Abbāsids on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third
 In 762, al-Mansur suppressed a rebellion in the
In 762, al-Mansur suppressed a rebellion in the
 Domestically, al-Rashid pursued policies similar to those of his father al-Mahdi. He released many of the Umayyads and Alids his brother
Domestically, al-Rashid pursued policies similar to those of his father al-Mahdi. He released many of the Umayyads and Alids his brother
 By the 870s, Egypt became autonomous under Ahmad ibn Tulun and his Tulunid successors, though they continued to acknowledge the caliph and generally sent tribute to Baghdad. For a time, they even controlled Syria and parts of the Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia). In 882, the caliph al-Mu'tamid even tried to move his residence to Egypt at Ibn Tulun's invitation, though this move was aborted by the intervention of al-Muwaffaq.
In the east, the
By the 870s, Egypt became autonomous under Ahmad ibn Tulun and his Tulunid successors, though they continued to acknowledge the caliph and generally sent tribute to Baghdad. For a time, they even controlled Syria and parts of the Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia). In 882, the caliph al-Mu'tamid even tried to move his residence to Egypt at Ibn Tulun's invitation, though this move was aborted by the intervention of al-Muwaffaq.
In the east, the
 Caliph al-Mustarshid () was the first caliph to build an army and to lead it in battle since the 10th century. He recruited Kurdish and Arab Bedouin tribes and re-fortified Baghdad. His first concern was not the Seljuks but the Banu Mazyad, Mazyadids of Hilla in central Iraq, whom he met in battle in 1123. His bid for independence was ultimately unsuccessful, as he was defeated by a Seljuk army in 1135 and assassinated soon after.
Under
Caliph al-Mustarshid () was the first caliph to build an army and to lead it in battle since the 10th century. He recruited Kurdish and Arab Bedouin tribes and re-fortified Baghdad. His first concern was not the Seljuks but the Banu Mazyad, Mazyadids of Hilla in central Iraq, whom he met in battle in 1123. His bid for independence was ultimately unsuccessful, as he was defeated by a Seljuk army in 1135 and assassinated soon after.
Under  The long reign of Caliph
The long reign of Caliph
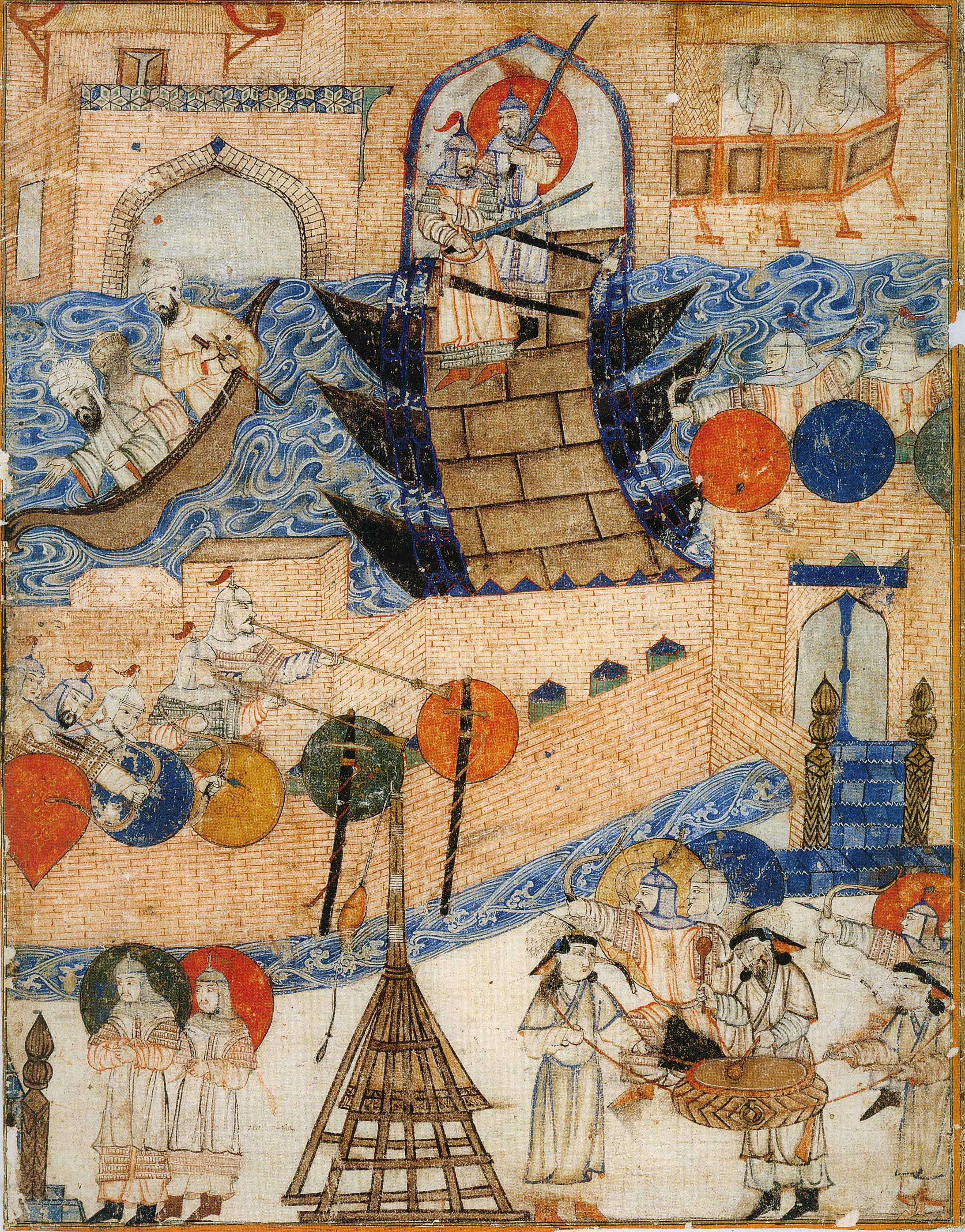 The Mongols began their siege of the city on 29 January 1258. On 10 February, al-Musta'sim agreed to meet with Hulagu, who demanded that the caliph order the defenders to stand down and come out of the city in exchange for mercy. The caliph complied, but the Mongols slaughtered the population and then began the sack of the city on 13 February. Contemporary accounts describe destruction, looting, rape, and killing on a massive scale over many days, with hundreds of thousands killed and the city reduced to near-empty ruins, though some, like the Christian and Shia communities, were spared. The Mongols feared rumours that a supernatural disaster would strike if the blood of al-Musta'sim, a direct descendant of Muhammad's uncle and part of a dynasty that had reigned for five centuries, was spilled. As a precaution and in accordance with a Mongol taboo against spilling royal blood, Hulagu had al-Musta'sim wrapped in a carpet and trampled to death by horses on 20 February 1258. The caliph's immediate family was also executed, with the lone exceptions of his youngest son who was sent to Mongolia and a daughter who became a slave in the harem of Hulagu.
The fall of Baghdad marked the effective end of the Abbasid Caliphate. It made a deep impression on contemporary and later writers both inside and outside the Muslim world, some of whom created legendary stories about the last caliph's demise. It is also traditionally seen as the approximate end to the "classical age" or Islamic Golden Age, "golden age" of Islamic civilization. The events brought profound geopolitical changes to the traditional lands of the Islamic caliphate, with Iraq, Iran, and most of the eastern lands falling under Mongol control while other Muslim rulers retained the lands to the west. Mongol expansion further west was eventually halted by the Mamluks of Egypt at the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260, followed by the conflict between the Ilkhanids (Hulagu and his successors) and their Golden Horde rivals, which diverted Mongol attention.
The Mongols began their siege of the city on 29 January 1258. On 10 February, al-Musta'sim agreed to meet with Hulagu, who demanded that the caliph order the defenders to stand down and come out of the city in exchange for mercy. The caliph complied, but the Mongols slaughtered the population and then began the sack of the city on 13 February. Contemporary accounts describe destruction, looting, rape, and killing on a massive scale over many days, with hundreds of thousands killed and the city reduced to near-empty ruins, though some, like the Christian and Shia communities, were spared. The Mongols feared rumours that a supernatural disaster would strike if the blood of al-Musta'sim, a direct descendant of Muhammad's uncle and part of a dynasty that had reigned for five centuries, was spilled. As a precaution and in accordance with a Mongol taboo against spilling royal blood, Hulagu had al-Musta'sim wrapped in a carpet and trampled to death by horses on 20 February 1258. The caliph's immediate family was also executed, with the lone exceptions of his youngest son who was sent to Mongolia and a daughter who became a slave in the harem of Hulagu.
The fall of Baghdad marked the effective end of the Abbasid Caliphate. It made a deep impression on contemporary and later writers both inside and outside the Muslim world, some of whom created legendary stories about the last caliph's demise. It is also traditionally seen as the approximate end to the "classical age" or Islamic Golden Age, "golden age" of Islamic civilization. The events brought profound geopolitical changes to the traditional lands of the Islamic caliphate, with Iraq, Iran, and most of the eastern lands falling under Mongol control while other Muslim rulers retained the lands to the west. Mongol expansion further west was eventually halted by the Mamluks of Egypt at the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260, followed by the conflict between the Ilkhanids (Hulagu and his successors) and their Golden Horde rivals, which diverted Mongol attention.
 The best-known fiction from the Islamic world is ''One Thousand and One Nights'', a collection of fantastical folk tales, legends and parables compiled primarily during the Abbasid era. The collection is recorded as having originated from an Arabic translation of a Sassanian-era Persian prototype, with likely origins in Indian literary traditions. Stories from Arabic literature, Arabic, Persian literature, Persian, Mesopotamian, and Egyptian literature, Egyptian folklore and literature were later incorporated. The epic is believed to have taken shape in the 10th century and reached its final form by the 14th century; the number and type of tales have varied from one manuscript to another.. All Arabian fantasy tales were often called "Arabian Nights" when translated into English, regardless of whether they appeared in ''The Book of One Thousand and One Nights''. This epic has been influential in the West since it was translated in the 18th century, first by Antoine Galland. Many imitations were written, especially in France. Various characters from this epic have themselves become cultural icons in Western culture, such as Aladdin, Sinbad and Ali Baba.
A famous example of Islamic poetry on romance (love), romance was ''Layla and Majnun'', an originally Arabic story which was further developed by Iranian peoples, Iranian, Azerbaijani people, Azerbaijani and other poets in the Persian language, Persian, Azerbaijani language, Azerbaijani, and Turkish language, Turkish languages. It is a Tragedy, tragic story of undying love much like the later ''Romeo and Juliet''.
Arabic poetry reached its greatest height in the Abbasid era, especially before the loss of central authority and the rise of the Persianate dynasties. Writers like Abu Tammam and Abu Nuwas were closely connected to the caliphal court in Baghdad during the early 9th century, while others such as al-Mutanabbi received their patronage from regional courts.
Under Harun al-Rashid, Baghdad was renowned for its bookstores, which proliferated after the making of paper was introduced. Chinese papermakers had been among those taken prisoner by the Arabs at the
The best-known fiction from the Islamic world is ''One Thousand and One Nights'', a collection of fantastical folk tales, legends and parables compiled primarily during the Abbasid era. The collection is recorded as having originated from an Arabic translation of a Sassanian-era Persian prototype, with likely origins in Indian literary traditions. Stories from Arabic literature, Arabic, Persian literature, Persian, Mesopotamian, and Egyptian literature, Egyptian folklore and literature were later incorporated. The epic is believed to have taken shape in the 10th century and reached its final form by the 14th century; the number and type of tales have varied from one manuscript to another.. All Arabian fantasy tales were often called "Arabian Nights" when translated into English, regardless of whether they appeared in ''The Book of One Thousand and One Nights''. This epic has been influential in the West since it was translated in the 18th century, first by Antoine Galland. Many imitations were written, especially in France. Various characters from this epic have themselves become cultural icons in Western culture, such as Aladdin, Sinbad and Ali Baba.
A famous example of Islamic poetry on romance (love), romance was ''Layla and Majnun'', an originally Arabic story which was further developed by Iranian peoples, Iranian, Azerbaijani people, Azerbaijani and other poets in the Persian language, Persian, Azerbaijani language, Azerbaijani, and Turkish language, Turkish languages. It is a Tragedy, tragic story of undying love much like the later ''Romeo and Juliet''.
Arabic poetry reached its greatest height in the Abbasid era, especially before the loss of central authority and the rise of the Persianate dynasties. Writers like Abu Tammam and Abu Nuwas were closely connected to the caliphal court in Baghdad during the early 9th century, while others such as al-Mutanabbi received their patronage from regional courts.
Under Harun al-Rashid, Baghdad was renowned for its bookstores, which proliferated after the making of paper was introduced. Chinese papermakers had been among those taken prisoner by the Arabs at the
 Another major development was the creation or vast enlargement of cities as they were turned into the capital of the empire, beginning with the creation of Baghdad in 762, which was planned as a walled city with four gates, and a mosque and palace in the center. Al-Mansur, who was responsible for the creation of Baghdad, also planned the city of
Another major development was the creation or vast enlargement of cities as they were turned into the capital of the empire, beginning with the creation of Baghdad in 762, which was planned as a walled city with four gates, and a mosque and palace in the center. Al-Mansur, who was responsible for the creation of Baghdad, also planned the city of
 A number of medieval thinkers and scientists living under Islamic rule played a role in transmitting Islamic science to the Christian West. In addition, the period saw the recovery of much of the Alexandrian mathematical, geometric and astronomical knowledge, such as that of Euclid and Claudius Ptolemy. These recovered mathematical methods were later enhanced and developed by other Islamic scholars, notably by Persian scientists Al-Biruni and Abu Nasr Mansur.
Christians (particularly Nestorianism, Nestorian Christians) contributed to the Arab Islamic Civilization during the Umayyads and the Abbasids by translating works of Greek philosophers to Syriac Language, Syriac and afterwards to Arabic Language, Arabic. Nestorians played a prominent role in the formation of Arab culture, with the Academy of Gondishapur being prominent in the late Sassanid, Umayyad and early Abbasid periods. Notably, eight generations of the Nestorian Bukhtishu family served as private doctors to caliphs and sultans between the eighth and eleventh centuries.
Algebra was significantly developed by Persian scientist Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī during this time in his landmark text, ''The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing, Kitab al-Jabr wa-l-Muqabala'', from which the term ''algebra'' is derived. He is thus considered to be the father of algebra by some, although the Greek mathematician Diophantus has also been given this title. The terms ''algorism'' and ''algorithm'' are derived from the name of al-Khwarizmi, who was also responsible for introducing the Arabic numerals and Hindu–Arabic numeral system beyond the Indian subcontinent.
A number of medieval thinkers and scientists living under Islamic rule played a role in transmitting Islamic science to the Christian West. In addition, the period saw the recovery of much of the Alexandrian mathematical, geometric and astronomical knowledge, such as that of Euclid and Claudius Ptolemy. These recovered mathematical methods were later enhanced and developed by other Islamic scholars, notably by Persian scientists Al-Biruni and Abu Nasr Mansur.
Christians (particularly Nestorianism, Nestorian Christians) contributed to the Arab Islamic Civilization during the Umayyads and the Abbasids by translating works of Greek philosophers to Syriac Language, Syriac and afterwards to Arabic Language, Arabic. Nestorians played a prominent role in the formation of Arab culture, with the Academy of Gondishapur being prominent in the late Sassanid, Umayyad and early Abbasid periods. Notably, eight generations of the Nestorian Bukhtishu family served as private doctors to caliphs and sultans between the eighth and eleventh centuries.
Algebra was significantly developed by Persian scientist Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī during this time in his landmark text, ''The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing, Kitab al-Jabr wa-l-Muqabala'', from which the term ''algebra'' is derived. He is thus considered to be the father of algebra by some, although the Greek mathematician Diophantus has also been given this title. The terms ''algorism'' and ''algorithm'' are derived from the name of al-Khwarizmi, who was also responsible for introducing the Arabic numerals and Hindu–Arabic numeral system beyond the Indian subcontinent.
 Arab scientist Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) developed an early scientific method in his ''Book of Optics'' (1021). The most important development of the scientific method was the use of experiments to distinguish between competing scientific theories set within a generally empiricism, empirical orientation, which began among Muslim scientists. Ibn al-Haytham's empirical proof of the intromission theory of light (that is, that light rays entered the eyes rather than being emission theory (vision), emitted by them) was particularly important. Ibn al-Haytham was significant in the history of scientific method, particularly in his approach to experimentation, and has been referred to as the "world's first true scientist".
Medicine in medieval Islam was an area of science that advanced particularly during the Abbasids' reign. During the 9th century, Baghdad contained over 800 doctors, and great discoveries in the understanding of anatomy and diseases were made. The clinical distinction between measles and smallpox was described during this time. Famous Persian scientist Ibn Sina (known to the West as Avicenna) produced treatises and works that summarized the vast amount of knowledge that scientists had accumulated, and was very influential through his encyclopedias, ''The Canon of Medicine'' and ''The Book of Healing''. The work of him and many others directly influenced the research of European scientists during the Renaissance.
Astronomy in medieval Islam was advanced by Al-Battani, who improved the precision of the measurement of the precession of the Earth's axis. The corrections made to the geocentric model by al-Battani, Averroes, Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, Mo'ayyeduddin Urdi and Ibn al-Shatir were later incorporated into the Copernican heliocentrism, Copernican heliocentric model. The astrolabe, though originally developed by the Greeks, was developed further by Islamic astronomers and engineers, and subsequently brought to medieval Europe.
Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, Muslim alchemists influenced medieval European alchemists, particularly the writings attributed to Jābir ibn Hayyān (Geber).
Arab scientist Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) developed an early scientific method in his ''Book of Optics'' (1021). The most important development of the scientific method was the use of experiments to distinguish between competing scientific theories set within a generally empiricism, empirical orientation, which began among Muslim scientists. Ibn al-Haytham's empirical proof of the intromission theory of light (that is, that light rays entered the eyes rather than being emission theory (vision), emitted by them) was particularly important. Ibn al-Haytham was significant in the history of scientific method, particularly in his approach to experimentation, and has been referred to as the "world's first true scientist".
Medicine in medieval Islam was an area of science that advanced particularly during the Abbasids' reign. During the 9th century, Baghdad contained over 800 doctors, and great discoveries in the understanding of anatomy and diseases were made. The clinical distinction between measles and smallpox was described during this time. Famous Persian scientist Ibn Sina (known to the West as Avicenna) produced treatises and works that summarized the vast amount of knowledge that scientists had accumulated, and was very influential through his encyclopedias, ''The Canon of Medicine'' and ''The Book of Healing''. The work of him and many others directly influenced the research of European scientists during the Renaissance.
Astronomy in medieval Islam was advanced by Al-Battani, who improved the precision of the measurement of the precession of the Earth's axis. The corrections made to the geocentric model by al-Battani, Averroes, Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, Mo'ayyeduddin Urdi and Ibn al-Shatir were later incorporated into the Copernican heliocentrism, Copernican heliocentric model. The astrolabe, though originally developed by the Greeks, was developed further by Islamic astronomers and engineers, and subsequently brought to medieval Europe.
Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, Muslim alchemists influenced medieval European alchemists, particularly the writings attributed to Jābir ibn Hayyān (Geber).
 In technology, the Abbasids adopted papermaking from China. The use of paper spread from China into the caliphate in the 8th century CE, arriving in
In technology, the Abbasids adopted papermaking from China. The use of paper spread from China into the caliphate in the 8th century CE, arriving in  Engineers in the Abbasid caliphate made a number of innovative industrial uses of hydropower, and early industrial uses of tidal power, wind power, and petroleum (notably by distillation into kerosene). The industrial uses of watermills in the Islamic world date back to the 7th century, while horizontal-Water wheel, wheeled and vertical-wheeled water mills were both in widespread use since at least the 9th century. By the time of the Crusades, every province throughout the Islamic world had mills in operation, from al-Andalus and North Africa to the Middle East and Central Asia. These mills performed a variety of agricultural and industrial tasks. Abbasid engineers also developed machines (such as pumps) incorporating crankshafts, employed gears in mills and water-raising machines, and used dams to provide additional power to watermills and water-raising machines. Such advances made it possible for many industrial tasks that were previously driven by manual labour in ancient times to be Mechanization, mechanized and driven by machinery instead in the medieval Islamic world. It has been argued that the industrial use of waterpower had spread from Islamic to Christian Spain, where fulling mills, paper mills, and forge mills were recorded for the first time in Catalonia.
A number of industries were generated during the Arab Agricultural Revolution, including early industries for textiles, sugar, rope-making, matting, silk, and paper. Latin translations of the 12th century passed on knowledge of chemistry and instrument making in particular. The agricultural and handicraft industries also experienced high levels of growth during this period.
Engineers in the Abbasid caliphate made a number of innovative industrial uses of hydropower, and early industrial uses of tidal power, wind power, and petroleum (notably by distillation into kerosene). The industrial uses of watermills in the Islamic world date back to the 7th century, while horizontal-Water wheel, wheeled and vertical-wheeled water mills were both in widespread use since at least the 9th century. By the time of the Crusades, every province throughout the Islamic world had mills in operation, from al-Andalus and North Africa to the Middle East and Central Asia. These mills performed a variety of agricultural and industrial tasks. Abbasid engineers also developed machines (such as pumps) incorporating crankshafts, employed gears in mills and water-raising machines, and used dams to provide additional power to watermills and water-raising machines. Such advances made it possible for many industrial tasks that were previously driven by manual labour in ancient times to be Mechanization, mechanized and driven by machinery instead in the medieval Islamic world. It has been argued that the industrial use of waterpower had spread from Islamic to Christian Spain, where fulling mills, paper mills, and forge mills were recorded for the first time in Catalonia.
A number of industries were generated during the Arab Agricultural Revolution, including early industries for textiles, sugar, rope-making, matting, silk, and paper. Latin translations of the 12th century passed on knowledge of chemistry and instrument making in particular. The agricultural and handicraft industries also experienced high levels of growth during this period.
 In Baghdad there were many Abbasid military leaders who were or said they were of Arab descent. However, it is clear that most of the ranks were of Iranian peoples, Iranian origin, the vast majority being from Khorasan Province, Khurasan and
In Baghdad there were many Abbasid military leaders who were or said they were of Arab descent. However, it is clear that most of the ranks were of Iranian peoples, Iranian origin, the vast majority being from Khorasan Province, Khurasan and
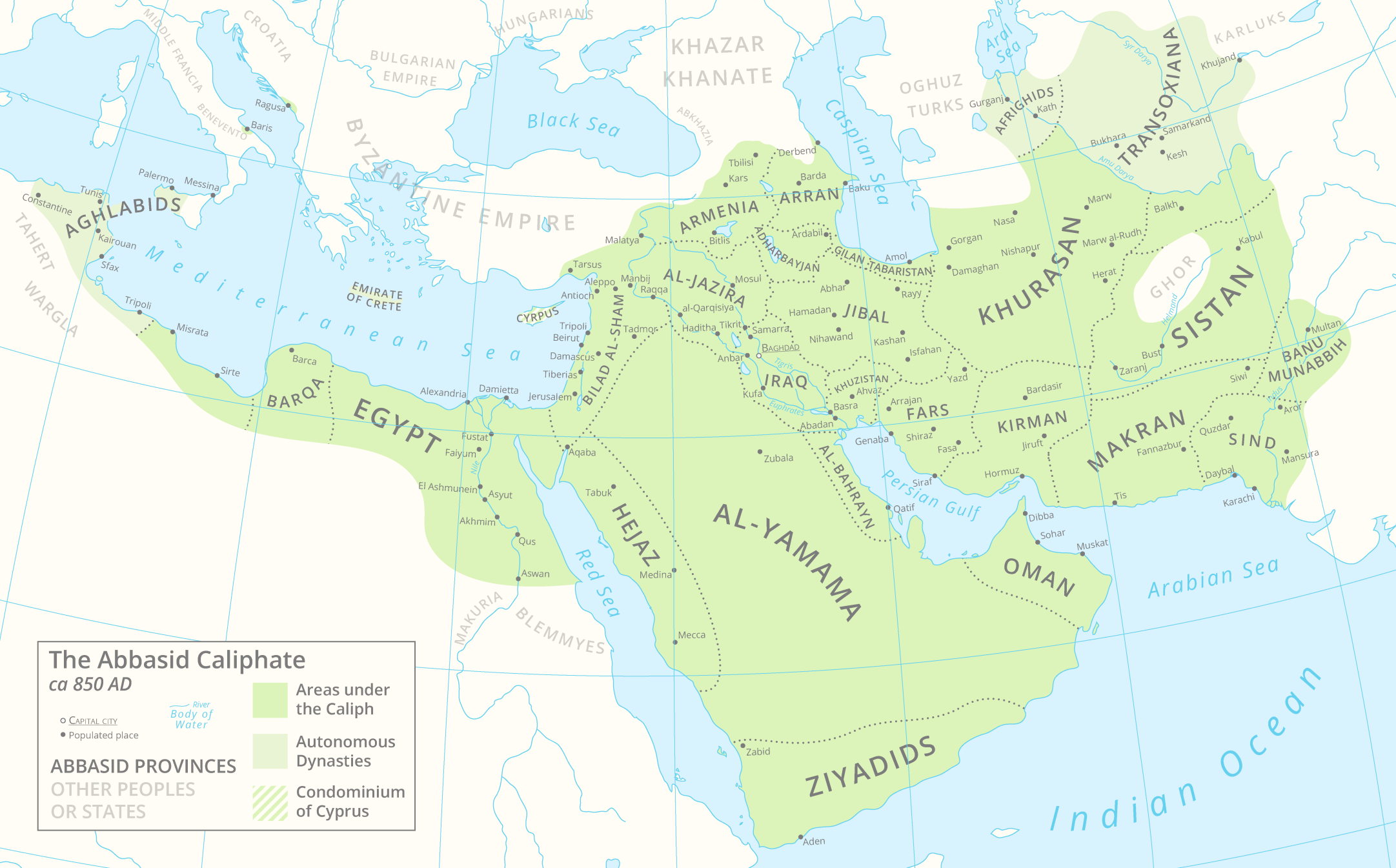 As a result of such a vast Empire, the caliphate was decentralized and divided into 24 provinces.
Harun's vizier enjoyed close to unchecked powers. Under Harun, a special "bureau of confiscation" was created. This governmental wing made it possible for the vizier to seize the property and riches of any corrupt governor or civil servant. In addition, it allowed governors to confiscate the estates of lower-ranking officials. Finally, the caliph could impose the same penalty on a vizier who fell from grace. As one later caliph put it: "The vizier is our representative throughout the land and amongst our subjects. Therefore, he who obeys him obeys us; and he who obeys us obeys God, and God shall cause him who obeys Him to enter paradise."
Every regional metropolis had a post office and hundreds of roads were paved in order to link the imperial capital with other cities and towns. The empire employed a system of relays to deliver mail. The central post office in Baghdad even had a map with directions that noted the distances between each town. The roads were provided with roadside inns, hospices, and wells and could reach eastward through Persia and
As a result of such a vast Empire, the caliphate was decentralized and divided into 24 provinces.
Harun's vizier enjoyed close to unchecked powers. Under Harun, a special "bureau of confiscation" was created. This governmental wing made it possible for the vizier to seize the property and riches of any corrupt governor or civil servant. In addition, it allowed governors to confiscate the estates of lower-ranking officials. Finally, the caliph could impose the same penalty on a vizier who fell from grace. As one later caliph put it: "The vizier is our representative throughout the land and amongst our subjects. Therefore, he who obeys him obeys us; and he who obeys us obeys God, and God shall cause him who obeys Him to enter paradise."
Every regional metropolis had a post office and hundreds of roads were paved in order to link the imperial capital with other cities and towns. The empire employed a system of relays to deliver mail. The central post office in Baghdad even had a map with directions that noted the distances between each town. The roads were provided with roadside inns, hospices, and wells and could reach eastward through Persia and
 Muslim merchants employed ports in Bandar Siraf, Basra, and Aden and some Red Sea ports to travel and trade with India and South East Asia. Land routes were also utilized through
Muslim merchants employed ports in Bandar Siraf, Basra, and Aden and some Red Sea ports to travel and trade with India and South East Asia. Land routes were also utilized through The Abbasid Caliphate: A History
Chapter 3: The Golden Age of the Abbasid Caliphate (775–833). 2021. Tayeb El-Hibri
caliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
to succeed the Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam () are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets are categorized as messengers (; sing. , ), those who transmit divine revelation, mos ...
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib
Al-Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib () was a paternal uncle and sahabi (companion) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, just three years older than his nephew. A wealthy merchant, during the early years of Islam he protected Muhammad while he was in Mecca, ...
(566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family, usually in the context of a monarchy, monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A dynasty may also be referred to as a "house", "family" or "clan", among others.
H ...
takes its name. After overthrowing the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member o ...
in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH), they ruled as caliphs
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the enti ...
based in modern-day Iraq, with Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
being their capital for most of their history.
The Abbasid Revolution had its origins and first successes in the easterly region of Khurasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses wes ...
, far from the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
ine center of Umayyad influence. The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa
Kufa ( ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates, Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000.
Along with Samarra, Karbala, Kadhimiya ...
, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph al-Mansur
Abū Jaʿfar ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad al-Manṣūr (; ; 714 – 6 October 775) usually known simply as by his laqab al-Manṣūr () was the second Abbasid caliph, reigning from 754 to 775 succeeding his brother al-Saffah (). He is known ...
founded the city of Baghdad as the new capital. Baghdad became the center of science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
, culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
, arts
The arts or creative arts are a vast range of human practices involving creativity, creative expression, storytelling, and cultural participation. The arts encompass diverse and plural modes of thought, deeds, and existence in an extensive ...
, and invention
An invention is a unique or novelty (patent), novel machine, device, Method_(patent), method, composition, idea, or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It m ...
in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. By housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom
The House of Wisdom ( ), also known as the Grand Library of Baghdad, was believed to be a major Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid-era public academy and intellectual center in Baghdad. In popular reference, it acted as one of the world's largest publ ...
, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, the city garnered an international reputation as a centre of learning. The Abbasid period was marked by the use of bureaucrats in governance, including the vizier
A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister in the Near East. The Abbasids, Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a help ...
, as well as an increasing inclusion of non-Arab Muslims in the ''ummah
' (; ) is an Arabic word meaning Muslim identity, nation, religious community, or the concept of a Commonwealth of the Muslim Believers ( '). It is a synonym for ' (, lit. 'the Islamic nation'); it is commonly used to mean the collective com ...
'' (Muslim community) and among the political elites.
The apogee of the caliphate's power and prestige is traditionally associated with Harun al-Rashid
Abū Jaʿfar Hārūn ibn Muḥammad ar-Rāshīd (), or simply Hārūn ibn al-Mahdī (; or 766 – 24 March 809), famously known as Hārūn al-Rāshīd (), was the fifth Abbasid caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate, reigning from September 786 unti ...
(). After his death, civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
brought new divisions and was followed by significant changes to the character of the state, including the creation of a new professional army recruited mainly from Turkic slaves and the construction of a new capital, Samarra
Samarra (, ') is a city in Iraq. It stands on the east bank of the Tigris in the Saladin Governorate, north of Baghdad. The modern city of Samarra was founded in 836 by the Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim as a new administrative capital and mi ...
, in 836. The 9th century also saw a growing trend of provincial autonomy spawning local dynasties who controlled different regions of the empire, such as the Aghlabids
The Aghlabid dynasty () was an Arab dynasty centered in Ifriqiya (roughly present-day Tunisia) from 800 to 909 that conquered parts of Sicily, Southern Italy, and possibly Sardinia, nominally as vassals of the Abbasid Caliphate. The Aghlabids ...
, Tahirids
The Tahirid dynasty (, ) was an Arabized Sunni Muslim dynasty of Persian dehqan origin that ruled as governors of Khorasan from 821 to 873 as well as serving as military and security commanders in Abbasid Baghdad until 891. The dynasty was f ...
, Samanids People
Samanid
Samanid
Samanid
The Samanid Empire () was a Persianate society, Persianate Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, ruled by a dynasty of Iranian peoples, Iranian ''dehqan'' origin. The empire was centred in Greater Khorasan, Khorasan an ...
, Saffarids
The Saffarid dynasty () was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian origin that ruled over parts of Persia, Greater Khorasan, and eastern Makran from 861 to 1002. One of the first indigenous Persian dynasties to emerge after the Islamic conq ...
, and Tulunids
The Tulunid State, also known as the Tulunid Emirate or The State of Banu Tulun, and popularly referred to as the Tulunids () was a Mamluk dynasty of Turkic peoples, Turkic origin who was the first independent dynasty to rule Egypt in the Middle ...
. Following a period of turmoil in the 860s, the caliphate regained some stability and its seat returned to Baghdad in 892.
During the 10th century, the authority of the caliphs was progressively reduced to a ceremonial function in the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
. Political and military power was transferred instead to the Iranian Buyids and the Seljuq Turks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; , ''Saljuqian'',) alternatively spelled as Saljuqids or Seljuk Turks, was an Oghuz Turkic, Sunni Muslim dynasty that gradually became Persianate and contributed to Turco-Persian culture.
The founder of t ...
, who took control of Baghdad in 945 and 1055, respectively. The Abbasids eventually regained control of Mesopotamia during the rule of Caliph al-Muqtafi
Abu Abdallah Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Mustazhir (; 9 April 1096 – 12 March 1160), better known by his laqab, regnal name al-Muqtafi li-Amr Allah (), was the List of Abbasid caliphs#Abbasid Caliphs (25 January 750 – 20 February 1258), Abbasid ca ...
() and extended it into Iran during the reign of Caliph al-Nasir
Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn al-Hasan al-Mustaḍīʾ (), better known by his al-Nāṣir li-Dīn Allāh (; 6 August 1158 – 5 October 1225) or simply as al-Nasir, was the Abbasid caliph in Baghdad from 1180 until his death. His literally can m ...
(). This revival ended in 1258 with the sack of Baghdad by the Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
under Hulagu Khan
Hulegu Khan, also known as Hülegü or Hulagu; ; ; ; ( 8 February 1265), was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of Western Asia. As a son of Tolui and the Keraite princess Sorghaghtani Beki, he was a grandson of Genghis Khan and brother of ...
and the execution of Caliph al-Musta'sim
Abu Ahmad Abdallah ibn al-Mustansir bi'llah (), better known by his laqab, regnal title Al-Mustaʿṣim bi-llāh (; 1213 – 20 February 1258), was the 37th and last caliph from the Abbasid dynasty ruling from Baghdad. He held the title from 12 ...
. A surviving line of Abbasids was re-installed in the Mamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
capital of Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
in 1261. Though lacking in political power, with the brief exception of Caliph al-Musta'in
Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad al-Mustaʿīn bi-ʾllāh (; 836 – 17 October 866), better known by his regnal title al-Mustaʿīn (836 – 17 October 866) was the Abbasid caliph from 862 to 866, during the "Anarchy at ...
, the dynasty continued to claim symbolic authority until a few years after the Ottoman conquest of Egypt in 1517, with the last Abbasid caliph being al-Mutawakkil III
Al-Mutawakkil III (; 1508–1543) was the seventeenth Abbasid caliph of Cairo for the Mamluk Sultanate from 1508 to 1516, and again in 1517.
Life
He was the last caliph of the later Egyptian-based Caliphate. Since the Mongol sack of Baghdad ...
.
History
Abbasid Revolution (747–750)
The Abbasid caliphs were descended fromAbbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib
Al-Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib () was a paternal uncle and sahabi (companion) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, just three years older than his nephew. A wealthy merchant, during the early years of Islam he protected Muhammad while he was in Mecca, ...
, one of the youngest uncles of Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
and of the same Banu Hashim
Banu Hashim () is an Arab clan within the Quraysh tribe to which the Islamic prophet Muhammad belonged, named after Muhammad's great-grandfather Hashim ibn Abd Manaf.
Members of this clan, and especially their descendants, are also referred ...
clan. The Abbasids claimed to be the true successors of Muhammad in replacing the Umayyad descendants of Banu Umayya by virtue of their closer bloodline to Muhammad.
The Abbasids also distinguished themselves from the Umayyads by attacking their moral character and administration in general. According to Ira Lapidus, "The Abbasid revolt was supported largely by Arabs, mainly the aggrieved settlers of Merv
Merv (, ', ; ), also known as the Merve Oasis, was a major Iranian peoples, Iranian city in Central Asia, on the historical Silk Road, near today's Mary, Turkmenistan. Human settlements on the site of Merv existed from the 3rd millennium& ...
with the addition of the Yemeni faction and their Mawali
''Mawlā'' (, plural ''mawālī'' ), is a polysemous Arabic word, whose meaning varied in different periods and contexts.A.J. Wensinck, Encyclopedia of Islam 2nd ed, Brill. "Mawlā", vol. 6, p. 874.
Before the Islamic prophet Muhammad, the te ...
". The Abbasids also appealed to non-Arab Muslims, known as ''mawali'', who remained outside the kinship-based society of the Arabs and were perceived as a lower class within the Umayyad empire. Muhammad ibn 'Ali, a great-grandson of Abbas, began to campaign in Persia for the return of power to the family of Muhammad, the Hashemites
The Hashemites (), also House of Hashim, are the royal family of Jordan, which they have ruled since 1921, and were the royal family of the kingdoms of Hejaz (1916–1925), Syria (1920), and Iraq (1921–1958). The family had ruled the city of Me ...
, during the reign of Umar II
Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz ibn Marwan (; February 720) was the eighth Umayyad caliph, ruling from 717 until his death in 720. He is credited to have instituted significant reforms to the Umayyad central government, by making it much more efficient and ...
.
During the reign of Marwan II
Marwan ibn Muhammad ibn Marwan (; – 6 August 750), commonly known as Marwan II, was the fourteenth and last caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 744 until his death. His reign was dominated by a Third Fitna, civil war, and he was the l ...
, this opposition culminated in the rebellion of Ibrahim al-Imam, the fourth in descent from Abbas. Supported by the province of Khurasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses wes ...
(eastern Iran), even though the governor opposed them, and the Shia Arabs, he achieved considerable success, but was captured in the year 747 and died, possibly assassinated, in prison.
On 9 June 747 (15 Ramadan AH 129), Abu Muslim, rising from Khurasan, successfully initiated an open revolt against Umayyad rule, which was carried out under the sign of the Black Standard. Close to 10,000 soldiers were under Abu Muslim's command when the hostilities officially began in Merv. General Qahtaba followed the fleeing governor Nasr ibn Sayyar
Naṣr ibn Sayyār al-Lāythi al-Kināni (; 663 – 9 December 748) was an Arab general and the last Umayyad governor of Khurasan in 738–748. Nasr played a distinguished role in the wars against the Turgesh, although he failed to decisively co ...
west defeating the Umayyads at the Battle of Gorgan, the Battle of Nahavand and finally in the Battle of Karbala, all in the year 748.
Ibrahim was captured by Marwan and was killed. The quarrel was taken up by Ibrahim's brother Abdallah, known by the name of Abu al-'Abbas as-Saffah, who defeated the Umayyads in 750 in the battle near the Great Zab and was subsequently proclaimed caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
. After this loss, Marwan fled to Egypt, where he was subsequently killed. The remainder of his family, barring one male, were also eliminated.
Establishment and consolidation (750–775)
Immediately after their victory, al-Saffah () sent his forces toCentral Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, where his forces fought against Tang expansion during the Battle of Talas
The Battle of Talas (; ) was an armed confrontation between the Abbasid Caliphate along with the Tibetan Empire against the Tang dynasty in 751. In July of that year, the Tang and Abbasid armies clashed at the Talas River over control of the r ...
. Al-Saffah focused on putting down numerous rebellions in Syria and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
. The Byzantines conducted raids during these early distractions.
One of the first major changes effected by Abbasid rule was the move of the caliphate's center of power from Syria to Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq). This was closer to the Persian ''mawali'' support base of the Abbasids and the move addressed their demand for reduced Arab dominance in the empire. However, no definitive capital was yet selected. In these early Abbasid years, Kufa
Kufa ( ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates, Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000.
Along with Samarra, Karbala, Kadhimiya ...
generally served as the administrative capital, but the caliphs were wary of the Alid sympathies in the city and did not always reside here. In 752, al-Saffah built a new city called al-Hashimiyya, at an uncertain location, most likely near Kufa. Later that same year, he moved to Anbar, where he built a new settlement for his Khurasani soldiers and a palace for himself.
It was al-Saffah's successor, Abu Ja'far al-Mansur () who firmly consolidated Abbasid rule and faced down internal challenges. His uncle, Abdallah ibn Ali, the victor over the Umayyads at the Battle of the Zab, was the most serious potential rival for leadership and al-Mansur sent Abu Muslim, the Khurasani revolutionary commander, against him in 754. After Abu Muslim successfully defeated him, al-Mansur then turned to eliminate Abu Muslim himself. He arranged to have him arrested and executed in 755.
On the western frontier, the Abbasids were unable to re-assert caliphal control over the western and central Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
, which the Umayyads had lost in the 740s. One member of the Umayyad dynasty, Abd ar-Rahman, also managed to escape the purge of his family and established independent rule in al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
(present-day Spain and Portugal) in 756, founding the Umayyad Emirate of Córdoba
An emirate is a territory ruled by an emir, a title used by monarchs or high officeholders in the Muslim world. From a historical point of view, an emirate is a political-religious unit smaller than a caliphate. It can be considered equivalen ...
.
In 756, al-Mansur had also sent over 4,000 Arab mercenaries to assist the Chinese Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
in the An Lushan Rebellion
The An Lushan rebellion was a civil war in China that lasted from 755 to 763, at the approximate midpoint of the Tang dynasty (618–907). It began as a commandery rebellion attempting to overthrow and replace the Tang government with the rogue ...
against An Lushan
An Lushan (; 20th day of the 1st month (19 February) 703 – 29 January 757) was a Chinese military general and rebel leader during the Tang dynasty and is primarily known for instigating the An Lushan Rebellion which devastated China and kill ...
. The Abbasids, or "Black Flags" as they were commonly called, were known in Tang dynasty chronicles as the ''hēiyī Dàshí'', "The Black-robed Tazi" () ("Tazi" being a borrowing from Persian '' Tāzī'', the word for "Arab"). Later, Caliph Harun al-Rashid
Abū Jaʿfar Hārūn ibn Muḥammad ar-Rāshīd (), or simply Hārūn ibn al-Mahdī (; or 766 – 24 March 809), famously known as Hārūn al-Rāshīd (), was the fifth Abbasid caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate, reigning from September 786 unti ...
sent embassies to the Chinese Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
and established good relations with them. After the war, these embassies remained in China with al-Rashid establishing an alliance with China. Several embassies from the Abbasid Caliphs to the Chinese court have been recorded in the ''Old Book of Tang
The ''Old Book of Tang'', or simply the ''Book of Tang'', is the first classic historical work about the Tang dynasty, comprising 200 chapters, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories. Originally compiled during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
'', the most important being those of al-Saffah, al-Mansur, and Harun al-Rashid.
 In 762, al-Mansur suppressed a rebellion in the
In 762, al-Mansur suppressed a rebellion in the Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
led by al-Nafs al-Zakiyya, a descendant from Ali ibn Abi Talib
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until Assassination of Ali, his assassination in 661, as well as the first imamate in Shia doctrine, Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muha ...
, whose challenge to the Abbasid claim to leadership was based on his Alid lineage and thus presented a serious political threat. He was defeated by an Abbasid army led by Isa ibn Musa. It was after this victory, in 762, that al-Mansur finally established a proper Abbasid capital, Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
– officially called ''Madinat al-Salam'' ('City of Peace') – located on the Tigris River
The Tigris ( ; see below) is the eastern of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, before merging ...
, near the former ancient capital city of Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; , ''Tyspwn'' or ''Tysfwn''; ; , ; Thomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modified July 28, 2014, http://syriaca.org/place/58.) was an ancient city in modern Iraq, on the eastern ba ...
. Prior to this, he had continued to consider multiple sites for a capital, including al-Hashimiyya, which he used as a capital for a while, and al-Rumiyya (near the ruins of Ctesiphon), which he used for a few months. Various other sites in the region also appear to have served as "capitals" under either al-Saffah or al-Mansur prior to the founding of Baghdad.
Al-Mansur centralised the judicial administration and, later, Harun al-Rashid established the institution of Chief Qadi to oversee it. The Umayyad empire was mostly Arab; however, the Abbasids progressively became made up of more and more converted Muslims in which the Arabs were only one of many ethnicities. The Abbasids had depended heavily on the support of Persians in their overthrow of the Umayyads. Al-Mansur welcomed non-Arab Muslims to his court. While this helped integrate Arab and Persian cultures, it alienated many of their Arab supporters, particularly the Khurasani Arabs who had supported them in their battles against the Umayyads.
Golden age (775–861)
The Abbasid leadership had to work hard in the last half of the 8th century (750–800) under several competent caliphs and their viziers to usher in the administrative changes needed to keep order of the political challenges created by the far-flung nature of the empire, and the limited communication across it. It was also during this early period of the dynasty, in particular during the rule of al-Mansur, Harun al-Rashid, andal-Ma'mun
Abū al-ʿAbbās Abd Allāh ibn Hārūn al-Maʾmūn (; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name al-Ma'mun (), was the seventh Abbasid caliph, who reigned from 813 until his death in 833. His leadership was marked by t ...
, that its reputation and power were created.
The position of ''wazir'' (vizier) developed in this period. It was initially akin to a secretary, but under the tenure of the Barmakids, an Iranian family close to the Abbasids, the position became powerful and Harun al-Rashid delegated state affairs to them for many years. This resulted in a more ceremonial role for many Abbasid caliphs relative to their time under the Umayyads; the viziers began to exert greater influence, and the role of the caliph's aristocracy was slowly replaced by a Barmakid bureaucracy. At the western end of the empire, Harun al-Rashid agreed to grant the province of Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya ( '), also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna (), was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia, eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania (roughly western Libya). It included all of what had previously been the Byzantine province of ...
(centered in present-day Tunisia) as a hereditary emirate to Ibrahim ibn al-Aghlab, who founded the Aghlabid dynasty
The Aghlabid dynasty () was an Arab dynasty centered in Ifriqiya (roughly present-day Tunisia) from 800 to 909 that conquered parts of Sicily, Southern Italy, and possibly Sardinia, nominally as vassals of the Abbasid Caliphate. The Aghlabids ...
there.
Under Harun al-Rashid's reign (), the Abbasid Empire reached its peak. His father, al-Mahdi
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd Allāh al-Manṣūr (; 744 or 745 – 785), better known by his regnal name al-Mahdī (, "He who is guided by God"), was the third Abbasid Caliph who reigned from 775 to his death in 785. He succeeded his ...
(), restarted the fighting with the Byzantines, and his sons continued the conflict until Empress Irene
Irene of Athens (, ; 750/756 – 9 August 803), surname Sarantapechaena (, ), was Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Eastern Roman empress, empress consort to Emperor Leo IV from 775 to 780, regent during the childhood of their son Constantine VI from ...
pushed for peace. After several years of peace, Nikephoros I
Nikephoros I (; 750 – 26 July 811), also known as Nicephorus I, was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. He was General Logothete (finance minister) under Empress Irene, but later overthrew her to seize the throne for himself. Prior to becomi ...
broke the treaty, then fended off multiple incursions during the first decade of the 9th century. These Abbasid attacks pushed into the Taurus Mountains
The Taurus Mountains (Turkish language, Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar,'' Greek language, Greek'':'' Ταύρος) are a mountain range, mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coastal reg ...
, culminating with a victory at the Battle of Krasos
The Battle of Krasos took place during the Arab–Byzantine Wars in August 804, between the Byzantines under Emperor Nikephoros I (r. 802–811) and an Abbasid army under Ibrahim ibn Jibril. Nikephoros' accession in 802 resulted in a resumption ...
and the massive invasion of 806, led by al-Rashid himself. Harun al-Rashid's navy also proved successful, taking Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
. Al-Rashid then focused on the rebellion of Rafi ibn al-Layth in Khurasan and died while there.
 Domestically, al-Rashid pursued policies similar to those of his father al-Mahdi. He released many of the Umayyads and Alids his brother
Domestically, al-Rashid pursued policies similar to those of his father al-Mahdi. He released many of the Umayyads and Alids his brother al-Hadi
Abū Muḥammad Mūsā ibn al-Mahdī al-Hādī (; 26 April 764 CE 14 September 786 CE) better known by his laqab al-Hādī () was the fourth Arab Abbasid caliph who succeeded his father al-Mahdi and ruled from 169 AH (785 CE) until his death in 1 ...
() had imprisoned and declared amnesty for all political groups of the Quraysh
The Quraysh () are an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe who controlled Mecca before the rise of Islam. Their members were divided into ten main clans, most notably including the Banu Hashim, into which Islam's founding prophet Muhammad was born. By ...
. While Baghdad remained the official capital, al-Rashid chose to reside in Raqqa
Raqqa (, also , Kurdish language, Kurdish: ''Reqa'') is a city in Syria on the North bank of the Euphrates River, about east of Aleppo. It is located east of the Tabqa Dam, Syria's largest dam. The Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine city and b ...
from 796 until the end of his reign. In 802, he established an unusual succession plan which decreed that his son al-Amin
Abū Mūsā Muḥammad bin Hārūn al-Amīn (; April 787 – 24/25 September 813), better known by just his laqab of al-Amīn (), was the sixth Abbasid caliph from 809 to 813.
Al-Amin succeeded his father, Harun al-Rashid, in 809 and ruled unt ...
would inherit the title of Caliph and have control of Iraq and the western empire while his other son al-Ma'mun
Abū al-ʿAbbās Abd Allāh ibn Hārūn al-Maʾmūn (; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name al-Ma'mun (), was the seventh Abbasid caliph, who reigned from 813 until his death in 833. His leadership was marked by t ...
would rule Khurasan and most eastern parts of the empire. In 803, he turned on and imprisoned or killed most of the Barmakids, who had wielded administrative power on his behalf. The reasons for this sudden and ruthless move remain unclear and have been the subject of much discussion by contemporary writers and later historians.
Al-Rashid's decision to split the succession proved to be damaging to the longevity of the empire. After his death in 809, his succession pact eventually collapsed and the empire was split by a civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
between al-Amin in Iraq and al-Ma'mun in Khurasan. This ended with a successful siege of Baghdad
The siege of Baghdad took place in early 1258. A large army commanded by Hulegu, a prince of the Mongol Empire, attacked the historic capital of the Abbasid Caliphate after a series of provocations from its ruler, caliph al-Musta'sim. Within ...
by al-Ma'mun's forces. When the city fell in 813, al-Amin was captured and executed on the orders of al-Ma'mun's general, Tahir ibn Husayn
Ṭāhir ibn Ḥusayn (, ''Tahir bin al-Husayn''), also known as Dhul-Yamīnayn (, "the ambidextrous"), and al-Aʿwar (, "the one-eyed"), was a general and governor during the Abbasid Caliphate. Specifically, he served under al-Ma'mun during the ...
. This marked the first time that an Abbasid ruler was publicly executed and it irrevocably damaged the prestige of the caliphate.
Al-Ma'mun became caliph and ruled until his death in 833. He initially ruled the empire from his established base in Merv, Khurasan, where his main support was found, but this prolonged the discontent and instability in Iraq and triggered further fighting in the years following his victory. In 817, he officially declared an Alid, 'Ali al-Rida, as his heir, instead of an Abbasid family member, perhaps hoping to promote Muslim unity, but the move backfired. Eventually, he was compelled to step back from these policies and move his court to Baghdad, where he arrived in August 819. After this, the rest of his reign was relatively peaceful. Exceptions included a rebellion in Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
by the Khurramites
The Khurramites ( , meaning "those of the Joyful Religion") were an IranianW. Madelung, "Khurrammiya" in ''Encyclopaedia of Islam''. Edited by: P. Bearman, Th. Bianchi, C.E. Bosworth, E. van Donzel and W.P. Heinrichs. Brill, 2009. Brill Online. ...
, supported by the Byzantines, which continued until 837. He also repulsed a Byzantine attack on Syria around 829, followed by counter-attacks into Anatolia, and suppressed a rebellion in Egypt in 832.
The later years of al-Ma'mun's reign are known for his intellectual interests and patronage. The so-called "translation movement" — the state-sponsored translation of scientific and literary works of antiquity into Arabic — that had begun under his predecessors was pushed even further during this time and al-Ma'mun shifted its focus to ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
works of science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
and philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
. In matters of religion, his interest in philosophy spurred him to endorse Mu'tazilism
Mu'tazilism (, singular ) is an Islamic theological school that appeared in early Islamic history and flourished in Basra and Baghdad. Its adherents, the Mu'tazilites, were known for their neutrality in the dispute between Ali and his opponents ...
, the rationalist school of Islamic thought. Under its influence, he officially endorsed the doctrine of createdness of the Qur'an in 827. In 833, he went further and forcibly imposed it on the ''ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' ( ; also spelled ''ulema''; ; singular ; feminine singular , plural ) are scholars of Islamic doctrine and law. They are considered the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam.
"Ulama ...
'', the Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
religious scholars. This controversial policy, known as the ''Mihna
The Mihna () was a period of religious persecution instituted by the Abbasid caliph al-Ma'mun in 833 in which Sunni scholars were punished, imprisoned, or even killed unless they conformed to Mu'tazilite doctrine. The policy lasted for eighteen y ...
'', was eventually abandoned in 848. Ultimately, it failed to convince the Sunni ''ulama'' and instead contributed to the emergence of the latter as a more cohesive social class whose views and interests did not always align with the caliph.
Following the civil war between al-Amin and al-Ma'mun, the traditional mainstay of the Abbasid army, the ''Khurasaniyya'' and '' al-Mu'tasim
Abū Isḥāq Muḥammad ibn Hārūn al-Rashīd (; October 796 – 5 January 842), better known by his laqab, regnal name al-Muʿtaṣim biʾllāh (, ), was the eighth Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid caliph, ruling from 833 until his death in 842. ...
(), who is known for its more radical implementation. Soldiers were recruited from several new sources, but the most important, especially under al-Mu'tasim, were the group referred to by Arabic chronicles as "Turks" (), who appear to have been mainly Turkic people from Central Asia. Some modern scholars refer to them as Mamluks
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-sold ...
, marking them as the antecedent of the later slave-soldiers known by that term, but their exact legal status has been a subject of scholarly debate. Many, perhaps the majority, were originally purchased or captured slaves, but they were paid regular salaries and thus likely manumitted
Manumission, or enfranchisement, is the act of freeing slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and ...
. In any case, these outsiders did not have political ties among the traditional elites and thus their loyalty was to the caliph alone.
These troops were likely the first standing army
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars ...
of the caliphate and provided the caliph with a strong base of military support. However, the influx of new foreign troops into the capital created tensions with its inhabitants and with older elites. This was one of the main reasons why, in 836, al-Mu'tasim decided to found a new capital, Samarra
Samarra (, ') is a city in Iraq. It stands on the east bank of the Tigris in the Saladin Governorate, north of Baghdad. The modern city of Samarra was founded in 836 by the Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim as a new administrative capital and mi ...
, on an open site to the north of Baghdad. The new capital housed the caliph's army, allowed for the unhindered construction of massive new palaces, and became the focus of an even more elaborate courtly culture.
Al-Mu'tasim's reign marked the end of the strong caliphs. He strengthened his personal army with the Mamluks and promptly restarted the war with the Byzantines. Though his attempt to seize Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
failed when his fleet was destroyed by a storm, his military excursions were generally successful, culminating with a resounding victory in the Sack of Amorium
The siege of Amorium by the Abbasid Caliphate in mid-August 838 was one of the major events in the long history of the Arab–Byzantine Wars. The Abbasid campaign was led personally by the Caliph al-Mu'tasim (), in retaliation to a virtually uno ...
.
Political fragmentation (861–945)
From the ninth century onward, the Abbasids found they could no longer keep together a centralized polity from Baghdad, which had grown larger than that ofRome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
. As mentioned, Harun al-Rashid had already granted the province of Ifriqiya to the Aghlabids, who ruled this region as an autonomous vassal state until its fall to the Fatimids
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimid dynasty, Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa ...
in 909. In al-Ma'mun's reign, Tahir ibn Husayn (al-Ma'mun's general in the civil war) was appointed viceroy of Iran and most of the eastern regions of the empire from 821 onward. His descendants, the Tahirids
The Tahirid dynasty (, ) was an Arabized Sunni Muslim dynasty of Persian dehqan origin that ruled as governors of Khorasan from 821 to 873 as well as serving as military and security commanders in Abbasid Baghdad until 891. The dynasty was f ...
, continued to govern in this position with significant autonomy until 873, although they remained loyal to the caliph and used only the title of ''amir
Emir (; ' (), also transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or ceremonial authority. The title has ...
''. From their capital at Nishapur
Nishapur or Neyshabur (, also ) is a city in the Central District (Nishapur County), Central District of Nishapur County, Razavi Khorasan province, Razavi Khorasan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.
Ni ...
, they were important patrons of Arabic literature and Sunni religious scholarship, in addition to making major improvements to agriculture. In Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
, the Persian Samanids People
Samanid
Samanid
Samanid
The Samanid Empire () was a Persianate society, Persianate Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, ruled by a dynasty of Iranian peoples, Iranian ''dehqan'' origin. The empire was centred in Greater Khorasan, Khorasan an ...
of Bukhara
Bukhara ( ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan by population, with 280,187 residents . It is the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and t ...
and Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
ruled as local governors, initially under the Tahirids. They oversaw the development of the region's cities into major trade centers, profiting from long-distance trade between China, Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and the Middle East.
The reign of al-Mutawakkil
Ja'far ibn al-Mu'tasim, Muḥammad ibn Harun al-Rashid, Hārūn al-Mutawakkil ʿalā Allāh (); March 82211 December 861, commonly known by his laqab, regnal name al-Mutawwakil ala Allah (), was the tenth Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid caliph, rul ...
() was characterized by the caliph's extravagant spending, his attempts to further consolidate power within the state, and his replacement of the ''Mihna'' policy with support for more orthodox Sunni scholars, in particular the Hanbali school
The Hanbali school or Hanbalism is one of the four major schools of Islamic jurisprudence, belonging to the Ahl al-Hadith tradition within Sunni Islam. It is named after and based on the teachings of the 9th-century scholar, jurist and traditio ...
. In 853, the Byzantines sacked Damietta in Egypt, and the caliph responded by sending troops into Anatolia, who sacked and marauded until they were eventually annihilated in 863.
Al-Mutawakkil's lifestyle and spending weakened his support among the military. In 861, he was murdered at a party by a group of Turkish soldiers. This was the first time the Abbasid military intervened so directly and violently at court and it set a precedent for further coups. The following period, sometimes known as the "Anarchy at Samarra
The Anarchy at Samarra () was a period of extreme internal instability from 861 to 870 in the history of the Abbasid Caliphate, marked by the violent succession of four caliphs, who became Puppet ruler, puppets in the hands of powerful rival milit ...
" (861–870), saw four different caliphs come and go. While they each attempted to reassert their authority, they were at the mercy of military and political factions. Tax collection lapsed and, along with al-Mutawakkil's previous spending, this left the state short on funds, which exacerbated the infighting. In 865, the Turkish soldiers of Samarra even besieged Baghdad to overthrow the caliph al-Musta'in
Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Muḥammad ibn Muḥammad al-Mustaʿīn bi-ʾllāh (; 836 – 17 October 866), better known by his regnal title al-Mustaʿīn (836 – 17 October 866) was the Abbasid caliph from 862 to 866, during the "Anarchy at ...
and, when the city fell the following year, they replaced him with al-Mu'tazz
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Jaʿfar ibn Muḥammad ibn Hārūn al-Muʿtazz bi-ʾLlāh (; 847 – 16 July 869), better known by his regnal title al-Muʿtazz bi-ʾLlāh (, "He who is strengthened by God") was the Abbasid caliph from 866 t ...
. The latter was overthrown by the same faction in 869 and replaced by al-Muhtadi, who was similarly overthrown in 870. Al-Muhtadi was succeeded by al-Mu'tamid, who was finally able to restore some order, in large part thanks to the help of his brother al-Muwaffaq, who kept the military under control and ran most government affairs. The restoration was hampered by the Zanj Rebellion, Zanj rebellion, which erupted in 869 and threatened the center of Abbasid control in Iraq. This major threat was not brought under control until a determined campaign was launched in 879.
 By the 870s, Egypt became autonomous under Ahmad ibn Tulun and his Tulunid successors, though they continued to acknowledge the caliph and generally sent tribute to Baghdad. For a time, they even controlled Syria and parts of the Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia). In 882, the caliph al-Mu'tamid even tried to move his residence to Egypt at Ibn Tulun's invitation, though this move was aborted by the intervention of al-Muwaffaq.
In the east, the
By the 870s, Egypt became autonomous under Ahmad ibn Tulun and his Tulunid successors, though they continued to acknowledge the caliph and generally sent tribute to Baghdad. For a time, they even controlled Syria and parts of the Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia). In 882, the caliph al-Mu'tamid even tried to move his residence to Egypt at Ibn Tulun's invitation, though this move was aborted by the intervention of al-Muwaffaq.
In the east, the Saffarids
The Saffarid dynasty () was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian origin that ruled over parts of Persia, Greater Khorasan, and eastern Makran from 861 to 1002. One of the first indigenous Persian dynasties to emerge after the Islamic conq ...
were former soldiers in the Abbasid army who were stationed in Sistan and remained there as local strongmen. They began to challenge the Tahirids from 854 onward and in 873 they captured Nishapur, ending Tahirid rule. They marched on Baghdad in 876 but Battle of Dayr al-Aqul, were defeated by al-Muwaffaq. The two sides were forced to come to terms and the Abbasids allowed the Saffarids to rule over Sistan, Fars province, Fars, Kerman province, Kirman, and Khurasan.
In 898, al-Mu'tadid set the Saffarids and Samanids against each other by formally endorsing a Saffarid claim over Transoxiana, the Samanid domain. The Samanids emerged triumphant in battle and were able to expand their control thenceforth to Khurasan, while the Saffarids were contained further south. The Samanids never threatened Iraq or western Iran, but they were also not as close to the caliphs as their Tahirid predecessors and in practice they were almost entirely independent of Baghdad. They became even greater patrons of religion and the arts than the Tahirids. They still maintained an orthodox Sunni ideology but they differed from their predecessors by promoting the Persian language.
There was a brief Abbasid political and military revival at the end of the 9th century, especially under the policies of caliphs al-Mu'tadid () and al-Muktafi (). Under al-Mu'tadid, the capital was moved from Samarra back to Baghdad. Incursions by the Qarmatians and allied Bedouin tribes posed a serious threat from 899 onwards, but the Abbasid army, led by Muhammad ibn Sulayman al-Katib, Muhammad ibn Sulayman, won a reprieve against them in 904 and 907. In 905, the same general invaded Egypt and overthrew the weakened Tulunids, re-establishing Abbasid control to the west. By the time caliph al-Muktafi died in 908, the Abbasid revival was at its peak and a strong centralized state was in place again.
After his death, however, the state became dominated by feuding bureaucrats. Under al-Muqtadir (), the Abbasid court continued to project power and wealth publicly but the politics and financial policies of the time compromised the caliphate's sustainability in the long-term. It was in this period that the practice of giving out iqta, ''iqta''s (fiefs in the form of tax farms) as favours began, which had the effect of reducing the caliphate's own tax revenues.
In 909, North Africa was lost to the Fatimid dynasty, an Isma'ilism, Isma'ili Shia sect tracing its roots to Muhammad's daughter Fatima. The Fatimids took control of Ifriqiya from the Aghlabids and eventually Fatimid conquest of Egypt, conquered Egypt in 969, where they established their capital, Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
, near Fustat. By the end of the century, they were one of the main political and ideological challenges to Sunni Islam and the Abbasids, contesting the Abbasids for the titular authority of the Islamic ummah, ''ummah''. The challenge of the Fatimid Caliphate only ended with their downfall in the 12th century.
Under the caliph al-Radi (), Baghdad's authority declined further as local governors refused to send payments to the capital. The Ikhshidids ruled Egypt and Syria autonomously prior to the Fatimid takeover. Even in Iraq, many governors refused to obey and the caliph was unable to send armies against them. Al-Radi was forced to invite the governor of Wasit, Muhammad ibn Ra'iq, to take over the administration under the newly-created position of ''amir al-umara'' ("Commander of Commanders"). Ibn Ra'iq disbanded the salaried army of the caliph and reduced much of the government's bureaucratic infrastructure, including the traditional vizierate, thus removing much of the Abbasid state's basis for power. He was overthrown in 938 and the following years were bogged down in political turmoil.
Al-Mustakfi had a short reign from 944 to 946, and it was during this period that the Persian faction known as the Buyids from Daylam swept into power and assumed control over the bureaucracy in Baghdad. According to the history of Miskawayh, they began distributing ''iqta''s to their supporters. This period of localized secular control was to last nearly 100 years.
Outside Iraq, all the autonomous provinces slowly took on the characteristic of de facto states with hereditary rulers, armies, and revenues and operated under only nominal caliph suzerainty, which may not necessarily be reflected by any contribution to the treasury, such as the Soomro emirs that had gained control of Sindh and ruled the entire province from their capital of Mansura, Sindh, Mansura. Mahmud of Ghazni took the title of sultan, as opposed to the ''amir'' that had been in more common usage, signifying the Ghaznavids, Ghaznavid Empire's independence from caliphal authority, despite Mahmud's ostentatious displays of Sunni orthodoxy and ritual submission to the caliph. In the 11th century, the loss of respect for the caliphs continued, as some Islamic rulers no longer mentioned the caliph's name in the Friday khutba, ''khutba'', or struck it off their coinage.
Buyid and Seljuq control (945–1118)
Despite the power of the Buyid amirs, the Abbasids retained a highly ritualized court in Baghdad, as described by the Buyid bureaucrat Hilal al-Sabi', and they retained a certain influence over Baghdad as well as religious life. As Buyid power waned with the rule of Baha' al-Daula, the caliphate was able to regain some measure of strength. The caliph al-Qadir, for example, led the ideological struggle against the Shia with writings such as the ''Baghdad Manifesto''. The caliphs kept order in Baghdad itself, attempting to prevent the outbreak of fitna (word), ''fitna''s in the capital, often contending with the ''ayyarun''. With the Buyid dynasty on the wane, a vacuum was created that was eventually filled by the dynasty of Oghuz Turks known as the Seljuqs. By 1055, the Seljuqs had wrested control from the Buyids and Abbasids, and took temporal power. When the amir and former slave Basasiri took up the Shia Fatimid banner in Baghdad in 1056–57, the caliph Al-Qa'im (Abbasid caliph at Baghdad), al-Qa'im was unable to defeat him without outside help. Toghril Beg, the Seljuq sultan, restored Baghdad to Sunni rule and took Iraq for his dynasty. Once again, the Abbasids were forced to deal with a military power that they could not match, though the Abbasid caliph remained the titular head of the Islamic community. The succeeding sultans Alp Arslan and Malikshah, as well as their vizier Nizam al-Mulk, took up residence in Persia, but held power over the Abbasids in Baghdad. When the dynasty began to weaken in the 12th century, the Abbasids gained greater independence once again.Revival of caliphal state (1118–1258)
 Caliph al-Mustarshid () was the first caliph to build an army and to lead it in battle since the 10th century. He recruited Kurdish and Arab Bedouin tribes and re-fortified Baghdad. His first concern was not the Seljuks but the Banu Mazyad, Mazyadids of Hilla in central Iraq, whom he met in battle in 1123. His bid for independence was ultimately unsuccessful, as he was defeated by a Seljuk army in 1135 and assassinated soon after.
Under
Caliph al-Mustarshid () was the first caliph to build an army and to lead it in battle since the 10th century. He recruited Kurdish and Arab Bedouin tribes and re-fortified Baghdad. His first concern was not the Seljuks but the Banu Mazyad, Mazyadids of Hilla in central Iraq, whom he met in battle in 1123. His bid for independence was ultimately unsuccessful, as he was defeated by a Seljuk army in 1135 and assassinated soon after.
Under al-Muqtafi
Abu Abdallah Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Mustazhir (; 9 April 1096 – 12 March 1160), better known by his laqab, regnal name al-Muqtafi li-Amr Allah (), was the List of Abbasid caliphs#Abbasid Caliphs (25 January 750 – 20 February 1258), Abbasid ca ...
(), a new caliphal state began to emerge with the help of his vizier Awn ad-Din ibn Hubayra, Ibn Hubayra. Ibn Hubayra concentrated on reasserting authority in Iraq while the Seljuk Empire deteriorated. The Abbasids successfully defended Baghdad against the Seljuqs in the siege of Baghdad (1157), siege of 1157 and then conquered their Mazyadid enemies in Hilla in 1162. By the end of al-Muqtafi's reign, Baghdad controlled a state stretching from Basra in the south to the edges of Mosul in the north. After over two hundred years of Abbasid subjection to foreign dynasties, Caliph al-Mustanjid () formally declared independence from the Seljuk sultans in 1165, when he dropped their names from Abbasid coinage. Initially, the caliphs were still vulnerable to the power of the viziers, but al-Mustadi () was able to further rally some support from the Baghdad public as well as symbolic support abroad from the Ayyubid dynasty, Ayyubid sultan Saladin and the Sultanate of Rum, Rum Seljuk sultan Kilij Arslan II.
 The long reign of Caliph
The long reign of Caliph al-Nasir
Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn al-Hasan al-Mustaḍīʾ (), better known by his al-Nāṣir li-Dīn Allāh (; 6 August 1158 – 5 October 1225) or simply as al-Nasir, was the Abbasid caliph in Baghdad from 1180 until his death. His literally can m ...
() marked a definitive shift in late Abbasid power. He reinvigorated public displays of caliphal prestige, removed officials who were too powerful, engaged in diplomacy with regions beyond Iraq, and extended his control over former Seljuk territories in western Iran — including Isfahan, Hamadan, Qazvin and Zanjan, Iran, Zanjan. He sought to build up his influence among Muslim rulers abroad largely through the Sufi-inspired futuwwa, ''futuwwa'' brotherhood that he headed. Under caliph Al-Mustansir I, al-Mustansir (), the Abbasid state achieved significant stability and many of the same policies continued. He built the Mustansiriyya Madrasa, inaugurated in 1234, the first madrasa to teach all four Sunni Madhhab, ''maddhab''s (schools of Fiqh, jurisprudence) and the first madrasa commissioned by an Abbasid caliph.
Mongol invasion and end
In 1206, Genghis Khan established a powerful dynasty among the Mongols of Central Asia. During the 13th century, this Mongol Empire conquered most of the Eurasian land mass, including both China in the east and much of the old Islamic caliphate and the Kievan Rus' in the west. In 1252,Hulagu Khan
Hulegu Khan, also known as Hülegü or Hulagu; ; ; ; ( 8 February 1265), was a Mongol ruler who conquered much of Western Asia. As a son of Tolui and the Keraite princess Sorghaghtani Beki, he was a grandson of Genghis Khan and brother of ...
, a grandson of Genghis Khan and brother of the new Mongol ruler, Möngke Khan, was placed in charge of a new western campaign to the Middle East that would culminate in the Siege of Baghdad, conquest of Baghdad in 1258.
In the years leading up the Mongol invasion, Baghdad's strength was sapped by political rivalries, sectarian tensions between Sunnis and Shias, and damaging floods. In 1257, after Mongol campaign against the Nizaris, destroying the Assassins in Iran, Hulagu wrote to the Abbasid caliph, al-Musta'sim
Abu Ahmad Abdallah ibn al-Mustansir bi'llah (), better known by his laqab, regnal title Al-Mustaʿṣim bi-llāh (; 1213 – 20 February 1258), was the 37th and last caliph from the Abbasid dynasty ruling from Baghdad. He held the title from 12 ...
, demanding his submission. The caliph refused, with Hulagu's status as a non-Muslim (unlike the earlier Buyids and Seljuks) likely a factor. There followed months of diplomacy, during which the Mongols may have been informed of Baghdad's weakness by correspondence with the caliph's vizier, Muhammad ibn al-Alqami, Ibn al-Alqami, a Shia who was later accused of colluding with them.
 The Mongols began their siege of the city on 29 January 1258. On 10 February, al-Musta'sim agreed to meet with Hulagu, who demanded that the caliph order the defenders to stand down and come out of the city in exchange for mercy. The caliph complied, but the Mongols slaughtered the population and then began the sack of the city on 13 February. Contemporary accounts describe destruction, looting, rape, and killing on a massive scale over many days, with hundreds of thousands killed and the city reduced to near-empty ruins, though some, like the Christian and Shia communities, were spared. The Mongols feared rumours that a supernatural disaster would strike if the blood of al-Musta'sim, a direct descendant of Muhammad's uncle and part of a dynasty that had reigned for five centuries, was spilled. As a precaution and in accordance with a Mongol taboo against spilling royal blood, Hulagu had al-Musta'sim wrapped in a carpet and trampled to death by horses on 20 February 1258. The caliph's immediate family was also executed, with the lone exceptions of his youngest son who was sent to Mongolia and a daughter who became a slave in the harem of Hulagu.
The fall of Baghdad marked the effective end of the Abbasid Caliphate. It made a deep impression on contemporary and later writers both inside and outside the Muslim world, some of whom created legendary stories about the last caliph's demise. It is also traditionally seen as the approximate end to the "classical age" or Islamic Golden Age, "golden age" of Islamic civilization. The events brought profound geopolitical changes to the traditional lands of the Islamic caliphate, with Iraq, Iran, and most of the eastern lands falling under Mongol control while other Muslim rulers retained the lands to the west. Mongol expansion further west was eventually halted by the Mamluks of Egypt at the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260, followed by the conflict between the Ilkhanids (Hulagu and his successors) and their Golden Horde rivals, which diverted Mongol attention.
The Mongols began their siege of the city on 29 January 1258. On 10 February, al-Musta'sim agreed to meet with Hulagu, who demanded that the caliph order the defenders to stand down and come out of the city in exchange for mercy. The caliph complied, but the Mongols slaughtered the population and then began the sack of the city on 13 February. Contemporary accounts describe destruction, looting, rape, and killing on a massive scale over many days, with hundreds of thousands killed and the city reduced to near-empty ruins, though some, like the Christian and Shia communities, were spared. The Mongols feared rumours that a supernatural disaster would strike if the blood of al-Musta'sim, a direct descendant of Muhammad's uncle and part of a dynasty that had reigned for five centuries, was spilled. As a precaution and in accordance with a Mongol taboo against spilling royal blood, Hulagu had al-Musta'sim wrapped in a carpet and trampled to death by horses on 20 February 1258. The caliph's immediate family was also executed, with the lone exceptions of his youngest son who was sent to Mongolia and a daughter who became a slave in the harem of Hulagu.
The fall of Baghdad marked the effective end of the Abbasid Caliphate. It made a deep impression on contemporary and later writers both inside and outside the Muslim world, some of whom created legendary stories about the last caliph's demise. It is also traditionally seen as the approximate end to the "classical age" or Islamic Golden Age, "golden age" of Islamic civilization. The events brought profound geopolitical changes to the traditional lands of the Islamic caliphate, with Iraq, Iran, and most of the eastern lands falling under Mongol control while other Muslim rulers retained the lands to the west. Mongol expansion further west was eventually halted by the Mamluks of Egypt at the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260, followed by the conflict between the Ilkhanids (Hulagu and his successors) and their Golden Horde rivals, which diverted Mongol attention.
Abbasid caliphs in Cairo (1261–1517)
Prior to the Mongol invasion, the later Ayyubid sultans of Egypt had built up an army recruited from slaves, theMamluks
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-sold ...
. During a political and military crisis in 1250, the Mamluks seized power and established what is now known as the Mamluk Sultanate. Following the devastation of Baghdad in 1258 and in an effort to secure political legitimacy for the new regime in Egypt, the Mamluk ruler Baybars invited a surviving member of the Abbasid family to establish himself in Cairo in 1260–1261. The new caliph was al-Mustansir II, a brother of the former caliph al-Mustansir. In 1262, he disappeared while leading a small army in an attempt to recapture Baghdad from the Mongols. Baybars subsequently replaced him with al-Hakim I, another Abbasid family member who had just been proclaimed in Aleppo.
Thereafter, the Abbasid caliphs in Cairo continued to exist as a strictly ceremonial but nonetheless important institution within the Mamluk Sultanate, conferring significant prestige on the Mamluks. It continued to be relevant even to other Muslim rulers until the 14th century; for example, the Delhi Sultanate, sultans of Delhi, the Muzaffarids (Iran), Muzaffarid sultan Mubariz al-Din Muhammad, Muhammad, the Jalayirid Sultanate, Jalayirid sultan Ahmad Jalayir, Ahmad, and the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman sultan Bayezid I all sought diplomas of investiture from the caliph or declared nominal allegiance to him. Caliph Al-Musta'in (Mamluk Sultanate), al-Musta'in even managed to reign as sultan in Cairo for a brief six months in 1412.
During the 15th century, however, the institution of the caliph declined in significance. The last Abbasid caliph in Cairo was al-Mutawakkil III
Al-Mutawakkil III (; 1508–1543) was the seventeenth Abbasid caliph of Cairo for the Mamluk Sultanate from 1508 to 1516, and again in 1517.
Life
He was the last caliph of the later Egyptian-based Caliphate. Since the Mongol sack of Baghdad ...
, who was in place when the Ottoman sultan Selim I Battle of Marj Dabiq, defeated the Mamluks in 1516 and Ottoman–Mamluk War (1516–1517), conquered Egypt in 1517, ending the Mamluk Sultanate. Selim I met with al-Mutawakkil III in Aleppo in 1516, prior to marching into Egypt, and the caliph was then sent to the Ottoman capital of Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
(present-day Istanbul), ending the Abbasid caliphate definitively. The idea of a "caliphate" subsequently became an ambiguous concept that was occasionally revisited by later Muslim rulers and intellectuals for political or religious reasons. The Ottoman sultans, who were thenceforth the most powerful Muslim rulers in western Asia and the Mediterranean, did not use the title of "caliph" at all before the mid-16th century and only did so vaguely and inconsistently afterwards. The claim that al-Mutawakkil III "transferred" the office of the caliph to the Ottoman sultan during their meeting in Aleppo is a legend that was elaborated in the 19th century and is not corroborated by contemporary accounts.
Culture
Islamic Golden Age
The Abbasid historical period lasting to the Mongol conquest of Baghdad in 1258 CE is considered the Islamic Golden Age. The Islamic Golden Age was inaugurated by the middle of the 8th century by the ascension of the Abbasid Caliphate and the transfer of the capital from Damascus to Baghdad. The Abbasids were influenced by the Qur'anic injunctions and hadith, such as "the ink of a scholar is more holy than the blood of a martyr", stressing the value of knowledge. During this period the Muslim world became an intellectual center for science, philosophy, medicine and education as the Abbasids championed the cause of knowledge and established theHouse of Wisdom
The House of Wisdom ( ), also known as the Grand Library of Baghdad, was believed to be a major Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid-era public academy and intellectual center in Baghdad. In popular reference, it acted as one of the world's largest publ ...
in Baghdad, where both Muslim and non-Muslim scholars sought to translate and gather all the world's knowledge into Arabic language, Arabic. Many classic works of antiquity that would otherwise have been lost were translated into Arabic and Persian and later in turn translated into Turkish, Hebrew and Latin. During this period the Muslim world was a cauldron of cultures which collected, synthesized and significantly advanced the knowledge gained from the Ancient Rome, Roman, Chinese, History of India, Indian, Sasanian Empire, Persian, Ancient Egypt, Egyptian, North African, Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek and Byzantine, Medieval Greek civilizations. According to Huff, "[i]n virtually every field of endeavor—in astronomy, alchemy, mathematics, medicine, optics and so forth—the Caliphate's scientists were in the forefront of scientific advance."
Literature
 The best-known fiction from the Islamic world is ''One Thousand and One Nights'', a collection of fantastical folk tales, legends and parables compiled primarily during the Abbasid era. The collection is recorded as having originated from an Arabic translation of a Sassanian-era Persian prototype, with likely origins in Indian literary traditions. Stories from Arabic literature, Arabic, Persian literature, Persian, Mesopotamian, and Egyptian literature, Egyptian folklore and literature were later incorporated. The epic is believed to have taken shape in the 10th century and reached its final form by the 14th century; the number and type of tales have varied from one manuscript to another.. All Arabian fantasy tales were often called "Arabian Nights" when translated into English, regardless of whether they appeared in ''The Book of One Thousand and One Nights''. This epic has been influential in the West since it was translated in the 18th century, first by Antoine Galland. Many imitations were written, especially in France. Various characters from this epic have themselves become cultural icons in Western culture, such as Aladdin, Sinbad and Ali Baba.
A famous example of Islamic poetry on romance (love), romance was ''Layla and Majnun'', an originally Arabic story which was further developed by Iranian peoples, Iranian, Azerbaijani people, Azerbaijani and other poets in the Persian language, Persian, Azerbaijani language, Azerbaijani, and Turkish language, Turkish languages. It is a Tragedy, tragic story of undying love much like the later ''Romeo and Juliet''.
Arabic poetry reached its greatest height in the Abbasid era, especially before the loss of central authority and the rise of the Persianate dynasties. Writers like Abu Tammam and Abu Nuwas were closely connected to the caliphal court in Baghdad during the early 9th century, while others such as al-Mutanabbi received their patronage from regional courts.
Under Harun al-Rashid, Baghdad was renowned for its bookstores, which proliferated after the making of paper was introduced. Chinese papermakers had been among those taken prisoner by the Arabs at the
The best-known fiction from the Islamic world is ''One Thousand and One Nights'', a collection of fantastical folk tales, legends and parables compiled primarily during the Abbasid era. The collection is recorded as having originated from an Arabic translation of a Sassanian-era Persian prototype, with likely origins in Indian literary traditions. Stories from Arabic literature, Arabic, Persian literature, Persian, Mesopotamian, and Egyptian literature, Egyptian folklore and literature were later incorporated. The epic is believed to have taken shape in the 10th century and reached its final form by the 14th century; the number and type of tales have varied from one manuscript to another.. All Arabian fantasy tales were often called "Arabian Nights" when translated into English, regardless of whether they appeared in ''The Book of One Thousand and One Nights''. This epic has been influential in the West since it was translated in the 18th century, first by Antoine Galland. Many imitations were written, especially in France. Various characters from this epic have themselves become cultural icons in Western culture, such as Aladdin, Sinbad and Ali Baba.
A famous example of Islamic poetry on romance (love), romance was ''Layla and Majnun'', an originally Arabic story which was further developed by Iranian peoples, Iranian, Azerbaijani people, Azerbaijani and other poets in the Persian language, Persian, Azerbaijani language, Azerbaijani, and Turkish language, Turkish languages. It is a Tragedy, tragic story of undying love much like the later ''Romeo and Juliet''.
Arabic poetry reached its greatest height in the Abbasid era, especially before the loss of central authority and the rise of the Persianate dynasties. Writers like Abu Tammam and Abu Nuwas were closely connected to the caliphal court in Baghdad during the early 9th century, while others such as al-Mutanabbi received their patronage from regional courts.
Under Harun al-Rashid, Baghdad was renowned for its bookstores, which proliferated after the making of paper was introduced. Chinese papermakers had been among those taken prisoner by the Arabs at the Battle of Talas
The Battle of Talas (; ) was an armed confrontation between the Abbasid Caliphate along with the Tibetan Empire against the Tang dynasty in 751. In July of that year, the Tang and Abbasid armies clashed at the Talas River over control of the r ...
in 751. As prisoners of war, they were dispatched to Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
, where they helped set up the first Arab paper mill. In time, paper replaced parchment as the medium for writing, and the production of books greatly increased. These events had an academic and societal impact that could be broadly compared to the introduction of the printing press in the West. Paper aided in communication and record-keeping, it also brought a new sophistication and complexity to businesses, banking, and the civil service. In 794, Jafa al-Barmak built the first paper mill in Baghdad, and from there the technology circulated. Harun required that paper be employed in government dealings, since something recorded on paper could not easily be changed or removed, and eventually, an entire street in Baghdad's business district was dedicated to selling paper and books.
Philosophy
One of the common definitions for "Islamic philosophy" is "the style of philosophy produced within the framework of Islamic culture". Islamic philosophy, in this definition is neither necessarily concerned with religious issues, nor is exclusively produced by Muslims. Their works on Aristotle were a key step in the transmission of learning from ancient Greeks to the Islamic world and the West. They often corrected the philosopher, encouraging a lively debate in the spirit of ijtihad. They also wrote influential original philosophical works, and their thinking was incorporated into Christian philosophy during the Middle Ages, notably by Thomas Aquinas. Three speculative thinkers, al-Kindi, al-Farabi, and Avicenna, combined Aristotelianism and Neoplatonism with other ideas introduced through Islam, and Avicennism was later established as a result. Other influential Abbasid philosophers include al-Jahiz, and Ibn al-Haytham (Alhacen).Architecture
As power shifted from the Umayyads to the Abbasids, the architectural styles changed also, from Greco-Roman tradition (which features elements of Hellenistic and Roman representative style) to Eastern tradition which retained their independent architectural traditions from Architecture of Mesopotamia, Mesopotamia and Persia. The Abbasid architecture was particularly influenced by Sasanian architecture, which in turn featured elements present since ancient Mesopotamia. The Christian styles evolved into a style based more on the Sasanian Empire, utilizing mud bricks and baked bricks with carved stucco. Other architectural innovations and styles were few, such as the four-centred arch, four-centered arch, and a dome erected on squinches. Unfortunately, much was lost due to the ephemeral nature of the stucco and luster tiles. Another major development was the creation or vast enlargement of cities as they were turned into the capital of the empire, beginning with the creation of Baghdad in 762, which was planned as a walled city with four gates, and a mosque and palace in the center. Al-Mansur, who was responsible for the creation of Baghdad, also planned the city of
Another major development was the creation or vast enlargement of cities as they were turned into the capital of the empire, beginning with the creation of Baghdad in 762, which was planned as a walled city with four gates, and a mosque and palace in the center. Al-Mansur, who was responsible for the creation of Baghdad, also planned the city of Raqqa
Raqqa (, also , Kurdish language, Kurdish: ''Reqa'') is a city in Syria on the North bank of the Euphrates River, about east of Aleppo. It is located east of the Tabqa Dam, Syria's largest dam. The Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine city and b ...
, along the Euphrates. Finally, in 836, al-Mu'tasim moved the capital to a new site that he created along the Tigris, called Samarra. This city saw 60 years of work, with race-courses and game preserves to add to the atmosphere. Due to the dry remote nature of the environment, some of the palaces built in this era were isolated havens. Al-Ukhaidir Fortress is a fine example of this type of building, which has stables, living quarters, and a mosque, all surrounding inner courtyards. Mesopotamia only has one surviving mausoleum from this era, in Samarra: an octagonal domed structure known as the ''Qubbat al-Sulaibiyya'', which is the first known monumental tomb in Islamic architecture and may be the final resting place of al-Muntasir.
Baghdad, the epicenter of the empire, was originally Round city of Baghdad, organized in a circular fashion next to the Tigris River, with massive brick walls being constructed in successive rings around the core by a workforce of 100,000 with four huge gates (named Kufa, Basra, Khurasan and Syria). The central enclosure of the city contained Mansur's palace of in area and the great mosque of Baghdad, encompassing . Travel across the Tigris and the network of waterways allowing the drainage of the Euphrates into the Tigris was facilitated by bridges and canals servicing the population.
Outside the Abbasid heartlands, architecture was still influenced by the capital. In present-day Tunisia, the Great Mosque of Kairouan was founded under the Umayyad dynasty but completely rebuilt in the 9th century under the Aghlabid architecture, patronage of the Aghlabids, vassals of the Abbasids. The styles utilized were mainly Abbasid. In Egypt, Ahmad Ibn Tulun commissioned the Mosque of Ibn Tulun, Ibn Tulun Mosque, completed in 879, that is based on the style of Samarra and is now one of the best-preserved Abbasid-style mosques from this period.
Arts
The establishment of Abbasid power based in Iraq, rather than Syria, resulted in a cultural and artistic development influenced not only by the Mediterranean and Middle Eastern traditions but also by connections further afield with India, Central Asia, and China. The importation of Chinese ceramics elicited local imitations but also stirred innovations in local production. Abbasid ceramics became a more important art form with greater emphasis on decoration. A major innovation was the emergence of monochrome and polychrome lustreware, a technical achievement that had an important impact on the wider development of Islamic ceramics. Islamic glass, Glassware also became a more important art form and was likely the origin of the lustre technique that was introduced into ceramics. Few textiles have survived but the production of ''tiraz'', textiles with royal inscriptions, is well attested. Another major art form was calligraphy and manuscript production. During the Abbasid period, Islamic calligraphy, Arabic calligraphy evolved into a more refined discipline. Rounded Kufic script was typical and became increasingly stylized. Parchment only allowed for a few lines of script, but from the late 8th century onward History of paper, paper began to be produced. Qur'ans are the main type of book to have survived from this period.Science and technology
Science
 A number of medieval thinkers and scientists living under Islamic rule played a role in transmitting Islamic science to the Christian West. In addition, the period saw the recovery of much of the Alexandrian mathematical, geometric and astronomical knowledge, such as that of Euclid and Claudius Ptolemy. These recovered mathematical methods were later enhanced and developed by other Islamic scholars, notably by Persian scientists Al-Biruni and Abu Nasr Mansur.
Christians (particularly Nestorianism, Nestorian Christians) contributed to the Arab Islamic Civilization during the Umayyads and the Abbasids by translating works of Greek philosophers to Syriac Language, Syriac and afterwards to Arabic Language, Arabic. Nestorians played a prominent role in the formation of Arab culture, with the Academy of Gondishapur being prominent in the late Sassanid, Umayyad and early Abbasid periods. Notably, eight generations of the Nestorian Bukhtishu family served as private doctors to caliphs and sultans between the eighth and eleventh centuries.
Algebra was significantly developed by Persian scientist Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī during this time in his landmark text, ''The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing, Kitab al-Jabr wa-l-Muqabala'', from which the term ''algebra'' is derived. He is thus considered to be the father of algebra by some, although the Greek mathematician Diophantus has also been given this title. The terms ''algorism'' and ''algorithm'' are derived from the name of al-Khwarizmi, who was also responsible for introducing the Arabic numerals and Hindu–Arabic numeral system beyond the Indian subcontinent.
A number of medieval thinkers and scientists living under Islamic rule played a role in transmitting Islamic science to the Christian West. In addition, the period saw the recovery of much of the Alexandrian mathematical, geometric and astronomical knowledge, such as that of Euclid and Claudius Ptolemy. These recovered mathematical methods were later enhanced and developed by other Islamic scholars, notably by Persian scientists Al-Biruni and Abu Nasr Mansur.
Christians (particularly Nestorianism, Nestorian Christians) contributed to the Arab Islamic Civilization during the Umayyads and the Abbasids by translating works of Greek philosophers to Syriac Language, Syriac and afterwards to Arabic Language, Arabic. Nestorians played a prominent role in the formation of Arab culture, with the Academy of Gondishapur being prominent in the late Sassanid, Umayyad and early Abbasid periods. Notably, eight generations of the Nestorian Bukhtishu family served as private doctors to caliphs and sultans between the eighth and eleventh centuries.
Algebra was significantly developed by Persian scientist Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī during this time in his landmark text, ''The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing, Kitab al-Jabr wa-l-Muqabala'', from which the term ''algebra'' is derived. He is thus considered to be the father of algebra by some, although the Greek mathematician Diophantus has also been given this title. The terms ''algorism'' and ''algorithm'' are derived from the name of al-Khwarizmi, who was also responsible for introducing the Arabic numerals and Hindu–Arabic numeral system beyond the Indian subcontinent.
 Arab scientist Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) developed an early scientific method in his ''Book of Optics'' (1021). The most important development of the scientific method was the use of experiments to distinguish between competing scientific theories set within a generally empiricism, empirical orientation, which began among Muslim scientists. Ibn al-Haytham's empirical proof of the intromission theory of light (that is, that light rays entered the eyes rather than being emission theory (vision), emitted by them) was particularly important. Ibn al-Haytham was significant in the history of scientific method, particularly in his approach to experimentation, and has been referred to as the "world's first true scientist".
Medicine in medieval Islam was an area of science that advanced particularly during the Abbasids' reign. During the 9th century, Baghdad contained over 800 doctors, and great discoveries in the understanding of anatomy and diseases were made. The clinical distinction between measles and smallpox was described during this time. Famous Persian scientist Ibn Sina (known to the West as Avicenna) produced treatises and works that summarized the vast amount of knowledge that scientists had accumulated, and was very influential through his encyclopedias, ''The Canon of Medicine'' and ''The Book of Healing''. The work of him and many others directly influenced the research of European scientists during the Renaissance.
Astronomy in medieval Islam was advanced by Al-Battani, who improved the precision of the measurement of the precession of the Earth's axis. The corrections made to the geocentric model by al-Battani, Averroes, Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, Mo'ayyeduddin Urdi and Ibn al-Shatir were later incorporated into the Copernican heliocentrism, Copernican heliocentric model. The astrolabe, though originally developed by the Greeks, was developed further by Islamic astronomers and engineers, and subsequently brought to medieval Europe.
Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, Muslim alchemists influenced medieval European alchemists, particularly the writings attributed to Jābir ibn Hayyān (Geber).
Arab scientist Ibn al-Haytham (Alhazen) developed an early scientific method in his ''Book of Optics'' (1021). The most important development of the scientific method was the use of experiments to distinguish between competing scientific theories set within a generally empiricism, empirical orientation, which began among Muslim scientists. Ibn al-Haytham's empirical proof of the intromission theory of light (that is, that light rays entered the eyes rather than being emission theory (vision), emitted by them) was particularly important. Ibn al-Haytham was significant in the history of scientific method, particularly in his approach to experimentation, and has been referred to as the "world's first true scientist".
Medicine in medieval Islam was an area of science that advanced particularly during the Abbasids' reign. During the 9th century, Baghdad contained over 800 doctors, and great discoveries in the understanding of anatomy and diseases were made. The clinical distinction between measles and smallpox was described during this time. Famous Persian scientist Ibn Sina (known to the West as Avicenna) produced treatises and works that summarized the vast amount of knowledge that scientists had accumulated, and was very influential through his encyclopedias, ''The Canon of Medicine'' and ''The Book of Healing''. The work of him and many others directly influenced the research of European scientists during the Renaissance.
Astronomy in medieval Islam was advanced by Al-Battani, who improved the precision of the measurement of the precession of the Earth's axis. The corrections made to the geocentric model by al-Battani, Averroes, Nasir al-Din al-Tusi, Mo'ayyeduddin Urdi and Ibn al-Shatir were later incorporated into the Copernican heliocentrism, Copernican heliocentric model. The astrolabe, though originally developed by the Greeks, was developed further by Islamic astronomers and engineers, and subsequently brought to medieval Europe.
Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, Muslim alchemists influenced medieval European alchemists, particularly the writings attributed to Jābir ibn Hayyān (Geber).
Technology
 In technology, the Abbasids adopted papermaking from China. The use of paper spread from China into the caliphate in the 8th century CE, arriving in
In technology, the Abbasids adopted papermaking from China. The use of paper spread from China into the caliphate in the 8th century CE, arriving in al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
(Islamic Spain) and then the rest of Europe in the 10th century. It was easier to manufacture than parchment, less likely to crack than papyrus, and could absorb ink, making it ideal for making records and copies of the Qur'an. "Islamic paper makers devised assembly-line methods of hand-copying manuscripts to turn out editions far larger than any available in Europe for centuries." It was from the Abbasids that the rest of the world learned to make paper from linen. The knowledge of gunpowder was also transmitted from China via the caliphate, where the formulas for pure potassium nitrate and an explosive gunpowder effect were first developed.
Advances were made in irrigation and farming, using new technology such as the windmill. Crops such as almonds and citrus fruit were brought to Europe through al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most o ...
, and sugar cultivation was gradually adopted by the Europeans. Apart from the Nile, Tigris and Euphrates, navigable rivers were uncommon, so transport by sea was very important. Navigational sciences were highly developed, making use of a rudimentary sextant (known as a ''kamal''). When combined with detailed maps of the period, sailors were able to sail across oceans rather than skirt along the coast. Abbasid sailors were also responsible for reintroducing large three masted merchant vessels to the Mediterranean. The name ''caravel'' may derive from an earlier Arab ship known as the ''qārib''. Arab merchants dominated trade in the Indian Ocean until the arrival of the Portuguese in the 16th century. Ormus, Hormuz was an important center for this trade. There was also a dense network of trade routes in the Mediterranean, along which Muslim countries traded with each other and with European powers such as Venice or Genoa. The Silk Road crossing Central Asia passed through the Abbasid caliphate between China and Europe.
 Engineers in the Abbasid caliphate made a number of innovative industrial uses of hydropower, and early industrial uses of tidal power, wind power, and petroleum (notably by distillation into kerosene). The industrial uses of watermills in the Islamic world date back to the 7th century, while horizontal-Water wheel, wheeled and vertical-wheeled water mills were both in widespread use since at least the 9th century. By the time of the Crusades, every province throughout the Islamic world had mills in operation, from al-Andalus and North Africa to the Middle East and Central Asia. These mills performed a variety of agricultural and industrial tasks. Abbasid engineers also developed machines (such as pumps) incorporating crankshafts, employed gears in mills and water-raising machines, and used dams to provide additional power to watermills and water-raising machines. Such advances made it possible for many industrial tasks that were previously driven by manual labour in ancient times to be Mechanization, mechanized and driven by machinery instead in the medieval Islamic world. It has been argued that the industrial use of waterpower had spread from Islamic to Christian Spain, where fulling mills, paper mills, and forge mills were recorded for the first time in Catalonia.
A number of industries were generated during the Arab Agricultural Revolution, including early industries for textiles, sugar, rope-making, matting, silk, and paper. Latin translations of the 12th century passed on knowledge of chemistry and instrument making in particular. The agricultural and handicraft industries also experienced high levels of growth during this period.
Engineers in the Abbasid caliphate made a number of innovative industrial uses of hydropower, and early industrial uses of tidal power, wind power, and petroleum (notably by distillation into kerosene). The industrial uses of watermills in the Islamic world date back to the 7th century, while horizontal-Water wheel, wheeled and vertical-wheeled water mills were both in widespread use since at least the 9th century. By the time of the Crusades, every province throughout the Islamic world had mills in operation, from al-Andalus and North Africa to the Middle East and Central Asia. These mills performed a variety of agricultural and industrial tasks. Abbasid engineers also developed machines (such as pumps) incorporating crankshafts, employed gears in mills and water-raising machines, and used dams to provide additional power to watermills and water-raising machines. Such advances made it possible for many industrial tasks that were previously driven by manual labour in ancient times to be Mechanization, mechanized and driven by machinery instead in the medieval Islamic world. It has been argued that the industrial use of waterpower had spread from Islamic to Christian Spain, where fulling mills, paper mills, and forge mills were recorded for the first time in Catalonia.
A number of industries were generated during the Arab Agricultural Revolution, including early industries for textiles, sugar, rope-making, matting, silk, and paper. Latin translations of the 12th century passed on knowledge of chemistry and instrument making in particular. The agricultural and handicraft industries also experienced high levels of growth during this period.
Society
Arabization
While the Abbasids originally gained power by exploiting the social inequalities against non-Arabs in the Umayyad Empire, during Abbasid rule the empire rapidly Arabized, particularly in the Fertile Crescent region (namelyMesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
and the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
) as had begun under Umayyad rule. As knowledge was shared in the Arabic language throughout the empire, many people from different nationalities and religions began to speak Arabic in their everyday lives. Resources from other languages began to be translated into Arabic, and a unique Islamic identity began to form that fused previous cultures with Arab culture, creating a level of civilization and knowledge that was considered a marvel in Europe at the time.
Status of women
In contrast to the earlier era, women in Abbasid society were absent from all arenas of the community's central affairs. While their Muslim forebears led men into battle, started rebellions, and played an active role in community life, as demonstrated in the Hadith literature, Abbasid women were ideally kept in seclusion. Conquests had brought enormous wealth and large numbers of slaves to the Muslim elite. The majority of the slaves were women and children, many of whom had been dependents or harem-members of the defeated Sassanian upper classes. In the wake of the conquests an elite man could potentially own a thousand slaves, and ordinary soldiers could have ten people serving them. It was narrated from Ibn Abbas that Muhammad said: Even so, slave courtesans (qiyans and jawaris) and princesses produced prestigious and important poetry. Enough survives to give us access to women's historical experiences, and reveals some vivacious and powerful figures, such as the Sufi mystic Rabia of Basra, Raabi'a al-Adwiyya (714–801 CE), the princess and poet 'Ulayya bint al-Mahdi (777–825 CE), and the qiyan, singing-girls Shāriyah (–870 CE), Fadl Ashsha'ira (d. 871 CE) and Arib al-Ma'muniyya (797–890 CE). Each wife in the Abbasid harem had an additional home or flat, with her own enslaved staff of eunuchs and maidservants. When a concubinage in Islam, concubine gave birth to a son, she was elevated in rank to umm walad and also received apartments and (slave) servants as a gift.Treatment of Jews and Christians
The status and treatment of Jews, Christians, and non-Muslims in the Abbasid Caliphate was a complex and continually changing issue. Non-Muslims were called dhimmis. Dhimmis faced some level of discrimination in Abbasid society: they did not have all the privileges of Muslims and had to pay jizya, a tax on non-Muslims. However, as people of the book (non-Muslim monotheists), Jews and Christians were allowed to practice their religion and were not required to convert. One of the common aspects of the treatment of the dhimmis is that their treatment depended on who the caliph was at the time. Some Abbasid rulers, like Al-Mutawakkil (822–861 CE) imposed strict restrictions on what dhimmis could wear in public, often yellow garments that distinguished them from Muslims. Other restrictions al-Mutawakkil imposed included limiting the role of the dhimmis in government, seizing dhimmi housing and making it harder for dhimmis to become educated. Most other Abbasid caliphs were not as strict as al-Mutawakkil. During the reign of Al-Mansur (754–775 CE), it was common for Jews and Christians to influence the overall culture in thecaliphate
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of ...
, specifically in Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
. Jews and Christians did this by participating in scholarly work.
It was common that laws that were imposed against dhimmis during one caliph's rule were either discarded or not practiced during future caliphs' reigns. Al-Mansur and al-Mutawakkil both instituted laws that forbade non-Muslims from participating in public office. Al-Mansur did not follow his own law very closely, bringing dhimmis back to the caliphate's treasury due to the needed expertise of dhimmis in the area of finance. Al-Mutawakkil followed the law banning dhimmis from public office more seriously, although, soon after his reign, many of the laws concerning dhimmis participating in government were completely unobserved or at least less strictly observed. Even Al-Muqtadir (), who held a similar stance as al-Mutawakkil on barring non-Muslims from public office, himself had multiple Christian secretaries, indicating that non-Muslims still had access to many of the most important figures within the caliphate. Past having a casual association or just being a secretary to high-ranking Islamic officials, some of them achieved the second highest office after the caliph: the vizier
A vizier (; ; ) is a high-ranking political advisor or Minister (government), minister in the Near East. The Abbasids, Abbasid caliphs gave the title ''wazir'' to a minister formerly called ''katib'' (secretary), who was at first merely a help ...
.
Jews and Christians may have had a lower overall status compared to Muslims in the Abbasid Caliphate, but dhimmis were often allowed to hold respectable and even prestigious occupations in some cases, such as doctors and public officeholders. Jews and Christians were also allowed to be rich even if they were taxed for being a dhimmi. Dhimmis were capable of moving up and down the social ladder, though this largely depended on the particular caliph. An indication as to the social standing of Jews and Christians at the time was their ability to live next to Muslim people. While al-Mansur was ruling the caliphate, for instance, it was not uncommon for dhimmis to live in the same neighborhoods as Muslims. One of the biggest reasons why dhimmis were allowed to hold prestigious jobs and positions in government is that they were generally important to the well-being of the state and were proficient to excellent with the work at hand. Some Muslims in the caliphate took offense to the idea that there were dhimmis in public offices who were in a way ruling over them although it was an Islamic state, while other Muslims were at time jealous of some dhimmis for having a level of wealth or prestige greater than other Muslims, even if Muslims were still the majority of the ruling class. In general, Muslims, Jews, and Christians had close relations that could be considered positive at times, especially for Jews, in contrast to how Jews were being treated in Europe.
Many of the laws and restrictions that were imposed on dhimmis often resembled other laws that previous states had used to discriminate against a minority religion, specifically Jewish people. Romans in the fourth century banned Jewish people from holding public offices, banned Roman citizens from converting to Judaism, and often demoted Jews who were serving in the Roman military. In direct contrast, there was an event in which two viziers, Ibn al-Furat and Ali ibn Isa ibn al-Jarrah, argued about Ibn al-Furat's decision to make a Christian the head of the military. A previous vizier, Abu Muhammad al-Hasan al-Bazuri, had done so. These laws predated al-Mansur's laws against dhimmis and often had similar restrictions, although Roman emperors were often much more strict on enforcing these laws than many Abbasid caliphs.
Most of History of the Jews in Baghdad, Baghdad's Jews were incorporated into the Arab community and considered Arabic their native language. Some Jews studied Hebrew in their schools and Jewish religious education flourished. The united Muslim empire allowed Jews to reconstruct links between their dispersed communities throughout the Middle East. The city's Talmudic institute helped spread the rabbinical tradition to Europe, and the Jewish community in Baghdad went on to establish ten rabbinical schools and twenty-three synagogues. Baghdad not only contained the tombs of Muslim saints and martyrs, but also the tomb of Joshua in Islam, Yusha, whose corpse had been brought to Iraq during the first migration of the Jews out of the Levant.
Holidays
There were large feasts on certain days, as the Muslims of the empire celebrated Christian holidays as well as their own. There were two main Islamic feasts: Eid al-Fitr, one marked by the end of Ramadan; the other, "Eid al-Adha, the Feast of Sacrifice". The former was especially joyful because children would purchase decorations and sweetmeats; people prepared the best food and bought new clothes. At midmorning, the caliph, wearing Muhammad's thobe, would guide officials, accompanied by armed soldiers to the Great Mosque of al-Mansur, Great Mosque, where he led prayers. After the prayer, all those in attendance would exchange the best wishes and hug their kin and companions. The festivities lasted for three days. During those limited number of nights, the palaces were lit up and boats on the Tigris hung lights. It was said that Baghdad "glittered 'like a bride. During Eid al-Adha, the Feast of Sacrifice, sheep were butchered in public arenas and the caliph participated in a large-scale sacrifice in the palace courtyard. Afterward, the meat would be divided and given to the poor. In addition to these two holidays, Shias celebrated the birthdays of Fatimah andAli ibn Abi Talib
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until Assassination of Ali, his assassination in 661, as well as the first imamate in Shia doctrine, Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muha ...
. Matrimonies and births in the royal family were observed by all in the empire. The announcement that one of the caliph's sons could Qira'at, recite the Koran smoothly was greeted by communal jubilation. When Harun developed this holy talent, the people lit torches and decorated the streets with wreaths of flowers, and his father, Al-Mahdi, freed 500 slaves.
Of all the holidays imported from other cultures and religions, the one most celebrated in Baghdad (a city with many Persians) was Nowruz, which celebrated the arrival of spring. In a ceremonial ablution introduced by Persian troops, residents sprinkled themselves with water and ate almond cakes. The palaces of the imperial family were lit up for six days and nights. The Abbasids also celebrated the Persian holiday of Mihraj, which marked the onset of winter (signified with pounding drums), and Sadar, when homes burned incense and the masses would congregate along the Tigris to witness princes and viziers pass by.
Military
The Abbasid army amassed an array of siege equipment, such as catapults, mangonels, battering rams, ladders, grappling irons, and hooks. All such weaponry was operated by military engineers. However, the primary siege weapon was the , a type of siege weapon that was comparable to the trebuchet employed in Western medieval times. From the seventh century onward, it had largely replaced Torsion siege engine, torsion artillery. By Harun al-Rashid's time, the Abbasid army employed fire grenades. The Abbasids also utilized field hospitals and ambulances drawn by camels. The cavalry was entirely covered in iron, with helmets. Similar to medieval knights, their only exposed spots were the end of their noses and small openings in front of their eyes. Their foot soldiers were issued spears, swords, and pikes, and (in line with Persian fashion) trained to stand so solidly that, one contemporary wrote "you would have thought them held fast by clamps of bronze". Although the Abbasids never retained a substantial regular army, the caliph could recruit a considerable number of soldiers in a short time when needed from levies. There were also cohorts of regular troops who received steady pay and a special forces unit. At any moment, 125,000 Muslim soldiers could be assembled along the Byzantine frontier,Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
, Medina, Damascus, Rayy, and other geostrategic locations in order to quell any unrest.
 In Baghdad there were many Abbasid military leaders who were or said they were of Arab descent. However, it is clear that most of the ranks were of Iranian peoples, Iranian origin, the vast majority being from Khorasan Province, Khurasan and
In Baghdad there were many Abbasid military leaders who were or said they were of Arab descent. However, it is clear that most of the ranks were of Iranian peoples, Iranian origin, the vast majority being from Khorasan Province, Khurasan and Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
, not from western Iran or Azerbaijan. Most of the Khurasani soldiers who brought the Abbasids to power were Arabs. The standing army of the Muslims in Khurasan was overwhelmingly Arab. The unit organization of the Abbasids was designed with the goal of ethnic and racial equality among supporters. When Abu Muslim recruited officers along the Silk Road, he registered them based not on their tribal or ethno-national affiliations but on their current places of residence. Under the Abbasids, Iranian peoples became better represented in the army and bureaucracy as compared to before. The Abbasid army was centred on the Khurasan Abna al-dawla infantry and the Khurasaniyya heavy cavalry, led by their own semi-autonomous commanders () who recruited and deployed their own men with Abbasid resource grants. al-Mu‘tasim began the practice of recruiting Turkic slave soldiers from the Samanids People
Samanid
Samanid
Samanid
The Samanid Empire () was a Persianate society, Persianate Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, ruled by a dynasty of Iranian peoples, Iranian ''dehqan'' origin. The empire was centred in Greater Khorasan, Khorasan an ...
into a private army, which allowed him to take over the reins of the caliphate. He abolished the old ''jund'' system created by Umar and diverted the salaries of the original Arab military descendants to the Turkic slave soldiers. The Turkic soldiers transformed the style of warfare, as they were known as capable horse archers, trained from childhood to ride. This military was now drafted from the ethnic groups of the faraway borderlands, and were completely separate from the rest of society. Some could not speak Arabic properly. This led to the decline of the caliphate starting with the Anarchy at Samarra.
Civil administration
 As a result of such a vast Empire, the caliphate was decentralized and divided into 24 provinces.
Harun's vizier enjoyed close to unchecked powers. Under Harun, a special "bureau of confiscation" was created. This governmental wing made it possible for the vizier to seize the property and riches of any corrupt governor or civil servant. In addition, it allowed governors to confiscate the estates of lower-ranking officials. Finally, the caliph could impose the same penalty on a vizier who fell from grace. As one later caliph put it: "The vizier is our representative throughout the land and amongst our subjects. Therefore, he who obeys him obeys us; and he who obeys us obeys God, and God shall cause him who obeys Him to enter paradise."
Every regional metropolis had a post office and hundreds of roads were paved in order to link the imperial capital with other cities and towns. The empire employed a system of relays to deliver mail. The central post office in Baghdad even had a map with directions that noted the distances between each town. The roads were provided with roadside inns, hospices, and wells and could reach eastward through Persia and
As a result of such a vast Empire, the caliphate was decentralized and divided into 24 provinces.
Harun's vizier enjoyed close to unchecked powers. Under Harun, a special "bureau of confiscation" was created. This governmental wing made it possible for the vizier to seize the property and riches of any corrupt governor or civil servant. In addition, it allowed governors to confiscate the estates of lower-ranking officials. Finally, the caliph could impose the same penalty on a vizier who fell from grace. As one later caliph put it: "The vizier is our representative throughout the land and amongst our subjects. Therefore, he who obeys him obeys us; and he who obeys us obeys God, and God shall cause him who obeys Him to enter paradise."
Every regional metropolis had a post office and hundreds of roads were paved in order to link the imperial capital with other cities and towns. The empire employed a system of relays to deliver mail. The central post office in Baghdad even had a map with directions that noted the distances between each town. The roads were provided with roadside inns, hospices, and wells and could reach eastward through Persia and Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
, to as far as China. The post office not only enhanced civil services but also served as intelligence for the caliph. Mailmen were employed as spies who kept an eye on local affairs.
Early in the days of the caliphate, the Barmakids took the responsibility of shaping the civil service. The family had roots in a Buddhist monastery in northern Afghanistan. In the early 8th century, the family converted to Islam and began to take on a sizable part of the civil administration for the Abbasids.
Capital poured into the caliphate's treasury from a variety of taxes, including a real estate tax; a levy on cattle, gold and silver, and commercial wares; a special tax on non-Muslims; and customs dues.
Trade
Under Harun al-Rashid, Harun, maritime trade through the Persian Gulf thrived, with Arab vessels trading as far south as Madagascar and as far east as China, Korea, and Japan. The growing economy of Baghdad and other cities inevitably led to the demand for luxury items and formed a class of entrepreneurs who organized long-range caravans for the trade and then the distribution of their goods. A whole section in the East Baghdad suq was dedicated to Chinese goods. Arabs traded with the Baltic region and made it as far north as the British Isles. Tens of thousands of Arab coins have been discovered in parts of Russia and Sweden, which bear witness to the comprehensive trade networks set up by the Abbasids. Offa of Mercia, King Offa of Mercia (in England) minted gold coins similar to those of the Abbasids in the eighth century. Muslim merchants employed ports in Bandar Siraf, Basra, and Aden and some Red Sea ports to travel and trade with India and South East Asia. Land routes were also utilized through
Muslim merchants employed ports in Bandar Siraf, Basra, and Aden and some Red Sea ports to travel and trade with India and South East Asia. Land routes were also utilized through Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
. Arab businessmen were present in China as early as the eighth century. Arab merchants sailed the Caspian Sea to reach and trade with Bukhara
Bukhara ( ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan by population, with 280,187 residents . It is the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and t ...
and Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: Самарқанд / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
.
Many caravans and goods never made it to their intended destinations. Some Chinese exports perished in fires, while other ships sank. It was said that anybody who made it to China and back unharmed was blessed by God. Common sea routes were also plagued by pirates who built and crewed vessels that were faster than most merchant ships. It is said that many of the adventures at sea in the Sinbad the Sailor, Sinbad tales were based on historical fiction of mariners of the day.
The Abbasids also established overland trade with Africa, largely for gold and Trans-Saharan slave trade, slaves. When trade with Europe ceased due to Arab–Byzantine wars, hostilities, Jews served as a link between the two hostile worlds.
The Abbasids engaged in extensive trade with the Italian maritime republics of Republic of Venice, Venice and Republic of Genoa, Genoa, from the 11th century. Venetian merchants facilitated the exchange of high-value goods such as spices, silk, and precious metals from the East. In return, Venice exported European manufactured goods and luxury items. While Genoese merchants traded in luxury goods like spices, textiles, and other high-demand items. Genoa's strategic position in the Mediterranean enabled it to integrate into the broader Mediterranean trade network, connecting the Abbasid Caliphate with other European markets. These trade relations played a key role in linking the medieval Mediterranean with the broader Islamic world. This exchange of goods, alongside cultural and technological transfers, fostered a more interconnected medieval global economy.Chapter 3: The Golden Age of the Abbasid Caliphate (775–833). 2021. Tayeb El-Hibri
List of caliphs
See also
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * . * . , - , - {{Authority control Abbasid Caliphate, Arab dynasties Muslim dynasties Former countries in Asia Countries in medieval Africa States in medieval Anatolia Former countries in Europe Iraq under the Abbasid Caliphate History of North Africa History of Asia Medieval countries in the Middle East History of South Asia History of the Mediterranean Medieval history of Iran States and territories established in the 750s States and territories disestablished in 1258 States and territories established in 1261 States and territories disestablished in 1517 750 establishments 1510s disestablishments in Asia 8th-century establishments in Africa 1258 disestablishments in Asia 13th-century disestablishments in Africa Historical transcontinental empires Caliphates Former empires Former monarchies