|
Terminal Ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum. Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum. The ileum follows the duodenum and jejunum and is separated from the cecum by the ileocecal valve (ICV). In humans, the ileum is about 2–4 m long, and the pH is usually between 7 and 8 (neutral or slightly basic). ''Ileum ''is derived from the Greek word ''eilein'', meaning "to twist up tightly". Structure The ileum is the third and final part of the small intestine. It follows the jejunum and ends at the ileocecal junction, where the terminal ileum communicates with the cecum of the large intestine through the ileocecal valve. The ileum, along with the jejunum, is suspended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cecum
The cecum or caecum is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body (the same side of the body as the appendix, to which it is joined). The word cecum (, plural ceca ) stems from the Latin '' caecus'' meaning blind. It receives chyme from the ileum, and connects to the ascending colon of the large intestine. It is separated from the ileum by the ileocecal valve (ICV) or Bauhin's valve. It is also separated from the colon by the cecocolic junction. While the cecum is usually intraperitoneal, the ascending colon is retroperitoneal. In herbivores, the cecum stores food material where bacteria are able to break down the cellulose. In humans, the cecum is involved in absorption of salts and electrolytes and lubricates the solid waste that passes into the large intestine. Structure Development The cecum and appendix are formed by the enlargement of the postarterial segment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ileocecal Valve
The ileocecal valve (ileal papilla, ileocaecal valve, Tulp's valve, Tulpius valve, Bauhin's valve, ileocecal eminence, valve of Varolius or colic valve) is a sphincter muscle valve that separates the small intestine and the large intestine. Its critical function is to limit the reflux of colonic contents into the ileum. Approximately two liters of fluid enters the colon daily through the ileocecal valve. Microanatomy The histology of the ileocecal valve shows an abrupt change from a villous mucosa pattern of the ileum to a more colonic mucosa. A thickening of the muscularis mucosa, which is the smooth muscle tissue found beneath the mucosal layer of the digestive tract. A thickening of the muscularis externa is also noted. There is also a variable amount of lymphatic tissue found at the valve. The ileocecal valve has a papillose structure. Clinical significance Colonoscopy During colonoscopy, the ileocecal valve is used, along with the appendiceal orifice, in the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity), and B cells (for humoral immunity, humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cell A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...s, B cells and Natural killer cell, natural killer (NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
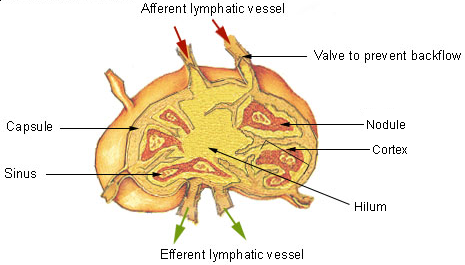
Lymphoid Nodule
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peyer's Patches
Peyer's patches (or aggregated lymphoid nodules) are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer. * Reprinted as: * Peyer referred to Peyer's patches as ''plexus'' or ''agmina glandularum'' (clusters of glands). From (Peyer, 1681), p. 7: ''"Tenui a perfectiorum animalium Intestina accuratius perlustranti, crebra hinc inde, variis intervallis, corpusculorum glandulosorum Agmina sive Plexus se produnt, diversae Magnitudinis atque Figurae."'' (I knew from careful study of more advanced animals, the intestines bear — often here and there, at various intervals — clusters of glandular small bodies or "plexuses" of diverse size and shape.) From p. 15: ''"(has Plexus seu agmina Glandularum voco)"'' (I call them "plexuses" or clusters of glands) He described their appearance. From p. 8: ''"Horum vero Plexuum facies modo in orbem concinnata; modo in Ovi aut Olivae oblongam, aliamve angulosam ac magis anomalam disposita figuram cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoid Tissue
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Folds
The circular folds (also known as valves of Kerckring, valves of Kerchkring, plicae circulares, ''plicae circulae, and'' ''valvulae conniventes'') are large valvular flaps projecting into the lumen of the small intestine. Structure The entire small intestine has circular folds of mucous membrane. The majority extend transversely around the cylinder of the small intestine, for about one-half or two-thirds of its circumference. Some form complete circles. Others have a spiral direction. The latter usually extend a little more than once around the bowel, but occasionally two or three times. The larger folds are about 1 cm. in depth at their broadest part; but the greater number are smaller. The larger and smaller folds alternate with each other. These can increase the surface area of the small intestine threefold. These larger folds are called ''plica circularis''. Distribution They are not found at the commencement of the duodenum, but begin to appear about 2.5 or 5 cm b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumen (anatomy)
In biology, a lumen (plural lumina) is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine. It comes . It can refer to: *The interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an artery, vein or capillary through which blood flows. *The interior of the gastrointestinal tract *The pathways of the bronchi in the lungs *The interior of renal tubules and urinary collecting ducts *The pathways of the female genital tract, starting with a single pathway of the vagina, splitting up in two lumina in the uterus, both of which continue through the Fallopian tubes In cell biology, a lumen is a membrane-defined space that is found inside several organelles, cellular components, or structures: * thylakoid, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondrion, or microtubule Transluminal procedures ''Transluminal procedures'' are procedures occurring through lumina, including: * Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery in the lumina of, for exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Mesenteric Vein
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a blood vessel that drains blood from the small intestine (jejunum and ileum). Behind the neck of the pancreas, the superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the hepatic portal vein. The superior mesenteric vein lies to the right of the similarly named artery, the superior mesenteric artery, which originates from the abdominal aorta. Structure Tributaries of the superior mesenteric vein drain the small intestine, large intestine, stomach, pancreas and appendix and include: * Right gastro-omental vein (also known as the right gastro-epiploic vein) * inferior pancreaticoduodenal veins * veins from jejunum * veins from ileum * middle colic vein – drains the transverse colon * right colic vein – drains the ascending colon * ileocolic vein The superior mesenteric vein combines with the splenic vein to form the portal vein. Clinical significance Thrombosis of the superior mesenteric vein is quite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Mesenteric Artery
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the duodenum through two-thirds of the transverse colon, as well as the pancreas. Structure It arises anterior to lower border of vertebra L1 in an adult. It is usually 1 cm lower than the celiac trunk. It initially travels in an anterior/inferior direction, passing behind/under the neck of the pancreas and the splenic vein. Located under this portion of the superior mesenteric artery, between it and the aorta, are the following: * left renal vein - travels between the left kidney and the inferior vena cava (can be compressed between the SMA and the abdominal aorta at this location, leading to nutcracker syndrome). * the third part of the duodenum, a segment of the small intestines (can be compressed by the SMA at this location, leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesothelium supported by a thin layer of connective tissue. This peritoneal lining of the cavity supports many of the abdominal organs and serves as a conduit for their blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. The abdominal cavity (the space bounded by the vertebrae, abdominal muscles, diaphragm, and pelvic floor) is different from the intraperitoneal space (located within the abdominal cavity but wrapped in peritoneum). The structures within the intraperitoneal space are called "intraperitoneal" (e.g., the stomach and intestines), the structures in the abdominal cavity that are located behind the intraperitoneal space are called "retroperitoneal" (e.g., the kidneys), and those structures below the intraperitoneal space are called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)