|
Tolvaptan
Tolvaptan, sold under the brand name Samsca among others, is an aquaretic drug that functions as a selective, competitive vasopressin receptor 2 (V2) antagonist used to treat hyponatremia (low blood sodium levels) associated with congestive heart failure, cirrhosis, and the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH). Tolvaptan was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on May 19, 2009, and is sold by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. under the trade name Samsca. Tolvaptan, as Jynarque, was granted approval for medical use in the United States in April 2018. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted tolvaptan a fast track designation for clinical trials investigating its use for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease. The FDA granted Jynarque an orphan drug designation in April 2012, for the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Tolvaptan is available as a generic medication. Medical uses Tolvaptan (Samsca) is indicated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolvaptan Phosphate
Tolvaptan phosphate is a drug used for the treatment of cardiac edema. It is a prodrug of tolvaptan, formulated as the salt tolvaptan sodium phosphate, for intravenous administration. Tolvaptan phosphate is converted into the active drug tolvaptan in the human body following administration. It was developed by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. (), abbreviated OPC, is a pharmaceutical company headquartered in Tokyo, Osaka and Naruto, Japan. The company was established August 10, 1964. History OPC's parent company Otsuka Holdings Co. Ltd. joined the Tokyo Stock Exchange through an in ... and was approved for use in Japan in 2022. References {{Cardiovascular-drug-stub Prodrugs Organophosphates Diuretics Chloroarenes Benzanilides Vasopressin receptor antagonists Benzazepanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
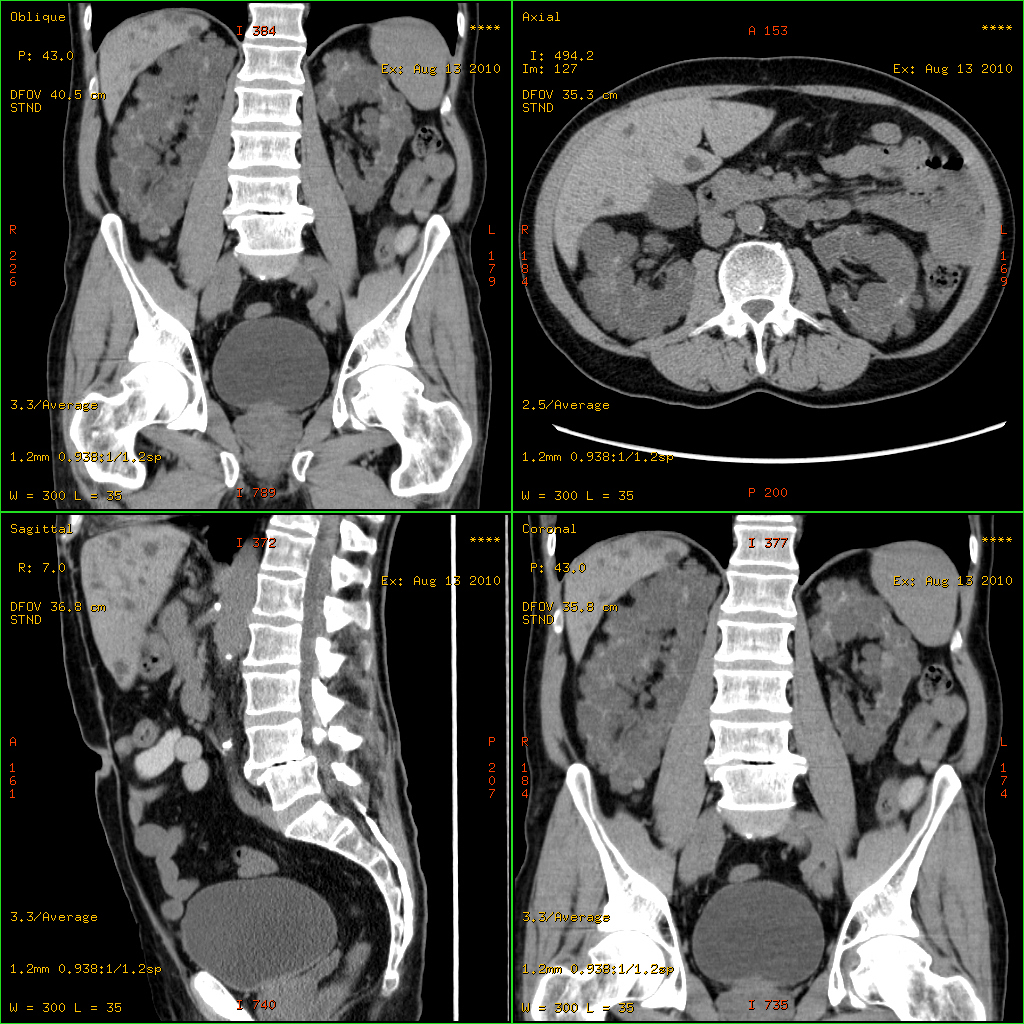
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD or PCKD, also known as polycystic kidney syndrome) is a genetic disorder in which the renal tubules become structurally abnormal, resulting in the development and growth of multiple cysts within the kidney. These cysts may begin to develop in utero, in infancy, in childhood, or in adulthood. Cysts are non-functioning tubules filled with fluid pumped into them, which range in size from microscopic to enormous, crushing adjacent normal tubules and eventually rendering them non-functional as well. PKD is caused by abnormal genes that produce a specific abnormal protein; this protein has an adverse effect on tubule development. PKD is a general term for two types, each having their own pathology and genetic cause: autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). The abnormal gene exists in all cells in the body; as a result, cysts may occur in the liver, seminal vesicles, and pancreas. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diuretics
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin ( antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine. Medical uses In medicine, diuretics are used to treat heart failure, liver cirrhosis, hypertension, influenza, water poisoning, and certain kidney diseases. Some diuretics, such as acetazolamide, help to make the urine more alkaline, and are helpful in increasing excretion of substances such as aspirin in cases of overdose or poisoning. Diuretics are sometimes abused by people with an eating disorder, especially people with bulimia nervosa, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasopressin Receptor Antagonist
A vasopressin receptor antagonist (VRA) is an agent that interferes with action at the vasopressin receptors. Most commonly VRAs are used in the treatment of hyponatremia, especially in patients with congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis or SIADH. Types Vaptans The "vaptan" drugs act by directly blocking the action of vasopressin at its receptors ( V1A, V1B and V2). These receptors have a variety of functions, with the V1A and V2 receptors are expressed peripherally and involved in the modulation of blood pressure and kidney function respectively, while the V1A and V1B receptors are expressed in the central nervous system. V1A is expressed in many regions of the brain, and has been linked to a variety of social behaviors in humans and animals. The vaptan class of drugs contains a number of compounds with varying selectivity, several of which are either already in clinical use or in clinical trials as of 2009. ;Unselective (mixed V1A/V2) * Conivaptan ;V1A selective (V1RA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndrome Of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) is characterized by excessive unsuppressible release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) either from the posterior pituitary gland, or an abnormal non-pituitary source. Unsuppressed ADH causes an unrelenting increase in solute-free water being returned by the tubules of the kidney to the venous circulation. The causes of SIADH are grouped into six categories: 1) central nervous system diseases that directly stimulate the hypothalamus, the site of control of ADH secretion; 2) various cancers that synthesize and secrete ectopic ADH; 3) various lung diseases; 4) numerous drugs that chemically stimulate the hypothalamus; 5) inherited mutations; and 6) miscellaneous largely transient conditions. ADH is derived from a preprohormone precursor that is synthesized in cells in the hypothalamus and stored in vesicles in the posterior pituitary. ''Appropriate'' ADH secretion is regulated by osmoreceptors on the hypothalamic cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Administration
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consumptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
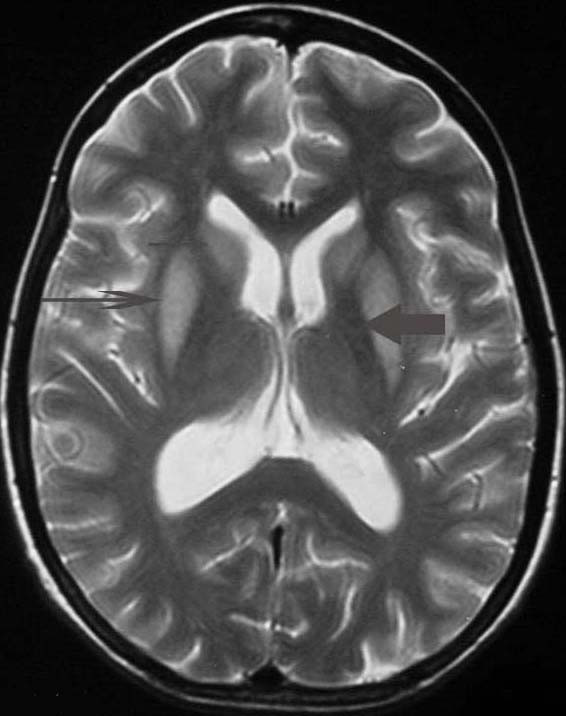
Central Pontine Myelinolysis
Central pontine myelinolysis is a neurological condition involving severe damage to the myelin sheath of nerve cells in the ''pons'' (an area of the brainstem). It is predominately iatrogenic (treatment-induced), and is characterized by acute paralysis, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), dysarthria (difficulty speaking), and other neurological symptoms. Central pontine myelinolysis was first described as a disorder in 1959. The original paper described four cases with fatal outcomes, and the findings on autopsy. The disease was described as a disease of alcoholics and malnutrition. 'Central pontine' indicated the site of the lesion and 'myelinolysis' was used to emphasise that myelin was affected. The authors intentionally avoided the term 'demyelination' to describe the condition, in order to differentiate this condition from multiple sclerosis and other neuroinflammatory disorders. Since this original description, demyelination in other areas of the central nervous system asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racemate
In chemistry, a racemic mixture, or racemate (), is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates. History The first known racemic mixture was racemic acid, which Louis Pasteur found to be a mixture of the two enantiomeric isomers of tartaric acid. He manually separated the crystals of a mixture by hand, starting from an aqueous solution of the sodium ammonium salt of racemate tartaric acid. Pasteur benefited from the fact that ammonium tartrate salt that gives enantiomeric crystals with distinct crystal forms (at 77 °F). Reasoning from the macroscopic scale down to the molecular, he reckoned that the molecules had to have non-superimposable mirror images. A sample with only a single enantiomer is an ''enantiomerically pure'' or ''enantiopure'' compound. Etymology From racemic acid found in grapes; from Latin ''racemus'', meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Medicines Agency
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).Set up by EC Regulation No. 2309/93 as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products, and renamed by EC Regulation No. 726/2004 to the European Medicines Agency, it had the acronym EMEA until December 2009. The European Medicines Agency does not call itself EMA either – it has no official acronym but may reconsider if EMA becomes commonly accepted (secommunication on new visual identity an). The EMA was set up in 1995, with funding from the European Union and the pharmaceutical industry, as well as indirect subsidy from member states, its stated intention to harmonise (but not replace) the work of existing national medicine regulatory bodies. The hope was that this plan would not onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroarenes
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications. Preparation The two main preparatory routes to aryl halides are direct halogenation and via diazonium salts. Direct halogenation In the Friedel-Crafts halogenation, Lewis acids serve as catalysts. Many metal chlorides are used, examples include iron(III) chloride or aluminium chloride. The most important aryl halide, chlorobenzene is produced by this route. Monochlorination of benzene is always accompanied by formation of the dichlorobenzene derivatives. Arenes with electron donating groups react with halogens even in the absence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |