|
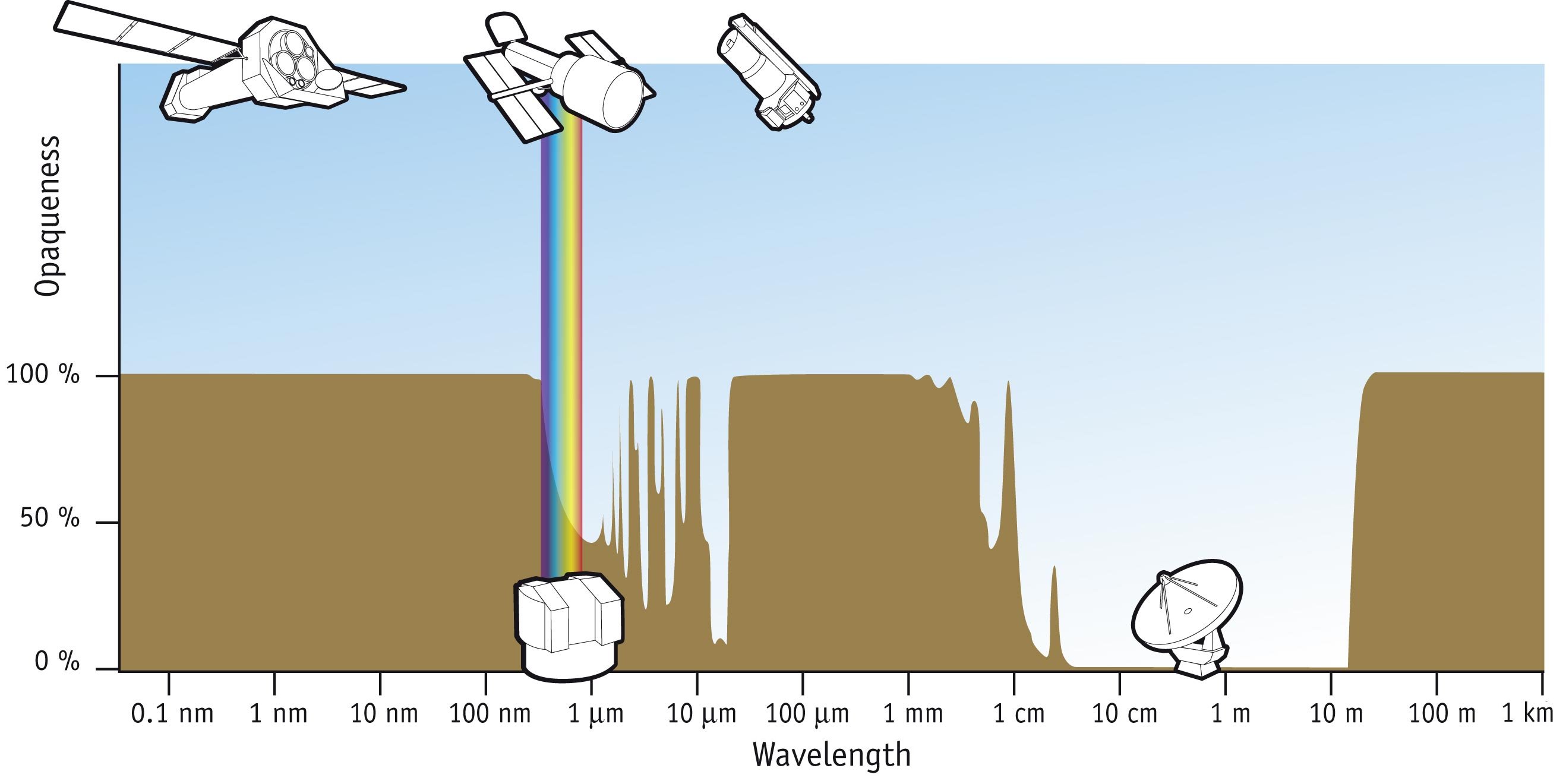
X-ray Astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by Balloon-borne telescope, balloons, sounding rockets, and X-ray astronomy satellite, satellites. X-ray astronomy uses a type of space telescope that can see x-ray radiation which standard optical telescopes, such as the Mauna Kea Observatories, cannot. X-ray generation, X-ray emission is expected from astronomical objects that contain extremely hot gases at temperatures from about a million kelvin (K) to hundreds of millions of kelvin (MK). Moreover, the maintenance of the E-layer of ionized gas high in the Earth's thermosphere also suggested a strong extraterrestrial source of X-rays. Although theory predicted that the Sun and the stars would be prominent X-ray sources, there was no way to verify this because Earth's atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The first constellations were likely defined in prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, and mythology. Different cultures and countries invented their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. Naming constellations also helped astronomers and navigators identify stars more easily. Twelve (or thirteen) ancient constellations belong to the zodiac (straddling the ecliptic, which the Sun, Moon, and planets all traver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermes Project
Hermes2D (''Higher-order modular finite element system'') is a C++/Python library of algorithms for rapid development of adaptive hp-FEM solvers. hp-FEM is a modern version of the finite element method (FEM) that is capable of extremely fast, exponential convergence. Main features of the library The Hermes library can be used for a large variety of PDE problems ranging from linear elliptic equations to time-dependent nonlinear multi-physics PDE systems arising in elasticity, structural mechanics, fluid mechanics, acoustics, electromagnetics, and other fields of computational engineering and science. The Hermes libraries are available for download under the GNU Lesser General Licence Terms as a means of providing open-source software for the development of Computational Scientific Research. Hermes implementation of adaptive hp-FEM for improved convergence and accuracy in non-linear systems is featured in the software. The software and underlying numerical methods are develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-2 Rocket
The V2 (), with the technical name ''Aggregat (rocket family), Aggregat-4'' (A4), was the world's first long-range missile guidance, guided ballistic missile. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed during the Second World War in Nazi Germany as a "V-weapons, vengeance weapon" and assigned to attack Allies of World War II, Allied cities as retaliation for the Strategic bombing during World War II#The British later in the war, Allied bombings of German cities. The rocket also became the first artificial object to travel into space by crossing the Kármán line (edge of space) with the vertical launch of MW 18014 on 20 June 1944. Research of military use of long-range rockets began when the graduate studies of Wernher von Braun were noticed by the German Army. A series of prototypes culminated in the A4, which went to war as the . Beginning in September 1944, more than 3,000 were launched by the Wehrmacht against Allied targets, first London and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert H
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of ''Hrōþ, Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use Robert (surname), as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert (name), Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta (given name), Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto (given name), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Institution Of Washington
The Carnegie Institution for Science, also known as Carnegie Science and the Carnegie Institution of Washington, is an organization established to fund and perform scientific research in the United States. This institution is headquartered in Washington, D.C. , the Institution's endowment was valued at $926.9 million. In 2018, the expenses for scientific programs and administration were $96.6 million. American astrophysicist John Mulchaey is the current president of the institution. Name More than 20 independent organizations were established through the philanthropy of Andrew Carnegie and feature his surname. In 2024, the "Carnegie Institution for Science" officially adopted the name "Carnegie Science", a name which has been used informally since 2007 when they first changed the name from "Carnegie Institution of Washington" to "Carnegie Institution for Science". History It is proposed to found in the city of Washington, an institution which ... shall in the broad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merle A
Merle may refer to: People and fictional characters *Merle (given name), a list of men, women and fictional characters *Merle (surname), a list of people Others *Merle (dog coat), a pattern in dogs’ coats *Merle (grape), another name for the wine grape Merlot *Akaflieg München Mü17 Merle, a German glider originally built in 1938 for the 1940 Olympics gliding competition * MS ''Phocine'', a ferry formerly named MS ''Merle'' *A Crusader fort near Tantura on the coast of Israel *The French name for the common blackbird See also *Merl (other) Merl or MERL may refer to: Merl * Merl (name), a list of people with the given name or surname * Merl, Luxembourg, a quarter of Luxembourg City * Merl (Buffyverse), a fictional character in the television series ''Angel'' MERL * Mechanical E ... * Merles, a commune in southern France {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory Breit
Gregory Breit (, ; July 14, 1899 – September 13, 1981) was an American physicist born in Mykolaiv, Russian Empire (now Mykolaiv, Ukraine). He was a professor at New York University (1929–1934), University of Wisconsin–Madison (1934–1947), Yale University (1947–1968), and University at Buffalo (1968–1973). In 1921, he was Paul Ehrenfest's assistant in Leiden University. Biography He was born in the city of Mykolaiv in the family of the book publisher Alfred Schneider. After the death of his mother in 1911, his father left for the United States of America. Until 1915, Gregory studied at the Mykolaiv Oleksandrivska gymnasium. In 1915, he followed his father to USA. He studied at Johns Hopkins University: in 1918 he obtained a Bachelor degree, in 1920 a Master degree, and in 1921 he earned a PhD in physics. In 1921-1922, he worked as a researcher at Leiden University. In 1922-1923, he was a research fellow at Harvard University. From 1923 to 1924, he was an assistant p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. Located in Washington, DC, it was founded in 1923 and conducts basic scientific research, applied research, technological development and prototyping. The laboratory's specialties include plasma physics, space physics, materials science, and tactical electronic warfare. NRL is one of the first US government scientific R&D laboratories, having opened in 1923 at the instigation of Thomas Edison, and is currently under the Office of Naval Research. As of 2016, NRL was a Navy Working Capital Fund activity, which means it is not a line-item in the US Federal Budget. Instead of direct funding from Congress, all costs, including overhead, were recovered through sponsor-funded research projects. NRL's research expenditures were approximately $1 billion per year. Research The Naval Research Laboratory conducts a wide variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sl2lab06
SL may refer to: Arts and entertainment * SL (rapper), a rapper from London * ''Second Life'', a multi-user 3D virtual world * Sensei's Library, an Internet site dedicated to the game of Go * Subdominant leittonwechselklänge * Leica SL, a mirrorless system camera by Leica Camera AG Business and organizations * Sociedad Limitada, the Spanish version of a private limited company Politics * Serbian Left (''Srpska levica''), a political party in Serbia * Stronnictwo Ludowe, a defunct Polish political party * Soyons Libres, a French political party Transportation and vehicles * SL Corporation, a Korean auto parts company * Rio Sul Serviços Aéreos Regionais (IATA code SL), a Brazilian airline * Salt Lake City Southern Railroad (reporting mark SL) * Stor-Oslo Lokaltrafikk, a public transport operator in Akershus, Norway * Storstockholms Lokaltrafik, the public transport operator in Stockholm, Sweden * Thai Lion Air (IATA airline code SL) * Mercedes-Benz SL-Class, an automo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warm–hot Intergalactic Medium
The warm–hot intergalactic medium (WHIM) is the sparse, warm-to-hot (105 to 107 K) plasma that cosmologists believe to exist in the spaces between galaxies and to contain 40–50% of the baryonic 'normal matter' in the universe at the current epoch. The WHIM can be described as a web of hot, diffuse gas stretching between galaxies, and consists of plasma, as well as atoms and molecules, in contrast to dark matter. The WHIM is a proposed solution to the missing baryon problem, where the observed amount of baryonic matter does not match theoretical predictions from cosmology. Much of what is known about the warmhot intergalactic medium comes from computer simulations of the cosmos. The WHIM is expected to form a filamentary structure of tenuous, highly ionized baryons with a density of 1−10 particles per cubic meter. Within the WHIM, gas shocks are created as a result of active galactic nuclei, along with the gravitationally-driven processes of merging and accretion. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Clusters
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. Clusters consist of galaxies, heated gas, and dark matter. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after superclusters. They were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. Together, galaxy groups and clusters form superclusters. Basic properties Galaxy clusters typically have the following properties: * They contain 100 to 1,000 galaxies, hot X-ray emitting gas and large amounts of dark matter. Details are described in the "Composition" section. * They have total masses of 1014 to 1015 solar masses. * They typically have diameters from 1 to 5 Mpc ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |