|
Truncated Icosidodecahedron
In geometry, a truncated icosidodecahedron, rhombitruncated icosidodecahedron,Wenninger Model Number 16 great rhombicosidodecahedron,Williams (Section 3-9, p. 94)Cromwell (p. 82) omnitruncated dodecahedron or omnitruncated icosahedronNorman Woodason Johnson, "The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs", 1966 is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen Convex polytope, convex, Isogonal figure, isogonal, non-Prism (geometry), prismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon, regular polygon Face (geometry), faces. It has 62 faces: 30 square (geometry), squares, 20 regular hexagons, and 12 regular decagons. It has the most edges and vertices of all Platonic solid, Platonic and Archimedean solids, though the snub dodecahedron has more faces. Of all vertex-transitive polyhedra, it occupies the largest percentage (89.80%) of the volume of a Circumscribed sphere, sphere in which it is inscribed, very narrowly beating the snub dodecahedron (89.63%) and small rhombicos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snub Dodecahedron
In geometry, the snub dodecahedron, or snub icosidodecahedron, is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex Isogonal figure, isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon Face (geometry), faces. The snub dodecahedron has 92 faces (the most of the 13 Archimedean solids): 12 are pentagons and the other 80 are equilateral triangles. It also has 150 edges, and 60 vertices. It has two distinct forms, which are mirror images (or "Chirality (mathematics), enantiomorphs") of each other. The union of both forms is a compound of two snub dodecahedra, and the convex hull of both forms is a truncated icosidodecahedron. Kepler first named it in Latin as dodecahedron simum in 1619 in his Harmonices Mundi. H. S. M. Coxeter, noting it could be derived equally from either the dodecahedron or the icosahedron, called it snub icosidodecahedron, with a vertical extended Schläfli symbol s \scriptstyle\begin 5 \\ 3 \end and flat Schläfli symbol Cartesian coord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''List of geometers, geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point (geometry), point, line (geometry), line, plane (geometry), plane, distance, angle, surface (mathematics), surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. Originally developed to model the physical world, geometry has applications in almost all sciences, and also in art, architecture, and other activities that are related to graphics. Geometry also has applications in areas of mathematics that are apparently unrelated. For example, methods of algebraic geometry are fundamental in Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem, Wiles's proof of Fermat's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
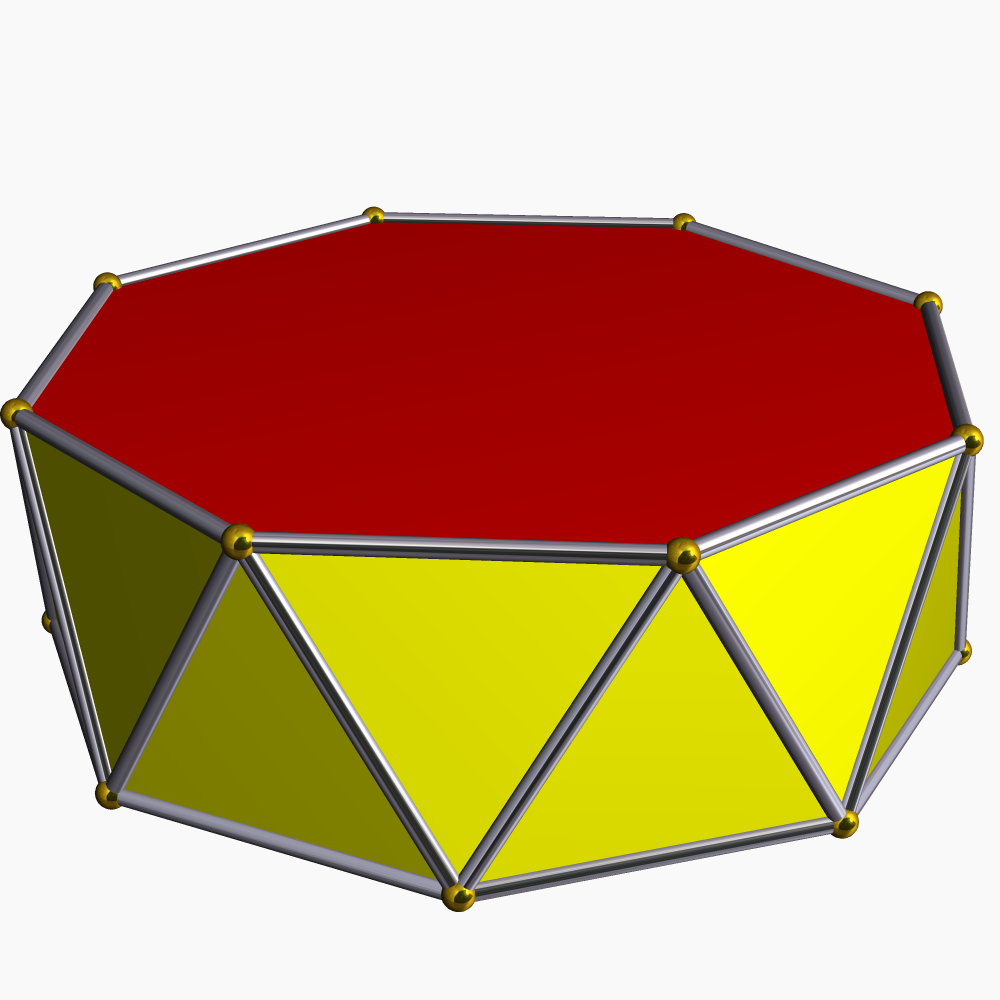
Antiprism
In geometry, an antiprism or is a polyhedron composed of two Parallel (geometry), parallel Euclidean group, direct copies (not mirror images) of an polygon, connected by an alternating band of triangles. They are represented by the Conway polyhedron notation, Conway notation . Antiprisms are a subclass of prismatoids, and are a (degenerate) type of snub polyhedron. Antiprisms are similar to Prism (geometry), prisms, except that the bases are twisted relatively to each other, and that the side faces (connecting the bases) are triangles, rather than quadrilaterals. The dual polyhedron of an -gonal antiprism is an -gonal trapezohedron. History In his 1619 book ''Harmonices Mundi'', Johannes Kepler observed the existence of the infinite family of antiprisms. This has conventionally been thought of as the first discovery of these shapes, but they may have been known earlier: an unsigned printing block for the net (geometry), net of a hexagonal antiprism has been attributed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Johnson (mathematician)
Norman Woodason Johnson (November 12, 1930 – July 13, 2017) was an American mathematician at Wheaton College, Norton, Massachusetts. Early life and education Norman Johnson was born on in Chicago. His father had a bookstore and published a local newspaper. Johnson earned his undergraduate mathematics degree in 1953 at Carleton College in Northfield, Minnesota followed by a master's degree from the University of Pittsburgh. After graduating in 1953, Johnson did alternative civilian service as a conscientious objector. He earned his PhD from the University of Toronto in 1966 with a dissertation title of ''The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs'' under the supervision of H. S. M. Coxeter. From there, he accepted a position in the Mathematics Department of Wheaton College in Massachusetts and taught until his retirement in 1998. Career In 1966, he enumerated 92 convex non-uniform polyhedra with regular faces. Victor Zalgaller later proved (1969) that Johnson's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnitruncation (geometry)
In geometry, an omnitruncation of a convex polytope is a simple polytope of the same dimension, having a vertex for each flag of the original polytope and a facet for each face of any dimension of the original polytope. Omnitruncation is the dual operation to barycentric subdivision. Because the barycentric subdivision of any polytope can be realized as another polytope, the same is true for the omnitruncation of any polytope. When omnitruncation is applied to a regular polytope (or honeycomb) it can be described geometrically as a Wythoff construction that creates a maximum number of facets. It is represented in a Coxeter–Dynkin diagram with all nodes ringed. It is a ''shortcut'' term which has a different meaning in progressively-higher-dimensional polytopes: * Uniform polytope truncation operators ** For regular polygons: An ordinary truncation, t_\ = t\ = \. *** Coxeter-Dynkin diagram ** For uniform polyhedra (3-polytopes): A cantitruncation, t_\ = tr\. (Application o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Williams (geometer)
Robert Edward Williams (born 1942) is an American designer, mathematician, and architect. He is noted for books on the geometry of natural structure, the discovery of a new space-filling polyhedron, the development of theoretical principles of Catenatic Geometry, and the invention of the ''Ars-Vivant Wild-life Protector System'' for repopulating the Western Mojave Desert in California, USA with desert tortoises. Biography—life, theories, and work Robert Williams was born in Cincinnati, Ohio, the son of Robert Finley Williams and Edna Rita Brotherton. His father was the oldest member of the Williams Brothers, a quartet of musical entertainers, who appeared on recordings, radio, and television, from the late 1930s to the present. Williams's work was originally inspired by the design principles in natural structure systems promoted by R. Buckminster Fuller. He was introduced to the work of Fuller by designer Peter Pearce in 1963. He finished graduate studies in structural desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnus Wenninger
Father Magnus J. Wenninger OSB (October 31, 1919Banchoff (2002)– February 17, 2017) was an American mathematician who worked on constructing polyhedron models, and wrote the first book on their construction. Early life and education Born to German immigrants in Park Falls, Wisconsin, Joseph Wenninger always knew he was going to be a priest. From an early age, it was understood that his brother Heinie would take after their father and become a baker, and that Joe, as he was then known, would go into the priesthood. When Wenninger was thirteen, after graduating from the parochial school in Park Falls, Wisconsin, his parents saw an advertisement in the German newspaper ''Der Wanderer'' that would help to shape the rest of his life. The ad was for a preparatory school in Collegeville, Minnesota, associated with the Benedictine St. John's University. While admitting to feeling homesick at first, Wenninger quickly made friends and, after a year, knew that this was where he nee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topologically
Topology (from the Greek words , and ) is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties of a geometric object that are preserved under continuous deformations, such as stretching, twisting, crumpling, and bending; that is, without closing holes, opening holes, tearing, gluing, or passing through itself. A topological space is a set endowed with a structure, called a ''topology'', which allows defining continuous deformation of subspaces, and, more generally, all kinds of continuity. Euclidean spaces, and, more generally, metric spaces are examples of topological spaces, as any distance or metric defines a topology. The deformations that are considered in topology are homeomorphisms and homotopies. A property that is invariant under such deformations is a topological property. The following are basic examples of topological properties: the dimension, which allows distinguishing between a line and a surface; compactness, which allows distinguishing between a line a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square
In geometry, a square is a regular polygon, regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal sides. As with all rectangles, a square's angles are right angles (90 degree (angle), degrees, or Pi, /2 radians), making adjacent sides perpendicular. The area of a square is the side length multiplied by itself, and so in algebra, multiplying a number by itself is called square (algebra), squaring. Equal squares can tile the plane edge-to-edge in the square tiling. Square tilings are ubiquitous in tiled floors and walls, graph paper, image pixels, and game boards. Square shapes are also often seen in building floor plans, origami paper, food servings, in graphic design and heraldry, and in instant photos and fine art. The formula for the area of a square forms the basis of the calculation of area and motivates the search for methods for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectangle
In Euclidean geometry, Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is a Rectilinear polygon, rectilinear convex polygon or a quadrilateral with four right angles. It can also be defined as: an equiangular quadrilateral, since equiangular means that all of its angles are equal (360°/4 = 90°); or a parallelogram containing a right angle. A rectangle with four sides of equal length is a ''square''. The term "wikt:oblong, oblong" is used to refer to a non-square rectangle. A rectangle with Vertex (geometry), vertices ''ABCD'' would be denoted as . The word rectangle comes from the Latin ''rectangulus'', which is a combination of ''rectus'' (as an adjective, right, proper) and ''angulus'' (angle). A #Crossed rectangles, crossed rectangle is a crossed (self-intersecting) quadrilateral which consists of two opposite sides of a rectangle along with the two diagonals (therefore only two sides are parallel). It is a special case of an antiparallelogram, and its angles are not right angles an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icosidodecahedron
In geometry, an icosidodecahedron or pentagonal gyrobirotunda is a polyhedron with twenty (''icosi-'') triangular faces and twelve (''dodeca-'') pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical Vertex (geometry), vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon. As such, it is one of the Archimedean solids and more particularly, a quasiregular polyhedron. Construction One way to construct the icosidodecahedron is to start with two pentagonal rotunda by attaching them to their bases. These rotundas cover their decagonal base so that the resulting polyhedron has 32 faces, 30 vertices, and 60 edges. This construction is similar to one of the Johnson solids, the pentagonal orthobirotunda. The difference is that the icosidodecahedron is constructed by twisting its rotundas by 36°, a process known as gyration, resulting in the pentagonal face connecting to the triangular one. The icosidodecahedr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truncation (geometry)
In geometry, a truncation is an operation in any dimension that cuts polytope vertices, creating a new Facet (geometry), facet in place of each vertex. The term originates from Kepler's names for the Archimedean solids. Uniform truncation In general any polyhedron (or polytope) can also be truncated with a degree of freedom as to how deep the cut is, as shown in Conway polyhedron notation truncation operation. A special kind of truncation, usually implied, is a uniform truncation, a truncation operator applied to a regular polyhedron (or regular polytope) which creates a resulting uniform polyhedron (uniform polytope) with equal edge lengths. There are no degrees of freedom, and it represents a fixed geometric, just like the regular polyhedra. In general all single ringed uniform polytopes have a uniform truncation. For example, the icosidodecahedron, represented as Schläfli symbols r or \begin 5 \\ 3 \end, and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram or has a uniform truncation, the truncate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |