ßÜĀ on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Fehu is the reconstructed
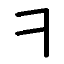 Ō¤®, like Greek
Ō¤®, like Greek  Ō¤®.
The change of the bistaves pointing upward could stem from visually diverging it from the rune ßÜ©, as well as linking it visually to the horns of cattle (see ).
Ō¤®.
The change of the bistaves pointing upward could stem from visually diverging it from the rune ßÜ©, as well as linking it visually to the horns of cattle (see ).
Rune Poem Page
Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic languages, Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from ...
name for the rune
Runes are the letters in a set of related alphabets, known as runic rows, runic alphabets or futharks (also, see '' futhark'' vs ''runic alphabet''), native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were primarily used to represent a sound value (a ...
(; ), found as the first rune in all futharks (runic alphabets starting with F, U, ├×, ─ä, R, K), i.e. the Germanic Elder Futhark, the Anglo-Frisian Futhark and the Norse Younger Futhark, with continued use in the later medieval runes, early modern runes and Dalecarlian runes.
It corresponds to the letter f in the Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also known as the Roman alphabet, is the collection of letters originally used by the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered except several letters splittingŌĆöi.e. from , and from Ō ...
, but it can periodically shift into the sound value of v (compare "leaf" and "leaves").
Character
The shape of the rune is likely based on Etruscan ''v'' Ō¤©ÉīģŌ¤® Ō¤©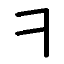 Ō¤®, like Greek
Ō¤®, like Greek Digamma
Digamma or wau (uppercase: Ž£, lowercase: ŽØ, numeral: Žø) is an Archaic Greek alphabets, archaic letter of the Greek alphabet. It originally stood for the sound but it has remained in use principally as a Greek numeral for 6 (number), 6. Whe ...
Ō¤©Ō¤® and Latin Ō¤© FŌ¤® ultimately from Phoenician waw Ō¤©Name
The root name is an ancient word for "livestock". Compare ("livestock, animal"), ("livestock, cattle"), ("livestock"), ("livestock, loose assets"), ("livestock, money"), ("livestock"), , ''pec┼½s'' ("livestock"), (''paß╣¦u'', "livestock, cattle"). By extension, it also means ' (loose) wealth' and thereof, thus surviving as '' fee'' in English with the meaning of "payment compensating for rights or services". TheProto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic languages, Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from ...
name has been reconstructed as , with the meaning of "livestock, cattle" and by extension "wealth". Page, Raymond I. (2005) ''Runes''. The British Museum Press. p. 15.
The corresponding letter of the Gothic alphabet
The Gothic alphabet is an alphabet for writing the Gothic language. It was developed in the 4th century AD by Ulfilas (or Wulfila), a Gothic preacher of Cappadocian Greek descent, for the purpose of translating the Bible.
The alphabet e ...
is Ō¤©ÉŹåŌ¤® Ō¤©fŌ¤®, called . Such correspondence between all rune poems and the Gothic letter name, as well, is uncommon, and gives the reconstructed name of the Old Futhark a high degree of certainty.
Rune poems
The name is recorded in all threerune poem
Rune poems are poems that list the letters of runic alphabets while providing an explanatory poetic stanza for each letter. Four different poems from before the mid-20th century have been preserved: the Anglo-Saxon Rune Poem, the Norwegian Rune ...
s:Original poems from thRune Poem Page
Old Norwegian
Old Norwegian ( and ), also called Norwegian Norse, is an early form of the Norwegian language that was spoken between the 11th and 14th century; it is a transitional stage between Old West Norse and Middle Norwegian.
Its distinction from O ...
:
Old Icelandic:
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
:
See also
* F├®lagReferences
{{Runes Runes