|
Triptans
Triptans are a family of tryptamine-based drugs used as abortive medication in the treatment of migraines and cluster headaches. This drug class was first commercially introduced in the 1990s. While effective at treating individual headaches, they do not provide preventive treatment and are not considered a cure. They are not effective for the treatment of tension–type headache, except in persons who also experience migraines. Triptans do not relieve other kinds of pain. The drugs of this class act as agonists for serotonin 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors at blood vessels and nerve endings in the brain. The first clinically available triptan was sumatriptan, which has been marketed since 1991. Triptans have largely replaced ergotamines, an older class of medications used to relieve migraine and cluster headaches. Medical uses Migraine Triptans are used for the treatment of severe migraine attacks or those that do not respond to NSAIDs or other over-the-counter drugs. Triptan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may include vomiting, cognitive dysfunction, allodynia, and dizziness. Exacerbation or worsening of headache symptoms during physical activity is another distinguishing feature. Up to one-third of people with migraine experience aura, a premonitory period of sensory disturbance widely accepted to be caused by cortical spreading depression at the onset of a migraine attack. Although primarily considered to be a headache disorder, migraine is highly heterogenous in its clinical presentation and is better thought of as a spectrum disease rather than a distinct clinical entity. Disease burden can range from episodic discrete attacks to chronic disease. Migraine is believed to be caused by a mixture of environmental and genetic factors that influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
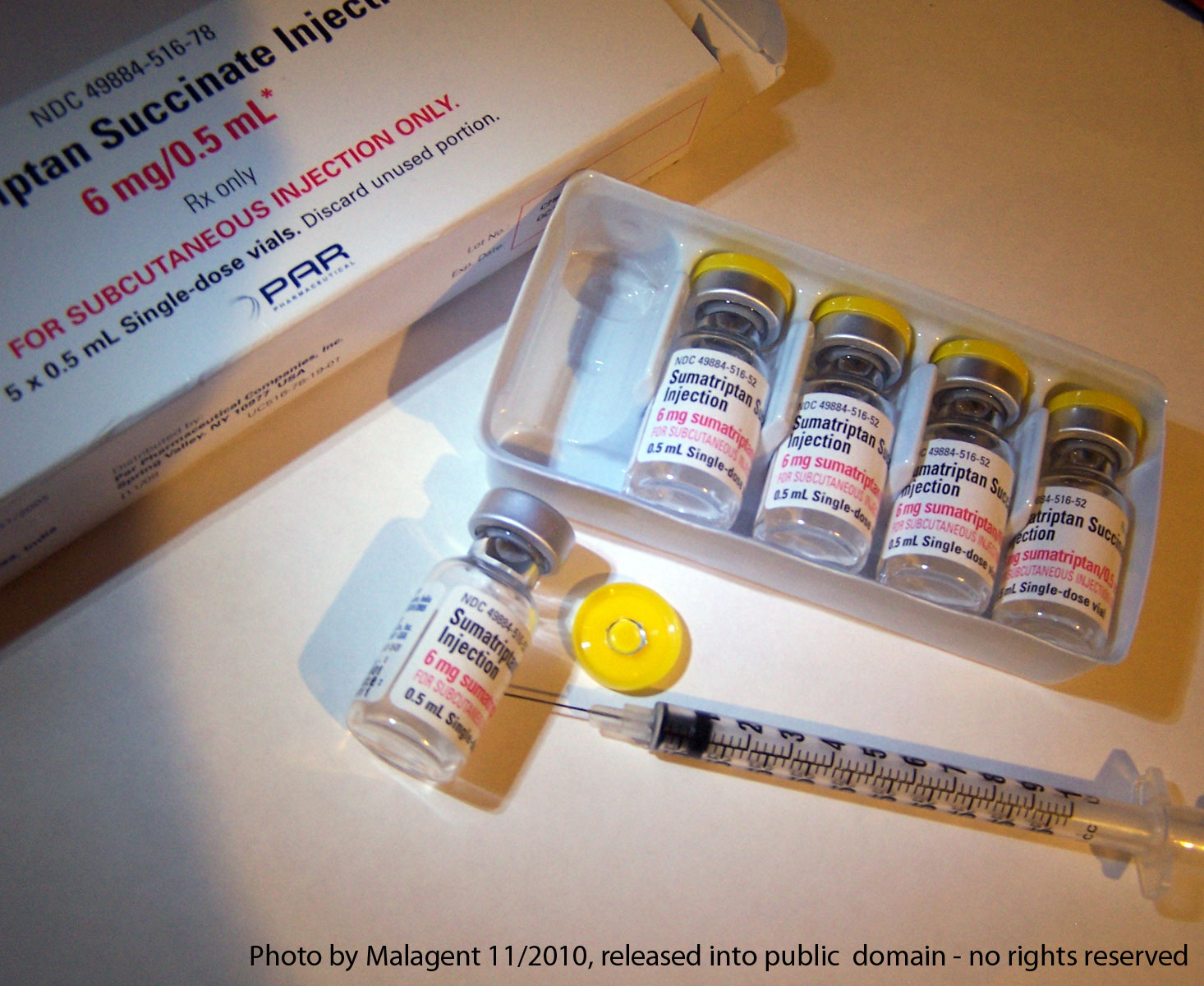
Sumatriptan
Sumatriptan, sold under the brand name Imitrex among others, is a medication used to treat migraine headaches and cluster headaches. It is taken Oral administration, orally, Nasal administration, intranasally, or by Subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous Injection under the skin, injection. Therapeutic effects generally occur within three hours. Its primary effect as a serotonin 5-HT1B, 5-HT1B/5-HT1D receptor, 5-HT1D receptor agonist can create common side effects such as chest pressure, fatigue, vomiting, tingling, and vertigo. Serious side effects may include serotonin syndrome, heart attack, stroke, and seizures. With excessive use, medication overuse headaches may occur. It is unclear if use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe. The mechanism of action is not entirely clear. It is in the triptan class of medications. Sumatriptan was patented in 1982 and approved for medical use in 1991. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may include vomiting, cognitive dysfunction, allodynia, and dizziness. Exacerbation or worsening of headache symptoms during physical activity is another distinguishing feature. Up to one-third of people with migraine experience aura, a premonitory period of sensory disturbance widely accepted to be caused by cortical spreading depression at the onset of a migraine attack. Although primarily considered to be a headache disorder, migraine is highly heterogenous in its clinical presentation and is better thought of as a spectrum disease rather than a distinct clinical entity. Disease burden can range from episodic discrete attacks to chronic disease. Migraine is believed to be caused by a mixture of environmental and genetic factors that influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naratriptan Structure
Naratriptan (trade names include Amerge) is a triptan drug marketed by GlaxoSmithKline and is used for the treatment of migraine headaches. It is a selective 5-HT1 receptor subtype agonist. It was patented in 1987 and approved for medical use in 1997. Medical uses Naratriptan is used for the treatment of the acute migraine attacks and the symptoms of migraine, including severe, throbbing headaches that sometimes are accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to sound or light. Efficacy A meta-analysis of 53 clinical trials has shown that all triptans are effective for treating migraine at marketed doses and that naratriptan, although less effective than sumatriptan and rizatriptan was more effective than placebo in reducing migraine symptoms at two hours and efficacy was demonstrated in almost two thirds of subjects after four hours of treatment. Side effects Side effects are similar to other triptan medications, with the incidence of side effects reportedly being lower than suma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumatriptan
Sumatriptan, sold under the brand name Imitrex among others, is a medication used to treat migraine headaches and cluster headaches. It is taken Oral administration, orally, Nasal administration, intranasally, or by Subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous Injection under the skin, injection. Therapeutic effects generally occur within three hours. Its primary effect as a serotonin 5-HT1B, 5-HT1B/5-HT1D receptor, 5-HT1D receptor agonist can create common side effects such as chest pressure, fatigue, vomiting, tingling, and vertigo. Serious side effects may include serotonin syndrome, heart attack, stroke, and seizures. With excessive use, medication overuse headaches may occur. It is unclear if use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is safe. The mechanism of action is not entirely clear. It is in the triptan class of medications. Sumatriptan was patented in 1982 and approved for medical use in 1991. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naratriptan
Naratriptan (trade names include Amerge) is a triptan drug marketed by GlaxoSmithKline and is used for the treatment of migraine headaches. It is a selective 5-HT1 receptor subtype agonist. It was patented in 1987 and approved for medical use in 1997. Medical uses Naratriptan is used for the treatment of the acute migraine attacks and the symptoms of migraine, including severe, throbbing headaches that sometimes are accompanied by nausea and sensitivity to sound or light. Efficacy A meta-analysis of 53 clinical trials has shown that all triptans are effective for treating migraine at marketed doses and that naratriptan, although less effective than sumatriptan and rizatriptan was more effective than placebo in reducing migraine symptoms at two hours and efficacy was demonstrated in almost two thirds of subjects after four hours of treatment. Side effects Side effects are similar to other triptan medications, with the incidence of side effects reportedly being lower than suma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rizatriptan
Rizatriptan, sold under the brand name Maxalt among others, is a medication used for the treatment of migraine headaches. It is taken by mouth. It can also be applied on the tongue. It is a serotonin (5-HT) 1B/1D receptor agonist (triptan). Common side effects include chest pain, dizziness, dry mouth, and tingling. Other side effects may include myocardial infarction, stroke, high blood pressure, serotonin syndrome, and anaphylaxis. Excessive use may result in medication overuse headaches. Use is not recommended during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended within 24 hours after taking a dose. Rizatriptan is in the triptan class and is believed to work by activating the 5-HT1 receptor. Rizatriptan was patented in 1991 and came into medical use in 1998. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 190th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than two million prescriptions. Rizatriptan is available in combination with melox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almotriptan
Almotriptan (trade name Axert and others) is a triptan medication discovered and developed by Almirall for the treatment of heavy migraine headache. It was patented in 1992 and approved for medical use in 2000. Medical uses Almotriptan is prescribed to treat the acute headache phase of migraine attacks with or without aura. Almotriptan is approved in the US for the treatment of migraine in adolescent from 12 to 17 years of age. Efficacy The efficacy and tolerability of almotriptan has been studied in numerous randomised, controlled trials totaling more than 4800 adults with either moderate or severe attacks of migraine. Its efficacy is significantly more effective than placebo and alleviates nausea, photophobia and phonophobia linked to migraine attacks. Almotriptan has similar efficacy as a standard dose of sumatriptan, another triptan drug, and fewer adverse effects. Contraindications As with other triptans, almotriptan should not be used in patients with a history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. In the CNS, serotonin regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. Most of the body's serotonin—about 90%—is synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract by enterochromaffin cells, where it regulates intestinal movements. It is also produced in smaller amounts in the brainstem's raphe nuclei, the skin's Merkel cells, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, and taste receptor cells of the tongue. Once secreted, serotonin is taken up by platelets in the blood, which release it during clotting to promote vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation. Around 8% of the body's serotonin is stored in platelets, and 1–2% is found in the CNS. Serotonin acts as both a vasoconstrictor and vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole—a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate serotonin receptors and trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |