Г–gedei Khan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Г–gedei Khan (also Г–gedei Khagan or Ogodei; 11 December 1241) was the second khan of the
 The Empress Yisui insisted that
The Empress Yisui insisted that
 The Mongols under Chormaqan returned to the
The Mongols under Chormaqan returned to the
 The Mongol Empire expanded westward under the command of Batu Khan to subdue the western steppes and drive into Europe. Their western conquests included
The Mongol Empire expanded westward under the command of Batu Khan to subdue the western steppes and drive into Europe. Their western conquests included
 Г–gedei abolished the branch departments of state affairs and divided the areas of Mongol-ruled China into ten routes according to the suggestion of YelГј Chucai. He also divided the empire into Beshbalik and Yanjing administration, while the headquarters in Karakorum directly dealt with Manchuria, Mongolia and Siberia. Late in his reign,
Г–gedei abolished the branch departments of state affairs and divided the areas of Mongol-ruled China into ten routes according to the suggestion of YelГј Chucai. He also divided the empire into Beshbalik and Yanjing administration, while the headquarters in Karakorum directly dealt with Manchuria, Mongolia and Siberia. Late in his reign,
 From 1235 to 1238 Г–gedei constructed a series of palaces and pavilions at stopping places in his annual
From 1235 to 1238 Г–gedei constructed a series of palaces and pavilions at stopping places in his annual
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
. The third son of Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born TemГјjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
, he continued the expansion of the empire that his father had begun.
Born in 1186 AD, Г–gedei fought in numerous battles during his father's rise to power. After being granted a large appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a monarch, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture (where only the eldest inherits). It was ...
and taking a number of wives, including Töregene, he played a prominent role in the Mongol invasion of the Khwarazmian Empire
Between 1219 and 1221, the Mongol Empire, Mongol forces under Genghis Khan invaded the lands of the Khwarazmian Empire in Central Asia. The campaign, which followed Mongol conquest of the Qara Khitai, the annexation of the Qara Khitai Khanate ...
. When his older brothers Jochi
Jochi (; ), also spelled JГјchi, was a prince of the early Mongol Empire. His life was marked by controversy over the circumstances of his birth and culminated in his estrangement from his family. He was nevertheless a prominent Military of the ...
and Chagatai quarrelled over strategies when besieging Gurganj
Konye-Urgench (, ; , ), also known as Old Urgench or Urganj, was a city in north Turkmenistan, just south from its border with Uzbekistan. It is the site of the ancient town of GurgДҒnj, which contains the ruins of the capital of Khwarazm. Its in ...
, Genghis appointed Г–gedei sole commander; his successful capture of the city in 1221 ensured his military reputation. He was confirmed as heir after further infighting between his elder brothers led to both being excluded from succession plans. Genghis died in 1227, and Г–gedei was elected as khan in 1229, after a two-year regency led by his younger brother Tolui
Tolui (born ; died 1232) was the youngest son of Genghis Khan and Börte. A prominent general during the early Mongol conquests, Tolui was a leading candidate to succeed his father after his death in 1227 and ultimately served as regent of th ...
.
As khan, Г–gedei pursued the expansionist policies of his father. He launched a second invasion of Persia led by Chormaqan Noyan in 1230, which subdued the Khwarazmian prince Jalal al-Din Mangburni and began to subjugate Georgia. He initiated the Mongol invasions of Korea
A series of campaigns were conducted between 1231 and 1270 by the Mongol Empire against the Korean kingdom of Goryeo. The last campaign concluded with a peace treaty with Goryeo becoming Korea under Yuan rule, a vassal state of the Yuan dynast ...
in 1231 and completed the Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty
The Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty, also known as the MongolвҖ“Jin War, was fought between the Mongol Empire and the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in Manchuria and North China. The war, which started in 1211, lasted over 23 years and ended with ...
in 1234, and his armies skirmished with the Song dynasty and in India. By the time of his death in 1241, large armies under the command of his nephew Batu Khan and Subutai
Subutai (c. 1175вҖ“1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and Г–gedei Khan. He ultimately directed more than 20 campaigns, during which he conquered more territory than any other commander in history a ...
had subdued the steppes and penetrated deep into Europe. These armies defeated Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
at Legnica
Legnica (; , ; ; ) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River and the Czarna Woda. As well as being the seat of the county, since 1992 the city has been the seat of the Diocese of Legnica. Le ...
and Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
at Mohi before retreating. It is likely that this retreat was caused by the need to find a successor after Г–gedei's death, although some scholars have speculated that the Mongols were simply unable to invade further because of logistical difficulties.
As an administrator, Г–gedei continued to develop the fast-growing Mongol state. Working with officials such as YelГј Chucai, he developed '' ortogh'' trading systems, instituted methods of tax collection, and established regional bureaucracies which controlled legal and economic affairs. He also founded the Mongol capital city, Karakorum
Karakorum (Khalkha Mongolian: РҘР°СҖС…РҫСҖСғРј, ''Kharkhorum''; Mongolian script:, ''Qaraqorum'') was the capital city, capital of the Mongol Empire between 1235 and 1260 and of the Northern Yuan, Northern Yuan dynasty in the late 14th and 1 ...
, in the 1230s. Although historically disregarded in comparison to his father, especially on account of his alcoholism, he was known to be charismatic
Charisma () is a personal quality of magnetic charm, persuasion, or appeal.
In the fields of sociology and political science, psychology, and management, the term ''charismatic'' describes a type of leadership.
In Christian theology, the term ...
, good-natured, and intelligent. He was succeeded by his son GГјyГјk.
Background
Ögedei was the third son of Temüjin and Börte Ujin. He participated in the turbulent events of his father's rise. When Ögedei was 17 years old, Temüjin experienced the disastrous defeat of Khalakhaljid Sands against the army ofJamukha
Jamukha (), a military and political leader of the Jadaran tribe who was proclaimed Gurkhan, ''Gur Khan'' ('Universal Ruler') in 1201 by opposing factions, was a principal rival to Genghis Khan, TemГјjin (proclaimed Genghis Khan in 1206) during ...
. Ögedei was heavily wounded and lost on the battlefield. His father's adopted brother and companion Borokhula rescued him. Although he was already married, in 1204 his father gave him Töregene, the wife of a defeated Merkit chief. The addition of such a wife was not uncommon in steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
culture.
After TemГјjin was proclaimed Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born TemГјjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
in 1206, ''myangans'' (thousands) of the Jalayir, Besud, Suldus, and Khongqatan clans were given to him as his appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a monarch, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture (where only the eldest inherits). It was ...
. Г–gedei's territory occupied the Emil and Hobok rivers. According to his father's wish, Ilugei, the commander of the Jalayir, became Г–gedei's tutor.
Г–gedei, along with his brothers, campaigned independently for the first time in November 1211 against the Jin dynasty. He was sent to ravage the land south through Hebei
Hebei is a Provinces of China, province in North China. It is China's List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, sixth-most populous province, with a population of over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. It bor ...
and then north through Shanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi a ...
in 1213. Г–gedei's force drove the Jin garrison out of the Ordos, and he rode to the juncture of the Xi Xia, Jin, and Song domains.
During the Mongol conquest of Khwarezmia, Г–gedei and Chagatai massacred the residents of Otrar after a five-month siege in 1219вҖ“20 and joined Jochi
Jochi (; ), also spelled JГјchi, was a prince of the early Mongol Empire. His life was marked by controversy over the circumstances of his birth and culminated in his estrangement from his family. He was nevertheless a prominent Military of the ...
who was outside the walls of Urganch. Because Jochi and Chagatai were quarreling over the military strategy, Г–gedei was appointed by Genghis Khan to oversee the siege of Urganch. They captured the city in 1221. When the rebellion broke out in southeast Persia and Afghanistan, Г–gedei also pacified Ghazni
Ghazni (, ), historically known as Ghaznayn () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana (), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan with a population of around 190,000 people. The city is strategica ...
.
Position as heir
 The Empress Yisui insisted that
The Empress Yisui insisted that Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born TemГјjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
designate an heir before the invasion of the Khwarezmid Empire in 1219. After the terrible brawl between two elder sons Jochi and Chagatai, they agreed that Г–gedei was to be chosen as heir. Genghis confirmed their decision.
Genghis Khan died in 1227, and Jochi had died a year or two earlier. Г–gedei's younger brother Tolui
Tolui (born ; died 1232) was the youngest son of Genghis Khan and Börte. A prominent general during the early Mongol conquests, Tolui was a leading candidate to succeed his father after his death in 1227 and ultimately served as regent of th ...
held the regency until 1229. Г–gedei was elected supreme khan in 1229, according to the kurultai held at Kodoe Aral on the Kherlen River after Genghis' death, although this was never really in doubt as it was Genghis' clear wish that he be succeeded by Г–gedei. After ritually declining three times, Г–gedei was proclaimed Khan of the Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
on 13 September 1229 at the '' Kurultai'' of the Kherlen's Khödöö Aral. Chagatai continued to support his younger brother's claim.
World conquests
Expansion in the Middle East
After destroying the Khwarazmian empire, Genghis Khan was free to move againstWestern Xia
The Western Xia or the Xi Xia ( zh, c=, w=Hsi1 Hsia4, p=XД« XiГ ), officially the Great Xia ( zh, c=еӨ§еӨҸ, w=Ta4 Hsia4, p=DГ XiГ , labels=no), also known as the Tangut Empire, and known as Stein (1972), pp. 70вҖ“71. to the Tanguts ...
. In 1226, however, Jalal ad-Din Mingburnu, the last of the Khwarezm monarchs, returned to Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
to revive the empire lost by his father, Muhammad вҖҳAla al-Din II. The Mongol forces sent against him in 1227 were defeated at Dameghan. Another army that marched against Jalal al-Din scored a pyrrhic victory in the vicinity of Isfahan
Isfahan or Esfahan ( ) is a city in the Central District (Isfahan County), Central District of Isfahan County, Isfahan province, Iran. It is the capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is located south of Tehran. The city ...
but was unable to follow up that success.
With Г–gedei's consent to launch a campaign, Chormaqan Noyan left Bukhara
Bukhara ( ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan by population, with 280,187 residents . It is the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and t ...
at the head of 30,000 to 50,000 Mongol soldiers. He occupied Persia and Khorasan, two long-standing bases of Khwarazmian support. Crossing the Amu Darya River in 1230 and entering Khorasan without encountering any opposition, Chormaqan passed through quickly. He left a sizable contingent behind under the command of Dayir Baghatur, who had further instructions to invade western Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the AfghanistanвҖ“Iran borde ...
. Chormaqan and the majority of his army then entered Tabaristan (modern-day Mazandaran), a region between the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
and Alborz mountains, in the autumn of 1230, thus avoiding the mountainous area to the south, which was controlled by the Nizari Ismailis (the Assassins).
Upon reaching the city of Rey, Chormaqan made his winter camp there and dispatched his armies to pacify the rest of northern Persia. In 1231, he led his army southward and quickly captured the cities of Qum and Hamadan
Hamadan ( ; , ) is a mountainous city in western Iran. It is located in the Central District of Hamadan County in Hamadan province, serving as the capital of the province, county, and district. As of the 2016 Iranian census, it had a po ...
. From there, he sent armies into the regions of Fars and Kirman, whose rulers quickly submitted, preferring to pay tribute to Mongol overlords rather than having their states ravaged. Meanwhile, further east, Dayir Baghatur steadily achieved his goals in capturing Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
, Ghazni, and Zabulistan. With the Mongols already in control of Persia, Jalal al-Din was isolated in Transcaucasia where he was banished. Thus all of Persia was added to the Mongol Empire.
The fall of the Jin dynasty
At the end of 1230, responding to the Jins' unexpected defeat of Doqolqu Cherbi (Mongol general), Г–gedei went south toShanxi
Shanxi; Chinese postal romanization, formerly romanised as Shansi is a Provinces of China, province in North China. Its capital and largest city of the province is Taiyuan, while its next most populated prefecture-level cities are Changzhi a ...
with Tolui
Tolui (born ; died 1232) was the youngest son of Genghis Khan and Börte. A prominent general during the early Mongol conquests, Tolui was a leading candidate to succeed his father after his death in 1227 and ultimately served as regent of th ...
, clearing the area of the Jin forces and taking the city of Fengxiang. After passing the summer in the north, they again campaigned against the Jin in Henan
Henan; alternatively Honan is a province in Central China. Henan is home to many heritage sites, including Yinxu, the ruins of the final capital of the Shang dynasty () and the Shaolin Temple. Four of the historical capitals of China, Lu ...
, cutting through territory of South China to assault the Jin's rear. By 1232 the Jin Emperor was besieged in his capital of Kaifeng
Kaifeng ( zh, s=ејҖе°Ғ, p=KДҒifД“ng) is a prefecture-level city in east-Zhongyuan, central Henan province, China. It is one of the Historical capitals of China, Eight Ancient Capitals of China, having been the capital eight times in history, and ...
. Г–gedei soon departed, leaving the final conquest to his generals. After taking several cities, the Mongols, with the belated assistance of the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
, destroyed the Jin with the fall of Caizhou in February 1234. However, a viceroy of the Song murdered a Mongol ambassador, and the Song armies recaptured the former imperial capitals of Kaifeng, Luoyang
Luoyang ( zh, s=жҙӣйҳі, t=жҙӣйҷҪ, p=LuГІyГЎng) is a city located in the confluence area of the Luo River and the Yellow River in the west of Henan province, China. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zheng ...
, and Chang'an
Chang'an (; zh, t=й•·е®ү, s=й•ҝе®ү, p=ChГЎng'ДҒn, first=t) is the traditional name of the city now named Xi'an and was the capital of several Chinese dynasties, ranging from 202 BCE to 907 CE. The site has been inhabited since Neolithic time ...
, which were now ruled by the Mongols.
In addition to the war with the Jin dynasty, Г–gedei crushed the Eastern Xia founded by Puxian Wannu in 1233, pacifying southern Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
. Г–gedei subdued the Water Tatars in the northern part of the region and suppressed their rebellion in 1237.
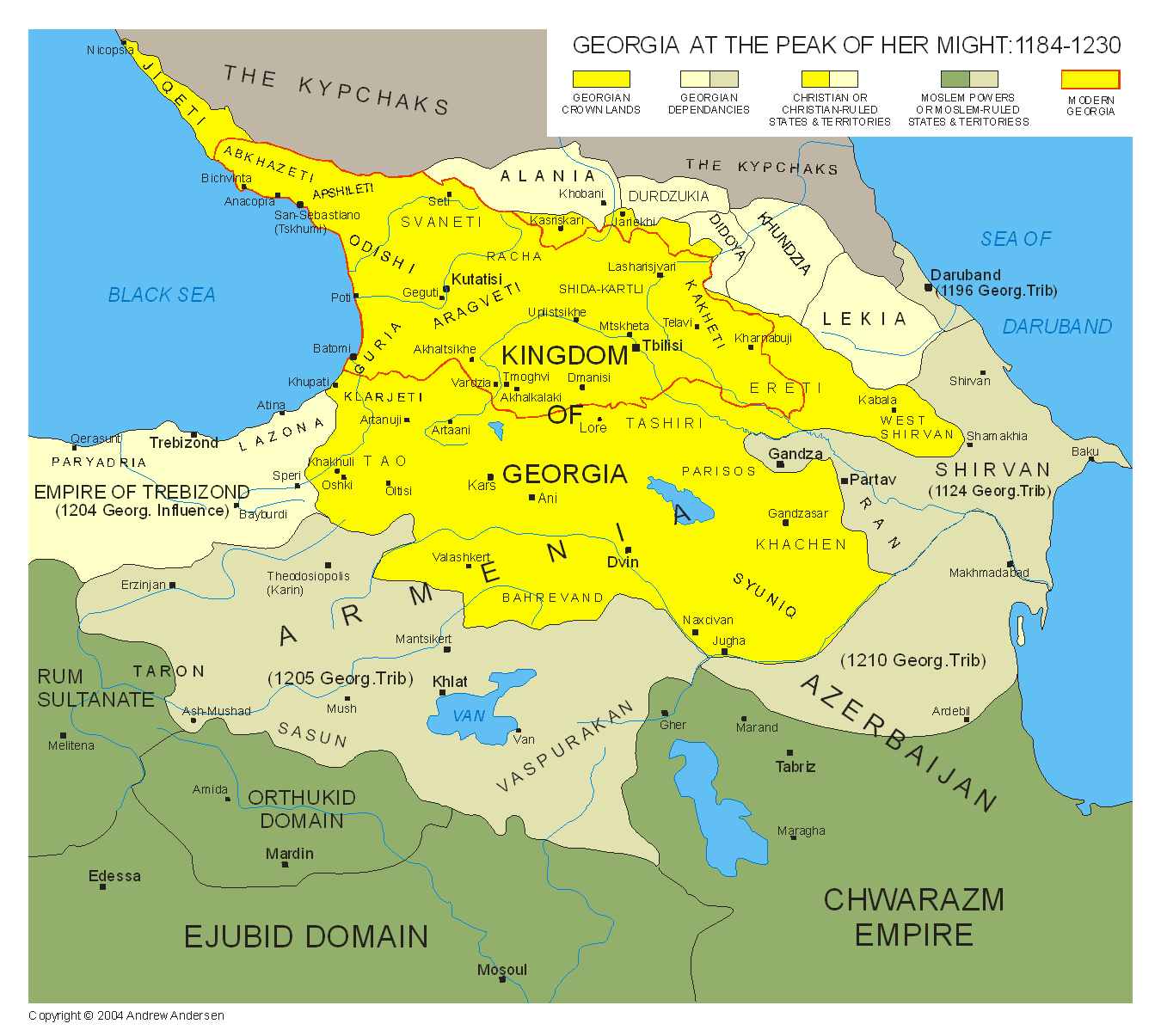
Conquest of Georgia and Armenia
 The Mongols under Chormaqan returned to the
The Mongols under Chormaqan returned to the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region spanning Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is situated between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, comprising parts of Southern Russia, Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan. The Caucasus Mountains, i ...
in 1232. The walls of Ganja were breached by catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants вҖ“ particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden rel ...
and battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried ...
in 1235. The Mongols eventually withdrew after the citizens of Irbil agreed to send a yearly tribute to Ögedei's court. Chormaqan waited until 1238, when the force of Möngke Khan
Möngke Khan (also Möngke Khagan or Möngke; 11 January 120911 August 1259) was the fourth khagan of the Mongol Empire, ruling from 1 July 1251 to 11 August 1259. He was the first Khagan from the Toluid line, and made significant reforms to im ...
was also active in the north Caucasus. After subduing Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
, Chormaqan took Tiflis
Tbilisi ( ; ka, бғ—бғ‘бғҳбғҡбғҳбғЎбғҳ, ), in some languages still known by its pre-1936 name Tiflis ( ), ( ka, бғўбғӨбғҳбғҡбғҳбғЎбғҳ, tr ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Georgia (country), largest city of Georgia ( ...
. In 1238, the Mongols captured Lorhe whose ruler, Shahanshah
ShДҒh (; ) is a royal title meaning "king" in the Persian language.Yarshater, Ehsa, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII, no. 1 (1989) Though chiefly associated with the List of monarchs of Iran, monarchs of Iran, it was also used to refer to the ...
, fled with his family before the Mongols arrived, leaving the rich city to its fate. After putting up a spirited defense at Hohanaberd, the city's ruler, Hasan Jalal, submitted to the Mongols. Another column then advanced against Gaian, ruled by Prince Avak. The Mongol commander Tokhta ruled out a direct assault and had his men construct a wall around the city, and Avak soon surrendered. By 1240, Chormaqan had completed the conquest of Transcaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
, forcing the Georgian nobles to surrender.
Korea
In 1224, a Mongol envoy was killed in obscure circumstances and Korea stopped payingtribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of lands which the state con ...
. Г–gedei dispatched Saritai Qorchi to subdue Korea and avenge the dead envoy in 1231. Thus, Mongol armies began to invade Korea in order to subdue the kingdom. The Goryeo
Goryeo (; ) was a Korean state founded in 918, during a time of national division called the Later Three Kingdoms period, that unified and ruled the Korea, Korean Peninsula until the establishment of Joseon in 1392. Goryeo achieved what has b ...
King temporarily submitted and agreed to accept Mongol overseers. When they withdrew for the summer, however, Ch'oe U moved the capital from Kaesong
Kaesong (, ; ) is a special city in the southern part of North Korea (formerly in North Hwanghae Province), and the capital of Korea during the Taebong kingdom and subsequent Goryeo dynasty. The city is near the Kaesong Industrial Region cl ...
to Ganghwa Island
Ganghwa Island (), also Ganghwado, is an island in Ganghwa County, Incheon, South Korea. It is in the Yellow Sea and in an estuary of the Han River.
The island is separated from Gimpo (on the South Korean mainland) by a narrow channel spanned ...
. Saritai was hit with a stray arrow and died as he campaigned against them.
Г–gedei announced plans for the conquest of the Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
, the Southern Song, the Kipchaks and their European allies, all of whom killed Mongol envoy
Envoy or Envoys may refer to:
Diplomacy
* Diplomacy, in general
* Envoy (title)
* Special envoy, a type of Diplomatic rank#Special envoy, diplomatic rank
Brands
*Airspeed Envoy, a 1930s British light transport aircraft
*Envoy (automobile), an au ...
s, at the kurultai in Mongolia in 1234. Г–gedei appointed Danqu commander of the Mongol army and made Bog Wong, a defected Korean general, governor of 40 cities with their subjects. When the court of Goryeo sued for peace in 1238, Г–gedei demanded that the king of Goryeo appear before him in person. The Goryeo king finally sent his relative Yeong Nong-gun Sung with ten noble boys to Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
as hostage
A hostage is a person seized by an abductor in order to compel another party, one which places a high value on the liberty, well-being and safety of the person seizedвҖ”such as a relative, employer, law enforcement, or governmentвҖ”to act, o ...
s, temporarily ending the war in 1241.
Europe
 The Mongol Empire expanded westward under the command of Batu Khan to subdue the western steppes and drive into Europe. Their western conquests included
The Mongol Empire expanded westward under the command of Batu Khan to subdue the western steppes and drive into Europe. Their western conquests included Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria or VolgaвҖ“Kama Bulgaria (sometimes referred to as the Volga Bulgar Emirate) was a historical Bulgar state that existed between the 9th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now Europea ...
, almost all of Alania, Cumania, and Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rus', also known as Kyivan Rus,.
* was the first East Slavs, East Slavic state and later an amalgam of principalities in Eastern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical At ...
, along with a brief occupation of Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
. They also invaded Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
, Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, the Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantin ...
, and Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
. During the siege of Kolomna
Kolomna (, ) is a historic types of inhabited localities in Russia, city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, situated at the confluence of the Moskva River, Moskva and Oka Rivers, (by rail) southeast of Moscow. Population:
History
Mentioned for the fir ...
, Г–gedei's half brother Khulgen was killed by an arrow.
Amid the conquest, Г–gedei's son GГјyГјk and Chagatai's grandson BГјri ridiculed Batu, and the Mongol camp suffered dissension. Г–gedei harshly criticized GГјyГјk: "You broke the spirit of every man in your army... Do you think that the Russians surrendered because of how mean you were to your own men?". He then sent GГјyГјk back to continue the conquest of Europe. GГјyГјk and another of Г–gedei's sons, Kadan
Kadan (also Qadan) was the son of the second Great Khan of the Mongols Г–gedei and a concubine. He was the grandson of Genghis Khan and the brother of GГјyГјk Khan. During the Mongol invasion of Europe, Kadan, along with his cousin Baidar ( ...
and Melig attacked Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
and Poland, respectively.
Although Г–gedei Khan had granted permission to invade the remainder of Europe, all the way to the "Great Sea", the Atlantic Ocean, the Mongol advance stopped in East Europe early in 1242, the year after his death. Most historians agree with Mongol accounts which attribute the drive's failure to his untimely demise necessitating Batu's withdrawal to personally participate in the election of Г–gedei's successor. Batu, however, never reached Mongolia for such an election and a successor wouldn't be named until 1246. A minority of historians have argued that the advance stalled because European fortifications posed a strategic problem for the Mongols.
Conflict with Song dynasty
In a series of razzias from 1235 to 1245, the Mongols commanded by Г–gedei's sons penetrated deep into the Song dynasty and reachedChengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
, Xiangyang
Xiangyang is the second-largest prefecture-level city by population in northwestern Hubei province, China. It was known as Xiangfan from 1950 to 2010. The Han River (Hanshui), Han River runs through Xiangyang's centre and divides the city n ...
and Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
. But they could not succeed in completing their conquest due to climate and the number of Song troops, and Г–gedei's son Khochu died in the process. In 1240, Г–gedei's other son Khuden dispatched a subsidiary expedition to Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
. The situation between the two nations worsened when Song officers murdered Г–gedei's envoys headed by Selmus.
The Mongol expansion throughout the Asian continent under the leadership of Г–gedei helped bring political stability and re-establish the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
, the primary trading route between East and West.
India
Г–gedei appointed Dayir Baghatur in Ghazni and Menggetu Noyan in Qonduz. In winter 1241 the Mongol force invaded theIndus valley
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the disp ...
and besieged Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
, which was controlled by the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.
. However, Dayir Baghatur died storming the town, on 30 December 1241, and the Mongols butchered the town before withdrawing from the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.
.
Some time after 1235 another Mongol force invaded Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
, stationing a darughachi
''Darughachi'' (Mongol form) or ''Basqaq'' (Turkic form) were originally designated officials in the Mongol Empire who were in charge of taxes and administration in a certain province. The singular form of the Mongolian word is ''darugha''. They ...
there for several years. Soon Kashmir became a Mongolian dependency. Around the same time, a Kashmiri Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
master, Otochi, and his brother Namo arrived at the court of Г–gedei.
Administration
Г–gedei began the bureaucratization of Mongol administration. Three divisions constituted his administration: * theChristian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
eastern Turks, represented by Chinqai, the Uyghur scribe
A scribe is a person who serves as a professional copyist, especially one who made copies of manuscripts before the invention of Printing press, automatic printing.
The work of scribes can involve copying manuscripts and other texts as well as ...
, and the Keraites
The Keraites (also ''Kerait, Kereit, Khereid'', Kazakh: РәРөСҖРөР№СӮ; Kyrgyz: РәРөСҖРөР№; Mongolian: РҘСҚСҖСҚР№Рҙ; Nogai: РҡРөСҖРөРёСӮ; Uzbek: ''Kerait''; Chinese: е…ӢзғҲ) were one of the five dominant Turco-Mongol tribal confederations ...
.
* the Islamic circle, represented by two Khorazmians, Mahmud Yalavach, and Masud Beg.
*the North Chinese Confucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, religion, theory of government, or way of life. Founded by Confucius ...
circle, represented by Yelu Chucai, a Khitan, and Nianhe Zhong-shan, a Jurchen.
Mahamud Yalavach promoted a system in which the government would delegate tax collection to tax farmers who collect payments in silver. Yelu Chucai encouraged Г–gedei to institute a traditional Chinese system of government, with taxation in the hands of government agents and payment in a government issued currency. The Muslim merchants, working with capital supplied by the Mongol aristocrats, loaned at higher interest
In finance and economics, interest is payment from a debtor or deposit-taking financial institution to a lender or depositor of an amount above repayment of the principal sum (that is, the amount borrowed), at a particular rate. It is distinct f ...
the silver needed for tax payments. In particular, Г–gedei actively invested in these ortoq enterprises. At the same time the Mongols began circulating paper currency backed by silver reserves.
Amu Darya
The Amu Darya ( ),() also shortened to Amu and historically known as the Oxus ( ), is a major river in Central Asia, which flows through Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Ku ...
administration was established. Turkestan was administered by Mahamud Yalavach, while Yelu Chucai administered North China from 1229 to 1240. Г–gedei appointed Shigi Khutugh chief judge in China. In Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, Г–gedei appointed first Chin-temur, a Kara-kitai, and then Korguz, an Uyghur who proved to be honest administrator. Later, some of Yelu Chucai's duties were transferred to Mahamud Yalavach and taxes were handed over to Abd-ur-Rahman, who promised to double the annual payments of silver. The Ortoq or partner merchants lent Г–gedei's money at exorbitant rates of interest to the peasants, though Г–gedei banned considerably higher rates. Despite it proving profitable, many people fled their homes to avoid the tax collectors and their strong-arm gangs.
Г–gedei had imperial princes tutored by the Christian scribe Qadaq and the Taoist
Taoism or Daoism (, ) is a diverse philosophical and religious tradition indigenous to China, emphasizing harmony with the Tao ( zh, p=dГ o, w=tao4). With a range of meaning in Chinese philosophy, translations of Tao include 'way', 'road', ...
priest Li Zhichang and built schools and an academy. Г–gedei Khan also decreed to issue paper currency backed by silk reserves and founded a department responsible for destroying old notes. Yelu Chucai protested to Г–gedei that his large-scale distribution of appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a monarch, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture (where only the eldest inherits). It was ...
s in Iran, Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and North China, and Khorazm could lead to a disintegration of the empire. Г–gedei thus decreed that the Mongol nobles could appoint overseers in the appanages, but the court would appoint other officials and collect taxes.
He proclaimed the Great Yassa
The Yassa (alternatively ''Yasa'', ''Yasaq'', ''Jazag'' or ''Zasag''; ) was the oral law code of the Mongols, gradually built up through the reign of Genghis Khan. It was the '' de facto'' law of the Mongol Empire, even though the "law" was kep ...
as an integral body of precedents, confirming the continuing validity of his father's commands and ordinances, while adding his own. Г–gedei codified rules of dress and conduct during the kurultais. Throughout the empire, in 1234, he created postroad stations ( Yam) with a permanent staff who would supply post riders' needs. Relay stations were set up every 25 miles and the yam staff supplied remounts to the envoys and served specified rations. The attached households were exempt from other taxes, but they had to pay a qubchuri tax to supply the goods. Г–gedei ordered Chagatai and Batu to control their yams separately. He also prohibited the nobility from issuing paizas (tablets that gave the bearer authority to demand goods and services from civilian populations) and jarliqs. Г–gedei decreed that within decimal units one out of every 100 sheep of the well-off should be levied for the poor of the unit, and that one sheep and one mare from every herd should be forwarded to form a herd
A herd is a social group of certain animals of the same species, either wild or domestic. The form of collective animal behavior associated with this is called '' herding''. These animals are known as gregarious animals.
The term ''herd'' ...
for the imperial table.
Karakorum
 From 1235 to 1238 Г–gedei constructed a series of palaces and pavilions at stopping places in his annual
From 1235 to 1238 Г–gedei constructed a series of palaces and pavilions at stopping places in his annual nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic route through central Mongolia. The first palace Wanangong was constructed by North Chinese artisans. The Emperor urged his relatives build residences nearby and settled the deported craftsmen from China near the site. The construction of the city, Karakorum
Karakorum (Khalkha Mongolian: РҘР°СҖС…РҫСҖСғРј, ''Kharkhorum''; Mongolian script:, ''Qaraqorum'') was the capital city, capital of the Mongol Empire between 1235 and 1260 and of the Northern Yuan, Northern Yuan dynasty in the late 14th and 1 ...
(РҘР°СҖС…РҫСҖСғРј), was finished in 1235, assigning different quarters to Islamic and North Chinese craftsmen, who competed to win Г–gedei's favor. Earthen walls with 4 gates surrounded the city. Attached were private apartments, while in front of stood a giant stone tortoise bearing an engraved pillar, like those that were commonly used in East Asia. There was a castle with doors like the gates of the garden and a series of lakes where many water fowl gathered. Г–gedei erected several houses of worship for his Buddhist, Muslim, Taoist, and Christian followers. In the Chinese ward, there was a Confucian temple where Yelu Chucai used to create or regulate a calendar on the Chinese model.
Character
Г–gedei was also known to be a humble man, who did not believe himself to be a genius, and who was willing to listen to and use the great generals that his father left him, as well as those he himself found to be most capable. He was the Emperor but not a dictator. Like all Mongols at his time, he was raised and educated as a warrior from childhood, and as the son of Genghis Khan, he was a part of his father's plan to establish a world empire. His military experience was notable for his willingness to listen to his generals and adapt to circumstances. He was a pragmatic person, much like his father, and looked at the end rather than the means. His steadiness of character and dependability were the traits that his father most valued, and that gained him the role of successor to his father, despite his two older brothers. Г–gedei was considered to be his father's favorite son, ever since his childhood. As an adult, he was known for his ability to sway doubters in any debate in which he was involved, simply by the force of his personality. He was a physically big, jovial, and charismatic man, who seemed mostly to be interested in enjoying good times. He was intelligent and steady in character. His charisma was partially credited for his success in keeping the Mongol Empire on the path that his father had set. Г–gedei was a pragmatic man, though he made some mistakes during his reign. Г–gedei had no delusions that he was his father's equal as a military commander or organizer and used the abilities of those he found most capable. Г–gedei was well known for his alcoholism. Chagatai entrusted an official to watch his habit, but Г–gedei managed to drink anyway. It is commonly told that Г–gedei did so by vowing to reduce the number of cups he drank a day then having cups twice the size created for his personal use. When he died at dawn on 11 December 1241, after a late-night drinking bout with Abd-ur-Rahman, the people blamed the sister of Tolui's widow and Abd-ur-Rahman. The Mongol aristocrats recognized, however, that the khan's own lack of self-control had killed him. The sudden death ofTolui
Tolui (born ; died 1232) was the youngest son of Genghis Khan and Börte. A prominent general during the early Mongol conquests, Tolui was a leading candidate to succeed his father after his death in 1227 and ultimately served as regent of th ...
in 1232 seems to have affected Г–gedei deeply. According to some sources, Tolui sacrificed his own life, accepting a poisoned drink in shamanist ritual in order to save Г–gedei who was suffering from illness. Other sources say Г–gedei orchestrated Tolui's death with the help of shamans who drugged the alcoholic Tolui.
According to Pamela Kyle Crossley, a posthumous Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=е…ғжңқ, p=YuГЎnchГЎo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
portrait of Г–gedei depicts him as having a stocky build, a red beard, and hazel eyes. Contemporary Chinese authors such as Xu Ting wrote that Г–gedei's beard was unusual for a Mongol because most had little facial hair.
Alleged mass rape
According to Persian chroniclers, Г–gedei ordered the rape of four thousand Oirat girls above the age of seven. These girls were then confiscated for Г–gedei's harem or given to caravan hostels throughout the Mongol Empire for use as prostitutes. This move brought the Oirat and their lands under Г–gedei's control following the death of Г–gedei's sister Checheyigen, who previously controlled Oirat lands. Anne F. Broadbridge links an "infamous alleged mass rape of Oirat girls" to Г–gedei's requisitioning of girls from his uncle TemГјge Otchigin's territories without TemГјge's approval. Broadbridge notes however that "with all the evidence suppressed, this can only be a surmise". The History of the Yuan or ''Yuanshi'' and Secret History of the Mongols speak of a forceful requisitioning of women by Г–gedei from the "left wing" and "uncle Otchigin's domain" respectively but do not mention a rape. In the Secret History Г–gedei expresses remorse for his act stating "as to my second fault, to listen to the word of a woman without principle, and to have the girls of my uncle Otchigin's domain brought to me was surely a mistake" but De Rachewiltz notes that the entire paragraph listing four good deeds and four mistakes may be a posthumous assessment. The only account alleging a rape is in Chapter 32 of theTarikh-i Jahangushay
''TДҒrД«kh-i JahДҒngushДҒy'' ( "The History of The World Conqueror") or ''TДҒrД«kh-i JahДҒngushДҒy-i JuwaynД«'' () is a detailed historical account written by the Persian people, Persian Ata-Malik Juvayni describing the Mongol, Hulegu Khan, and I ...
(History of the World Conqueror) written in 1252 by Juvayni (1226вҖ“1283). In Chapter 32 Juvayni starts by praising Г–gedei Khan then proceeds to give 50 highly detailed anecdotes to illustrate Г–gedei's "clemency, forgiveness, justice and generosity" followed by one anecdote to illustrate his "violence, severity, fury and awesomeness" which was the rape incident. This anecdote closes the chapter. The name of the tribe is unclear in two manuscripts of Juvayni but Manuscript D and Rashid-Al-Din give it as Oirat. Broadbridge and De Rachewiltz questioned the factual accuracy of this identification with the Oirats.
Death and aftermath
In the Tarikh-i Jahangushay claims Ögedei died shortly after his lion-like hounds chased and tore to pieces a wolf he saved and released despite his having hoped God Almighty would spare his ill bowels if he released a living creature. This anecdote (Anecdote 47) contradicts the standard account of Ögedei's death from a late-night drinking bout with Abd-ur-Rahman. In the early 1230s, Ögedei had nominated his son Kuchu as his heir; following Kuchu's death in 1236, he named his grandson Shiremun as his heir. His preference was not binding on the Mongols. Güyük eventually succeeded him after the five-year regency of his widow Töregene Khatun. However, Batu, the Khan of theGolden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of ...
(also known as the Kipchak Khanate or the Ulus of Jochi), only nominally accepted Güyük, who died on the way to confront Batu. It was not until 1255, well into the reign of Möngke Khan
Möngke Khan (also Möngke Khagan or Möngke; 11 January 120911 August 1259) was the fourth khagan of the Mongol Empire, ruling from 1 July 1251 to 11 August 1259. He was the first Khagan from the Toluid line, and made significant reforms to im ...
, that Batu felt secure enough to again prepare to invade Europe. He died before his plans could be implemented.
When Kublai Khan
Kublai Khan (23 September 1215 вҖ“ 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder and first emperor of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China. He proclaimed the ...
established the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=е…ғжңқ, p=YuГЎnchГЎo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
in 1271, he had Г–gedei Khan placed on the official record as Taizong ( zh, еӨӘе®—, TГ izЕҚng). Г–gedei was also given the posthumous name of Emperor Yingwen (иӢұж–ҮзҡҮеёқ) in 1266.
Wives, concubines, and children
Like his father Genghis Khan, Г–gedei had many wives and sixty concubines: Г–gedei married first Boraqchin and then TГ¶regene. Other wives included MГ¶ge Khatun (former concubine of Genghis Khan) and Jachin Khatun. ''Principal wives:'' * Empress Boraqchin (еӯӣеүҢеҗҲзңҹзҡҮеҗҺ) * Empress Zhaoci, of the Naiman tribe (жҳӯж…ҲзҡҮеҗҺ д№ғи »ж°Ҹ; d.1246), personal name TГ¶regene (и„ұеҲ—е“ҘйӮЈ) ** GГјyГјk, ''Khan of the Mongols'' (иІҙз”ұжұ—; c. 19 March 1206 вҖ“ 20 April 1248), 1st son ** KГ¶chГј ( й—ҠеҮә; died 1237), 3rd son ** Qarachar (е“ҲеүҢеҜҹе…җ), 4th son ** Qashi (еҗҲеӨұ; d.1234), 5th son * Empress MГ¶ge, of the Bakrin tribe (жңЁе“Ҙ; d.1242) *Empress Hutieni (д№һйҮҢеҗүеҝҪеё–е°ј дёәд№һйҮҢеҗүжҖқж°Ҹ) of the Chingissid clan ** Koden (й—Ҡз«ҜеӨӘеӯҗ; 1206вҖ“1251), 2nd son ''Concubines:'' * Concubine Ergene (дёҡйҮҢеҗүзәіеҰғеӯҗ) **Kadan
Kadan (also Qadan) was the son of the second Great Khan of the Mongols Г–gedei and a concubine. He was the grandson of Genghis Khan and the brother of GГјyГјk Khan. During the Mongol invasion of Europe, Kadan, along with his cousin Baidar ( ...
He is one of the 3 noble princes who participated in the European expedition (еҗҲдё№), 6th son
** Melik (зҒӯйҮҢ), 7th son
''Unknown:''
**SГјrkhakhan, Princess of Lu State (йІҒеӣҪе…¬дё» е”Ҷе„ҝе“ҲзҪ•)
***married Nahe (зәіеҗҲ) of the Hongjila tribe, grandson of AnchenBrother of Borte
Family
Khagan
Khagan or Qaghan (Middle Mongol:; or ''Khagan''; ) or zh, c=еӨ§жұ—, p=DГ hГЎn; ''KhДҒqДҒn'', alternatively spelled KaДҹan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, ТҡР°РҪ, or Kha'an is a title of empire, im ...
s or regents of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
are in bold. Source:
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* Amitai-Preiss, Reuven, ''The Mamluk-Ilkhanid War'', 1998 * Chambers, James, ''The Devil's Horsemen: The Mongol Invasion of Europe'' * Hildinger, Erik, ''Warriors of the Steppe: A Military History of Central Asia, 500 B.C. to A.D. 1700'' * Morgan, David, ''The Mongols'', * * Nicolle, David, ''The Mongol Warlords'' Brockhampton Press, 1998 * Reagan, Geoffry, ''The Guinness Book of Decisive Battles'', Canopy Books, New York (1992) * Saunders, J.J., ''The History of the Mongol Conquests'', Routledge & Kegan Paul Ltd, 1971, * Sicker, Martin ''The Islamic World in Ascendancy: From the Arab Conquests to the Siege of Vienna, Praeger Publishers, 2000'' * Soucek, Svatopluk, ''A History of Inner Asia'', Cambridge, 2000 * {{DEFAULTSORT:Ogedei Khan Generals of the Mongol Empire 1180s births 1241 deaths Great Khans of the Mongol Empire 13th-century Mongol khans 13th-century Chinese monarchs Year of birth uncertain House of Г–gedei Tengrist monarchs Children of Genghis Khan