|
Troff
troff (), short for "typesetter roff", is the major component of a document processing system developed by Bell Labs for the Unix operating system. troff and the related nroff were both developed from the original roff. While nroff was intended to produce output on terminals and line printers, troff was intended to produce output on typesetting systems, specifically the Graphic Systems CAT that had been introduced in 1972. Both used the same underlying markup language and a single source file could normally be used by nroff or troff without change. ''troff'' features commands to designate fonts, spacing, paragraphs, margins, footnotes and more. Unlike many other text formatters, ''troff'' can position characters arbitrarily on a page, even overlapping them, and has a fully programmable input language. Separate preprocessors are used for more convenient production of tables, diagrams, and mathematics. Inputs to troff are plain text files that can be created by any text edit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nroff
nroff (short for "new roff") is a text-formatting program on Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It produces output suitable for simple fixed-width printers and terminal windows. It is an integral part of the Unix help system, being used to format man pages for display. nroff and the related troff were both developed from the original roff. While nroff was intended to produce output on terminals and line printers, troff was intended to produce output on typesetting systems. Both used the same underlying markup and a single source file could normally be used by nroff or troff without change. History nroff was written by Joe Ossanna for Version 2 Unix, in Assembly language and then ported to C. It was a descendant of the RUNOFF program from CTSS, the first computerized text-formatting program, and is a predecessor of the Unix troff document processing system. There is also a free software version of nroff in the groff package. Variants The Minix operating system, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAT (phototypesetter)
The GSI C/A/T (Computer Assisted Typesetter) is a phototypesetter developed by Graphic Systems in 1972. This phototypesetter, along with troff software for UNIX, revolutionized the typesetting and document printing industry. Phototypesetting is most often used with offset printing technology. The GSI C/A/T phototypesetter was marketed by Singer Corporation in 1974 before the company was purchased by Wang Laboratories in 1978. Graphic Systems designed a simple computer front end to print basic text as display type. Full-scale page-composition computing was designed at Bell Laboratories as part of the UNIX project. Features The C/A/T phototypesetter features: * Punched paper tape for document input * Four font film strips with 102 characters or glyphs per strip * Canisters of photographic paper or film to receive the image * Fifteen distinct font sizes (5 pt to 72pt) * Horizontal positioning precision of 432 units per inch * Vertical positioning precision of 144 units per inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNIX Manual
A man page (short for manual page) is a form of software documentation usually found on a Unix or Unix-like operating system. Topics covered include computer programs (including library and system calls), formal standards and conventions, and even abstract concepts. A user may invoke a man page by issuing the man command. By default, man typically uses a terminal pager program such as more or less to display its output. Man pages are often referred to as an ''on-line'' or '' online'' form of software documentation, * even though the man command does not require internet access, dating back to the times when printed '' out-of-band'' manuals were the norm. History In the first two years of the history of Unix, no documentation existed. The Unix Programmer's Manual' was first published on November 3, 1971. The first actual man pages were written by Dennis Ritchie and Ken Thompson at the insistence of their manager Doug McIlroy in 1971. Aside from the man pages, the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Markup Language
Markup language refers to a text-encoding system consisting of a set of symbols inserted in a text document to control its structure, formatting, or the relationship between its parts. Markup is often used to control the display of the document or to enrich its content to facilitating automated processing. A markup language is a set of rules governing what markup information may be included in a document and how it is combined with the content of the document in a way to facilitate use by humans and computer programs. The idea and terminology evolved from the "marking up" of paper manuscripts (i.e., the revision instructions by editors), which is traditionally written with a red pen or blue pencil on authors' manuscripts. Older markup languages, which typically focus on typography and presentation, include troff, TeX, and LaTeX. Scribe and most modern markup languages, for example XML, identify document components (for example headings, paragraphs, and tables), with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joe Ossanna
Joseph Frank Ossanna, Jr. (December 10, 1928 – November 28, 1977) was an electrical engineer and computer programmer who worked as a member of the technical staff at the Bell Telephone Laboratories in Murray Hill, New Jersey. He became actively engaged in the software design of Multics (Multiplexed Information and Computing Service), a general-purpose operating system used at Bell. Education and career Ossanna received his Bachelor of Engineering (B.S.E.E.) from Wayne State University in 1952. At Bell Telephone Labs, Ossanna was concerned with low-noise amplifier design, feedback amplifier design, satellite look-angle prediction, mobile radio fading theory, and statistical data processing. He was also concerned with the operation of the Murray Hill Computation Center and was actively engaged in the software design of Multics. After learning how to program the PDP-7 computer, Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Joe Ossanna, and Rudd Canaday began to program the operating syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley ( BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems ( SunOS/ Solaris), HP/ HPE ( HP-UX), and IBM (AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are characterized by a modular design that is sometimes called the "Unix philosophy". According to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typesetting
Typesetting is the composition of text by means of arranging physical ''type'' (or ''sort'') in mechanical systems or '' glyphs'' in digital systems representing '' characters'' (letters and other symbols).Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House, Inc. 23 December 2009Dictionary.reference.com/ref> Stored types are retrieved and ordered according to a language's orthography for visual display. Typesetting requires one or more fonts (which are widely but erroneously confused with and substituted for typefaces). One significant effect of typesetting was that authorship of works could be spotted more easily, making it difficult for copiers who have not gained permission. Pre-digital era Manual typesetting During much of the letterpress era, movable type was composed by hand for each page by workers called compositors. A tray with many dividers, called a case, contained cast metal '' sorts'', each with a single letter or symbol, but backwards (so they would print correctly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roff (software)
roff is a typewriter-oriented markup language. As the first Unix text-formatting computer program, it is a predecessor of the nroff and troff document processing systems. Roff was a Unix version of the runoff text-formatting program from Multics, which was a descendant of RUNOFF for CTSS (the first computerized text-formatting application). History CTSS ''roff'' is a descendant of the RUNOFF program by Jerry Saltzer, which ran on CTSS. Douglas McIlroy and Robert Morris wrote runoff for Multics in BCPL based on Saltzer's program written in MAD assembler. Their program in turn was "transliterated" by Ken Thompson into PDP-7 assembler language for his early Unix operating system, circa 1970. APDF/ref> When the first PDP-11 was acquired for Unix in late 1970 (a PDP-11/20), the justification cited to management for the funding required was that it was to be used as a word processing system, and so ''roff'' was quickly transliterated again, into PDP-11 assembly, in 1971. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Text Formatting
Typesetting is the composition of text by means of arranging physical ''type'' (or ''sort'') in mechanical systems or '' glyphs'' in digital systems representing '' characters'' (letters and other symbols).Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House, Inc. 23 December 2009Dictionary.reference.com/ref> Stored types are retrieved and ordered according to a language's orthography for visual display. Typesetting requires one or more fonts (which are widely but erroneously confused with and substituted for typefaces). One significant effect of typesetting was that authorship of works could be spotted more easily, making it difficult for copiers who have not gained permission. Pre-digital era Manual typesetting During much of the letterpress era, movable type was composed by hand for each page by workers called compositors. A tray with many dividers, called a case, contained cast metal '' sorts'', each with a single letter or symbol, but backwards (so they would print correctly). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Projector
An overhead projector (often abbreviated to OHP), like a film or slide projector, uses light to project an enlarged image on a screen, allowing the view of a small document or picture to be shared with a large audience. In the overhead projector, the source of the image is a page-sized sheet of transparent plastic film (also known as "foils" or " transparencies") with the image to be projected either printed or hand-written/drawn. These are placed on the glass platen of the projector, which has a light source below it and a projecting mirror and lens assembly above it (hence, "overhead"). They were widely used in education and business before the advent of video projectors. Optical system An overhead projector works on the same principle as a slide projector, in which a focusing lens projects light from an illuminated slide onto a projection screen where a real image is formed. However some differences are necessitated by the much larger size of the transparencies used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
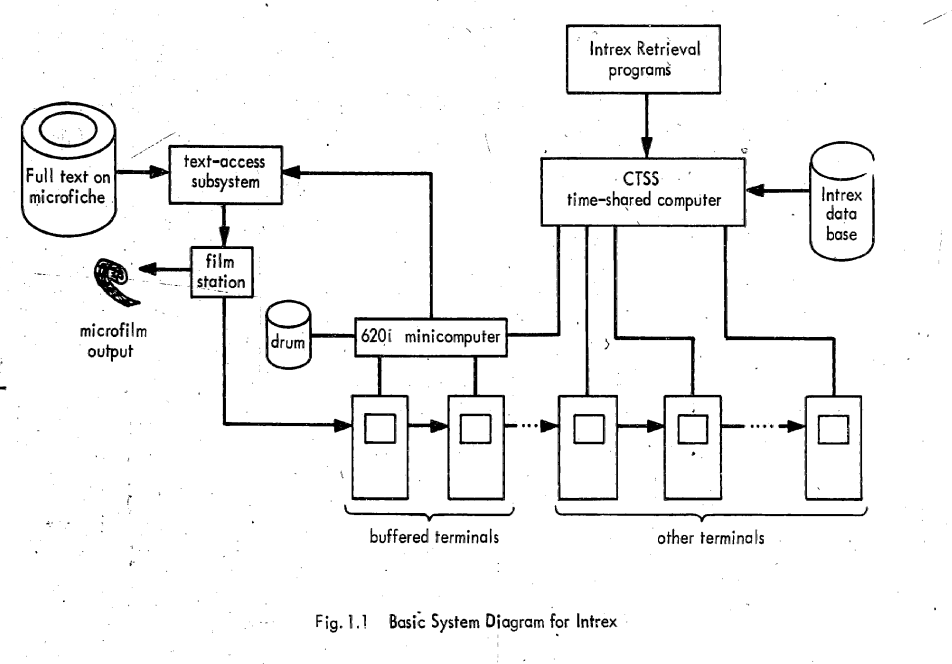
Compatible Time-Sharing System
The Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS) was the first general purpose time-sharing operating system. Compatible Time Sharing referred to time sharing which was compatible with batch processing; it could offer both time sharing and batch processing concurrently. CTSS was developed at the MIT Computation Center ("Comp Center"). CTSS was first demonstrated on MIT's modified IBM 709 in November 1961. The hardware was replaced with a modified IBM 7090 in 1962 and later a modified IBM 7094 called the "blue machine" to distinguish it from the Project MAC CTSS IBM 7094. Routine service to MIT Comp Center users began in the summer of 1963 and was operated there until 1968. A second deployment of CTSS on a separate IBM 7094 that was received in October 1963 (the "red machine") was used early on in Project MAC until 1969 when the red machine was moved to the Information Processing Center and operated until July 20, 1973. CTSS ran on only those two machines however there were remote CT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RUNOFF
Runoff, run-off or RUNOFF may refer to: * RUNOFF, the first computer text-formatting program * Runoff or run-off, another name for bleed, printing that lies beyond the edges to which a printed sheet is trimmed * Runoff or run-off, a stock market term * Runoff curve number, an empirical parameter used in hydrology * Runoff model (reservoir), a mathematical model describing the relationship between rainfall and surface runoff (see below) in a rainfall catchment area or watershed * Runoff voting system, also known as the two-round system, a voting system where a second round of voting is used to elect one of the two candidates receiving the most votes in the first round ** Instant-runoff voting, an extension or variation of runoff voting where a second round can be rendered unnecessary by voters ranking candidates in order of preference * Run-off area, a racetrack safety feature * Surface runoff, the flow of water over land as a consequence of rain, melting snow, etc. See als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |