Aethrioscope on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
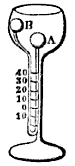 An aethrioscope (or æthrioscope) is a meteorological device invented by Sir John Leslie in 1818 for measuring the chilling effect of a clear sky. The name is from the Greek word for clear – ''αίθριος''.
It consists of a metallic cup standing upon a tall hollow pedestal, with a differential
An aethrioscope (or æthrioscope) is a meteorological device invented by Sir John Leslie in 1818 for measuring the chilling effect of a clear sky. The name is from the Greek word for clear – ''αίθριος''.
It consists of a metallic cup standing upon a tall hollow pedestal, with a differential
 An aethrioscope (or æthrioscope) is a meteorological device invented by Sir John Leslie in 1818 for measuring the chilling effect of a clear sky. The name is from the Greek word for clear – ''αίθριος''.
It consists of a metallic cup standing upon a tall hollow pedestal, with a differential
An aethrioscope (or æthrioscope) is a meteorological device invented by Sir John Leslie in 1818 for measuring the chilling effect of a clear sky. The name is from the Greek word for clear – ''αίθριος''.
It consists of a metallic cup standing upon a tall hollow pedestal, with a differential thermometer
A thermometer is a device that measures temperature (the hotness or coldness of an object) or temperature gradient (the rates of change of temperature in space). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb ...
placed so that one of its bulbs is in the focus of the paraboloid formed by the cavity of the cup. The interior of the cup is highly polished and is kept covered by a plate of metal, being opened when an observation is made. The second bulb is always screened from the sky and so is not affected by the radiative effect of the clear sky, the action of which is concentrated upon the first bulb. The contraction of the air in the second bulb by its sudden exposure to a clear sky causes the liquid in the stem to rise.
The device will respond in a contrary fashion when exposed to heat radiation and so may be used as a pyrometer
A pyrometer, or radiation thermometer, is a type of remote sensing thermometer used to measure the temperature of distant objects. Various forms of pyrometers have historically existed. In the modern usage, it is a device that from a distance de ...
too.
References
Thermometers 1818 in Scotland 1818 in science Atmospheric physics Atmospheric radiation {{climate-stub