|
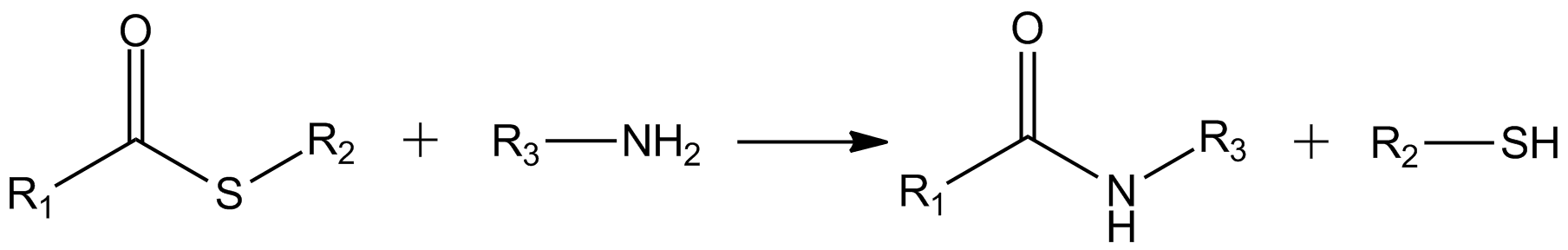
Thioesters
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the functional group . They are analogous to carboxylate esters () with the sulfur in the thioester playing the role of the linking oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix. They are the product of esterification between a carboxylic acid () and a thiol (). In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA.Matthys J. Janssen "Carboxylic Acids and Esters" in PATAI's Chemistry of Functional Groups: Carboxylic Acids and Esters, Saul Patai, Ed. John Wiley, 1969, New York: pp. 705–764. Synthesis The most typical route to thioester involves the reaction of an acid chloride with an alkali metal salt of a thiol: :RSNa + R'COCl -> R'COSR + NaCl Another common route entails the displacement of halides by the alkali metal salt of a thiocarboxylic acid. For example, thioacetate esters are commonly prepared by alkylation of potassium thioacetate: :CH3COSK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Thioacetate
Potassium thioacetate is an organosulfur compound and a salt with the formula . This white, water-soluble solid is used as a reagent for preparing thioacetate esters and other derivatives. Synthesis and reactions Potassium thioacetate, which is commercially available, can be prepared by combining acetyl chloride and potassium hydrogen sulfide: :CH3COCl + 2 KSH -> KCl + CH3COSK + H2S It arises also by the neutralization of thioacetic acid with potassium hydroxide. Use in preparation of thiols In a common application, potassium thioacetate is combined with alkylating agents to give thioacetate esters (X = halide): :CH3COSK + RX -> CH3COSR + KX Hydrolysis of these esters affords thiol In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl gro ...s: :CH3COSR + H2O -> CH3CO2H + RSH The thioac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin, that is, any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds.H. Stephen Stoker (2015): General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry'. 1232 pages. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished: terminal and internal. Also called α-olefins, terminal alkenes are more useful. However, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) recommends using the name "alkene" only for acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 121 picometers is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (134 pm) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. The sigma bond contri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonylation
Carbonylation refers to reactions that introduce carbon monoxide into organic and inorganic substrates. Carbon monoxide is abundantly available and conveniently reactive, so it is widely used as a reactant in industrial chemistry. The term carbonylation also refers to oxidation of protein side chains. Organic chemistry Several industrially useful organic chemicals are prepared by carbonylations, which can be highly selective reactions. Carbonylations produce organic carbonyls, i.e., compounds that contain the C=O functional group such as aldehydes, carboxylic acids and esters. Carbonylations are the basis of many types of reactions, including hydroformylation and Reppe reactions. These reactions require metal catalysts, which bind and activate the CO. These processes involve transition metal acyl complexes as intermediates. Much of this theme was developed by Walter Reppe. Hydroformylation Hydroformylation entails the addition of both carbon monoxide and hydrogen to unsaturated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedron Letters
''Tetrahedron Letters'' is a weekly international journal for rapid publication of full original research papers in the field of organic chemistry. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 2.415. Indexing ''Tetrahedron Letters'' is indexed in: References See also *''Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all ...'' *'' Tetrahedron: Asymmetry'' Chemistry journals Weekly journals Publications established in 1959 Elsevier academic journals {{chem-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thioacetic Acid
Thioacetic acid is an organosulfur compound with the molecular formula . It is the sulfur analogue of acetic acid (), as implied by the ''thio-'' prefix. It is a yellow liquid with a strong thiol-like odor. It is used in organic synthesis for the introduction of thiol groups () in molecules. Synthesis and properties Thioacetic acid is prepared by the reaction of acetic anhydride with hydrogen sulfide: :(CH3C(O))2O + H2S -> CH3C(O)SH + CH3C(O)OH It has also been produced by the action of phosphorus pentasulfide on glacial acetic acid, followed by distillation. :CH3C(O)OH + P2S5 -> CH3C(O)SH + P2OS4 Thioacetic acid is typically contaminated by acetic acid. The compound exists exclusively as the thiol tautomer, consistent with the strength of the double bond. Reflecting the influence of hydrogen-bonding, the boiling point (93 °C) and melting points are 20 and 75 K lower than those for acetic acid. Reactivity Acidity With a p''K''a near 3.4, thioacetic acid is about 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitsunobu Reaction
The Mitsunobu reaction is an organic reaction that converts an alcohol into a variety of functional groups, such as an ester, using triphenylphosphine and an azodicarboxylate such as diethyl azodicarboxylate (DEAD) or diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (DIAD). Although DEAD and DIAD are most commonly used, there are a variety of other azodicarboxylates available which facilitate an easier workup and/or purification and in some cases, facilitate the use of more basic nucleophiles. It was discovered by Oyo Mitsunobu (1934–2003). Typical protocol is to add the phosphine and azodicarboxylate together at −10 °C, typically in THF or toluene, until a white precipitate forms. This white, cloudy suspension is the ylide. Then a solution of the nucleophile and alcohol are added together and the reaction can be, and in many cases is, heated to reflux. The alcohol reacts with the phosphine to create a good leaving group then undergoes an inversion of stereochemistry in classic SN2 fashion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
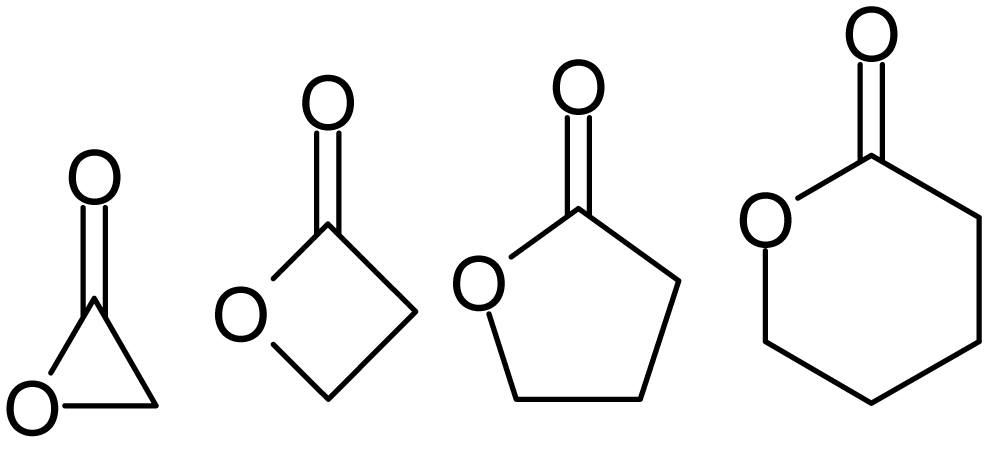
Lactone
Lactones are cyclic carboxylic esters, containing a 1-oxacycloalkan-2-one structure (), or analogues having unsaturation or heteroatoms replacing one or more carbon atoms of the ring. Lactones are formed by intramolecular esterification of the corresponding hydroxycarboxylic acids, which takes place spontaneously when the ring that is formed is five- or six-membered. Lactones with three- or four-membered rings (α-lactones and β-lactones) are very reactive, making their isolation difficult. Special methods are normally required for the laboratory synthesis of small-ring lactones as well as those that contain rings larger than six-membered. Nomenclature Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (''aceto'' = 2 carbon atoms, ''propio'' = 3, ''butyro'' = 4, ''valero'' = 5, ''capro'' = 6, etc.), with a ''-lactone'' suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid Anhydride
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid. In organic chemistry, organic acid anhydrides contain the functional group R(CO)O(CO)R'. Organic acid anhydrides often form when one equivalent of water is removed from two equivalents of an organic acid in a dehydration reaction. In inorganic chemistry, an acid anhydride refers to an acidic oxide, an oxide that reacts with water to form an oxyacid (an inorganic acid that contains oxygen or carbonic acid), or with a base to form a salt. Nomenclature The nomenclature of organic acid anhydrides is derived from the names of the constituent carboxylic acids which underwent dehydration to form the compound. In symmetrical acid anhydrides, where only one constituent carboxylic acid was used to form the compound (such as the dehydration of propanoic acid, 2CH3CH2COOH → CH3CH2C(O)OC(O)CH2CH3 + H2O), only the prefix of the original carboxylic acid is used and the suffix "anhydri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentanone
Cyclopentanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)4CO. This cyclic ketone is a colorless volatile liquid. Preparation Upon treatment with barium hydroxide at elevated temperatures, adipic acid undergoes ketonization to give cyclopentanone: :(CH2)4(CO2H)2 → (CH2)4CO + H2O + CO2 Uses Cyclopentanone is common precursor to fragrances, especially those related to jasmine and jasmone. Examples include 2-pentyl- and 2-heptylcyclopentanone.Johannes Panten and Horst Surburg "Flavors and Fragrances, 2. Aliphatic Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2015, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. It is a versatile synthetic intermediate, being a precursor to cyclopentobarbital Cyclopentobarbital sodium (Cyclopal, Dormisan) is a barbiturate derivative invented in the 1940s. It has sedative and anticonvulsant properties, and was used primarily as an anaesthetic in veterinary medicine. Cyclopal is considered similar in e .... Cyclopentanone is also used to make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propanephosphonic Acid Anhydride
Propanephosphonic acid anhydride (PPAA, T3P) is an anhydride of propane phosphonic acid. Its structure is a cyclic trimer, with a phosphorus–oxygen core and propyl groups and additional oxygens attached. The chemical is a useful reagent for peptide synthesis reactions, where it activates the carboxylic acid partner for subsequent reaction with amines. It is commercially available as 50 % solution in DMF or ethyl acetate Ethyl acetate ( systematically ethyl ethanoate, commonly abbreviated EtOAc, ETAC or EA) is the organic compound with the formula , simplified to . This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues ... as a slightly yellow mixture. References Reagents for organic chemistry Phosphonates {{organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |