|
Wildlife Forensics
Wildlife forensic science is forensic science applied to legal issues involving wildlife. Wildlife forensic sciences also deal with conservation and identification of rare species and is a useful tool for non-invasive studies. Methods can be used to determine relatedness of the animals in the area allowing them to determine rare and endangered species that are candidates for genetic rescue. Techniques using things such as the SSCP or Single-strand conformation polymorphism, Single-Strand Conformational Polymorphism gel electrophoresis technique, microscopy, DNA barcoding, Mitochondrial Microsatellite Analysis and some DNA and Isotope analysis can identify species and individual animals in most cases if they have already been captured . Unlike human identification, animal identification requires determination of its Family (biology), family, genus, and species, and sex in order to individualize the animal, typically through the use of DNA based analyses. History Wildlife forensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USFWS Forensics Laboratory Criminalistics
The United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS or FWS) is a List of federal agencies in the United States, U.S. federal government agency within the United States Department of the Interior which oversees the management of fish, wildlife, and natural habitats in the United States. The mission of the agency is "working with others to conserve, protect, and enhance fish, wildlife, plants and their habitats for the continuing benefit of the American people." Among the responsibilities of the USFWS are enforcing federal wildlife laws; protecting endangered species; managing migratory birds; restoring nationally significant fisheries; conserving and restoring wildlife habitats, such as wetlands; helping foreign governments in international conservation efforts; and distributing money to fish and wildlife agencies of U.S. states through the Wildlife Sport Fish and Restoration Program. The vast majority of fish and wildlife habitats are on U.S. state, state or private land not co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research and forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Extraction
The first isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was done in 1869 by Friedrich Miescher. DNA extraction is the process of isolating DNA from the cells of an organism isolated from a sample, typically a biological sample such as blood, saliva, or tissue. It involves breaking open the cells, removing proteins and other contaminants, and purifying the DNA so that it is free of other cellular components. The purified DNA can then be used for downstream applications such as PCR, sequencing, or cloning. Currently, it is a routine procedure in molecular biology or forensic analyses. This process can be done in several ways, depending on the type of the sample and the downstream application, the most common methods are: mechanical, chemical and enzymatic lysis, precipitation, purification, and concentration. The specific method used to extract the DNA, such as phenol-chloroform extraction, alcohol precipitation, or silica-based purification. For the chemical method, many different k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
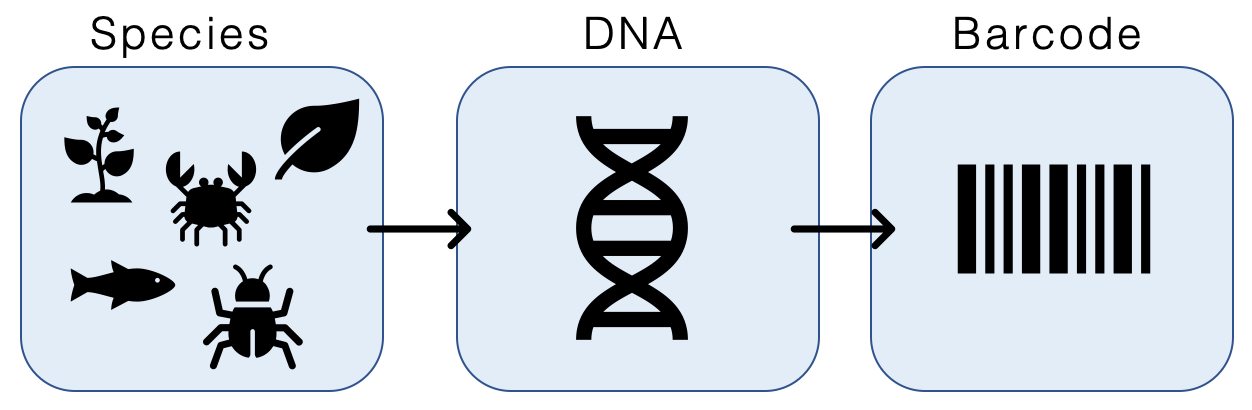
DNA Barcoding
DNA barcoding is a method of species identification using a short section of DNA from a specific gene or genes. The premise of DNA barcoding is that by comparison with a reference library of such DNA sections (also called " sequences"), an individual sequence can be used to uniquely identify an organism to species, just as a supermarket scanner uses the familiar black stripes of the UPC barcode to identify an item in its stock against its reference database. These "barcodes" are sometimes used in an effort to identify unknown species or parts of an organism, simply to catalog as many taxa as possible, or to compare with traditional taxonomy in an effort to determine species boundaries. Different gene regions are used to identify the different organismal groups using barcoding. The most commonly used barcode region for animals and some protists is a portion of the cytochrome ''c'' oxidase I (COI or COX1) gene, found in mitochondrial DNA. Other genes suitable for DNA barcoding a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome B
Cytochrome b is a protein found in the membranes of aerobic cells. In eukaryotic mitochondria (inner membrane) and in aerobic prokaryotes, cytochrome b is a component of respiratory chain complex III () — also known as the bc1 complex or ubiquinol-cytochrome c reductase. In plant chloroplasts and cyanobacteria, there is a homologous protein, cytochrome b6, a component of the plastoquinone-plastocyanin reductase (), also known as the b6f complex. These complexes are involved in electron transport, the pumping of protons to create a proton-motive force ( PMF). This proton gradient is used for the generation of ATP. These complexes play a vital role in cells. Structure and function Cytochrome b/b6 is an integral membrane protein of approximately 400 amino acid residues that probably has 8 transmembrane segments. In plants and cyanobacteria, cytochrome b6 consists of two protein subunits encoded by the petB and petD genes. Cytochrome b/b6 non-covalently binds two heme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome C Oxidase
The enzyme cytochrome c oxidase or Complex IV (was , now reclassified as a translocasEC 7.1.1.9 is a large transmembrane protein complex found in bacteria, archaea, and the mitochondria of eukaryotes. It is the last enzyme in the Cellular respiration, respiratory electron transport chain of cell (biology), cells located in the membrane. It receives an electron from each of four cytochrome c molecules and transfers them to one oxygen molecule and four protons, producing two molecules of water. In addition to binding the four protons from the inner aqueous phase, it transports another four protons across the membrane, increasing the transmembrane difference of proton electrochemical potential, which the ATP synthase then uses to synthesize Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Structure The complex The complex is a large integral membrane protein composed of several Cofactor (biochemistry)#Metal ions, metal prosthetic sites and 13 protein subunits in mammals. In mammals, ten subunits a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barcode Of Life Data System
The Barcode of Life Data System (commonly known as BOLD or BOLDSystems) is a web platform specifically devoted to DNA barcoding. It is a cloud-based data storage and analysis platform developed at the Centre for Biodiversity Genomics in Canada. It consists of four main modules, a data portal, an educational portal, a registry of BINs (putative species), and a data collection and analysis workbench which provides an online platform for analyzing DNA sequences. Since its launch in 2005, BOLD has been extended to provide a range of functionality including data organization, validation, visualization and publication. The most recent version of the system, version 5, launched in 2024. Version 4, launched in 2017, brought a set of improvements supporting data collection and analysis but also included novel functionality improving data dissemination, citation, and annotation. Before November 16, 2020, BOLD already contained barcode sequences for 318,105 formally described species covering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Molecular Biology Laboratory
The European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) is an intergovernmental organization dedicated to molecular biology research and is supported by 29 member states, two prospect member states, and one associate member state. EMBL was created in 1974 and is funded by public research money from its member states. Research at EMBL is conducted by more than 110 independent research groups and service teams covering the spectrum of molecular biology. The Laboratory operates from six sites: the main laboratory in Heidelberg (Germany), and sites in Barcelona (Spain), Grenoble (France), Hamburg (Germany), Hinxton (the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), in England), and Rome (Italy). EMBL groups and laboratories perform basic research in molecular biology and molecular medicine as well as train scientists, students, and visitors. The organization aids in the development of services, new instruments and methods, and technology in its member states. Israel is the only full member stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration
The International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC) consists of a joint effort to collect and disseminate databases containing DNA and RNA sequences. It involves the following computerized databases: NIG's DNA Data Bank of Japan (Japan), NCBI's GenBank ( USA) and the EMBL- EBI's European Nucleotide Archive ( EMBL). New and updated data on nucleotide sequences contributed by research teams to each of the three databases are synchronized on a daily basis through continuous interaction between the staff at each the collaborating organizations. All of the data in INSDC is available for free and unrestricted access, for any purpose, with no restrictions on analysis, redistribution, or re-publication of the data. This policy has been a foundational principle of the INSDC since its inception. Since the 1990s, most of the world's major scientific journals have required that sequence data be deposited in an INSDC database as a pre-condition for publication. The DDBJ/ E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsatellite
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain Sequence motif, DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic genetics, forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as variable number tandem repeat, VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name Satellite DNA, "satellite" DNA refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying "satellite" layers of repetitive DNA. They are widely used for DNA profiling in Loss of heterozygos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCR Tubes
PCR or pcr may refer to: Science and medicine * Pathologic complete response (pCR), in neoadjuvant therapy * Polymerase chain reaction ** COVID-19 testing, often performed using the polymerase chain reaction method * Phosphocreatine, a phosphorylated creatine molecule * Principal component regression, a statistical technique * Protein/creatinine ratio, in urine Technology * Passport Carrier Release, telecommunications software * Peak cell rate, on ATM networks * Platform Configuration Register, a Trusted Execution Technology implemented using a TPM * Processor Control Region, a Windows data structure * Program clock reference, in MPEG transport streams * XM PCR, a satellite receiver Political parties * ''Parti Communiste Réunionnais'' or Communist Party of Réunion * ''Partido Comunista Revolucionário'' or Revolutionary Communist Party * ''Partido Cívico Renovador'' or Civic Renovation Party, Dominican Republic * ''Partidul Comunist Român'' or Romanian Communist Party Other u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |