|
White Magic
White magic has traditionally referred to the use of supernatural powers or magic for selfless purposes. Practitioners of white magic have been given titles such as wise men or women, healers, white witches or wizards. Many of these people claimed to have the ability to do such things because of knowledge or power that was passed on to them through hereditary lines, or by some event later in their lives. White magic was practiced through healing, blessing, charms, incantations, prayers, and songs. White magic is the benevolent counterpart of malicious black magic. History Early origins In his 1978 book, ''A History of White Magic'', recognised occult author Gareth Knight traces the origins of white magic to early adaptations of Paleolithic religion and early religious history in general, including the polytheistic traditions of Ancient Egypt and the later monotheistic ideas of Judaism and early Christianity. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic (supernatural)
Magic, sometimes spelled magick, is the application of beliefs, rituals or actions employed in the belief that they can manipulate natural or supernatural beings and forces. It is a category into which have been placed various beliefs and practices sometimes considered separate from both religion and science. Connotations have varied from positive to negative at times throughout history. Within Western culture, magic has been linked to ideas of the Other (philosophy), Other, foreignness, and primitivism; indicating that it is "a powerful marker of cultural difference" and likewise, a non-modern phenomenon. During the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, Western intellectuals perceived the practice of magic to be a sign of a primitive mentality and also commonly attributed it to marginalised groups of people. Aleister Crowley (1875–1947), a British occultist, defined "magick" as "the Science and Art of causing Change to occur in conformity with Will", adding a 'k' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witchcraft
Witchcraft is the use of Magic (supernatural), magic by a person called a witch. Traditionally, "witchcraft" means the use of magic to inflict supernatural harm or misfortune on others, and this remains the most common and widespread meaning. According to ''Encyclopedia Britannica'', "Witchcraft thus defined exists more in the imagination", but it "has constituted for many cultures a viable explanation of evil in the world". The belief in witches has been found throughout history in a great number of societies worldwide. Most of these societies have used Apotropaic magic, protective magic or counter-magic against witchcraft, and have shunned, banished, imprisoned, physically punished or killed alleged witches. Anthropologists use the term "witchcraft" for similar beliefs about harmful occult practices in different cultures, and these societies often use the term when speaking in English. Belief in witchcraft as malevolent magic is attested from #Ancient Mesopotamian religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemy
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.. Greek-speaking alchemists often referred to their craft as "the Art" (τέχνη) or "Knowledge" (ἐπιστήμη), and it was often characterised as mystic (μυστική), sacred (ἱɛρά), or divine (θɛíα). Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of " base metals" (e.g., lead) into "noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an elixir of immortality; and the creation of panaceas able to cure any disease. The perfection of the human body and soul was thought to result from the alchemical ''magnum opus'' ("Great Work"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrying
Scrying, also referred to as "seeing" or "peeping," is a practice rooted in divination and fortune-telling. It involves gazing into a medium, hoping to receive significant messages or visions that could offer personal guidance, prophecy, revelation, or inspiration. The practice lacks a definitive distinction from other forms of clairvoyance or divination but generally relies on visions within the chosen medium. Unlike augury, which interprets observable events, or divination, which follows standardized rituals, scrying's impressions arise within the medium itself. The terminology and methods of scrying are diverse and lack a standardized structure. Practitioners coin terms such as "crystallomancy," "spheromancy," or " catoptromancy," naming practices based on the medium or technique employed. These practices have been reinvented throughout history, spanning cultures and regions. Scrying media encompass reflective, refractive, or luminescent surfaces like crystals, mirrors, wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabbalah
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal (). List of Jewish Kabbalists, Jewish Kabbalists originally developed transmissions of the primary texts of Kabbalah within the realm of Jewish tradition and often use classical Jewish scriptures to explain and demonstrate its mystical teachings. Kabbalists hold these teachings to define the inner meaning of both the Hebrew Bible and traditional rabbinic literature and their formerly concealed transmitted dimension, as well as to explain the significance of Jewish religious observances. Historically, Kabbalah emerged from earlier forms of Jewish mysticism, in 12th- to 13th-century Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain, al-Andalus (Spain) and in Hakhmei Provence, and was reinterpreted during the Jewish mystical renaissance in 16th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions of Celestial objects in astrology, celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in Calendrical calculation, calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindu astrology, Hindus, Chinese astrology, Chinese, and the Maya civilization, Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerology
Numerology (known before the 20th century as arithmancy) is the belief in an occult, divine or mystical relationship between a number and one or more coinciding events. It is also the study of the numerical value, via an alphanumeric system, of the letters in words and names. When numerology is applied to a person's name, it is a form of onomancy. It is often associated with astrology and other divinatory arts. Number symbolism is an ancient and pervasive aspect of human thought, deeply intertwined with religion, philosophy, mysticism, and mathematics. Different cultures and traditions have assigned specific meanings to numbers, often linking them to divine principles, cosmic forces, or natural patterns. The term numerologist can be used for those who place faith in numerical patterns and draw inferences from them, even if those people do not practice traditional numerology. For example, in his 1997 book ''Numerology: Or What Pythagoras Wrought'' (), mathematician Underwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
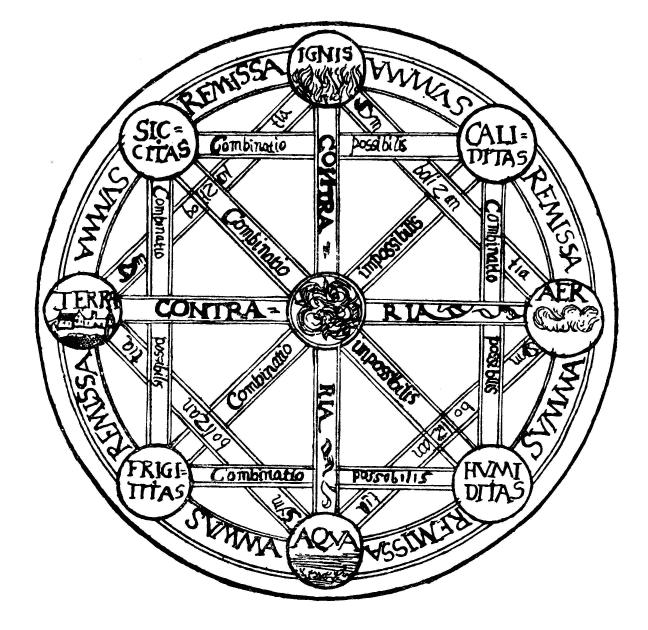
Classical Element
The classical elements typically refer to Earth (classical element), earth, Water (classical element), water, Air (classical element), air, Fire (classical element), fire, and (later) Aether (classical element), aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler Substance theory, substances. Ancient cultures in Ancient Greece, Greece, Angola, Ancient Tibet, Tibet, Ancient India, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personification, personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Occulta Philosophia Libri Tres
''Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' (''De Occulta Philosophia libri III'') is Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa's study of occult philosophy, acknowledged as a significant contribution to the Renaissance philosophical discussion concerning the powers of magic, and its relationship with religion. The first book was printed in 1531 in Paris, Cologne, and Antwerp, while the full three volumes first appeared in Cologne in 1533. The three books deal with elemental, celestial and intellectual magic. The books outline the four elements, astrology, Kabbalah, numerology, angels, names of God, the virtues and relationships with each other as well as methods of utilizing these relationships and laws in medicine, scrying, alchemy, ceremonial magic, origins of what are from the Hebrew, Greek and Chaldean context. These arguments were common amongst other hermetic philosophers at the time and before. In fact, Agrippa's interpretation of magic is similar to the authors Marsilio Ficino, Pico dell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim (; ; 14 September 1486 – 18 February 1535) was a German Renaissance polymath, physician, legal scholar, soldier, knight, theologian, and occult writer. Agrippa's ''Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' published in 1533 drew heavily upon Kabbalah, Hermeticism, and Neoplatonism. His book was widely influential among esotericists of the early modern period, and was condemned as heretical by the inquisitor of Cologne. Early life and education Agrippa was born in Nettesheim, near Cologne, on 14 September 1486, to a family of middle nobility.. In letters later in life he wrote that members of his family had been in the service of the House of Habsburg, although such claims may have been motivated by a desire to gain the support of potential patrons. On the record of his matriculation at the University of Cologne in 1499, he is listed simply as a citizen of Cologne, and his father's name is recorded as Henricus de Nettesheym. Agrippa studied at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Librorum Prohibitorum
The (English: ''Index of Forbidden Books'') was a changing list of publications deemed heretical or contrary to morality by the Sacred Congregation of the Index (a former dicastery of the Roman Curia); Catholics were forbidden to print or read them, subject to the local bishop. The Holy Office justified that decision by referring to chapter 13 of Paul the Apostle's Epistle to the Romans regarding state authority coming from God. However, somewhat later, the Vatican criticized in the encyclical (March 1937) about the challenges of the church in Nazi Germany. Abolition (1966) On 7 December 1965, Pope Paul VI issued the that reorganized the Holy Office as the ''Sacred Congregation for the Doctrine of the Faith''. The Index was not listed as being a part of the newly constituted congregation's competence, leading to questioning whether it still was. This question was put to Cardinal Alfredo Ottaviani, pro-prefect of the congregation, who responded in the negative. The Cardinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |