|
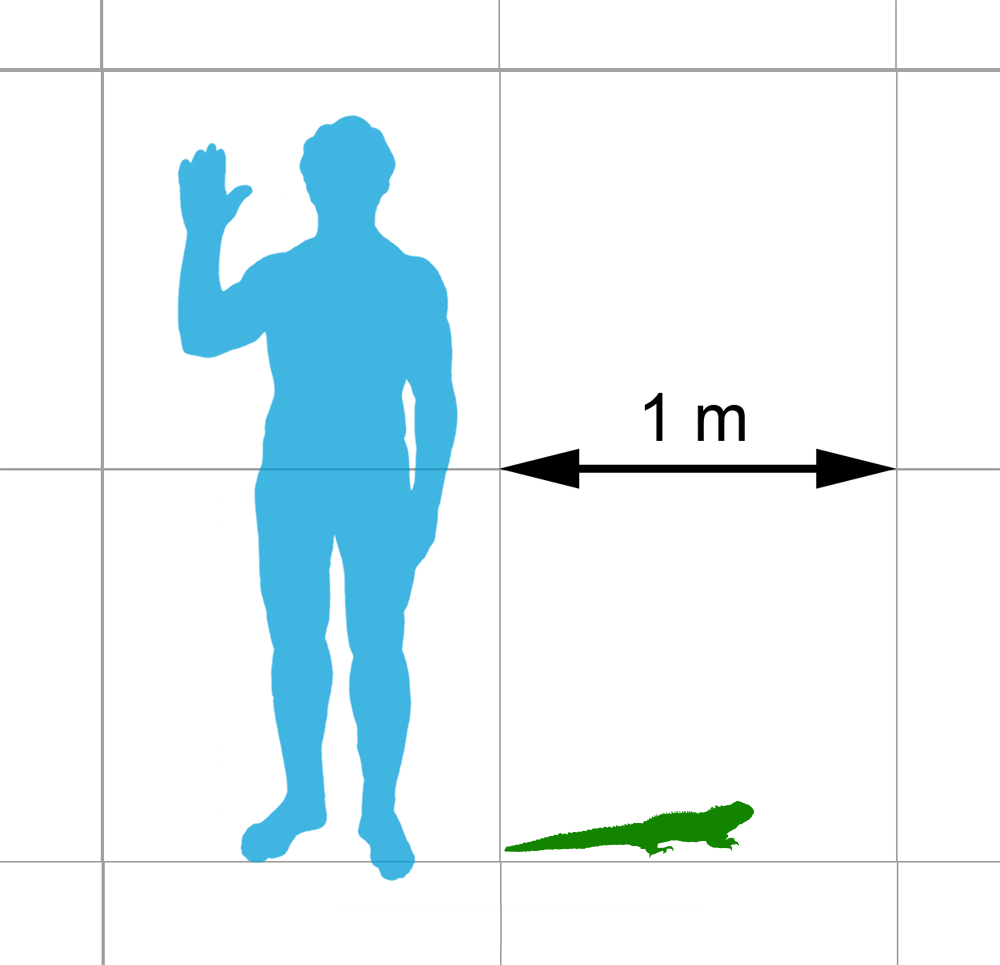
Wētā
Wētā (also spelled weta in English) is the common name for a group of about 100 insect species in the families Anostostomatidae and Rhaphidophoridae endemism, endemic to New Zealand. They are giant wingless insect, flightless cricket (insect), crickets, and some are among the List of largest insects, heaviest insects in the world. Generally nocturnality, nocturnal, most small species are carnivores and scavengers while the larger species are herbivore, herbivorous. Although some List of endemic birds of New Zealand, endemic birds (and tuatara) likely prey on them, wētā are disproportionately preyed upon by introduced mammals, and some species are now critically endangered. Name Wētā is a loanword, from the Māori language, Māori-language word , which refers to this whole group of large insects; some types of wētā have a specific Māori name. In New Zealand English, it is spelled either "weta" or "wētā". The form with Macron (diacritic), macrons is increasingly com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Wētā
Giant wētā are several species of wētā in the genus ''Deinacrida'' of the family Anostostomatidae. Giant wētā are endemic to New Zealand and all but one species are protected by law because they are considered at risk of extinction. There are eleven species of giant wētā, most of which are larger than other wētā, despite the latter also being large by insect standards. Large species can be up to , not inclusive of legs and antennae, with body mass usually no more than .McIntyre, M. 2001. The Ecology of Some Large Weta Species of New Zealand, Chapter 12, Pp: 225-242. ''In:'' Field, L. d''Biology of weta, King Crickets and their Allies''. CABI Publishing, Oxford One gravid captive female reached a mass of about , making it one of the heaviest insects in the world and heavier than a sparrow. This is, however, abnormal, as this individual was unmated and retained an abnormal number of eggs. The largest species of giant wētā is the Little Barrier Island giant wētā ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anostostomatidae
Anostostomatidae is a family of insects in the order Orthoptera, widely distributed in the southern hemisphere. It is named Mimnermidae or Henicidae in some taxonomies, and common names include ''king crickets'' in Australia and South Africa, and ''wētā'' in New Zealand (although not all wētā are in Anostostomatidae). Prominent members include the Parktown prawn of South Africa, and the giant wētā of New Zealand. General characteristics Some members of this family can be quite large: Parktown prawn can exceed 6 cm and tree weta can exceed 8 cm in length. Some Australian and Asian anostostomatids have wings (e.g. '' Exogryllacris'', '' Gryllotaurus'', '' Transaevum''), while most lack wings (e.g. '' Anostostoma'', '' Hypocophoides'', '' Penalva''). Males of some species have highly modified heads, which they use in male-male conflicts. Diet The wētā of New Zealand, such as '' Hemideina'', are mostly herbivores that feed on leaves, fruit and flowers, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhaphidophoroidea
The orthopteran family Rhaphidophoridae of the suborder Ensifera has a worldwide distribution. Common names for these insects include cave crickets, camel crickets, spider crickets (sometimes shortened to "criders" or "sprickets"), and sand treaders. Those occurring in New Zealand are typically referred to as jumping or cave wētā. Most are found in forest environments or within caves, animal burrows, cellars, under stones, or in wood or similar environments. All species are flightless and nocturnal, usually with long antennae and legs. More than 500 species of Rhaphidophoridae are described. The well-known field crickets are from a different superfamily (Grylloidea) and only look vaguely similar, while members of the family Tettigoniidae may look superficially similar in body form. Description Most cave crickets have very large hind legs with "drumstick-shaped" femora and equally long, thin tibiae, and long, slender antennae. The antennae arise closely and next to each oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricket (insect)
Crickets are orthopteran insects which are related to Tettigoniidae, bush crickets and more distantly, to grasshoppers. In older literature, such as Augustus Daniel Imms, Imms,Imms AD, rev. Richards OW & Davies RG (1970) ''A General Textbook of Entomology'' 9th Ed. Methuen 886 pp. "crickets" were placed at the family level (''i.e.'' Gryllidae), but contemporary authorities including Dan Otte, Otte now place them in the superfamily Grylloidea. The word has been used in combination to describe more distantly related taxa in the suborder Ensifera, such as Stenopelmatoidea, king crickets and mole crickets. Crickets have mainly cylindrically shaped bodies, round heads, and long antenna (biology), antennae. Behind the head is a smooth, robust pronotum. The abdomen ends in a pair of long Cercus, cerci; females have a long, cylindrical ovipositor. Diagnostic features include legs with 3-segmented Arthropod leg#Tarsus, tarsi; as with many Orthoptera, the hind legs have enlarged femora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuatara
The tuatara (''Sphenodon punctatus'') is a species of reptile endemic to New Zealand. Despite its close resemblance to lizards, it is actually the only extant member of a distinct lineage, the previously highly diverse order Rhynchocephalia. The name is derived from the Māori language and means "peaks on the back". The single extant species of tuatara is the only surviving member of its order, which was highly diverse during the Mesozoic era. Rhynchocephalians first appeared in the fossil record during the Triassic, around 240 million years ago, and reached worldwide distribution and peak diversity during the Jurassic, when they represented the world's dominant group of small reptiles. Rhynchocephalians declined during the Cretaceous, with their youngest records outside New Zealand dating to the Paleocene. Their closest living relatives are squamates (lizards and snakes). Tuatara are of interest for studying the evolution of reptiles. Tuatara are greenish brown an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenopelmatoidea
Stenopelmatoidea is a superfamily of insects in the order Orthoptera; in some older classifications this group was referred to as Gryllacridoidea. Classification The classification and constituency of Stenopelmatoidea is an ongoing source of controversy, with different authorities proposing radically different arrangements. At present, the majority of researchers appear to be mostly in consensus that Stenopelmatoidea comprises several well-separated lineages, at least three of which (Anostostomatidae, Gryllacrididae, and Stenopelmatidae) can be reasonably well-defined, and have molecular evidence that supports their recognition as monophyletic groups.Vandergast, A.G., Weissman, D.B., Wood, D.A., Rentz, D.C., Bazelet, C.S., and Ueshima, N. (2017) Tackling an intractable problem: Can greater taxon sampling help resolve relationships within the Stenopelmatoidea (Orthoptera: Ensifera)? ''Zootaxa'' 4291, no. 1, p. 1. DOI:10.11646/zootaxa.4291.1.1 At least one other authority, workin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loanword
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term that is well established in the linguistic field despite its acknowledged descriptive flaws: nothing is taken away from the donor language and there is no expectation of returning anything (i.e., the loanword). Loanwords may be contrasted with calques, in which a word is borrowed into the recipient language by being directly translated from the donor language rather than being adopted in (an approximation of) its original form. They must also be distinguished from cognates, which are words in two or more related languages that are similar because they share an etymological origin in the ancestral language, rather than because one borrowed the word from the other. Examples and related terms A loanword is distinguished from a calque (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller islands. It has a total area of , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, sixth-largest country in the world and the largest in Oceania. Australia is the world's flattest and driest inhabited continent. It is a megadiverse countries, megadiverse country, and its size gives it a wide variety of landscapes and Climate of Australia, climates including deserts of Australia, deserts in the Outback, interior and forests of Australia, tropical rainforests along the Eastern states of Australia, coast. The ancestors of Aboriginal Australians began arriving from south-east Asia 50,000 to 65,000 years ago, during the Last Glacial Period, last glacial period. By the time of British settlement, Aboriginal Australians spoke 250 distinct l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite. Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed senses of hearing (sense), hearing, olfaction, smell, and specially adapted eyesight. Some animals, such as ferrets, have eyes that can adapt to both low-level and bright day levels of illumination (see metaturnal). Others, such as bushbaby, bushbabies and (some) bats, can function only at night. Many nocturnal creatures including tarsier, tarsiers and some owl, owls have large eyes in comparison with their body size to compensate for the lower light levels at night. More specifically, they have been found to have a larger cornea relative to their eye size than diurnal creatures to increase their : in the low-light conditions. Nocturnality helps wasps, such as ''Apoica flavissima'', avoid hunting in intens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod Leg
The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip (anatomy), hip, : ''coxae''), ''trochanter'', ''femur'' (: ''femora''), ''tibia'' (: ''tibiae''), ''tarsus'' (: ''tarsi''), ''ischium'' (: ''ischia''), ''metatarsus'', ''carpus'', ''dactylus'' (meaning finger), ''patella'' (: ''patellae''). Homology (biology), Homologies of leg segments between groups are difficult to prove and are the source of much argument. Some authors posit up to eleven segments per leg for the most recent common ancestor of Neontology, extant arthropods but modern arthropods have eight or fewer. It has been argued that the ancestral leg need not have been so complex, and that other events, such as successive loss of function of a Homeobox, ''Hox''-gene, could result in Parallel evolution, parallel gains of leg segments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |