|
White-bellied Heron
The white-bellied heron (''Ardea insignis'') also known as the imperial heron or great white-bellied heron, is a large heron species living in the foothills of the eastern Himalayas in northeast India and Bhutan to northern Myanmar. It inhabits undisturbed rivers and wetlands. It has been listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List since 2007, because the global population is estimated at less than 250 mature individuals and threatened by habitat loss and human disturbance. It is mostly dark grey with a white throat and underparts. Taxonomy The scientific name ''Ardea insignis'' was suggested by Brian Houghton Hodgson in 1844; he had presented a zoological specimen to the British Museum but a description was not published. This name was therefore considered a ''nomen nudum''. In 1878, Allan Octavian Hume described the differences between the white-bellied and the great-billed heron (''Ardea sumatrana'') while using the binomial name suggested by Hodgson. E. C. Stuart B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namdapha National Park
Namdapha National Park is a large national park in Arunachal Pradesh of Northeast India. The park was established in 1983. With more than 1,000 floral and about 1,400 faunal species, it is a biodiversity hotspot in the Eastern Himalayas. It harbours the northernmost lowland evergreen forest, evergreen rainforests in the world at 27°N latitude. It also harbours extensive dipterocarp forests, comprising the northwestern parts of the Mizoram-Manipur-Kachin rain forests ecoregion. It is the fourth largest national park in India. In 2024, it was declared as a Eco-Sensitive Zone. History Namdapha was originally declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1972, a national park in 1983 and became a tiger reserve under Project Tiger in the same year. Its name was a combination of two Singpho words, namely "nam" which means water, and "dapha" which means origin; The park is located between the Dapha bum range of the Mishmi Hills and the Patkai range. Geography and vegetation Namdapha Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biswamoy Biswas
Biswamoy Biswas (2 June 1923 – 10 August 1994) was an Indian ornithologist who was born in Calcutta, the son of a professor of geology.Mayr, E. (2000) "In Memoriam: Biswamoy Biswas, 1923–1994." ''The Auk'' 117(4):103PDF/ref> In 1947, he was awarded a three-year fellowship by Sunderlal Hora, then director of the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI). It enabled him to study at the British Museum, at the Berlin Zoological Museum under Erwin Stresemann and also at the American Museum of Natural History under Ernst Mayr. Biswas studied biology in his college instead of geology as his father wished. He graduated from the University of Calcutta in 1943 and received an MSc in 1945. He received a Ph.D. in 1952 from the University of Calcutta working under J.L. Bhaduri. He was part of the Daily Mail expedition sent to look for the Yeti around Mount Everest in 1954. He was elected Corresponding Fellow of The American Ornithologists' Union in 1963. He later took charge of the Bird and M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnolia Champaca
''Magnolia champaca'', known in English as champak (), is a large evergreen tree in the family Magnoliaceae. It was previously classified as ''Michelia champaca''. It is known for its fragrant flowers, and its timber used in woodworking. Etymology The species epithet, ''champaca'', comes from the Sanskrit word "चम्पक" (). Vernacular names Other vernacular names in English include joy perfume tree, Pacific Horticulture Society: "Striving for Diversity: Fragrant Champaca" . accessed 7.12.2015 yellow jade orchid tree and fragrant Himalayan champaca. Distribution and habitat The tree is native to the |
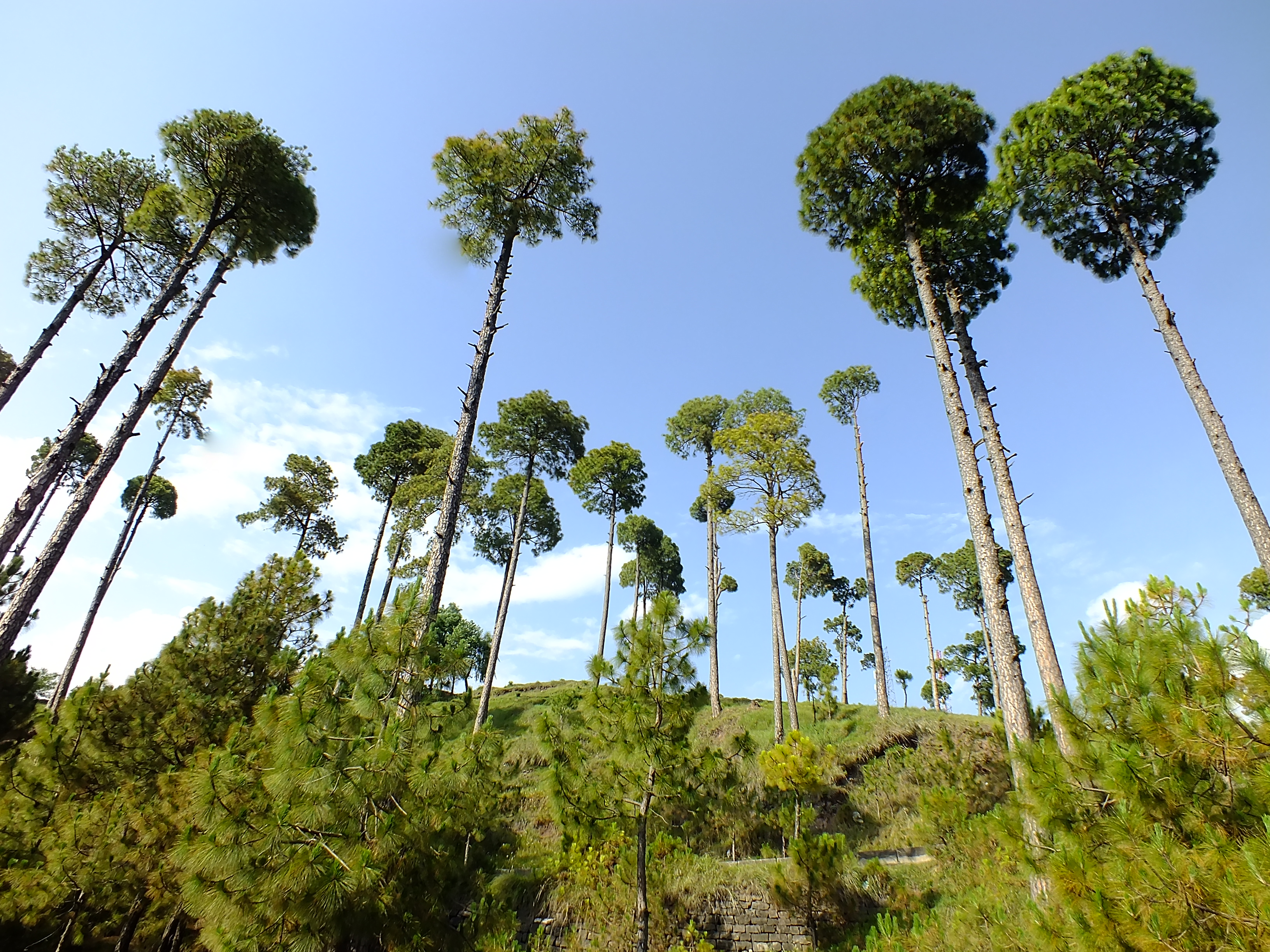
Pinus Roxburghii
''Pinus roxburghii'', commonly known as chir pine or longleaf Indian pine, is a species of pine tree Native plant, native to the Himalayas. It was named after William Roxburgh. Description ''Pinus roxburghii'' is a large tree reaching with a trunk diameter of up to , exceptionally . The Bark (botany), bark is red-brown, thick and deeply fissured at the base of the trunk, thinner and flaky in the upper crown. The leaves are needle-like, in fascicles of three, very slender, long, and distinctly yellowish green. The conifer cone, cones are ovoid conic, long and broad at the base when closed, green at first, ripening glossy chestnut-brown when 24 months old. They open slowly over the next year or so, or after being heated by a wildfire, forest fire, to release the seeds, opening to broad. The seeds are long, with a wing, and are wind-Seed dispersal, dispersed. Similar species ''Pinus roxburghii'' is closely related to ''Pinus canariensis, P. canariensis'' (Canary I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sankosh River
Sankosh (also Puna Thsang Chu, and Svarnakosha) is a river that rises in northern Bhutan and empties into the Brahmaputra in the state of Assam in India. In Bhutan, it is known as the Puna Tsang Chu below the confluences of several tributaries near the town of Wangdue Phodrang. The two largest tributaries are the Mo Chhu and Pho Chhu, which flow together at Punakha. The Punakha dzong, which is situated immediately above the confluence of the two rivers, is one of the most beautiful dzongs in Bhutan and the winter residence of the Dratshang Lhentshog. The upper reaches of the Pho Chhu are susceptible to ice blockages, and the dzong has been damaged on several occasions by glacial lake outburst floods. After it enters in India, it flows on the border of Assam and West Bengal. At Wangdue Phodrang, elevation , the river is joined by the west flowing Tang Chuu The Tang Chuu is a tributary of the Mo Chhu in western Bhutan. Course It originates in the Himalayas near Thowadra Gom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
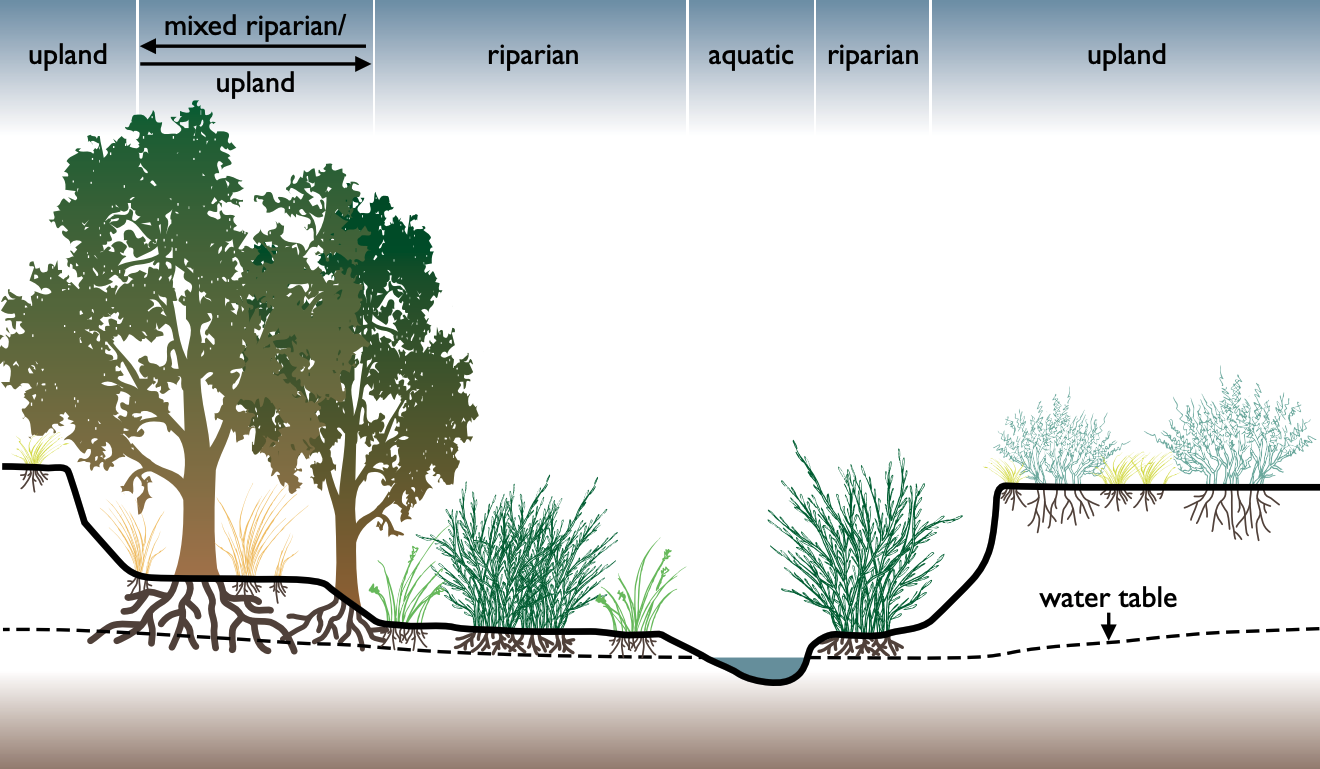
Riparian Zone
A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word ''riparian'' is derived from Latin ''wiktionary:ripa, ripa'', meaning "bank (geography), river bank". Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by aquatic plant, hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic fauna as well as aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, and even non-vegetative areas. Riparian zones may be natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wing Chord (biology)
Wing chord is an anatomical measurement of a bird's wing A wing is a type of fin that produces both Lift (force), lift and drag while moving through air. Wings are defined by two shape characteristics, an airfoil section and a planform (aeronautics), planform. Wing efficiency is expressed as lift-to-d .... The measurement is taken with the wing bent at a 90-degree angle, from the most prominent point of the wrist joint to the most prominent point of the longest primary feather. It is often taken as a standard measurement of the proportions of a bird and used to differentiate between species and subspecies. See also * Bird measurement References {{Bird-stub Bird anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayeyarwady River
The Irrawaddy River (, , Ayeyarwady) is the principal river of Myanmar, running through the centre of the country. Myanmar’s most important commercial waterway, it is about 1,350 miles (2,170 km) long. Originating from the confluence of the N'mai and Mali rivers, it flows from north to south before emptying through the Irrawaddy Delta in the Ayeyarwady Region into the Andaman Sea. Its drainage basin of about covers 61% of the land area of Burma, and contains five of its largest cities. As early as the sixth century, the river was used for trade and transport, and an extensive network of irrigation canals was developed to support agriculture. The river is still of great importance as the largest commercial waterway of Myanmar. It also provides important ecosystem services to different communities and economic sectors, including agriculture, fisheries, and tourism. In 2007, Myanmar's military dictatorship signed an agreement for the construction of seven hydroelectric d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covert Feather
A covert feather or tectrix on a bird is one of a set of feathers, called coverts (or ''tectrices''), which cover other feathers. The coverts help to smooth airflow over the wings and tail. Ear coverts The ear coverts are small feathers behind the bird's eye which cover the ear opening (the ear of a bird has no external features). Tail coverts The uppertail and undertail coverts cover the base of the tail feathers above and below. Sometimes these coverts are more specialised. The "tail" of a peacock is made of elongated uppertail coverts. Wing coverts The upperwing coverts fall into two groups: those on the inner wing, which overlay the secondary flight feathers, known as the secondary coverts, and those on the outer wing, which overlay the primary flight feathers, the primary coverts. Within each group, the feathers form a number of rows. The feathers of the outermost, largest, row are termed greater (primary-/secondary-) coverts; those in the next row are the median (primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within city limits,Barcelona: Población por municipios y sexo – Instituto Nacional de Estadística. (National Statistics Institute) its urban area extends to numerous neighbouring municipalities within the province of Barcelona and is home to around 5.3 million people, making it the fifth most populous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |