|
Trichinosis
Trichinosis, also known as trichinellosis, is a parasitic disease caused by roundworms of the '' Trichinella'' genus. During the initial infection, invasion of the intestines can result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Migration of larvae to muscle, which occurs about a week after being infected, can cause swelling of the face, inflammation of the whites of the eyes, fever, muscle pains, and a rash. Minor infection may be without symptoms. Complications may include inflammation of heart muscle, central nervous system involvement, and inflammation of the lungs. Trichinosis is mainly spread when undercooked meat containing ''Trichinella'' cysts is eaten. Wild meat is more likely to contain the parasite. In North America this is most often bear, but infection can also occur from pork, boar, and dog meat. Several species of ''Trichinella'' can cause disease, with ''T. spiralis'' being the most common. After the infected meat has been eaten, the larvae are release ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
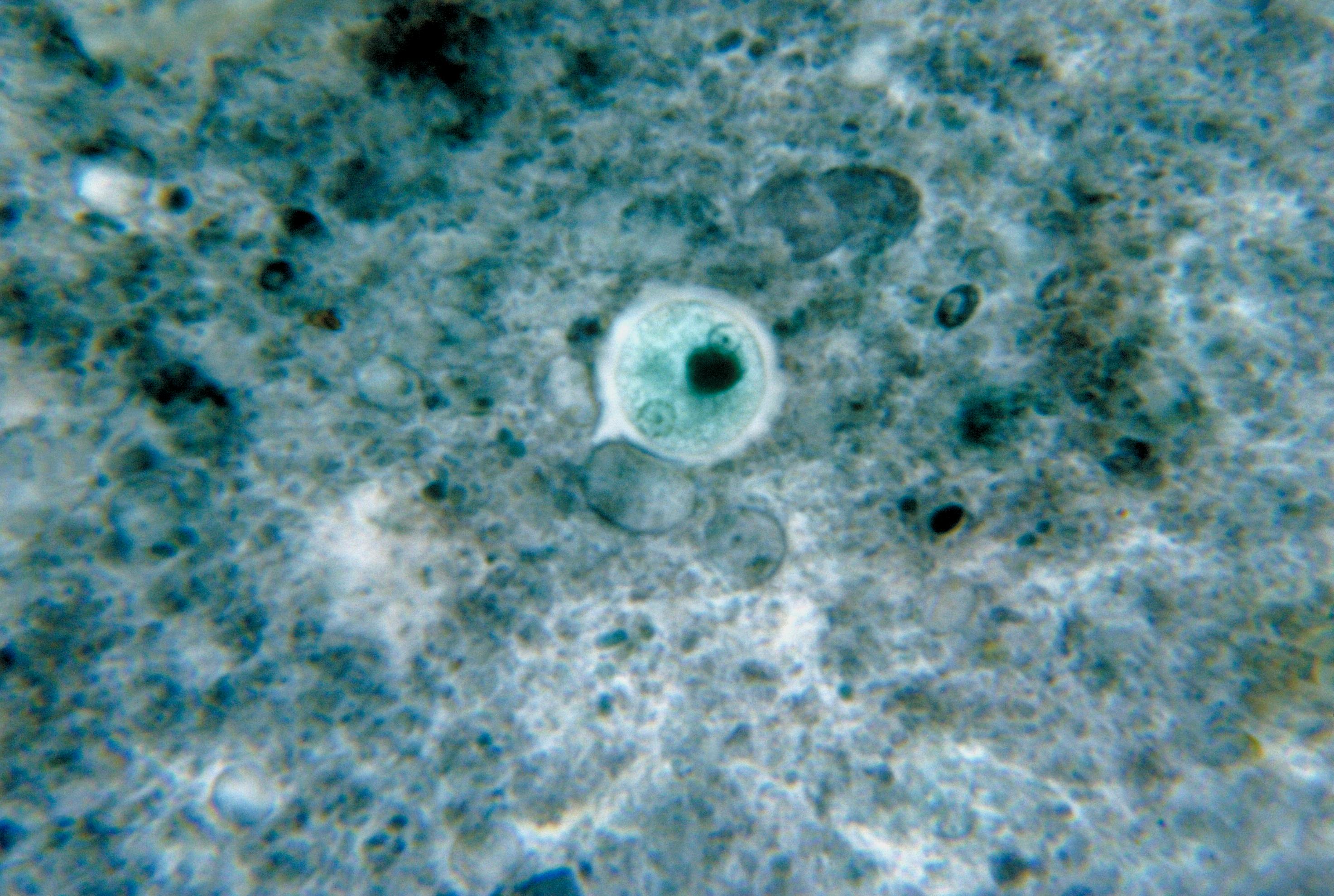
Trichinella Spiralis
''Trichinella spiralis'' is a viviparous nematode parasite, occurring in rodents, pigs, bears, hyenas and humans, and is responsible for the disease trichinosis. It is sometimes referred to as the "pork worm" due to it being typically encountered in undercooked pork products. It should not be confused with the distantly related pork tapeworm. Description ''Trichinella'' species, the smallest nematode parasite of humans, has an unusual life cycle, and are one of the most widespread and clinically important parasites in the world. The small adult worms mature in the small intestine of a definitive host, such as a pig. Each adult female produces batches of live larvae, which bore through the intestinal wall, enters the blood (to feed on it) and lymphatic system, and are carried to striated muscle. Once in the muscle, they encyst, or become enclosed in a capsule. Humans can become infected by eating infected pork, horsemeat, or wild carnivores such as fox, cat, hyena or bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Pains
Myalgia or muscle pain is a painful sensation evolving from muscle tissue. It is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another likely cause is viral infection, especially when there has been no injury. Long-lasting myalgia can be caused by metabolic myopathy, some nutritional deficiencies, ME/CFS, fibromyalgia, and amplified musculoskeletal pain syndrome. Causes The most common causes of myalgia are overuse, injury, and strain. Myalgia might also be caused by allergies, diseases, medications, or as a response to a vaccination. Dehydration at times results in muscle pain as well, especially for people involved in extensive physical activities such as workout. Muscle pain is also a common symptom in a variety of diseases, including infectious diseases, such as influenza, muscle abscesses, Lyme disease, malaria, trichinosis or poliomyelitis; autoimmune diseases, such as celiac disease, systemic l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematodes
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (helminths) are the cause of soil-transmitted helminthiases. They are classified along with arthropods, tardigrades and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa. Unlike the flatworms, nematodes have a tubular digestive system, with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species are uncertain. A 2013 survey of animal biodiversity suggested there are over 25,000. Estimates of the total number of extant species are subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trichinella
''Trichinella'' is the genus of parasitic roundworms of the phylum Nematoda that cause trichinosis (also known as trichinellosis). Members of this genus are often called trichinella or trichina worms. A characteristic of Nematoda is the one-way digestive tract, with a pseudocoelom (body cavity made up of only an ectoderm and endoderm). The genus was first recognised in a larval form in 1835. The L1 larvae live in a modified skeletal muscle cell. The adult worms occupy a membrane-bound portion of columnar epithelium, living as intramulticellular parasites of animals, including humans. Infections with this genus have been reported from more than 150 different naturally or experimentally infected hosts. It has been shown to have a worldwide distribution in domestic and/or sylvatic animals. ''Trichinella'' is the smallest human nematode parasite, yet it is also the largest of all intracellular parasites. Oral ingestion of cyst- or larvae-contaminated tissue is the usual route of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mebendazole
Mebendazole (MBZ), sold under the brand name Vermox among others, is a medication used to treat a number of parasitic worm infestations. This includes ascariasis, pinworm infection, hookworm infections, guinea worm infections and hydatid disease, among others. It has been used for treatment of giardiasis but is not a preferred agent. It is taken by mouth. Mebendazole is usually well tolerated. Common side effects include headache, vomiting, and ringing in the ears. If used at large doses it may cause bone marrow suppression. It is unclear if it is safe in pregnancy. Mebendazole is a broad-spectrum antihelminthic agent of the benzimidazole type. Mebendazole came into use in 1971, after it was developed by Janssen Pharmaceutica in Belgium. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Mebendazole is available as a generic medication. Medical use Mebendazole is a highly effective, broad-spectrum antihelmintic indicated for the treatment of nema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larvae
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect developmental biology, development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their Biological life cycle, life cycle. A larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterfly, butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. In the case of smaller primitive arachnids, the larval stage differs by having three instead of four pairs of legs. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of energy, and dehydration may also occur. This typically lasts less than two weeks. Although it is not related to influenza, in the U.S it is sometimes called the "stomach flu". Gastroenteritis is usually caused by viruses; however, gut bacteria, parasites, and fungus, fungi can also cause gastroenteritis. In children, rotavirus is the most common cause of severe disease. In adults, norovirus and ''Campylobacter'' are common causes. Eating improperly prepared food, drinking contaminated water or close contact with a person who is infected can #Transmission, spread the disease. Treatment is generally the same with or without a definitive diagnosis, so testing to confirm is usually not needed. For young children in impoverished countries, pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum, the shortest, is where preparation for absorption through small finger-like protrusions called intestinal villus, intestinal villi begins. The jejunum is specialized for the absorption through its lining by enterocytes: small nutrient particles which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Cyst
A microbial cyst is a resting or dormant stage of a microorganism, that can be thought of as a state of suspended animation in which the metabolic processes of the cell are slowed and the cell ceases all activities like feeding and locomotion. Many groups of single-celled, microscopic organisms, or microbes, possess the ability to enter this dormant state. Encystment, the process of cyst formation, can function as a method for dispersal and as a way for an organism to survive in unfavorable environmental conditions. These two functions can be combined when a microbe needs to be able to survive harsh conditions between habitable environments (such as between hosts) in order to disperse. Cysts can also be sites for nuclear reorganization and cell division, and in parasitic species they are often the infectious stage between hosts. When the encysted microbe reaches an environment favorable to its growth and survival, the cyst wall breaks down by a process known as excystation. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilateria, bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and Coelenterata, diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the Anatomical_terms_of_location#Rostral,_cranial,_and_caudal, rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain, though precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets. The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |