|
Witches' Mark
A witch's mark, devil's mark or stigma diabolicum was a bodily mark that witch-hunters believed indicated that an individual was a witch, during the height of the witch trials. The beliefs about the mark differed, depending on the trial location and the accusation made against the witch. Use of the term is found earliest in the 16th century, and reaching its peak in 1645, but then essentially disappearing by 1700. The Witch or Devil's mark was believed to be the permanent marking of the Devil on his initiates to seal their obedience and service to him. He is said to create the mark by raking his claw across their flesh, licking the skin to produce a death skull pattern, or using a hot iron to produce a blue or red brand. The Devil was thought to mark the individual at the end of nocturnal initiation rites.Devil's mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Examination Of A Witch - Tompkins Matteson (cropped)
Examination may refer to: * Physical examination, a medical procedure * Questioning and more specific forms thereof, for example in law: ** Cross-examination ** Direct examination * Exam as assessment, also "test", "exams", "evaluation" ** Civil service entrance examination *** Imperial examination See also * Analysis * Appraisal (other) * Assessment (other) * Evaluation * Evaluation (other) Evaluation is the process of judging something or someone based on a set of standards. Evaluation may also refer to: Measurement or appraisal * Education: ** Educational assessment ** Competency evaluation (language), a means for teachers to ... * Exam (other) * Investigation (other) * Study (other) * * {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
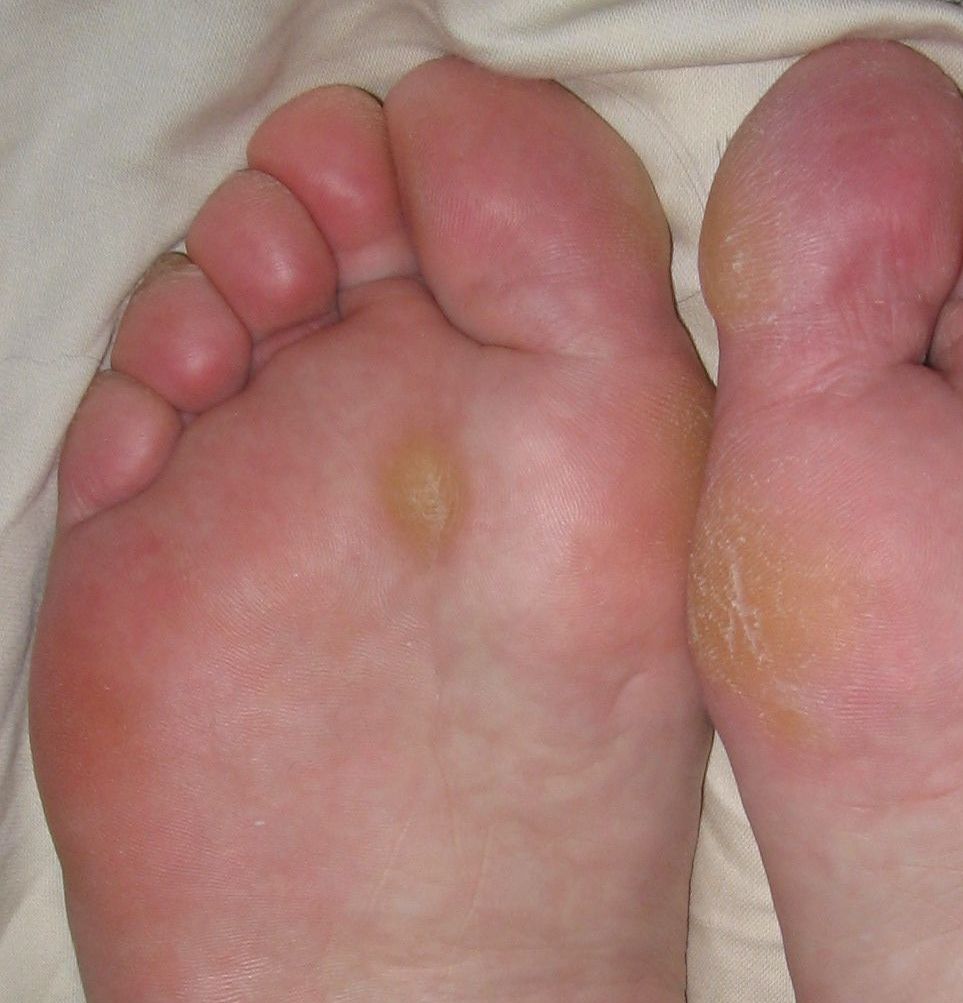
Callus
A callus (: calluses) is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, but they may occur anywhere on the skin. Some degree of callus, such as on the bottom of the foot, is normal. Calluses are generally not harmful and help prevent blisters, as well as offering protection. However, excessive formation may sometimes lead to other problems, such as a skin ulceration or infection, or cause the affected person to try to offload the affected painful area, which can place excessive stress on the asymptomatic side. Rubbing that is too frequent or forceful will cause blisters, as opposed to calluses, to form. Cause Normally, a callus will form on any part of the skin exposed to excess friction over a long period of time. Activities that are known for causing calluses include construction work and craftwork, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa, various islands in Asia and Oceania, as well as territory in other parts of Europe. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, becoming known as "the empire on which the sun never sets". At its greatest extent in the late 1700s and early 1800s, the Spanish Empire covered , making it one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history. Beginning with the 1492 arrival of Christopher Columbus and continuing for over three centuries, the Spanish Empire would expand across the Caribbean Islands, half of South America, most of Central America and much of North America. In the beginning, Portugal was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borrelia Burgdorferi
''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a bacterial species of the spirochete class in the genus '' Borrelia'', and is one of the causative agents of Lyme disease in humans. Along with a few similar genospecies, some of which also cause Lyme disease, it makes up the species complex of ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' sensu lato. The complex currently comprises 20 accepted and 3 proposed genospecies. ''B. burgdorferi'' sensu stricto exists in North America and Eurasia and until 2016 was the only known cause of Lyme disease in North America. ''B. burgdorferi'' are often mistakenly described as Gram negative because of their two external membranes, but they lack lipopolysaccharide and possess many surface lipoproteins, unlike true Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is named after the researcher Willy Burgdorfer, who first isolated the bacterium in 1982. ''Borrelia burgdorferi'' is a microaerophile, requiring small amounts of oxygen in order to undergo glycolysis and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbian Exchange
The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the New World (the Americas) in the Western Hemisphere, and the Old World (Afro-Eurasia) in the Eastern Hemisphere, from the late 15th century on. It is named after the explorer Christopher Columbus and is related to the European colonization of the Americas, European colonization and global trade following his Voyages of Christopher Columbus#First voyage, 1492 voyage. Some of the exchanges were deliberate while others were unintended. Communicable diseases of Old World origin resulted in an 80 to 95 percent reduction in the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous population of the Americas from the 15th century onwards, and their extinction in the Influx of disease in the Caribbean, Caribbean. The cultures of both hemispheres were significantly impacted by the migration of people, both free and enslaved, from the Old World to the New. Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
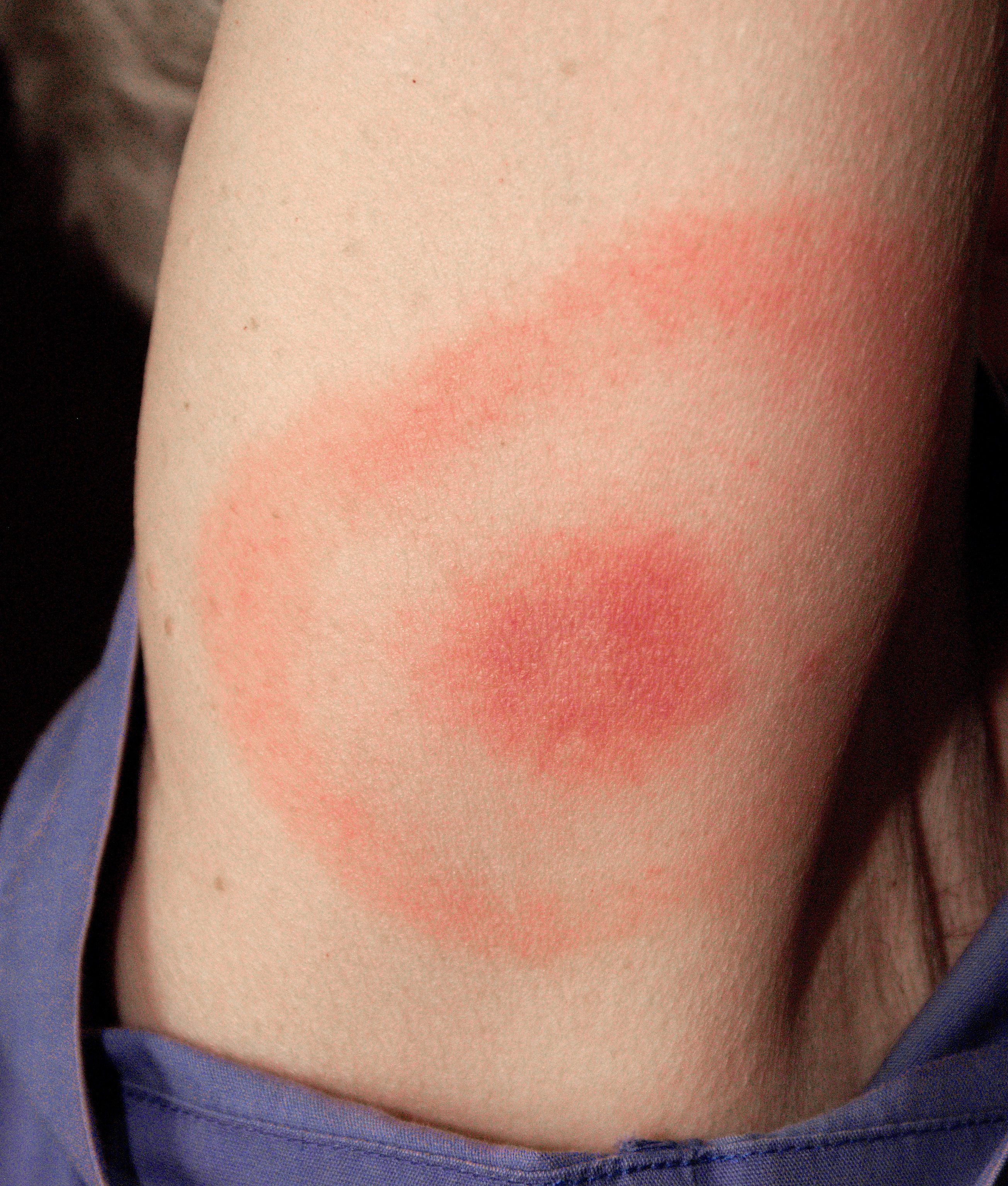
Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a tick-borne disease caused by species of ''Borrelia'' bacteria, Disease vector, transmitted by blood-feeding ticks in the genus ''Ixodes''. It is the most common disease spread by ticks in the Northern Hemisphere. Infections are most common in the spring and early summer. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema migrans (EM), which appears at the site of the tick bite about a week afterwards. The rash is typically neither itchy nor painful. Approximately 70–80% of infected people develop a rash. Other early symptoms may include fever, headaches and fatigue (medical), tiredness. If untreated, symptoms may include Facial nerve paralysis, loss of the ability to move one or both sides of the face, arthritis, joint pains, Meningitis, severe headaches with neck stiffness or heart palpitations. Months to years later, repeated episodes of joint pain and swelling may occur. Occasionally, shootin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wicca
Wicca (), also known as "The Craft", is a Modern paganism, modern pagan, syncretic, Earth religion, Earth-centred religion. Considered a new religious movement by Religious studies, scholars of religion, the path evolved from Western esotericism, developed in England during the first half of the 20th century, and was Witchcraft Today, introduced to the public in 1954 by Gerald Gardner, a retired British civil servant. Wicca draws upon paganism, ancient pagan and Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, 20th-century Hermetic motif (folkloristics), motifs for theology, theological and ritual purposes. Doreen Valiente joined Gardner in the 1950s, further building Wicca's liturgical tradition of beliefs, principles, and practices, disseminated through published books as well as secret written and oral teachings passed along to Initiation, initiates. Many variations of the religion have grown and evolved over time, associated with a number of diverse lineages, sects, and Religious den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paganism
Paganism (, later 'civilian') is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Christianity, Judaism, and Samaritanism. In the time of the Roman Empire, individuals fell into the pagan class either because they were increasingly rural and provincial relative to the Christian population, or because they were not '' milites Christi'' (soldiers of Christ).J. J. O'Donnell (1977)''Paganus'': Evolution and Use, ''Classical Folia'', 31: 163–69. Alternative terms used in Christian texts were '' hellene'', '' gentile'', and '' heathen''. Ritual sacrifice was an integral part of ancient Greco-Roman religion and was regarded as an indication of whether a person was pagan or Christian. Paganism has broadly connoted the "religion of the peasantry". During and after the Middle Ages, the term ''paganism'' was applied to any non-Christian religion, and the term presumed a belief in fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tattoo
A tattoo is a form of body modification made by inserting tattoo ink, dyes, or pigments, either indelible or temporary, into the dermis layer of the skin to form a design. Tattoo artists create these designs using several tattooing processes and techniques, including hand-tapped traditional tattoos and modern tattoo machines. The history of tattooing goes back to Neolithic times, practiced across the globe by many cultures, and the symbolism and impact of tattoos varies in different places and cultures. Tattoos may be decorative (with no specific meaning), symbolic (with a specific meaning to the wearer), pictorial (a depiction of a specific person or item), or textual (words or pictographs from written languages). Many tattoos serve as rites of passage, marks of status and rank, symbols of religious and spiritual devotion, decorations for bravery, marks of fertility, pledges of love, amulets and talismans, protection, and as punishment, like the marks of outcasts, slaves, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Murray
Margaret Alice Murray (13 July 1863 – 13 November 1963) was an Anglo-Indian Egyptologist, archaeologist, anthropologist, historian, and folklorist. The first woman to be appointed as a lecturer in archaeology in the United Kingdom, she worked at University College London (UCL) from 1898 to 1935. She was president of the Folklore Society from 1953 to 1955, and published widely. Born to a wealthy middle-class English family in Calcutta, British India, Murray divided her youth between India, Britain, and Germany, training as both a nurse and a social worker. Moving to London, in 1894 she began studying Egyptology at UCL, developing a friendship with department head Flinders Petrie, who encouraged her early academic publications and appointed her junior lecturer in 1898. In 1902–1903, she took part in Petrie's Excavation (archaeology), excavations at Abydos, Egypt, there discovering the Osireion temple, and the following season investigated the Saqqara cemetery, both of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, society, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including archaic humans. Social anthropology studies patterns of behaviour, while cultural anthropology studies cultural meaning, including norms and values. The term sociocultural anthropology is commonly used today. Linguistic anthropology studies how language influences social life. Biological anthropology, Biological (or physical) anthropology studies the biology and evolution of Human evolution, humans and their close primate relatives. Archaeology, often referred to as the "anthropology of the past," explores human activity by examining physical remains. In North America and Asia, it is generally regarded as a branch of anthropology, whereas in Europe, it is considered either an independent discipline or classified under related fields like history and palaeontology. Etymology The abstract noun ''wikt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, the struggle consisted of the First English Civil War and the Second English Civil War. The Anglo-Scottish war (1650–1652), Anglo-Scottish War of 1650 to 1652 is sometimes referred to as the ''Third English Civil War.'' While the conflicts in the three kingdoms of England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland had similarities, each had their own specific issues and objectives. The First English Civil War was fought primarily over the correct balance of power between Parliament of England, Parliament and Charles I of England, Charles I. It ended in June 1646 with Royalist defeat and the king in custody. However, victory exposed Parliamentarian divisions over the nature of the political settlemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |