|
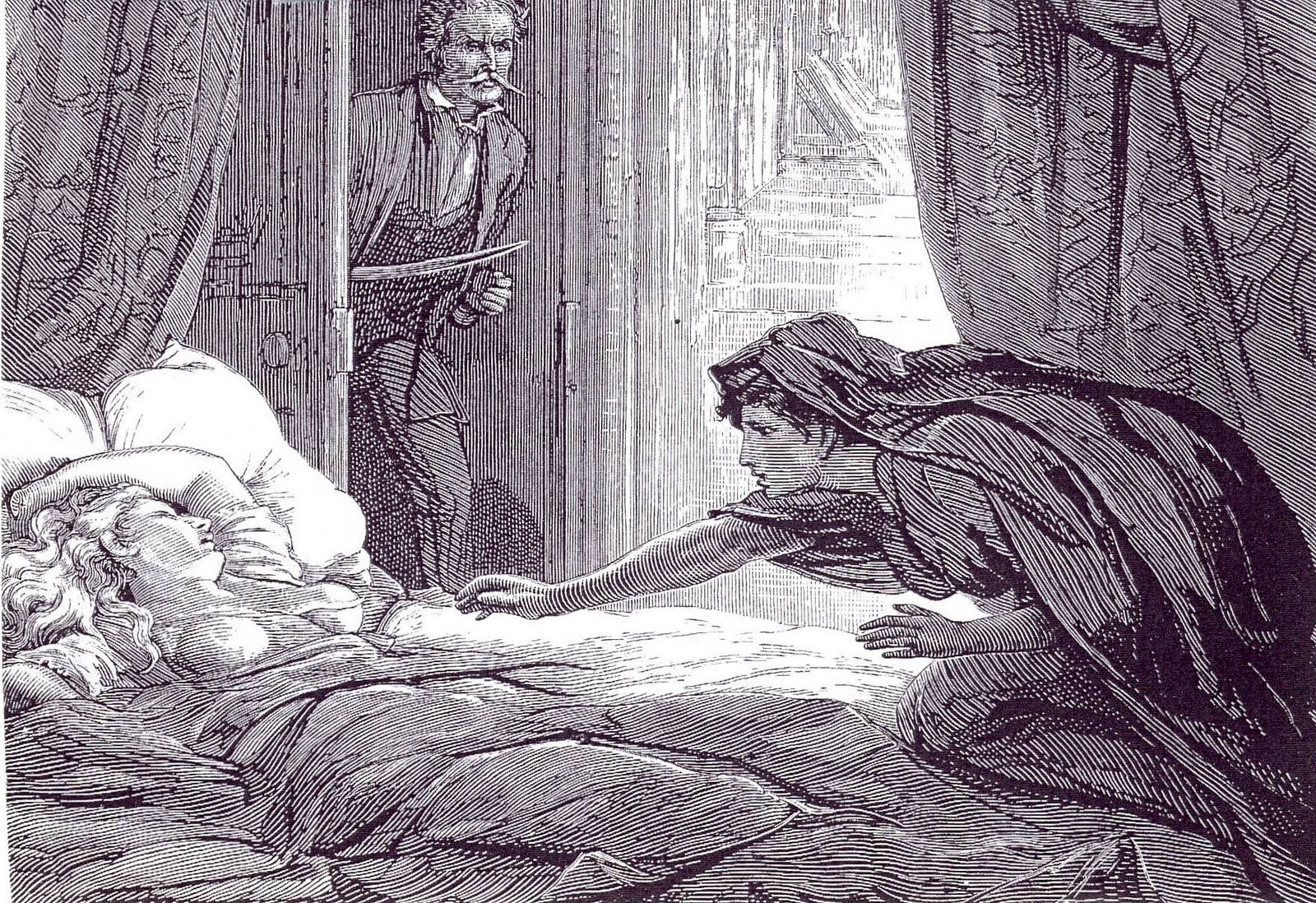
Vampire Fiction
Vampire literature covers the spectrum of literary work concerned principally with the subject of vampires. The literary vampire first appeared in 18th-century poetry, before becoming one of the stock figures of gothic fiction with the publication of Polidori's ''The Vampyre'' (1819), inspired by a story told to him by Lord Byron. Later influential works include the penny dreadful ''Varney the Vampire'' (1847); Sheridan Le Fanu's tale of a lesbian vampire, ''Carmilla'' (1872), and the most well known: Bram Stoker's ''Dracula'' (1897). Some authors created a more "sympathetic vampire", with ''Varney'' being the first, and more recent examples such as Moto Hagio's series ''The Poe Clan'' (1972–1976) and Anne Rice's novel ''Interview with the Vampire'' (1976) proving influential. History 18th century Vampire fiction is rooted in the "vampire craze" of the 1720s and 1730s, which culminated in the somewhat bizarre official exhumations of suspected vampires Petar Blagojevich and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carmilla
''Carmilla'' is an 1872 Gothic fiction, Gothic novella by Irish author Sheridan Le Fanu, Joseph Sheridan Le Fanu. It is one of the earliest known works of vampire fiction, predating Bram Stoker's ''Dracula'' (1897) by 25 years. First published as a Serial (literature), serial in ''The Dark Blue'' (1871–72), the story is narrated by a young woman who is preyed upon by a female vampire named "Carmilla". The titular character is the prototypical example of the fictional lesbian vampire, expressing romantic desires toward the protagonist. ''Carmilla'' is regarded as one of the most influential vampire stories of all time, and the work is popularly Anthology, anthologised, having been adapted extensively for films, movies, operas, video games, comics, songs, cartoons, television, and other media. Publication ''Carmilla'', serialised in the literary magazine ''The Dark Blue'' in late 1871 and early 1872, was reprinted in Le Fanu's short-story collection ''In a Glass Darkly'' (1872). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petar Blagojevich
Petar (, sr-Cyrl, Петар) is a South Slavic masculine given name, their variant of the Biblical name Petros cognate to Peter. Derivative forms include Pero, Pejo, Pera, Perica, Petrica, Periša. Feminine equivalent is Petra. People mononymously known as Petar include: * * * Petar of Serbia ( – 917), early Prince of the Serbs * Petar of Duklja (), early archont in Dioclea * Petar Krešimir (died 1074/1075), King of Croatia and Dalmatia * Petar Delyan (r. 1040-1041), Bulgarian rebel, declared Emperor of Bulgaria Notable people with the name are numerous: * See also * Sveti Petar (other) * Petrov (other) * Petrić * Petričević Petričević ( sr-Cyrl, Петричевић) is a Serbo-Croatian surname, a patronymic A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather (more specifically an avonymic), or an ea ... References {{reflist Bulgarian masculine given names Croatian mascu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlegon Of Tralles
Phlegon of Tralles () was a Greek writer and freedman of the emperor Hadrian, who lived in the 2nd century AD. Works His chief work was the ''Olympiads'', an historical compendium in sixteen books, from the 1st down to the 229th Olympiad (776 BC to AD 137), of which several chapters are preserved in Eusebius' ''Chronicle'', Photius, and George Syncellus. Two short works by him are extant. ''On Marvels'' consists of "anecdotes culled from sources as diverse as the Greek poet Hesiod and the Roman natural historian Pliny the Elder. Each... recounts a fantastical or paranormal event." ''On Long-Lived Persons'' contains a list of Italians who had passed the age of 100, taken from the censuses of the Roman Empire. Other works ascribed to Phlegon in the ''Suda'' are a description of Sicily, a work on the Roman festivals in three books, and a topography of Rome: :"Phlegon of Tralles, freedman of Augustus Caesar, but some say of Hadrian: historian. He wrote Olympiads in 16 books. Up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paganism
Paganism (, later 'civilian') is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Christianity, Judaism, and Samaritanism. In the time of the Roman Empire, individuals fell into the pagan class either because they were increasingly rural and provincial relative to the Christian population, or because they were not '' milites Christi'' (soldiers of Christ).J. J. O'Donnell (1977)''Paganus'': Evolution and Use, ''Classical Folia'', 31: 163–69. Alternative terms used in Christian texts were '' hellene'', '' gentile'', and '' heathen''. Ritual sacrifice was an integral part of ancient Greco-Roman religion and was regarded as an indication of whether a person was pagan or Christian. Paganism has broadly connoted the "religion of the peasantry". During and after the Middle Ages, the term ''paganism'' was applied to any non-Christian religion, and the term presumed a belief in fal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Wolfgang Von Goethe
Johann Wolfgang (von) Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German polymath who is widely regarded as the most influential writer in the German language. His work has had a wide-ranging influence on Western literature, literary, Political philosophy#European Enlightenment, political, and Western philosophy, philosophical thought in the Western world from the late 18th century to the present.. A poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre-director, and critic, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe bibliography, his works include plays, poetry and aesthetic criticism, as well as treatises on botany, anatomy, and colour. Goethe took up residence in Weimar in 1775 following the success of his first novel, ''The Sorrows of Young Werther'' (1774), and joined a thriving intellectual and cultural environment under the patronage of Duchess Anna Amalia of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Duchess Anna Amalia that formed the basis of Weimar Classicism. He was ennobled by Karl August, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gottfried August Bürger
Gottfried August Bürger (31 December 1747 – 8 June 1794) was a German poet. His ballads were very popular in Germany. His most noted ballad, ''Lenore (ballad), Lenore'', found an audience beyond readers of the German language in an English language, English and Russian language, Russian adaptation and a French language, French translation. Biography Bürger was born in Molmerswende (now a part of Mansfeld), Principality of Halberstadt, where his father was the Lutheran pastor. He showed an early predilection for solitary and gloomy places and the making of verses, for which he had no other model than hymnals. At the age of twelve, he was practically adopted by his maternal grandfather, Bauer, at Aschersleben, who sent him to the Pädagogium at Halle, Saxony-Anhalt, Halle. He learned Latin with difficulty. In 1764, he gained admission into the University of Halle as a student of theology, which, however, he soon abandoned for the study of jurisprudence. There he fell under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenore (ballad)
''Lenore'', sometimes translated as ''Leonora'', ''Leonore'', or ''Ellenore'', is a poem written by German author Gottfried August Bürger in 1773, and published in 1774 in the ''Göttinger Musenalmanach''. ''Lenore'' is generally characterised as being part of the 18th-century Gothic fiction, Gothic ballads, and although the character that returns from its grave in the poem is not considered to be a vampire, the poem has been very influential on vampire literature. William Taylor (scholar), William Taylor, who published the first English translation of the ballad, would later claim that "no German poem has been so repeatedly translated into English as 'Ellenore. Background In the 18th century there were more than eighteen hundred different Unification of Germany#German-speaking Central Europe in the early nineteenth century, German-speaking political entities in Central Europe. During this period, due to influences from the Renaissance and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narrative Poem
Narrative poetry is a form of poetry that tells a story, often using the voices of both a narrator and characters; the entire story is usually written in metered verse. Narrative poems do not need to rhyme. The poems that make up this genre may be short or long, and the story it relates to may be complex. It is normally dramatic, with various characters. Narrative poems include all epic poetry, and the various types of "lay", most ballads, and some idylls, as well as many poems not falling into a distinct type. Some narrative poetry takes the form of a novel in verse. An example of this is '' The Ring and the Book'' by Robert Browning. In terms of narrative poetry, romance is a narrative poem that tells a story of chivalry. Examples include the '' Romance of the Rose'' or Tennyson's '' Idylls of the King''. Although those examples use medieval and Arthurian materials, romances may also tell stories from classical mythology. Sometimes, these short narratives are collected i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose coming as the Messiah#Christianity, messiah (Christ (title), Christ) was Old Testament messianic prophecies quoted in the New Testament, prophesied in the Old Testament and chronicled in the New Testament. It is the Major religious groups, world's largest and most widespread religion with over 2.3 billion followers, comprising around 28.8% of the world population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in Christianity by country, 157 countries and territories. Christianity remains Christian culture, culturally diverse in its Western Christianity, Western and Eastern Christianity, Eastern branches, and doctrinally diverse concerning Justification (theology), justification and the natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich August Ossenfelder
Heinrich may refer to: People * Heinrich (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name) * Heinrich (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) *Hetty (given name), a given name (including a list of people with the name) Places * Heinrich (crater), a lunar crater * Heinrich-Hertz-Turm, a telecommunication tower and landmark of Hamburg, Germany Other uses * Heinrich event, a climatic event during the last ice age * Heinrich (card game), a north German card game * Heinrich (farmer), participant in the German TV show a ''Farmer Wants a Wife'' * Heinrich Greif Prize, an award of the former East German government * Heinrich Heine Prize, the name of two different awards * Heinrich Mann Prize, a literary award given by the Berlin Academy of Art * Heinrich Tessenow Medal, an architecture prize established in 1963 * Heinrich Wieland Prize, an annual award in the fields of chemistry, biochemistry and physiology * Heinrich, known as Haida in Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |