|
Wound, Ostomy, And Continence Nursing
Wound, ostomy, and continence nursing is a nursing specialty involved with the treatment of patients with acute and chronic wounds, patients with an ostomy (those who have had some kind of bowel or bladder diversion), and patients with incontinence conditions (those with issues of bladder control, bowel control, and associated skin care). Nurses in this specialty are often referred to as wound, ostomy, and continence nurses (WOC nurses). They use evidence-based knowledge and skills to manage the care of these patients, whose needs can often be complex. In the United States, certification is available for this specialty from the Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing Certification Board; for example, the postnominals "CWON" represent the title of Certified Wound and Ostomy Nurse. There are additional organizations that offer varying levels of certification in this field (e.g., American Board of Wound Management). In some countries, such as the United Kingdom, WOC nursing is not seen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nursing
Nursing is a health care profession that "integrates the art and science of caring and focuses on the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and human functioning; prevention of illness and injury; facilitation of healing; and alleviation of suffering through compassionate presence". Nurses practice in many specialties with varying levels of certification and responsibility. Nurses comprise the largest component of most healthcare environments. There are shortages of qualified nurses in many countries. Nurses develop a plan of care, working collaboratively with physicians, therapists, patients, patients' families, and other team members that focuses on treating illness to improve quality of life. In the United Kingdom and the United States, clinical nurse specialists and nurse practitioners diagnose health problems and prescribe medications and other therapies, depending on regulations that vary by state. Nurses may help coordinate care performed by other provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wound
A wound is any disruption of or damage to living tissue, such as skin, mucous membranes, or organs. Wounds can either be the sudden result of direct trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical), or can develop slowly over time due to underlying disease processes such as diabetes mellitus, venous/arterial insufficiency, or immunologic disease. Wounds can vary greatly in their appearance depending on wound location, injury mechanism, depth of injury, timing of onset ( acute vs chronic), and wound sterility, among other factors. Treatment strategies for wounds will vary based on the classification of the wound, therefore it is essential that wounds be thoroughly evaluated by a healthcare professional for proper management. In normal physiology, all wounds will undergo a series of steps collectively known as the wound healing process, which include hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and tissue remodeling. Age, tissue oxygenation, stress, underlying medical conditions, and certain m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoma (medicine)
In anatomy, a stoma (: stomata or stomas) is any opening in the body. For example, a mouth, a nose, and an anus are natural stomata. Any hollow organ can be manipulated into an artificial stoma as necessary. This includes the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, ileum, colon, pleural cavity, ureters, urinary bladder, and renal pelvis. Such a stoma may be permanent or temporary. Surgical procedures that involve the creation of an artificial stoma have names that typically end with the suffix "-ostomy", and the same names are also often used to refer to the stoma thus created. For example, the word " colostomy" often refers either to an artificial anus or the procedure that creates one. Accordingly, it is not unusual for a stoma to be called an ostomy (plural ostomies), as is the norm in wound, ostomy, and continence nursing. Gastrointestinal stomata Stomata are created in particular in surgical procedures involving the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) or gastrointestinal system (GIS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digestion, digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Nephrozoa, Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostium (sponges), ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
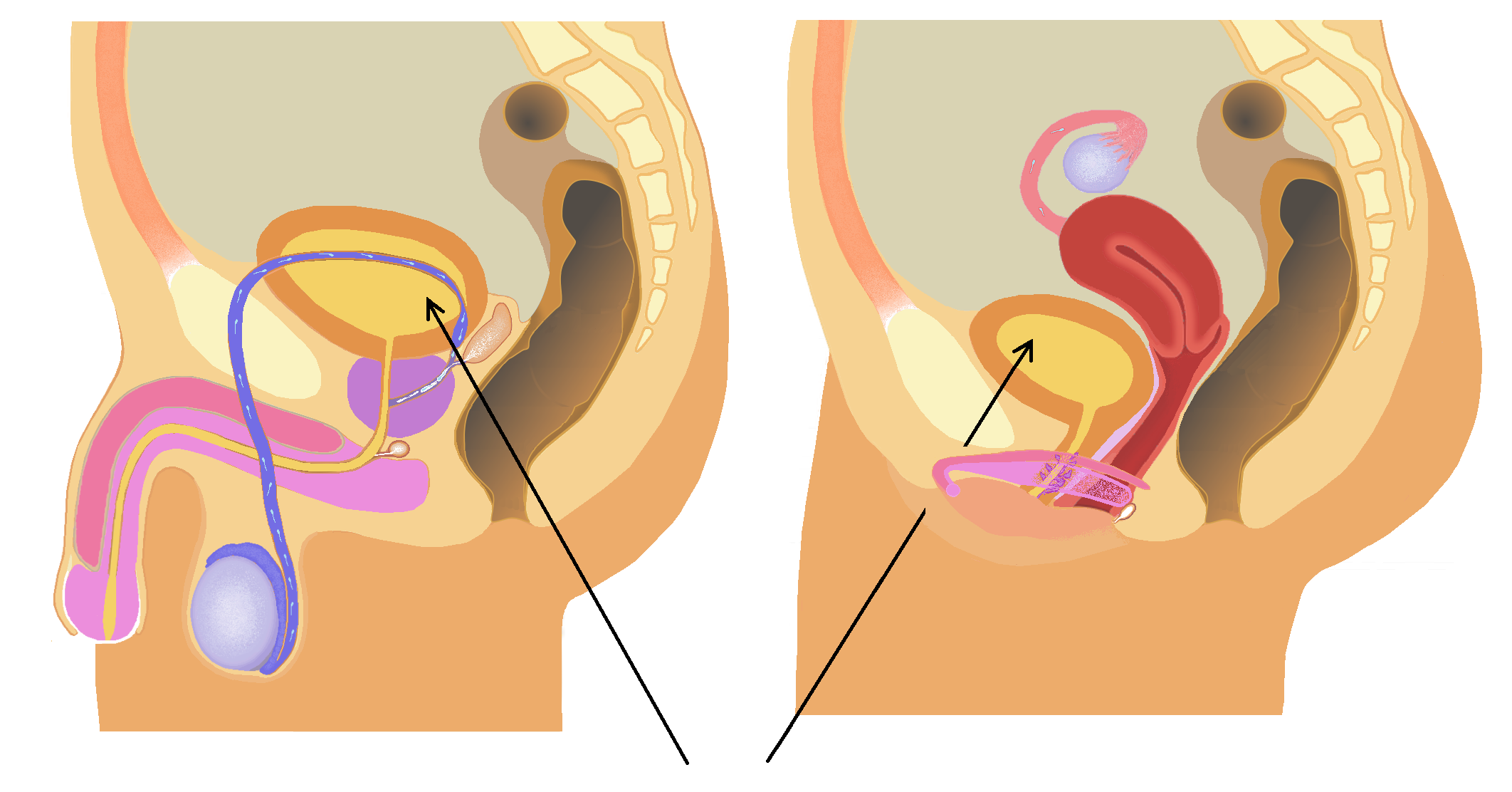
Urinary Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a significant effect on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women and has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care. The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis (bed wetting). UI is an example of a stigmatized medical condition, which creates barriers to successful management and makes the problem worse. People may be too embarrassed to seek medical help, and attempt to self-manage the symptom in secrecy from others. Pelvic surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, attention deficit disorder (ADHD), and menopause are major risk factors. Urinary incontinence is often a result of an underlying medical condition but is under-reported to medical practitioners. There are four main types of incontinence: * Urge incontinence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fecal Incontinence
Fecal incontinence (FI), or in some forms, encopresis, is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents—including flatus (gas), liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. FI is a sign or a symptom, not a diagnosis. Incontinence can result from different causes and might occur with either constipation or diarrhea. Continence is maintained by several interrelated factors, including the anal sampling mechanism, and incontinence usually results from a deficiency of multiple mechanisms. The most common causes are thought to be immediate or delayed damage from childbirth, complications from prior anorectal surgery (especially involving the anal sphincters or hemorrhoidal vascular cushions), altered bowel habits (e.g., caused by irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, food intolerance, or constipation with overflow incontinence). Reported prevalence figures vary: an estimated 2.2% of community-dwelling adult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nursing Credentials And Certifications
Nursing credentials and certifications are the various credentials and certifications that a person must have to practice nursing legally. Nurses' postnominal letters (abbreviations listed after the name) reflect their credentials—that is, their achievements in nursing education, licensure, certification, and fellowship. The letters usually appear in the following order: * Highest earned academic degree in or related to nursing (e.g. " DNP" or " PhD") * Nursing licensure (e.g. "APRN," " RN," " LPN") * Nursing certification (e.g. " CCRN") * Nursing fellowship (e.g. " FAAN") Generally, credentials are listed from most to least permanent. A degree, once earned, cannot, in normal circumstances, be taken away. State licensure is active until retirement and otherwise only revoked in cases of serious professional misconduct. Certifications generally must be periodically renewed by examination or the completion of a prescribed number of continuing education units (CEUs). This is of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-nominal Letters
Post-nominal letters, also called post-nominal initials, post-nominal titles, designatory letters, or simply post-nominals, are letters placed after a person's name to indicate that the individual holds a position, an academic degree, accreditation, an office, a military decoration, or honour, or is a member of a religious institute or fraternity. An individual may use several different sets of post-nominal letters, but in some contexts it may be customary to limit the number of sets to one or just a few. The order in which post-nominals are listed after a name is based on rules of precedence and what is appropriate for a given situation. Post-nominal letters are one of the main types of Suffix (name), name suffix. In contrast, pre-nominal letters precede the name rather than following it, such as addressing a physician or professor as "Dr. Smith". List Different awards and post-nominal letters are in use in the English-speaking countries. Usage Listing order The order in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nursing In The United Kingdom
Nursing in the United Kingdom is the profession of ''registered nurses'' and nursing associates in the Primary care, primary and secondary care of patients. It has evolved from assisting physicians to encompass a variety of professional roles. Over 700,000 registered nurses practice in the UK, working in settings such as hospitals, Clinic, health centres, nursing homes, hospices, communities, military, prisons, and academia. Most are employed by the National Health Service (NHS). Nursing is split into four fields: adults, children, mental health, and learning disability. Within these nurses may work within specialties such as medical care or theatres, and may specialise further in areas such as cardiac care. Nurses often work in multi-disciplinary teams, but increasingly work independently, and may work in supporting sectors such as education or research. The UK-wide regulator for nursing is the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC), and all nurses and nursing associates must b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nursing Specialties
This is a list of different nursing specialities. In recent decades, the number of non-bedside nursing roles has increased. Professional organizations or certifying boards issue voluntary Nursing board certification, certification in many of these specialties. * Advanced practice nurse, Advanced practice nursing * Aesthetic medicine, Aesthetic nursing/cosmetic nursing * Ambulatory care nursing * Burn nursing * Camp nursing * Cardiac nursing * Cardiac Intervention nursing * Diabetes Nursing * Registered Dental Nurse, Dental nursing * Medical case management * Community health nursing * Correctional nursing * Critical care nursing * Emergency nursing * Environmental health nursing * Faith community nursing * Flight nurse, Flight nursing * Forensic nursing * Gastroenterology nursing * Genetics nursing * Geriatric nursing * Haematology nursing * Health visitor, Health visiting * Holistic nursing * Home health nursing * Hospice nursing, Hospice and palliative care nursing * Hyperbaric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |