the Continental Air Defense Command (CONAD) and ADC were combined on 1 July 1973. Six months later in February 1973, ADC was reduced to 20 fighter squadrons and a complete phaseout of air defense missile batteries. Continental Air Command was disestablished on 1 July 1975 and Aerospace Defense Command became a specified command by direction of the JCS. Reductions and reorganizations continued into the last half of the 1970s, but while some consideration was given to closing down the major command headquarters altogether and redistributing field resources to other commands, such a move lacked support in the Air Staff.Inactivation
 In early 1977 strong Congressional pressure to reduce management "overhead", and the personal conviction of the USAF Chief of Staff that substantial savings could be realized without a reduction in operational capability, moved the final "reorganization" of ADCOM to center stage. Two years of planning followed, but by late 1979 the Air Force was ready to carry it through. It was conducted in two phases:
On 1 October 1979 ADCOM atmospheric defense resources (interceptors, warning radars, and associated bases and personnel) were transferred to Tactical Air Command. They were placed under Air Defense, Tactical Air Command (ADTAC), compatible to a
In early 1977 strong Congressional pressure to reduce management "overhead", and the personal conviction of the USAF Chief of Staff that substantial savings could be realized without a reduction in operational capability, moved the final "reorganization" of ADCOM to center stage. Two years of planning followed, but by late 1979 the Air Force was ready to carry it through. It was conducted in two phases:
On 1 October 1979 ADCOM atmospheric defense resources (interceptors, warning radars, and associated bases and personnel) were transferred to Tactical Air Command. They were placed under Air Defense, Tactical Air Command (ADTAC), compatible to a Numbered Air Force
A Numbered Air Force (NAF) is a type of organization in the United States Air Force that is subordinate to a List of Major Commands of the United States Air Force, major command (MAJCOM) and has assigned to it operational units such as wings, squ ...
under TAC. With this move many Air National Guard
The Air National Guard (ANG), also known as the Air Guard, is a Reserve components of the United States Armed Forces, federal military reserve force of the United States Air Force, as well as the air militia (United States), militia of each U.S. ...
units that had an air defense mission also came under the control of TAC. ADTAC was headquartered at Ent Air Force Base, Colorado
Colorado is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States. It is one of the Mountain states, sharing the Four Corners region with Arizona, New Mexico, and Utah. It is also bordered by Wyoming to the north, Nebraska to the northeast, Kansas ...
, with North American Aerospace Defense Command
North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD ; , CDAAN), known until March 1981 as the North American Air Defense Command, is a Combined operations, combined organization of the United States and Canada that provides aerospace warning, air ...
. In essence, Tactical Air Command became the old Continental Air Command. On the same date, electronic assets went to the Air Force Communications Service (AFCS).
On 1 December 1979 missile warning and space surveillance assets were transferred to Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile compon ...
. On the same date the Aerospace Defense Center, a Direct Reporting Unit, was established from the remnants of ADCOM headquarters.
ADCOM, as a specified command, continued as the United States component of NORAD, but the major air command was inactivated on 31 March 1980. The unit designation of the MAJCOM reverted to the control of the Department of the Air Force.
Commanders
*Lt. Gen George Stratemeyer *Maj. Gen Gordon Saville *Lt. Gen Ennis Whitehead *Gen Benjamin W. Chidlaw *Maj. Gen Frederick Smith Jr. – from 31 May 1955 *Gen Earle Partridge (acting) *Lt. Gen Joseph H. Atkinson – became ADC commander on 22 September *Lt. Gen Robert Lee *Lt. Gen Herbert Thatcher *Lt. Gen Arthur AganLineage
* Established as Air Defense Command on 21 March 1946 : Activated as a major command on 27 March 1946 : Became a subordinate operational command of Continental Air Command on 1 December 1948 : Discontinued on 1 July 1950 * Reestablished as a major command, and organized, on 1 January 1951 : Became a specified command in 1975 : Redesignated Aerospace Defense Command on 15 January 1968 : Major Command inactivated on 31 March 1980Components
Air Defense Forces
* Central Air Defense Force (CADF) : Activated on 1 March 1951 at Kansas City, Missouri : Moved to Grandview AFB, 10 March 1954 : Station redesignated Richards-Gebaur AFB, 27 April 1952 : Inactivated, 1 January 1960 * Eastern Air Defense Force (EADF) : Activated by Continental Air Command on 1 September 1949 at Mitchel AFB, New York : Moved to Stewart AFB and assigned to Air Defense Command on 1 January 1951 : Inactivated, 1 January 1960 * Western Air Defense Force (WADF) : Activated by Continental Air Command on 1 September 1949 at Hamilton AFB, California : Reassigned to Air Defense Command, 1 January 1951 : Inactivated, 1 July 1960Air Forces
* First Air Force : Assigned to Air Defense Command, 27 March 1946 at Mitchel Field, New York : Moved to Fort Slocum, New York, 3 June 1946 : Reassigned to Continental Air Command, 1 December 1948 : Reassigned to Air Defense Command, 1 April 1966 : Inactivated, 31 December 1969 * Second Air Force : Reactivated on 6 June 1946 at Fort Crook, Nebraska : Assigned to Air Defense Command : Inactivated, 1 July 1948 *Fourth Air Force
The Fourth Air Force (4 AF) is a numbered air force of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC). It is headquartered at March Air Reserve Base, California.
4 AF directs the activities and supervises the training of more than 30,000 Air Force Reserv ...
: Assigned to Air Defense Command, 21 March 1946 at March Field, California
: Moved to Hamilton Field, California on 19 June 1946
: Reassigned to Continental Air Command, 1 December 1948
: Discontinued, 1 September 1960
: Reactivated 1 April 1966 and assigned to Air Defense Command
: Inactivated, 30 September 1969
* Tenth Air Force, 21 March 1946 – 1 December 1948; 20 January 1966 – 8 October 1976
: Reactivated 27 May 1946 at Brooks Field, Texas
: Assigned to Air Defense Command
: Reassigned to Continental Air Command, 1 December 1948
: Inactivated, 1 September 1960
: Reactivated 1 April 1966 and assigned to Air Defense Command
: Assigned to Richards-Gebaur AFB
: Inactivated, 30 September 1969
* Eleventh Air Force*
: Activated 13 June 1946 at Olmsted Field, Middletown, Pennsylvania
: Assigned to Air Defense Command
: Inactivated, 1 July 1948
* Fourteenth Air Force, 21 March 1946 – 1 December 1948; 20 January 1966 – 8 October 1976
: Reactivated 24 May 1945 at Orlando Air Base, Florida
: Assigned to Air Defense Command
: Reassigned to Continental Air Command, 1 December 1948
: Inactivated, 1 September 1960
: Reactivated 1 April 1966 and assigned to Air Defense Command
: Assigned to Gunter AFB, Alabama
: Redesignated Fourteenth Aerospace Force, 1 July 1968
: Moved to Ent AFB, Colorado
: Inactivated, 1 October 1976
* Air Forces Iceland
: Assigned to Air Defense Command from Military Air Transport Service
The Military Air Transport Service (MATS) is an inactive United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense Unified Command. Activated on 1 June 1948, MATS was a consolidation of the United States Navy's Naval Air Transport Service (NA ...
, 1 July 1962
: Stationed at Keflavik Airport, Iceland
: Assigned to 64th Air Division
: Transferred to: 26th Air Division, 1 July 1963
: Transferred to: Goose Air Defense Sector, 4 September 1963
: Transferred to: 37th Air Division, 1 April 1966
: Transferred to: 21st Air Division, 31 December 1969
: Reassigned to Tactical Air Command
Tactical Air Command (TAC) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. It was a List of Major Commands of the United States Air Force, Major Command of the United States Air Force, established on 21 March 1946 and headquartered at Lang ...
, 1 October 1979
.Note: Assigned to Olmsted AFB
Harrisburg Air National Guard Base is a United States Air Force base, located at Harrisburg International Airport, Pennsylvania. It is located west-southwest of Middletown, Dauphin County, Pennsylvania, Middletown, Pennsylvania.
The Pennsylv ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, but never equipped or manned. Not to be confused with Eleventh Air Force, which was assigned to Alaskan Air Command
Regions
* Alaskan ADCOM Region : Designated and activated at Elmendorf AFB, Alaska, 1 October 1975 : Missile warning and space surveillance forces reassigned toStrategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile compon ...
, 1 December 1979
: Redesignated as Alaska NORAD Region (ANR), 14 June 1983
:: Operational atmospheric defense units under operational control of Eleventh Air Force
* 20th ADCOM Region
: Designated and activated at Fort Lee AFS, Virginia, 8 December 1978
: Supplementary ADCOM designation of 20th Air Division
* 21st ADCOM Region
: Designated and activated at Hancock AFS, New York, 8 December 1978
: Supplementary ADCOM designation of 21st Air Division
* 23d ADCOM Region
: Designated and activated at Duluth AFS, Minnesota, 8 December 1978
: Supplementary ADCOM designation of 23d Air Division
* 24th ADCOM Region
: Designated and activated at Malmstrom AFB, Montana, 8 December 1978
: Supplementary ADCOM designation of 24th Air Division
* 25th ADCOM Region
: Designated and activated at McChord AFB, Washington, 8 December 1978
: Supplementary ADCOM designation of 25th Air Division
* 26th ADCOM Region
: Designated and activated at Luke AFB, Arizona, 8 December 1978
: Supplementary ADCOM designation of 26th Air Division
Air Divisions
* 8th Air Division (Aircraft Early Warning & Control) : Activated 1 May 1954 at McClellan AFB, California : Assigned to Western Air Defense Force : Transferred to Air Defense Command, 1 May 1955 : Inactivated, 1 July 1957 * 9th Air Division (Defense) : Activated 8 October 1954 at Geiger Field, Washington : Assigned to Western Air Defense Force : Inactivated, 15 August 1958 : Reactivated on 15 July 1961 as 9th Aerospace Air Division at Ent AFB, Colorado : Assigned to Air Defense Command : Designated 9th Aerospace Defense Division by 31 May 1963 : Discontinued, 1 July 1968 * 20th Air Division : Activated on 8 October 1955 at Grandview AFB, Missouri : Assigned to Central Air Defense Force : Station renamed Richards-Gebaur AFB, 27 April 1957 : Inactivated 1 January 1960 : Reactivated on 1 April 1966 at Truax Field, Wisconsin : Assigned to Tenth Air Force : Discontinued 31 December 1967 : Reactivated on 19 November 1969 at Fort Lee AFS, Virginia : Assigned to Air Defense Command : Reassigned toTactical Air Command
Tactical Air Command (TAC) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. It was a List of Major Commands of the United States Air Force, Major Command of the United States Air Force, established on 21 March 1946 and headquartered at Lang ...
, 1 October 1979
* 21st Air Division
: Activated 20 January 1966
: Organized at McGuire AFB, New Jersey 1 April 1966
: Assigned to First Air Force
: Discontinued and inactivated 31 December 1967
: Reactivated on 19 November 1969 at Hancock AFS, New York
: Assigned to Air Defense Command
: Reassigned to Tactical Air Command, 1 October 1979
* 23d Air Division
: Activated 19 November 1969 at Duluth AFS, Minnesota
: Assigned to First Air Force
: Reassigned to Air Defense Command on 1 December 1969
: Reassigned to Tactical Air Command, 1 October 1979
* 24th Air Division
: Activated 19 November 1969 at Malmstrom AFB, Montana
: Assigned to Tenth Air Force
: Reassigned to Air Defense Command on 1 December 1969
: Reassigned to Tactical Air Command, 1 October 1979
* 25th Air Division
: Activated 25 October 1948 as 25th Air Division (Defense) at Silver Lake, Washington
: Assigned to Fourth Air Force
The Fourth Air Force (4 AF) is a numbered air force of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC). It is headquartered at March Air Reserve Base, California.
4 AF directs the activities and supervises the training of more than 30,000 Air Force Reserv ...
: Reassigned to Western Air Defense Force, 1 February 1950
: Moved to McChord AFB, 15 September 1951
: Redesignated 25th Air Division (SAGE), 1 March 1959
: Reassigned to Air Defense Command on 1 July 1960
: Reassigned to Fourth Air Force
The Fourth Air Force (4 AF) is a numbered air force of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC). It is headquartered at March Air Reserve Base, California.
4 AF directs the activities and supervises the training of more than 30,000 Air Force Reserv ...
, 1 April 1966
: Reassigned to Tenth Air Force, 1 April 1966
: Reassigned to Aerospace Defense Command, 1 December 1969
: Reassigned to Tactical Air Command, 1 October 1979
* 26th Air Division
: Activated 16 November 1948 at Mitchel AFB, New York
: Assigned to First Air Force
: Moved to Roslyn AFS, New York 18 April 1949
: Redesignated 26th Air Division (Defense), 20 June 1949
: Reassigned to Eastern Air Defense Force, 1 September 1950
: Redesignated 26th Air Division (SAGE), 8 August 1958 and moved to Syracuse AFS, New York
: Transferred to Air Defense Command on 1 August 1959
: Moved to Stewart AFB, New York, 15 June 1964
: Redesignated 26th Air Division, 20 January 1966 and moved to Adair AFS, Oregon
: Inactivated, 30 September 1969
: Reactivated 19 November 1969 at Luke AFB, Arizona
: Reassigned to Tactical Air Command, 1 October 1979
* 27th Air Division
: Activated as 27th Air Division (Defense) on 20 November 1950 at Norton AFB, California
: Assigned to Western Air Defense Force
: Inactivated, 1 October 1959
: Organized as 27th Air Division on 1 April 1966 at Luke AFB, Arizona
: Assigned to Fourth Air Force
The Fourth Air Force (4 AF) is a numbered air force of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC). It is headquartered at March Air Reserve Base, California.
4 AF directs the activities and supervises the training of more than 30,000 Air Force Reserv ...
: Reassigned to Tenth Air Force on 15 September 1969
: Inactivated 19 November 1969
* 28th Air Division
: Assigned to Western Air Defense Force on 1 January 1951 as 28th Air Division (Defense)
: Assigned to Hamilton AFB, California
: Redesignated as 28th Air Division (SAGE) and transferred to Air Defense Command, 1 July 1960
: Redesignated 28th Air Division, 1 April 1966
: Moved to Malmstrom AFB, Montana and assigned to Tenth Air Force, 1 April 1966
: Inactivated 19 November 1969
* 29th Air Division
: Activated 1 March 1951 at Great Falls AFB, Montana
: Assigned to Western Air Defense Force
: Transferred to Central Air Defense Force, 16 February 1953
: Great Falls AFB renamed Malmstrom AFB, Montana, 1 October 1955
: Redesignated as 29th Air Division (SAGE) and transferred to Air Defense Command, 1 July 1960
: Moved to Richards-Gebaur AFB, Missouri, 1 July 1961
: Redesignated 29th Air Division, 1 April 1966
: Moved to Duluth AFS, Minnesota, and assigned to Tenth Air Force, 1 April 1966
: Reassigned to First Air Force on 15 September 1969
: Inactivated 19 November 1969
* 30th Air Division
The 30th Air Division (30th AD) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with Air Defense Command, assigned to Tenth Air Force, being stationed at Sioux City Air National Guard Base, Sioux City Municipal Air ...
,
: Activated on 16 December 1949 as 30th Air Division (Defense) at Selfridge AFB, Michigan
: Assigned to Air Defense Command
: Moved to Willow Run AFS, Michigan on 1 April 1952
: Assigned to Eastern Air Defense Force, 1 April 1952
: Redesignated 30th Air Division (SAGE), 1 April 1959 and moved to Truax Field, Wisconsin
: Reassigned to Air Defense Command on 1 July 1959
: Redesignated 30th Air Division and moved to Sioux City AFS, Iowa (w/o p/e), 1 April 1966
: Reassigned to Tenth Air Force, 1 April 1966
: Discontinued 18 September 1968
* 31st Air Division
: Activated on 8 October 1950 as 31st Air Division (Defense) at Selfridge AFB, Michigan
: Assigned to Eastern Air Defense Force
: Reassigned to Air Defense Command on 1 January 1951
: Moved to Snelling AFS, Minnesota on 18 December 1950
: Reassigned to Central Air Defense Force, 20 May 1950
: Inactivated 1 January 1960
: Organized at Oklahoma City AFS, Oklahoma on 1 April 1966
: Assigned to Fourteenth Air Force, 1 April 1966
: Reassigned to Tenth Air Force on 1 July 1968
: Inactivated on 31 December 1969
* 32d Air Division
: Assigned on 1 January 1951 to Eastern Air Defense Force at Stewart AFB, New York
: Moved to Syracuse AFS, New York, 15 February 1952
: Inactivated on 15 August 1958
: Reactivated on 15 November 1958 as 32d Air Division (SAGE) at Dobbins AFB, Georgia
: Assigned to Eastern Air Defense Force
: Reassigned to Air Defense Command, 1 August 1959
: Moved to Oklahoma City AFS, Oklahoma, 1 August 1961
: Discontinued 4 September 1963
: Organized at Gunter AFB, Alabama, 1 April 1966
: Assigned to Fourteenth Air Force
: Reassigned to Tenth Air Force, 1 July 1968
: Inactivated 31 December 1969
* 33d Air Division
: Activated on 19 March 1951 as 33d Air Division (Defense) at Tinker AFB
Tinker Air Force Base is a major United States Air Force base, with tenant United States Navy, U.S. Navy and other United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense missions, located in Oklahoma City, Oklahoma in Oklahoma County, Okl ...
, Oklahoma
: Assigned to Eastern Air Defense Force
: Reassigned to Central Air Defense Force, 20 May 1951
: Moved to Oklahoma City AFS, Oklahoma, 1 July 1956
: Redesignated 33d Air Division (SAGE) and moved to Richards-Gebaur AFB, Missouri, 1 January 1960
: Reassigned to Air Defense Command
: Discontinued 1 July 1961
: Organized on 1 April 1966 as 33d Air Division at Fort Lee AFS, Virginia
: Assigned to First Air Force
: Inactivated 19 November 1969
* 34th Air Division
: Activated on 5 January 1951 at Kirtland AFB, New Mexico
: Assigned to Western Air Defense Force
: Reassigned to Central Air Defense Force 15 February 1953
: Inactivated 1 January 1960
: Organized at Custer AFS, Michigan, 1 April 1966
: Assigned to First Air Force
: Inactivated 31 December 1969
* 35th Air Division
: Activated on 1 July 1951 at Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City, Missouri, abbreviated KC or KCMO, is the largest city in the U.S. state of Missouri by List of cities in Missouri, population and area. The city lies within Jackson County, Missouri, Jackson, Clay County, Missouri, Clay, and Pl ...
: Assigned to Central Air Defense Force
: Moved to Dobbins AFB, Georgia, 1 September 1951
: Reassigned to Eastern Air Defense Force, 10 April 1955
: Inactivated 15 November 1958
: Organized on 1 April 1966 at Syracuse AFS, New York
: Inactivated 19 November 1968
* 36th Air Division
: Activated 1 April 1966 at Topsham AFS, Maine
: Assigned to First Air Force
: Inactivated 30 September 1969
* 37th Air Division
: Activated on 10 October 1951 at Lockborne AFB, Ohio under Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile compon ...
: Moved to Truax Field, Wisconsin 8 September 1955 and transferred to Air Defense Command
: Assigned to Eastern Air Defense Force
: Inactivated 1 April 1959
: Organized on 1 April 1966 at Goose AFB, Labrador, Canada
: Assigned to First Air Force
: Reassigned to Aerospace Defense Command, 1 December 1969
: Inactivated 10 June 1970
* 58th Air Division (Defense)
: Activated 8 September 1955 at Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio
: Assigned to Eastern Air Defense Force
: Inactivated 1 February 1959
* 64th Air Division
: Transferred on 1 April 1957 to Air Defense Command from Northeast Air Command
: Assigned to Pepperrell AFB, Newfoundland
: Moved to Stewart AFB, New York, 26 May 1960
: Discontinued, 1 July 1963
* 73d Air Division
: Activated 1 July 1957 as 73d Air Division (Weapons) at Tyndall AFB, Florida
: Assigned to Air Defense Command
: Redesignated 73d Air Division, 1 March 1963
: Discontinued 1 April 1966
* 85th Air Division
: Activated 8 September 1955 at Andrews AFB, Maryland
: Assigned to Eastern Air Defense Force
: Inactivated 1 September 1958
Air Defense Sectors
* Albuquerque Air Defense Sector : Activated on 1 January 1960 at Kirtland AFB, New Mexico : Assigned to 33d Air Division : Discontinued 1 November 1960 * Bangor Air Defense Sector : Activated on 8 January 1957 at Topsham AFS, Maine : Assigned to 32d Air Division : Reassigned to 26th Air Division, 15 August 1958 : Discontinued 1 April 1966 * Boston Air Defense Sector : 4622d Air Defense Wing (SAGE) redesignated 8 January 1957 : Activated at Stewart AFB, New York : Assigned to 26th Air Division : Moved to Syracuse AFS, New York 1 April 1966 : Discontinued 1 April 1966 * Chicago Air Defense Sector : 4628th Air Defense Wing redesignated 8 March 1957 : Activated at Truax Field, Wisconsin : Assigned to 37th Air Division : Reassigned to 30th Air Division, 1 April 1959 : Discontinued 1 April 1966 * Detroit Air Defense Sector : 4627th Air Defense Wing redesignated, 8 January 1957 : Activated at Custer AFS, Michigan : Assigned to 30th Air Division : Reassigned to 26th Air Division, 4 September 1963 : Discontinued 1 April 1966 * Duluth Air Defense Sector : Activated 8 October 1957 at Duluth AFS, Minnesota : Assigned to 37th Air Division (EADF) : Reassigned to 31st Air Division (CADF), 20 December 1957 : Reassigned to 37th Air Division, 1 January 1959 : Reassigned to 30th Air Division, 1 April 1959 : Discontinued 1 April 1966 * Goose Air Defense Sector : Activated on 1 April 1960 at Goose AFB, Labrador, Canada : Assigned to 64th Air Division : Reassigned to 26th Air Division (SAGE), 1 July 1963 : Discontinued on 1 April 1966 * Grand Forks Air Defense Sector : Activated on 8 December 1957 at Grand Forks AFB, North Dakota : Assigned to 31st Air Division : Reassigned to 29th Air Division, 1 January 1959 : Discontinued on 1 December 1963 * Great Falls Air Defense Sector : Activated on 1 March 1959 at Malmstrom AFB, Montana : Assigned to 29th Air Division : Discontinued on 1 April 1966 * Kansas City Air Defense Sector : Activated on 1 January 1960 at Richards-Gebaur AFB, Missouri : Assigned to 33d Air Division : Reassigned to 29th Air Division, 1 July 1961 : Discontinued 1 January 1962 * Los Angeles Air Defense Sector : Activated on 15 February 1959 at Norton AFB, California : Assigned to 27th Air Division : Reassigned to Western Air Defense Force, 1 October 1959 : Reassigned to 28th Air Division, 1 July 1960 : Reassigned toFourth Air Force
The Fourth Air Force (4 AF) is a numbered air force of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC). It is headquartered at March Air Reserve Base, California.
4 AF directs the activities and supervises the training of more than 30,000 Air Force Reserv ...
, 1 April 1966
: Discontinued 25 June 1966
* Minot Air Defense Sector
: Activated on 1 April 1959 at Minot AFB, North Dakota
: Assigned to 29th Air Division
: Discontinued 15 August 1963
* Montgomery Air Defense Sector
: Activated on 8 September 1957 at Gunter AFB, Alabama
: Assigned to 35th Air Division
: Reassigned to 32d Air Division, 15 November 1958
: Reassigned to 26th Air Division (SAGE), 1 July 1963
: Assigned to Air Defense Command, 1 October 1964
: Discontinued 1 April 1966
* New York Air Defense Sector
: 4621st Air Defense Wing (SAGE) redesignated, 8 January 1957
: Assigned to McGuire AFB, New Jersey
: Assigned to 26th Air Division
: Discontinued 1 April 1966
* Oklahoma City Air Defense Sector
: Activated on 1 January 1960 at Oklahoma City AFS, Oklahoma
: Assigned to 33d Air Division
: Reassigned to 32d Air Division, 1 July 1961
: Discontinued 1 September 1961
: Reactivated 25 June 1963 at Oklahoma City AFS
: Assigned to 29th Air Division (SAGE)
: Discontinued 1 April 1966
* Phoenix Air Defense Sector
: Activated on 15 June 1959 at Luke AFB, Arizona
: Assigned to Western Air Defense Force
: Reassigned to 28th Air Division, 1 July 1960
: Discontinued 1 April 1966
* Portland Air Defense Sector
: Activated on 1 September 1958 at Adair AFS, Oregon
25th Air Division
: Discontinued 1 April 1966
* Reno Air Defense Sector
: Activated on 15 February 1959 at Stead AFB, Nevada
: Assigned to 25th Air Division
: Reassigned to 28th Air Division, 1 July 1960
: Reassigned to Fourth Air Force
The Fourth Air Force (4 AF) is a numbered air force of the Air Force Reserve Command (AFRC). It is headquartered at March Air Reserve Base, California.
4 AF directs the activities and supervises the training of more than 30,000 Air Force Reserv ...
, 1 April 1966
: Discontinued 25 June 1966
* San Francisco Air Defense Sector
: Activated on 15 February 1959 at Beale AFB, California
: Assigned to 28th Air Division
: Discontinued 1 August 1963
* Sault Sainte Marie Air Defense Sector
: Activated on 8 November 1958 at K. I. Sawyer AFB, Michigan
: Assigned to 37th Air Division
: Reassigned to 30th Air Division, 1 April 1959
: Discontinued 15 December 1963
* Seattle Air Defense Sector
The Western Air Defense Sector (WADS) is a unit of the Washington Air National Guard located at Joint Base Lewis-McChord, Tacoma, Washington.
As a state militia unit, the Western Air Defense Sector is not in the normal United States Air Force com ...
: Activated on 8 January 1958 at McChord AFB, Washington
: Assigned to 25th Air Division
: Discontinued 1 April 1966
* Sioux City Air Defense Sector
: Activated on 1 October 1959 at Sioux City AFS, Iowa
: Assigned to 20th Air Division
: Reassigned to 33d Air Division, 1 January 1960
: Reassigned to 29th Air Division, 1 July 1961
: Discontinued 1 April 1966
* Spokane Air Defense Sector
: Activated on 8 September 1958 at Larson AFB, Washington
: Assigned to 25th Air Division
: Discontinued 1 September 1963
* Syracuse Air Defense Sector
: 4624th Air Defense Wing (SAGE), redesignated 8 January 1957
: Activated at Syracuse AFS, New York
: Assigned to 32d Air Division
: Reassigned to 25th Air Division, 15 August 1958
: Discontinued 4 September 1963
* Washington Air Defense Sector
: 4625th Air Defense Wing (SAGE) redesignated 8 January 1957
: Activated at Fort Lee AFS, Virginia
: Assigned to 85th Air Division
: Reassigned to 26th Air Division, 1 September 1958
: Discontinued 1 April 1966
Other
* Air Force Element, NORAD/ADCOM (AFENA) : Activated tbd : Redesignated a Direct Reporting Unit of USAF as Aerospace Defense Center, 1 December 1979 * Air Defense Weapons Center : Organized at Tyndall AFB, Florida, 31 October 1967 : Assigned to Air Defense Command : Transferred to Tactical Air Command, 1 October 1979 * Aerospace Defense Command Combat Operations Center (COC) : Designated and activated as NORAD Combat Operations Center, 21 April 1976 : Assigned to Cheyenne Mountain Complex City, Colorado : Assigned to Aerospace Defense Command, 21 April 1976 : Redesignated ADCOM CONIC, 30 June 1976 : Transferred to Tactical Air Command, 1 October 1979 * Cheyenne Mountain Support Group - Unit activated 1 October 1981. Its mission was to provide for upkeep, maintenance, ana management of the Cheyenne Mountain Complex. The 4800 Special SEcurity Squadron was to provide physical protection; the 4801 Civil Engineering Squadron was to administer and operate real property facilities.ADC SPECIAL ORDER GC-12, 15 SEP 81. https://airforcehistoryindex.org/data/001/049/977.xmlReferences
* * {{Aerospace Defense Command, state=collapsed Major commands of the United States Air Force Air defense units and formations of the United States Air Force Military units and formations of the United States in the Cold War Military units and formations established in 1968 Military units and formations disestablished in 1980