ОІ Pegasi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Beta Pegasi (ОІ Pegasi, abbreviated Beta Peg, ОІ Peg), formally named Scheat , is a
 Based upon
Based upon
red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The stellar atmosphere, outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface t ...
star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
and the second-brightest star (after Epsilon Pegasi
Epsilon Pegasi ( Latinised from Оµ Pegasi, abbreviated Epsilon Peg, Оµ Peg), formally named Enif , is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Pegasus.
With an average apparent visual magnitude of 2.4, this is a second-magnit ...
) in the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
of Pegasus
Pegasus (; ) is a winged horse in Greek mythology, usually depicted as a white stallion. He was sired by Poseidon, in his role as horse-god, and foaled by the Gorgon Medusa. Pegasus was the brother of Chrysaor, both born from Medusa's blood w ...
. It forms the upper right corner of the Great Square of Pegasus, a prominent rectangular asterism.
Nomenclature
''ОІ Pegasi'' ( Latinised to ''Beta Pegasi'') is the star'sBayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek alphabet, Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive case, genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer design ...
.
It bore the traditional name of ''Scheat'', a name that had also been used for Delta Aquarii. The name was derived from the Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
''Al SДЃ'id'' "the upper arm", or from ''Sa'd''. In 2016, the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and developmen ...
organised a Working Group on Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education ...
(WGSN) to catalog and standardise proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two batches of names approved by the WGSN; which included ''Scheat'' for this star (the name ''Skat'' was later approved for Delta Aquarii).
In Chinese
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic ...
, (), meaning ''Encampment
Camp may refer to:
Areas of confinement, imprisonment, or for execution
* Concentration camp, an internment camp for political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or minority ethnic groups
* Extermination ...
'', refers to an asterism consisting ОІ Pegasi and О± Pegasi. Consequently, the Chinese name
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethni ...
for ОІ Pegasi itself is (), "the Second Star of Encampment".
Distance and properties
 Based upon
Based upon parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphica ...
measurements, Beta Pegasi is located about from the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
. It is unusual among bright stars in having a relatively cool surface temperature compared to stars like the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
.
This star has a stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction gratin ...
of M2.3 II–III, which indicates the spectrum
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of co ...
has characteristics partway between a bright giant
A giant star has a substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature. They lie above the main sequence (luminosity class V in the Yerkes spectral classification) on the Hertzspr ...
and a giant star
A giant star has a substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature. They lie above the main sequence (luminosity class V in the Yerkes spectral classification) on the Hertzsp ...
. It has expanded until it is 109 times as large, and has a total luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic energy per unit time, and is synonymous with the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electroma ...
of 1,640 times that of the Sun. The effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
of the star's outer envelope is about 3,600 K, giving the star the characteristic orange-red hue of an M-type star. The photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will esc ...
is sufficiently cool for molecules of titanium oxide
Titanium oxide may refer to:
* Titanium dioxide (titanium(IV) oxide), TiO2
* Titanium(II) oxide (titanium monoxide), TiO, a non-stoichiometric oxide
* Titanium(III) oxide (dititanium trioxide), Ti2O3
* Ti3O
* Ti2O
* δ-TiOx (x= 0.68–0.75)
* Ti ...
to form.
Johann Friedrich Julius Schmidt
Johann Friedrich Julius Schmidt (25 October 1825 in Eutin, German Confederation, Germany – 7 February 1884 in Athens, Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece) was a German astronomer and geophysicist. He was the director of the National Observa ...
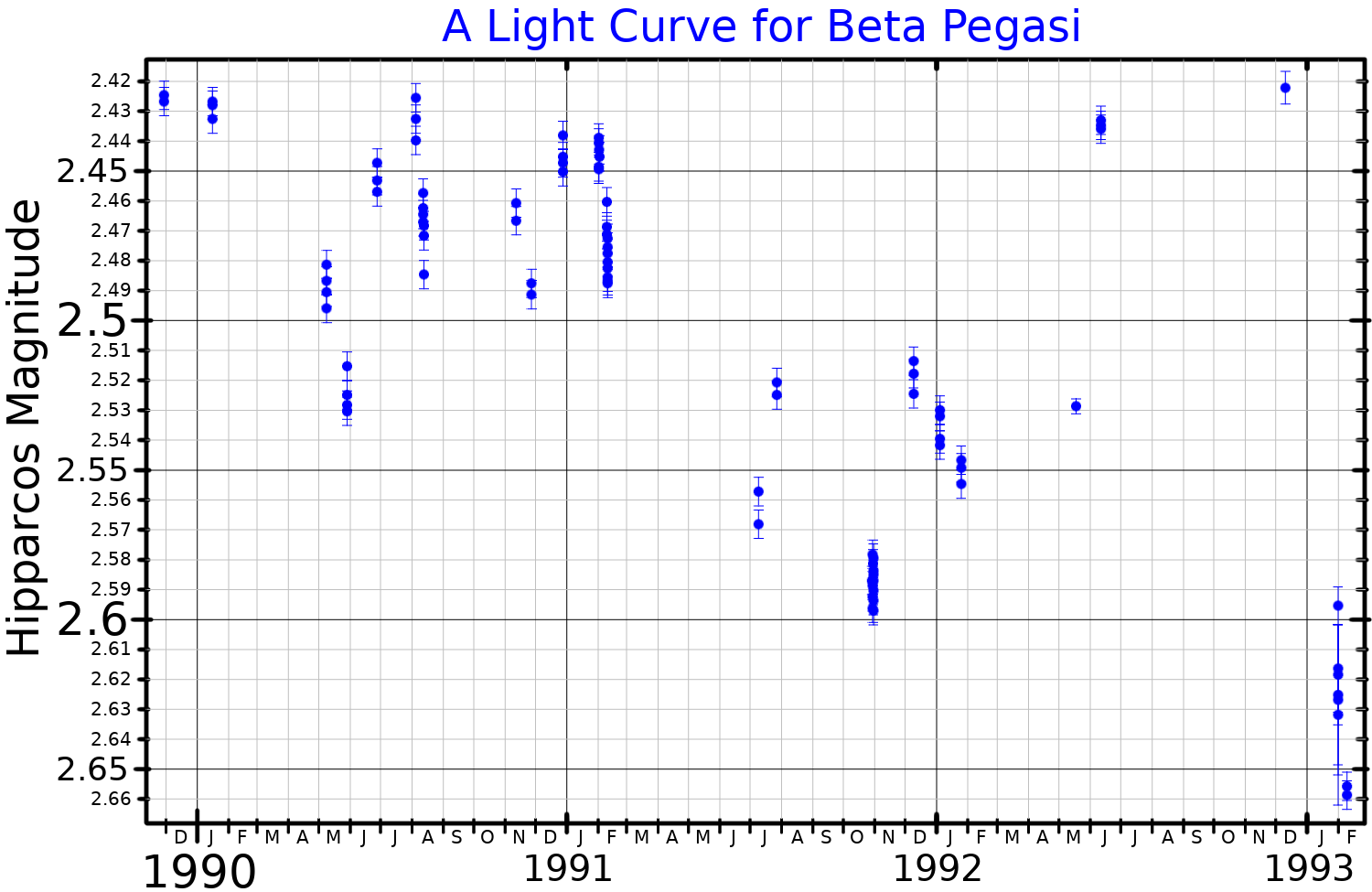
discovered that Beta Pegasi is a variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are ...
, in 1847. Beta Pegasi is a semi-regular variable with a period of 43.3 days and a brightness that varies from magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
+2.31 to +2.74 (averaging 2.42). It is losing mass at a rate at or below 10в€’8 times the Sun's mass
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies a ...
per year, which is creating an expanding shell of gas and dust with a radius of about 3,500 times the Sun's radius
Solar radius is a unit of distance used to express the size of objects in astronomy relative to the Sun. The solar radius is usually defined as the radius to the layer in the Sun's photosphere where the optical depth equals 2/3:
1\,R_ = 6.957\ti ...
(16 astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to . Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its m ...
s).
Notes
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Beta Pegasi Pegasi, Beta M-type bright giants M-type giants Pegasus (constellation) Scheat Pegasi, 53 8775 217906 113881 BD+27 4480 Semiregular variable stars Emission-line stars TIC objects Asymptotic-giant-branch stars