|
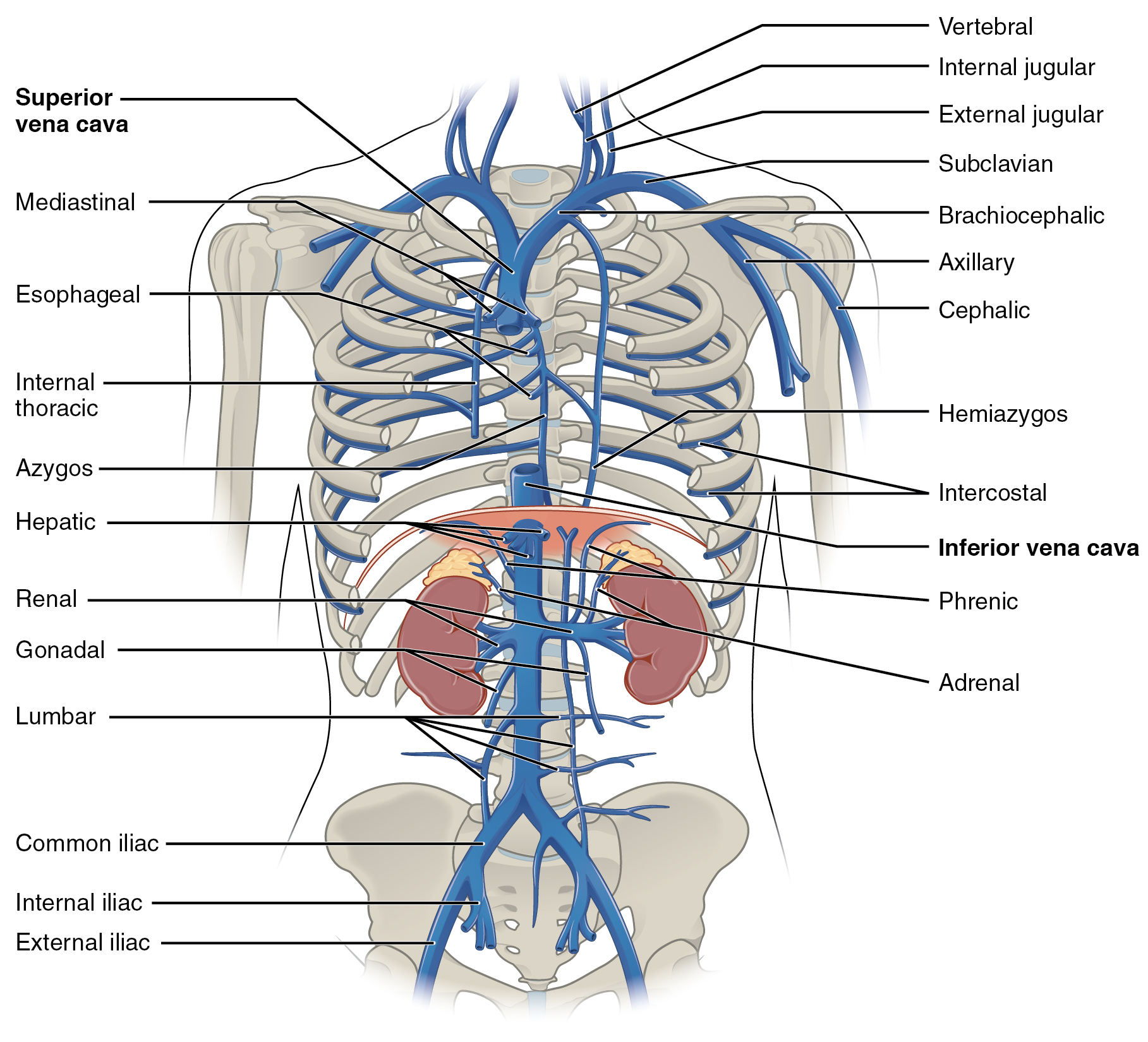
Vertebral Veins
The vertebral vein is formed in the suboccipital triangle, from numerous small tributaries which spring from the internal vertebral venous plexuses and issue from the vertebral canal above the posterior arch of the atlas. They unite with small veins from the deep muscles at the upper part of the back of the neck, and form a vessel which enters the foramen in the transverse process of the atlas, and descends, forming a dense plexus around the vertebral artery, in the canal formed by the transverse foramina of the upper six cervical vertebrae. This plexus ends in a single trunk, which emerges from the transverse foramina of the sixth cervical vertebra, and opens at the root of the neck into the back part of the innominate vein near its origin, its mouth being guarded by a pair of valves. On the right side, it crosses the first part of the subclavian artery In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Cervical Vein
The deep cervical vein (posterior vertebral or posterior deep cervical vein) accompanies its artery between the Semispinales capitis and colli. It begins in the suboccipital region by communicating branches from the occipital vein and by small veins from the deep muscles at the back of the neck. It receives tributaries from the plexuses around the spinous processes of the cervical vertebræ, and terminates in the lower part of the vertebral vein The vertebral vein is formed in the suboccipital triangle, from numerous small tributaries which spring from the internal vertebral venous plexuses and issue from the vertebral canal above the posterior arch of the atlas. They unite with small v .... References External links Veins of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiocephalic Vein
The left and right brachiocephalic veins (previously called innominate veins) are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of each corresponding internal jugular vein and subclavian vein. This is at the level of the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is nearly always longer than the right. These veins merge to form the superior vena cava, a great vessel, posterior to the junction of the first costal cartilage with the manubrium of the sternum. The brachiocephalic veins are the major veins returning blood to the superior vena cava. Tributaries The brachiocephalic vein is formed by the confluence of the subclavian and internal jugular veins. In addition it receives drainage from: * Left and right internal thoracic vein (Also called internal mammary veins): drain into the inferior border of their corresponding vein * Left and right inferior thyroid veins: drain into the superior aspect of their corresponding veins near the confluence * Left and righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Artery
The vertebral arteries are major arteries An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ... of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the ''vertebrobasilar vascular system'', the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and Cerebral circulation#Posterior cerebral circulation, posterior part of brain. Structure The vertebral arteries usually arise from the posterosuperior aspect of the central subclavian arteries on each side of the body, then enter deep to the transverse process at the level of the 6th cervical vertebrae (C6), or occasio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suboccipital Triangle
The suboccipital triangle is a region of the neck bounded by the following three muscles of the suboccipital group of muscles: * Rectus capitis posterior major - above and medially * Obliquus capitis superior - above and laterally * Obliquus capitis inferior - below and laterally (Rectus capitis posterior minor is also in this region but does not form part of the triangle) It is covered by a layer of dense fibro-fatty tissue, situated beneath the semispinalis capitis. The floor is formed by the posterior atlantooccipital membrane, and the posterior arch of the atlas. In the deep groove on the upper surface of the posterior arch of the atlas are the vertebral artery and the first cervical or suboccipital nerve. In the past, the vertebral artery was accessed here in order to conduct angiography of the circle of Willis. Presently, formal angiography of the circle of Willis is performed via catheter angiography, with access usually being acquired at the common femoral artery. Alter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Vertebral Venous Plexuses
The internal vertebral venous plexuses (intraspinal veins) lie within the vertebral canal in the epidural space, and receive tributaries from the bones and from the spinal cord. They form a closer network than the external plexuses, and, running mainly in a vertical direction, form four longitudinal veins, two in front and two behind; they therefore may be divided into anterior and posterior groups. * The ''anterior internal plexuses'' consist of large veins which lie on the posterior surfaces of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral fibrocartilages on either side of the posterior longitudinal ligament; under cover of this ligament they are connected by transverse branches into which the basivertebral veins open. * The ''posterior internal plexuses'' are placed, one on either side of the middle line in front of the vertebral arches and ligamenta flava, and anastomose by veins passing through those ligaments with the posterior external plexuses. The anterior and posterior plexuses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Canal
The spinal canal (or vertebral canal or spinal cavity) is the canal that contains the spinal cord within the vertebral column. The spinal canal is formed by the vertebrae through which the spinal cord passes. It is a process of the dorsal body cavity. This canal is enclosed within the foramen of the vertebrae. In the intervertebral spaces, the canal is protected by the ligamentum flavum posteriorly and the posterior longitudinal ligament anteriorly. Structure The outermost layer of the meninges, the dura mater, is closely associated with the arachnoid mater which in turn is loosely connected to the innermost layer, the pia mater. The meninges divide the spinal canal into the epidural space and the subarachnoid space. The pia mater is closely attached to the spinal cord. A subdural space is generally only present due to trauma and/or pathological situations. The subarachnoid space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid and contains the vessels that supply the spinal cord, namely th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas (anatomy)
In anatomy, the atlas (C1) is the most superior (first) cervical vertebra of the spine and is located in the neck. It is named for Atlas of Greek mythology because, just as Atlas supported the globe, it supports the entire head. The atlas is the topmost vertebra and, with the axis (the vertebra below it), forms the joint connecting the skull and spine. The atlas and axis are specialized to allow a greater range of motion than normal vertebrae. They are responsible for the nodding and rotation movements of the head. The atlanto-occipital joint allows the head to nod up and down on the vertebral column. The dens acts as a pivot that allows the atlas and attached head to rotate on the axis, side to side. The atlas's chief peculiarity is that it has no body. It is ring-like and consists of an anterior and a posterior arch and two lateral masses. The atlas and axis are important neurologically because the brainstem extends down to the axis. Structure Anterior arch The anterio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments; vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles. In anatomy, the neck is also called by its Latin names, or , although when used alone, in context, the word ''cervix'' more often refers to the uterine cervix, the neck of the uterus. Thus the adjective ''cervical'' ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Artery
The vertebral arteries are major arteries An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ... of the neck. Typically, the vertebral arteries originate from the subclavian arteries. Each vessel courses superiorly along each side of the neck, merging within the skull to form the single, midline basilar artery. As the supplying component of the ''vertebrobasilar vascular system'', the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord, brainstem, cerebellum, and Cerebral circulation#Posterior cerebral circulation, posterior part of brain. Structure The vertebral arteries usually arise from the posterosuperior aspect of the central subclavian arteries on each side of the body, then enter deep to the transverse process at the level of the 6th cervical vertebrae (C6), or occasio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a foramen (hole) in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, vertebral veins, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innominate Vein
The left and right brachiocephalic veins (previously called innominate veins) are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of each corresponding internal jugular vein and subclavian vein. This is at the level of the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is nearly always longer than the right. These veins merge to form the superior vena cava, a great vessel, posterior to the junction of the first costal cartilage with the manubrium of the sternum. The brachiocephalic veins are the major veins returning blood to the superior vena cava. Tributaries The brachiocephalic vein is formed by the confluence of the subclavian and internal jugular veins. In addition it receives drainage from: * Left and right internal thoracic vein (Also called internal mammary veins): drain into the inferior border of their corresponding vein * Left and right inferior thyroid veins: drain into the superior aspect of their corresponding veins near the confluence * Left and right ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subclavian Artery
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery. The usual branches of the subclavian on both sides of the body are the vertebral artery, the internal thoracic artery, the thyrocervical trunk, the costocervical trunk and the dorsal scapular artery, which may branch off the transverse cervical artery, which is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk. The subclavian becomes the axillary artery at the lateral border of the first rib. Structure From its origin, the subclavian artery t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |