|
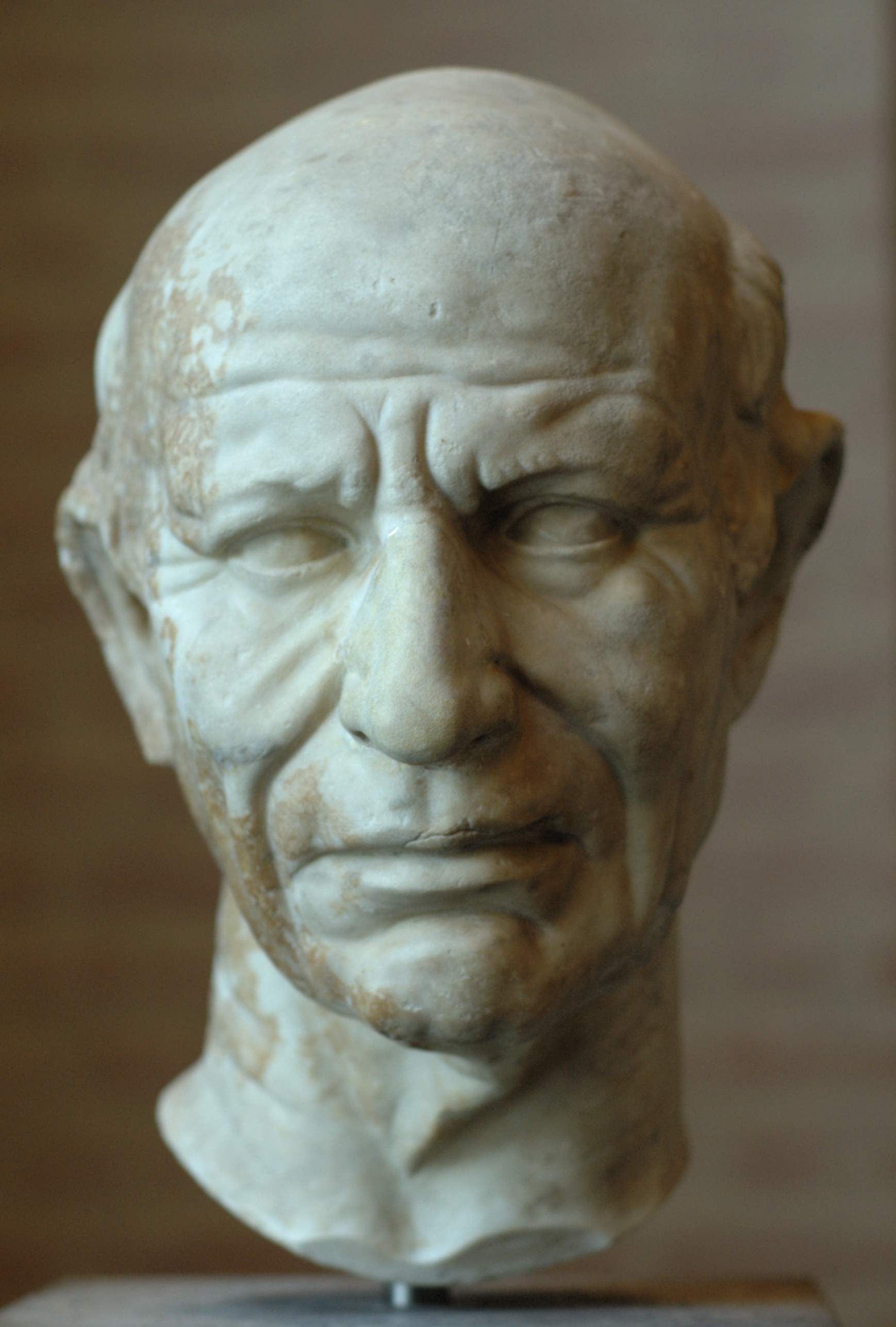
Verism
Verism was a realistic style in Roman art. It principally occurred in portraiture of politicians, whose imperfections of the face were exacerbated in order to highlight their old age and ''gravitas''. The word comes from Latin ''verus'' (true). Roman art Verism first appeared as the artistic preference of the Roman people during the late Roman Republic (147–30 BC) and was often used for Republican portraits or for the head of “ pseudo-athlete” sculptures. Verism, often described as "warts and all," shows the imperfections of the subject, such as warts, wrinkles, and furrows. It should be clearly noted that the term veristic in no way implies that these portraits are more "real." Rather, they too can be highly exaggerated or idealised, but within a different visual idiom, one which favours wrinkles, furrows, and signs of age as indicators of gravity and authority. Age during the Late Republic was very highly valued and was synonymous with power, since one of the only ways to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Realism (arts)
Realism in the arts is generally the attempt to represent subject matter truthfully, without artificiality and avoiding speculative and supernatural elements. The term is often used interchangeably with naturalism, although these terms are not synonymous. Naturalism, as an idea relating to visual representation in Western art, seeks to depict objects with the least possible amount of distortion and is tied to the development of linear perspective and illusionism in Renaissance Europe. Realism, while predicated upon naturalistic representation and a departure from the idealization of earlier academic art, often refers to a specific art historical movement that originated in France in the aftermath of the French Revolution of 1848. With artists like Gustave Courbet capitalizing on the mundane, ugly or sordid, realism was motivated by the renewed interest in the common man and the rise of leftist politics. The Realist painters rejected Romanticism, which had come to dominate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-athlete
The term Pseudo-athlete is used to describe works of art from the Late Republican period in Rome that combine a veristic head with an idealized body that references Classical Greek sculpture. Verism is a style of Roman portraiture that portrays an individual with aging facial features, most notably sagging skin around the mouth and eyes, short-cropped or balding hair, and deep wrinkles on the forehead and around the eyes and mouth. These features were emphasized under the tradition of verism in order to stress an advanced moral and psychological consciousness that comes along with advanced age. The veristic features of the pseudo-athlete's head are juxtaposed with the figure's body, which is depicted in the guise of an athletic youth from Classical Greece. The pseudo-athlete's body is typically depicted in heroic-nudity with highly smooth muscular forms and are often shown in an active stance or standing in an S-shaped curved known as contrapposto. Potential origins Veristic sty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Old Roman Glyptothek Munich 320
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may not have a head, but many bilaterally symmetric forms do, regardless of size. Heads develop in animals by an evolutionary trend known as cephalization. In bilaterally symmetrical animals, nervous tissue concentrate at the anterior region, forming structures responsible for information processing. Through biological evolution, sense organs and feeding structures also concentrate into the anterior region; these collectively form the head. Human head The human head is an anatomical unit that consists of the skull, hyoid bone and cervical vertebrae. The term "skull" collectively denotes the mandible (lower jaw bone) and the cranium (upper portion of the skull that houses the brain). Sculptures of human heads are generally based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face Of A Child-MGR Lyon-IMG 9850
The face is the front of an animal's head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may affect the psyche adversely. Structure The front of the human head is called the face. It includes several distinct areas, of which the main features are: *The forehead, comprising the skin beneath the hairline, bordered laterally by the temples and inferiorly by eyebrows and ears *The eyes, sitting in the orbit and protected by eyelids and eyelashes * The distinctive human nose shape, nostrils, and nasal septum *The cheeks, covering the maxilla and mandibula (or jaw), the extremity of which is the chin *The mouth, with the upper lip divided by the philtrum, sometimes revealing the teeth Facial appearance is vital for human recognition and communication. Facial muscles in humans allow expression of emotions. The face is itself a highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death Mask
A death mask is a likeness (typically in wax or plaster cast) of a person's face after their death, usually made by taking a cast or impression from the corpse. Death masks may be mementos of the dead, or be used for creation of portraits. It is sometimes possible to identify portraits that have been painted from death masks because of the characteristic slight distortions of the features caused by the weight of the plaster during the making of the mould. The main purpose of the death mask from the Middle Ages until the 19th century was to serve as a model for sculptors in creating statues and busts of the deceased person. Not until the 1800s did such masks become valued for themselves. In other cultures a death mask may be a funeral mask, an image placed on the face of the deceased before burial rites, and normally buried with them. The best known of these are the masks used in ancient Egypt as part of the mummification process, such as Tutankhamun's mask, and those from My ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruria
Etruria () was a region of Central Italy, located in an area that covered part of what are now most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and northern and western Umbria. Etruscan Etruria The ancient people of Etruria are identified as Etruscans. Their complex culture centered on numerous city-states that arose during the Villanovan period in the ninth century BCE, and they were very powerful during the Orientalizing Archaic periods. The Etruscans were a dominant culture in Italy by 650 BCE,Rix, Helmut. "Etruscan." In ''The Ancient Languages of Europe,'' ed. Roger D. Woodard. Cambridge University Press, 2008, pp. 141–164. surpassing other ancient Italic peoples such as the Ligures. Their influence may be seen beyond Etruria's confines in the Po River Valley and Latium, as well as in Campania and through their contact with the Greek colonies in Southern Italy (including Sicily). Indeed, at some Etruscan tombs, such as those of the Tumulus di Montefortini at Comeana (see Carmigna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Art
Etruscan art was produced by the Etruscan civilization in central Italy between the 10th and 1st centuries BC. From around 750 BC it was heavily influenced by Greek art, which was imported by the Etruscans, but always retained distinct characteristics. Particularly strong in this tradition were figurative sculpture in terracotta (especially life-size on sarcophagi or temples), wall-painting and metalworking especially in bronze. Jewellery and engraved gems of high quality were produced. Etruscan sculpture in cast bronze was famous and widely exported, but relatively few large examples have survived (the material was too valuable, and recycled later). In contrast to terracotta and bronze, there was relatively little Etruscan sculpture in stone, despite the Etruscans controlling fine sources of marble, including Carrara marble, which seems not to have been exploited until the Romans. The great majority of survivals came from tombs, which were typically crammed with sarcophagi a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscan Civilization
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and western Campania. The earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be the earliest phase of Etruscan civilization, which itself developed from the previous late Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture in the same region. Etruscan civilization endured until it was assimilated into Roman society. Assimilation began in the late 4thcenturyBC as a result of the Roman–Etruscan Wars; it accelerated with the grant of Roman citizenship in 90 BC, and became complete in 27 BC, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such as arsenic or silicon. These additions produce a range of alloys that may be harder than copper alone, or have other useful properties, such as strength, ductility, or machinability. The archaeological period in which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia and India is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age starting from about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in modern times. Because historical artworks w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terracotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based unglazed or glazed ceramic where the fired body is porous. In applied art, craft, construction, and architecture, terracotta is the term normally used for sculpture made in earthenware and also for various practical uses, including vessels (notably flower pots), water and waste water pipes, roofing tiles, bricks, and surface embellishment in building construction. The term is also used to refer to the natural brownish orange color of most terracotta. In archaeology and art history, "terracotta" is often used to describe objects such as figurines not made on a potter's wheel. Vessels and other objects that are or might be made on a wheel from the same material are called earthenware pottery; the choice of term depends on the type of object rather than the material or firing technique. Unglazed pieces, and those made for building construction and industry, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italic Peoples
The Italic peoples were an ethnolinguistic group identified by their use of Italic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family. The Italic peoples are descended from the Indo-European speaking peoples who inhabited Italy from at least the second millennium BC onwards. Latins achieved a dominant position among these tribes, establishing ancient Roman civilization. During this development, other Italic tribes adopted Latin language and culture in a process known as Romanization. This process was eventually extended to certain parts of Europe. The ethnic groups which emerged as a result are known as Romance peoples. Classification The Italics were an ethnolinguistic group who are identified by their use of the Italic languages, which form one of the branches of Indo-European languages. Outside of the specialised linguistic literature, the term is also used to describe the ancient peoples of Italy as defined in Roman times, including pre-Roman peoples like the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IMG 1075 - Perugia - Museo Archeologico - Urna Etrusca - 7 Ago 2006 - Foto G
img or IMG is an abbreviation for image. img or IMG may also refer to: * IMG (company), global sports and media business headquartered in New York City but with its main offices in Cleveland, originally known as the "International Management Group", with divisions including: ** IMG Academy, an athletic training complex in Bradenton, Florida with facilities for multiple sports ** IMG Artists, a performing arts management company with multiple worldwide offices ** IMG College, a college sports marketing agency based in Winston-Salem, North Carolina ** IMG Models, a modeling agency based in New York * IMG (file format), the file extension of several different disk image formats which store a full digital representation (image) of disk drive or storage media * IMG, a prefix for camera image file names commonly used in Design rule for Camera File system * mg/code>, a tag used in BBCode to place an image * , an HTML element used to place an image; see * IMG Worlds of Adventure, the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
