|
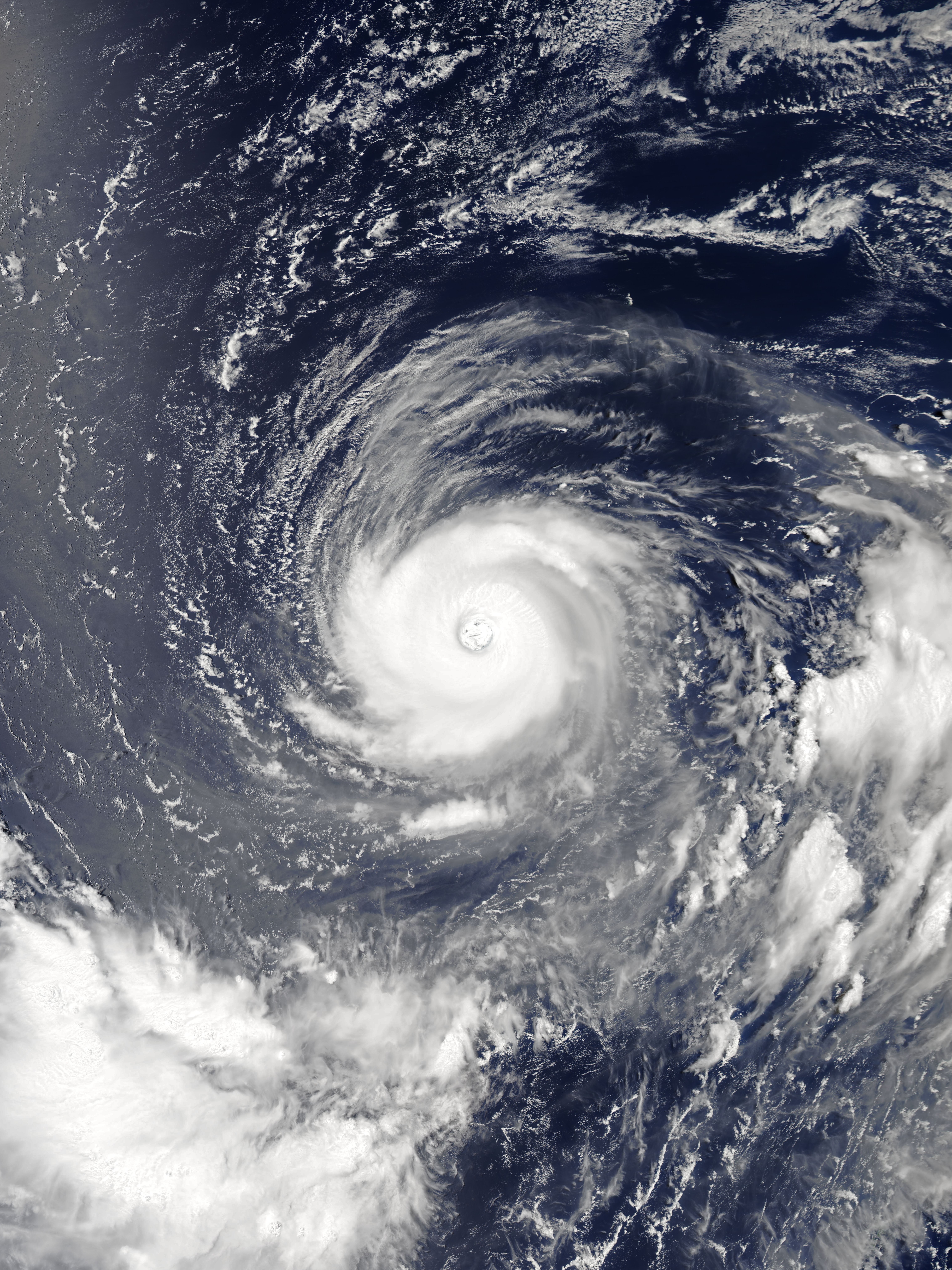
Typhoons
A typhoon is a tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere and which produces sustained hurricane-force winds of at least . This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, accounting for almost one third of the world's tropical cyclones. For organizational purposes, the northern Pacific Ocean is divided into three regions: the eastern (North America to 140°W), central (140°W to 180°), and western (180° to 100°E). The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center (RSMC) for tropical cyclone forecasts is in Japan, with other tropical cyclone warning centres for the northwest Pacific in Hawaii (the Joint Typhoon Warning Center), the Philippines, and Hong Kong. Although the RSMC names each system, the main name list itself is coordinated among 18 countries that have territories threatened by typhoons each year. Within most of the northwestern Pacific, there are no official typhoon seasons as tropical cyclones form througho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chu Coching
Coching Chu (; March 7, 1890 – February 7, 1974), also romanized as Zhu Kezhen, was a Chinese geologist and meteorologist. Life and career Born in Shangyu, Zhejiang, Chu received his secondary education at the Tangshan School of Rail and Mining in Shanghai. Upon receiving the Boxer Indemnity Scholarship, Chu went to United States for his college education in 1910. He graduated from the College of Agriculture, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, University of Illinois in 1913. He then studied under Robert DeCourcy Ward at Harvard University and received his Ph.D. in meteorology in 1918. From 1920 to 1929, he was chairperson of Department of Meteorology, Nanjing University (formerly known as the Nanking Higher Normal School, National Southeastern University, and National Central University). From 1929 to 1936 he served as director of the Chinese Institute of Meteorology of the Academia Sinica, which at the time was located in mainland China. Academia Sinica later b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the China, People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. It has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its Urbanization by country, highly urbanized population is concentrated. The combined Free area of the Republic of China, territories under ROC control consist of list of islands of Taiwan, 168 islands in total covering . The Taipei–Keelung metropolitan area, largest metropolitan area is formed by Taipei (the capital), New Taipei City, and Keelung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated countries. Tai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a total area of roughly 300,000 square kilometers, which are broadly categorized in Island groups of the Philippines, three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. With a population of over 110 million, it is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, twelfth-most-populous country. The Philippines is bounded by the South China Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south. It shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east and southeast, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest. It has Ethnic groups in the Philippines, diverse ethnicities and Culture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Specialized Meteorological Center
A Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) is responsible for the distribution of information, advisories, and warnings regarding the specific program they have a part of, agreed by consensus at the World Meteorological Organization as part of the World Weather Watch. Environmental emergency response programme As a result of the poor communications between countries following the Chernobyl disaster in the Spring of 1986, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) was requested by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and other international organizations to arrange for early warning messages about nuclear accidents to be transmitted over the Global Telecommunications System (GTS). In addition some WMO member countries that lacked extensive forecasting capability requested that specialized pollutant transport and dispersion forecasts be provided during these emergencies. As a result, during 1989 Meteo-France (MF), Environment Canada (EC) and the United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon is the same thing which occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Tropical cyclones tropical cyclogenesis, typically form over large bodies of relatively warm water. They derive their energy through the evaporation of water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin ( ; zh, s=, t=, p=Guānhuà, l=Mandarin (bureaucrat), officials' speech) is the largest branch of the Sinitic languages. Mandarin varieties are spoken by 70 percent of all Chinese speakers over a large geographical area that stretches from Yunnan in the southwest to Xinjiang in the northwest and Heilongjiang in the northeast. Its spread is generally attributed to the greater ease of travel and communication in the North China Plain compared to the more mountainous south, combined with the relatively recent spread of Mandarin to frontier areas. Many varieties of Mandarin, such as Southwestern Mandarin, those of the Southwest (including Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese) and the Lower Yangtze Mandarin, Lower Yangtze, are not mutually intelligible with the Beijing dialect (or are only partially intelligible). Nevertheless, Mandarin as a group is often placed first in lists of languages by number of native speakers (with nearly one billion). Because Mandarin originated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tale Of The Lychee Mirror
The ''Tale of the Lychee Mirror'' () is a 16th-century Ming dynasty play written by an unknown author. History The play was written in a mixture of the Southern Min dialects of Quanzhou and Chaozhou ( Teochew), and is one of the earliest sources on those dialects. The oldest extant manuscripts date from 1566 and 1581. This story is widely spread in Minnan-speaking areas, mainly the south part of Fujian, Chaoshan ( Chaozhou, Jieyang and Shantou), Southeast Asia and Taiwan. ''Tân Saⁿ and Gō͘-niû'' (; ''Teochew'': ''Dang5 San1 Ngou6 Niê5'') is a popular Taiwanese opera adaptation based on the play. Story Tân Saⁿ (Tan) is a scholar who is native to Quanzhou in southern Fujian province. When he sent his brother- and sister-in-law to Guangnan, he stopped in Chaozhou. During the Lantern Festival The Lantern Festival ( zh, t=wikt:元宵節, 元宵節, s=wikt:元宵节, 元宵节, first=t, hp=Yuánxiāo jié), also called Shangyuan Festival ( zh, t=上元節, s= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Three Kingdoms
The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is a Chinese official history written by Chen Shou in the late 3rd century CE, covering the end of the Han dynasty (220 CE) and the subsequent Three Kingdoms period (220–280 CE). It is regarded as to be the authoritative source text for these periods. Compiled following the reunification of China under the Jin dynasty (266–420), the work chronicles the political, social, and military events within rival states Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu into a single text organized by individual biography. The ''Records'' are the primary source of information for the 14th-century historical novel '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', considered to be one of the four classic novels emblematic of written vernacular Chinese. While large subsections of the work have been selected and translated into English, the entire corpus has yet to receive an unabridged English translation. Origin and structure The '' Book of Han'' and ''Records of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Min Chinese
Min ( zh, t=, s=闽语, p=Mǐnyǔ, poj=Bân-gú / Bân-gír / Bân-gí; Bàng-uâ-cê, BUC: ''Mìng-ngṳ̄'') is a broad group of Sinitic languages with about 75 million native speakers. These languages are spoken in Fujian province and Chaoshan, as well as by the descendants of Min-speaking colonists on the Leizhou Peninsula, Hainan, parts of Zhongshan, three counties in southern Wenzhou, the Zhoushan archipelago, Taiwan, and scattered in pockets or sporadically across Hong Kong, Macau, and several countries in Southeast Asia, particularly Singapore, Malaysia, the Philippines, Indonesia, Thailand, Myanmar, Cambodia, Vietnam, and Brunei. The name is derived from the Min River (Fujian), Min River in Fujian, which is also the abbreviated name of Fujian Province. Min varieties are not mutually intelligible with one another nor with any other variety of Chinese (such as Mandarin Chinese, Mandarin, Cantonese, Wu Chinese, Wu, Gan Chinese, Gan, Xiang Chinese, Xiang, or Hakka Chinese, Hak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Iranian Languages
The Indo-Iranian languages (also known as Indo-Iranic languages or collectively the Aryan languages) constitute the largest branch of the Indo-European language family. They include over 300 languages, spoken by around 1.7 billion speakers worldwide, predominantly in South Asia, West Asia and parts of Central Asia. Indo-Iranian languages are divided into three major branches: Indo-Aryan, Iranian, and Nuristani languages. The Badeshi language remains unclassified within the Indo-Iranian branch. The largest Indo-Iranian language is the Hindustani language (Hindi-Urdu)."Hindi" L1: 322 million (2011 Indian census), including perhaps 150 million speakers of other languages that reported their language as "Hindi" on the census. L2: 274 million (2016, source unknown). Urdu L1: 67 million (2011 & 2017 censuses), L2: 102 million (1999 Pakistan, source unknown, and 2001 Indian census): ''Ethnologue'' 21. . . The areas with Indo-Iranian languages stretch from Europe ( Romani) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone Basin
Traditionally, areas of tropical cyclone formation are divided into seven basins. These include the North Atlantic Ocean, the eastern and western parts of the North Pacific Ocean, the Southwest Pacific, the Southwest and Southeast Indian Oceans, and the North Indian Ocean (Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal). The West Pacific is the most active and the north Indian the least active. An average of 86 tropical cyclones of tropical storm intensity form annually worldwide, with 47 reaching hurricane/typhoon strength, and 20 becoming intense tropical cyclones, super typhoons, or major hurricanes (at least of Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale, Category 3 intensity). __TOC__ Overview Northern Hemisphere North Atlantic Ocean This region includes the North Atlantic Ocean, the Caribbean Sea, and the Gulf of Mexico. Tropical cyclone formation here varies widely from year to year, ranging from one to over twenty-five per year. Most Atlantic tropical cyclone, tropical storms and hurricane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troposphere
The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere of Earth. It contains 80% of the total mass of the Atmosphere, planetary atmosphere and 99% of the total mass of water vapor and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. From the planetary surface of the Earth, the average height of the troposphere is in the tropics; in the middle latitudes; and in the high latitudes of the polar regions in winter; thus the average height of the troposphere is . The term ''troposphere'' derives from the Greek words ''tropos'' (rotating) and ''sphere, sphaira'' (sphere) indicating that rotational turbulence mixes the layers of air and so determines the structure and the phenomena of the troposphere. The rotational friction of the troposphere against the planetary surface affects the flow of the air, and so forms the planetary boundary layer (PBL) that varies in height from hundreds of meters up to . The measures of the PBL vary according to the latitude, the landform, and the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |