|
Tumbleweed
A tumbleweed is a structural part of the above-ground anatomy of a number of species of plants. It is a diaspore that, once mature and dry, detaches from its root or stem and rolls due to the force of the wind. In most such species, the tumbleweed is in effect the entire plant apart from the root system, but in other plants, a hollow fruit or inflorescence might detach instead. Xerophyte tumbleweed species occur most commonly in steppe and arid ecosystems, where frequent wind and the open environment permit rolling without prohibitive obstruction. Apart from its primary vascular system and roots, the tissues of the tumbleweed structure are dead; their death is functional because it is necessary for the structure to degrade gradually and fall apart so that its seeds or spores can escape during the tumbling, or germinate after the tumbleweed has come to rest in a moist location. In the latter case, many species of tumbleweed open mechanically, releasing their seeds as they swel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumbleweed In Motion
A tumbleweed is a structural part of the above-ground anatomy of a number of species of plants. It is a diaspore that, once mature and dry, detaches from its root or stem and rolls due to the force of the wind. In most such species, the tumbleweed is in effect the entire plant apart from the root system, but in other plants, a hollow fruit or inflorescence might detach instead. Xerophyte tumbleweed species occur most commonly in steppe and arid ecosystems, where frequent wind and the open environment permit rolling without prohibitive obstruction. Apart from its primary vascular system and roots, the tissues of the tumbleweed structure are dead; their death is functional because it is necessary for the structure to degrade gradually and fall apart so that its seeds or spores can escape during the tumbling, or germinate after the tumbleweed has come to rest in a moist location. In the latter case, many species of tumbleweed open mechanically, releasing their seeds as they swell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotating Locomotion In Living Systems
Several organisms are capable of rolling locomotion. However, true wheels and propellers—despite their utility in human vehicles—do not play a significant role in the movement of living things (with the exception of the corkscrew-like flagella of many prokaryotes). Biologists have offered several explanations for the apparent absence of biological wheels, and wheeled creatures have appeared often in speculative fiction. Given the ubiquity of wheels in human technology, and the existence of biological analogues of many other technologies (such as wings and lenses), the lack of wheels in nature has seemed, to many scientists, to demand explanation—and the phenomenon is broadly explained by two factors: first, there are several developmental and evolutionary obstacles to the advent of a wheel by natural selection, and secondly, wheels have several drawbacks relative to other means of propulsion (such as walking, running, or slithering) in natural environments, which would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaspore (botany)
In botany, a diaspore is a plant dispersal unit consisting of a seed or spore plus any additional tissues that assist dispersal. Examples of such additional structures includes elaiosomes, fruits, pseudofruits or arils, as well as pappi. In a few plants, the diaspore is a tumbleweed and comprises most of the plant. Diaspores are common in weedy and ruderal species. Collectively, diaspores, seeds, and spores that have been modified for migration are known as ''disseminules''. __TOC__ Role in dispersal A diaspore of seed plus elaiosome is a common adaptation to seed dispersal by ants (myrmecochory). This is most notable in Australian and South African sclerophyll plant communities. Typically, ants carry the diaspore to their nest, where they may eat the elaiosome and discard the seed, and the seed may subsequently germinate. A diaspore of seed(s) plus fruit is common in plants dispersed by frugivores. Fruit-eating bats typically carry the diaspore to a favorite perch, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind
Wind is the natural movement of atmosphere of Earth, air or other gases relative to a planetary surface, planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hours, to global winds resulting from the difference in absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of solar energy between the climate zones on Earth. The study of wind is called anemology. The two main causes of large-scale atmospheric circulation are the differential heating between the equator and the poles, and the rotation of the planet (Coriolis effect). Within the tropics and subtropics, thermal low circulations over terrain and high plateaus can drive monsoon circulations. In coastal areas the sea breeze/land breeze cycle can define local winds; in areas that have variable terrain, mountain and valley breezes can prevail. Winds are commonly classified by their scale (spatial), spatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruderal Species
A ruderal species is a plant species that is first to colonize disturbed lands. The disturbance may be natural for example, wildfires or avalanchesor the consequences of human activities, such as construction ( of roads, of buildings, mining, etc.) or agriculture (abandoned fields, irrigation, etc.). The term '' ruderal'' originates from the Latin word '' rudus'', meaning " rubble". Ruderal species typically dominate the disturbed area for a few years, gradually losing the competition to other native species. However, in extreme disturbance circumstances, such as when the natural topsoil is covered with a foreign substance, a single-species ruderal community may become permanently established. In addition, some ruderal invasive species may have such a competitive advantage over the native species that they, too, may permanently prevent a disturbed area from returning to its original state despite natural topsoil. Features Features contributing to a species' success as ruder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
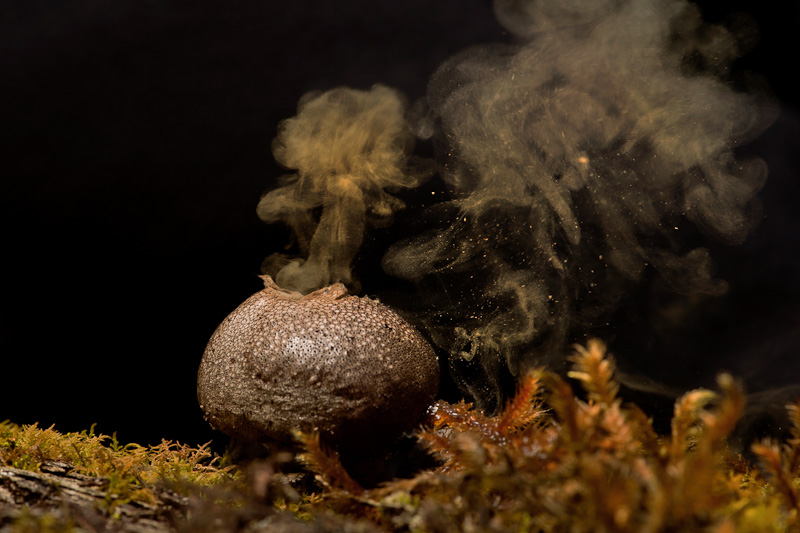
Puffballs
Puffballs are a type of fungus featuring a ball-shaped fruit body that (when mature) bursts on contact or impact, releasing a cloud of dust-like spores into the surrounding area. Puffballs belong to the division Basidiomycota and encompass several genera, including '' Calvatia'', ''Calbovista'' and ''Lycoperdon''. The puffballs were previously treated as a taxonomic group called the Gasteromycetes or Gasteromycetidae, but they are now known to be a polyphyletic assemblage. The distinguishing feature of all puffballs is that they do not have an open cap with spore-bearing gills. Instead, spores are produced internally, in a spheroidal fruit body called a ''gasterothecium'' (gasteroid 'stomach-like' basidiocarp). As the spores mature, they form a mass called a gleba in the centre of the fruitbody that is often of a distinctive color and texture. The basidiocarp remains closed until after the spores have been released from the basidia. Eventually, it develops an aperture, or dries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio State University
The Ohio State University (Ohio State or OSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Columbus, Ohio, United States. A member of the University System of Ohio, it was founded in 1870. It is one of the List of largest United States university campuses by enrollment, largest universities by enrollment in the United States, with nearly 50,000 undergraduate students and nearly 15,000 graduate students. The university consists of sixteen colleges and offers over 400 degree programs at the undergraduate and Graduate school, graduate levels. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". the university has an List of colleges and universities in the United States by endowment, endowment of $7.9 billion. Its athletic teams compete in NCAA Division I as the Ohio State Buckeyes as a member of the Big Ten Conference for the majority of fielde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salsola Tragus Tumbleweed
''Salsola'' is a genus of the subfamily Salsoloideae in the family Amaranthaceae. The genus ''sensu stricto'' is distributed in Australia, central and southwestern Asia, North Africa, and the Mediterranean. Common names of various members of this genus and related genera are saltwort (for their salt tolerance) and tumbleweed or roly-poly. The genus name ''Salsola'' is from the Latin , meaning . Description The species of ''Salsola'' are mostly subshrubs, shrubs, small trees, and rarely annuals. The leaves are mostly alternate, rarely opposite, simple, and entire. The bisexual flowers have five tepals and five stamens. The pistil ends in two stigmata. The fruit is spherical with a spiral embryo and no perisperm. Systematics The genus name ''Salsola'' was first published in 1753 by Linnaeus in ''Species Plantarum''. The type species is ''Salsola soda'' L. The genus ''Salsola'' belongs to the tribe Salsoleae ''s.s.'' of the subfamily Salsoloideae in the family Amaranthaceae. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
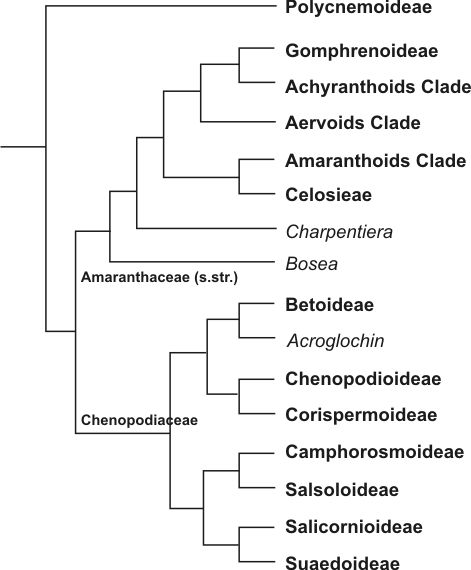
Amaranthaceae
Amaranthaceae ( ) is a family of flowering plants commonly known as the amaranth family, in reference to its type genus '' Amaranthus''. It includes the former goosefoot family Chenopodiaceae and contains about 165 genera and 2,040 species, making it the most species-rich lineage within its parent order, Caryophyllales. Description Most species in the Amaranthaceae are annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs; others are shrubs; very few species are vines or trees. Some species are succulent. Many species have stems with thickened nodes. The wood of the perennial stem has a typical "anomalous" secondary growth; only in subfamily Polycnemoideae is secondary growth normal. The leaves are simple and mostly alternate, sometimes opposite. They never possess stipules. They are flat or terete, and their shape is extremely variable, with entire or toothed margins. In some species, the leaves are reduced to minute scales. In most cases, neither basal nor terminal aggregations of leav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opportunism
300px, ''Opportunity Seized, Opportunity Missed'', engraving by Theodoor Galle, 1605 Opportunism is the practice of taking advantage of circumstances — with little regard for principles or with what the consequences are for others. Opportunist actions are expedient actions guided primarily by self-interested motives. The term can be applied to individual humans and living organisms, groups, organizations, styles, behaviors and trends. Opportunism or "opportunistic behaviour" is an important concept in such fields of study as biology, transaction cost economics, game theory, ethics, psychology, sociology and politics. Etymology In the early 19th century, the term "opportunist" as a noun or adjective was already known and used in several European languages, but initially, it rarely referred to political processes or to a political tendency. The English term "opportunism" is possibly borrowed originally from the Italian expression ''opportunismo''. In 19th-century Itali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, growing where it conflicts with human preferences, needs, or goals.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. Plants with characteristics that make them hazardous, aesthetically unappealing, difficult to control in managed environments, or otherwise unwanted in agriculture, farm land, Orchard, orchards, gardens, lawns, Park, parks, recreational spaces, residential and industrial areas, may all be considered weeds.Holzner, W., & Numata, M. (Eds.). (2013). ''Biology and ecology of weeds'' (Vol. 2). Springer Science & Business Media. The concept of weeds is particularly significant in agriculture, where the presence of weeds in fields used to grow crops may cause major losses in yields. Invasive species, plants introduced to an environment where their presence negatively impacts the overall functioning and biodiversity of the ecosystem, may also sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |