|
Urine Test
A urine test is any medical test performed on a urine specimen. The analysis of urine is a valuable diagnostic tool because its composition reflects the functioning of many body systems, particularly the kidneys and urinary system, and specimens are easy to obtain. Common urine tests include the routine urinalysis, which examines the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of the urine; urine drug screening; and urine pregnancy testing. Background The value of urine for diagnostic purposes has been recognized since ancient times. Urine examination was practiced in Sumer and Babylonia as early as 4000 BC, and is described in ancient Greek and Sanskrit texts. Contemporary urine testing uses a range of methods to investigate the physical and biochemical properties of the urine. For instance, the results of the routine urinalysis can provide information about the functioning of the kidneys and urinary system; suggest the presence of a urinary tract infection (UTI); and screen f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Test
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic testing, chemical and cellular analysis, relating to clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics, are typically performed in a medical setting. Types of tests By purpose Medical tests can be classified by their purposes, the most common of which are diagnosis, screening and evaluation. Diagnostic A diagnostic test is a procedure performed to confirm or determine the presence of disease in an individual suspected of having a disease, usually following the report of symptoms, or based on other medical test results. This includes posthumous diagnosis. Examples of such tests are: * Using nuclear medicine to examine a patient suspected of having a lymphoma. * Measuring the blood sugar in a person suspected of having diabetes mellitus after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-of-care Test
Point-of-care testing (POCT or bedside testing) is defined as medical diagnostic testing at or near the point of care—that is, at the time and place of patient care. This contrasts with the historical pattern in which testing was wholly or mostly confined to the medical laboratory, which entailed sending off Biological specimen, specimens away from the point of care and then waiting hours or days to learn the results, during which time care must continue without the desired information. Technology Point-of-care tests are simple medical tests that can be performed at the bedside. In many cases, the simplicity was not achievable until technological change, technology developed not only to make a test possible at all but then also to mask its complexity. For example, various kinds of urine test strips have been available for decades, but portable ultrasound, portable ultrasonography did not reach the stage of being advanced, affordable, and widespread until the 2000s and 2010s. To ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry. In 1828 Friedrich Wöhler discovered that urea can be produced from inorganic starting materials, which was an important conceptual milestone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine Creatinine
Creatinine (; ) is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass). Biological relevance Serum creatinine (a blood measurement) is an important indicator of kidney health, because it is an easily measured byproduct of muscle metabolism that is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Creatinine itself is produced via a biological system involving creatine, phosphocreatine (also known as creatine phosphate), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP, the body's immediate energy supply). Creatine is synthesized primarily in the liver from the methylation of glycocyamine (guanidino acetate, synthesized in the kidney from the amino acids arginine and glycine) by S-Adenosyl methionine. It is then transported through blood to the other organs, muscle, and brain, where, through phosphorylation, it becomes the high-energy compound phosphocreatine. Creatine conversion to phosphocreatine is catalyzed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity And Specificity
''Sensitivity'' and ''specificity'' mathematically describe the accuracy of a test which reports the presence or absence of a condition. Individuals for which the condition is satisfied are considered "positive" and those for which it is not are considered "negative". *Sensitivity (true positive rate) refers to the probability of a positive test, conditioned on truly being positive. *Specificity (true negative rate) refers to the probability of a negative test, conditioned on truly being negative. If the true condition can not be known, a " gold standard test" is assumed to be correct. In a diagnostic test, sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives. For all testing, both diagnostic and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensitivities will mean lower specificities and vice versa. If the goal is to return the ratio at w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trace Metal-free 24 Hour Urine Container
Trace may refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * ''Trace'' (Son Volt album), 1995 * ''Trace'' (Died Pretty album), 1993 * Trace (band), a Dutch progressive rock band * ''The Trace'' (album) Other uses in arts and entertainment * ''Trace'' (magazine), British hip-hop magazine * ''Trace'' (manhwa), a Korean internet cartoon * ''Trace'' (novel), a novel by Patricia Cornwell * ''The Trace'' (film), a 1994 Turkish film * ''The Trace'' (video game), 2015 video game * ''Sama'' (film), alternate title ''The Trace'', a 1988 Tunisian film * Trace, a fictional character in the game ''Metroid Prime Hunters'' * Trace, the protagonist of ''Axiom Verge'' * Trace, another name for Portgas D. Ace, a fictional character in the manga ''One Piece'' * TRACE, the main brand for a number of music channels such as Trace Urban Language * Trace (deconstruction), a concept in Derridian deconstruction * Trace (linguistics), a syntactic placeholder resulting from a transformation * TRACE (psycho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be Heredity, inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y linkage, Y chromosome or Mitochondrial disease#Causes, mitochondrial DNA (due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminoaciduria
Aminoaciduria occurs when the urine contains abnormally high amounts of amino acids. In the healthy kidney, the glomeruli filter all amino acids out of the blood, and the renal tubules then reabsorb over 95% of the filtered amino acids back into the blood. In overflow aminoaciduria, abnormally high concentrations of amino acids in the blood plasma overwhelm the resorptive capacity of the renal tubules, resulting in high concentrations of amino acids in the urine. This may be caused by congenital disorders of amino acid metabolism, for example, phenylketonuria, or may be secondary to liver disease. In renal aminoaciduria, the renal tubules are unable to reabsorb the filtered amino acids back into the blood, causing high concentrations of amino acids in the urine. This may be caused by a defect in the transport proteins in the renal tubule, for example, as occurs in Hartnup disease, or may be due to damage to the kidney tubule, for example, as occurs in Fanconi syndrome Fanconi s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine Organic Acids
Urine organic acids is a medical diagnostic test that measures organic acid metabolites in the urine. The metabolites can come from host cells or from flora. The test can be used to exclude the possibility that a person has an inborn error of metabolism, usually one of the organic acidemias. It is also used to look for problems with nutrition or evidence of certain infections or bacterial overgrowth. The usual method of analysis is tandem mass spectrometry Tandem mass spectrometry, also known as MS/MS or MS2, is a technique in instrumental analysis where two or more mass analyzers are coupled together using an additional reaction step to increase their abilities to analyse chemical samples. A comm .... References Urine tests Inborn errors of metabolism {{med-diagnostic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
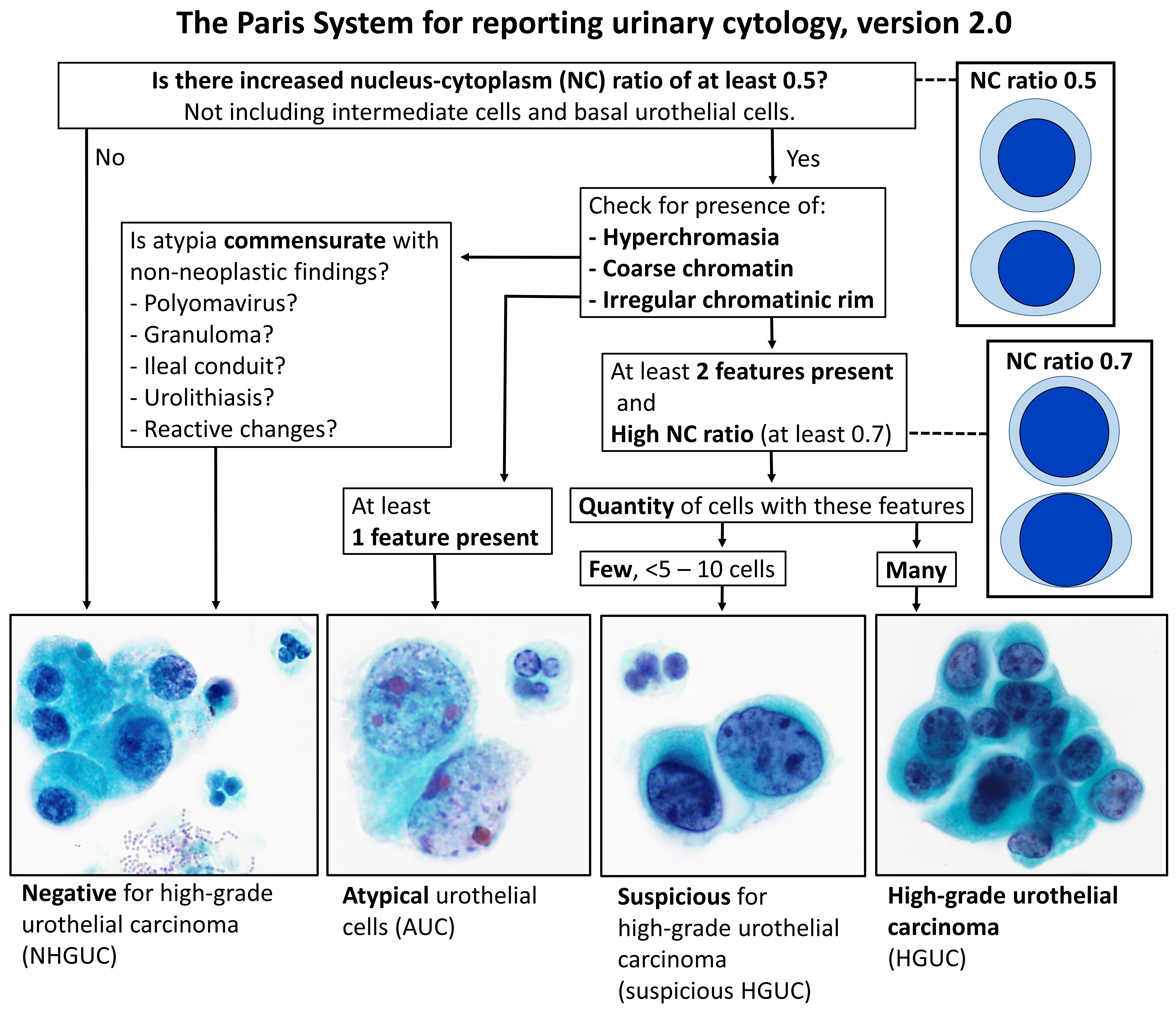
Urine Cytology
Urine cytology is a test that looks for abnormal cells in urine under a microscope. The test commonly checks for infection, inflammatory disease of the urinary tract, cancer, or precancerous conditions. It can be part of a broader urinalysis. If a cancerous condition is detected, other tests and procedures are usually recommended to diagnose cancers, including bladder cancer, ureteral cancer and cancer of the urethra. It is especially recommended when blood in the urine (hematuria) has been detected. Urine typically contains epithelial cells shed from the urinary tract, and urine cytology evaluates this urinary sediment for the presence of cancerous cells from the lining of the urinary tract, and it is a convenient noninvasive technique for follow-up analysis of patients treated for urinary tract cancers. For this process, urine must be collected in a reliable fashion, and if urine samples are inadequate, the urinary tract can be assessed via instrumentation, such as a catheter. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urine Drug Screen
A drug test is a technical analysis of a biological specimen, for example urine, hair, blood, breath, sweat, or oral fluid/saliva—to determine the presence or absence of specified parent drugs or their metabolites. Major applications of drug testing include detection of the presence of performance enhancing steroids in sport, employers and parole/probation officers screening for drugs prohibited by law (such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and heroin) and police officers testing for the presence and concentration of alcohol (ethanol) in the blood commonly referred to as BAC (blood alcohol content). BAC tests are typically administered via a breathalyzer while urinalysis is used for the vast majority of drug testing in sports and the workplace. Numerous other methods with varying degrees of accuracy, sensitivity (detection threshold/cutoff), and detection periods exist. A drug test may also refer to a test that provides quantitative chemical analysis of an illegal drug, typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |