|
Triceps Brachii
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of three parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. All three heads cross the elbow joint. However, the long head also crosses the shoulder joint. The triceps muscle contracts when the elbow is straightened and expands when the elbow is bent. The long head gets a further contraction when the arm is behind the torso due to how it crosses the shoulder joint. It is the muscle principally responsible for extension of the elbow joint (straightening of the arm). Structure * The long head arises from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. It extends distally anterior to the teres minor and posterior to the teres major. * The medial head arises proximally in the humerus, just inferior to the groove of the radial nerve; from the dorsal (back) surface of the humerus; from the medial intermuscular septum; and its distal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraglenoid Tubercle Of Scapula
The infraglenoid tubercle is the part of the scapula from which the long head of the triceps brachii muscle originates. The infraglenoid tubercle is a tubercle located on the lateral part of the scapula, inferior to (below) the glenoid cavity The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word ''glenoid'' is pronounced or (both are common) and is from , "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a shallow, pyri .... The name infraglenoid tubercle refers to its location below the glenoid cavity. Function The infraglenoid tubercle is the origin of the long head of the triceps brachii muscle. It helps to stabilise the muscle origin. Additional images File:Infraglenoid tubercle of left scapula - animation.gif, Left scapula. Infraglenoid tubercle shown in red. File:Infraglenoid tubercle of scapula - animation01.gif, Animation. Infraglenoid tubercle shown in red. File:Infraglenoid tubercle of left sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synovial Bursa
A synovial bursa, usually simply bursa (: bursae or bursas), is a small fluid-filled sac lined by synovial membrane with an inner capillary layer of viscous synovial fluid (similar in consistency to that of a raw egg white). It provides a cushion between bones and tendons and/or muscles around a joint. This helps to reduce friction between the bones and allows free movement. Bursae are found around most major joints of the body. Structure Based on location, there are three types of bursa: subcutaneous, submuscular and subtendinous. A subcutaneous bursa is located between the skin and an underlying bone. It allows skin to move smoothly over the bone. Examples include the prepatellar bursa located over the kneecap and the olecranon bursa at the tip of the elbow. A submuscular bursa is found between a muscle and an underlying bone, or between adjacent muscles. These prevent rubbing of the muscle during movements. A large submuscular bursa, the trochanteric bursa, is found at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olecranon
The olecranon (, ), is a large, thick, curved bony process on the proximal, posterior end of the ulna. It forms the protruding part of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit (trochlear notch). The olecranon serves as a lever for the extensor muscles that straighten the elbow joint. Structure The olecranon is situated at the proximal end of the ulna, one of the two bones in the forearm. When the hand faces forward ( supination) the olecranon faces towards the back (posteriorly). It is bent forward at the summit so as to present a prominent lip which is received into the olecranon fossa of the humerus during extension of the forearm. Its base is contracted where it joins the body and the narrowest part of the upper end of the ulna. Its posterior surface, directed backward, is triangular, smooth, subcutaneous, and covered by a bursa. Its superior surface is of quadrilateral form, marked behind by a rough impression for the insertion of the triceps brachi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
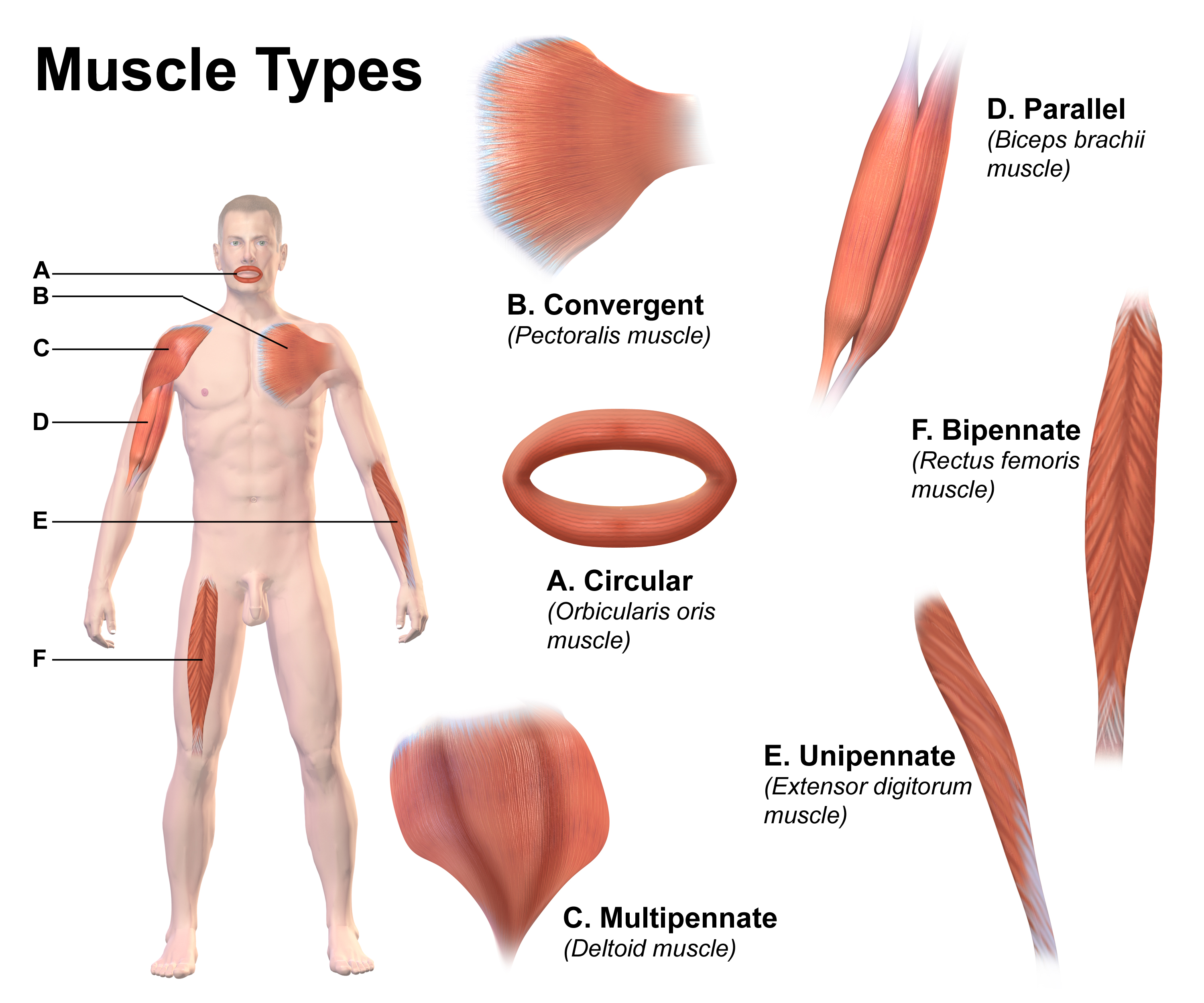
Skeletal Striated Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
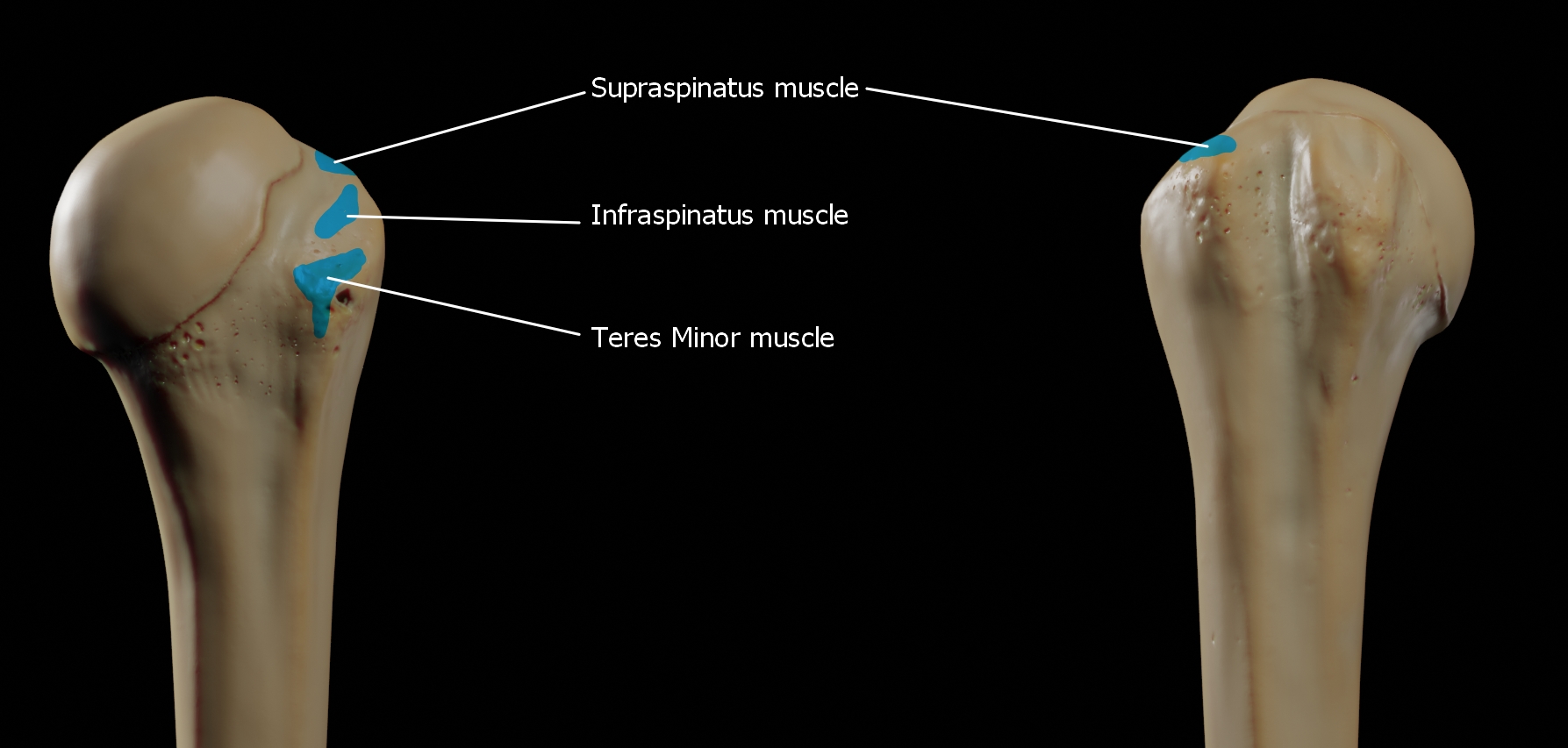
Greater Tubercle
The greater tubercle of the humerus is the outward part the upper end of that bone, adjacent to the large rounded prominence of the humerus head. It provides attachment points for the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor muscles, three of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, a muscle group that stabilizes the shoulder joint. In doing so the tubercle acts as a location for the transfer of forces from the rotator cuff muscles to the humerus. Structure The upper surface of the greater tubercle is rounded, and marked by three flat impressions: * the highest ("superior facet") gives insertion to the supraspinatus muscle. * the middle ("middle facet") gives insertion to the infraspinatus muscle. * the lowest ("inferior facet"), and the body of the bone for about 2.5 cm, gives insertion to the teres minor muscle. The lateral surface of the greater tubercle is convex, rough, and continuous with the lateral surface of the body of the humerus. It can be describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Intermuscular Septum Of Arm
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may also refer to: Biology and healthcare * Lateral (anatomy), a term of location meaning "towards the side" * Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle, an intrinsic muscle of the larynx * Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure to release tight capsular structures Other uses * ''Lateral'', a digital journal and production of the Cultural Studies Association * ''Lateral'', a podcast by English YouTuber and web developer Tom Scott * Lateral canal, a canal built along the same right-of-way as an existing stream * Lateral consonant, a consonant in which the airstream proceeds along one or both of the sides of the tongue * Lateral mark, a sea mark used in maritime pilotage to indicate the edge of a channel * Lateral modes, an aspect of dynamic stability and control in the field of aircraft flight dynamics * Lateral pass, a non-advancing move in gridiron football * Lateral release (phonetics), the release of a plosive consonant into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Intermuscular Septum Of Arm
Medial may refer to: Mathematics * Medial magma, a mathematical identity in algebra Geometry * Medial axis, in geometry the set of all points having more than one closest point on an object's boundary * Medial graph, another graph that represents the adjacencies between edges in the faces of a plane graph * Medial triangle, the triangle whose vertices lie at the midpoints of an enclosing triangle's sides * Polyhedra: ** Medial deltoidal hexecontahedron ** Medial disdyakis triacontahedron ** Medial hexagonal hexecontahedron ** Medial icosacronic hexecontahedron ** Medial inverted pentagonal hexecontahedron ** Medial pentagonal hexecontahedron ** Medial rhombic triacontahedron Linguistics * A medial sound or letter is one that is found in the middle of a larger unit (like a word) ** Syllable medial, a segment located between the onset and the rime of a syllable * In the older literature, a term for the voiced stops (like ''b'', ''d'', ''g'') * Medial or second person d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Sulcus
The radial groove (also known as the musculospiral groove, radial sulcus, or spiral groove) is a broad but shallow oblique depression for the radial nerve and deep brachial artery. It is located on the center of the lateral border of the humerus bone. It is situated alongside the posterior margin of the deltoid tuberosity, ending at its inferior margin. Although it provides protection to the radial nerve, it is often involved in compressions on the nerve (due to external pressure due to surgery) that can cause radial nerve palsy. See also * Intertubercular groove * Triceps brachii muscle The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of three parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. All three heads cross the elbow jo ... Additional images File:Gray413_color.png, Cross-section through the middle of upper arm. File:Gray525.png, The brachial artery. File:Gray818. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humerus
The humerus (; : humeri) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius (bone), radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity of humerus, upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercles, sometimes called tuberosities). The body of humerus, body is cylindrical in its upper portion, and more prism (geometry), prismatic below. The lower extremity of humerus, lower extremity consists of 2 epicondyles, 2 processes (trochlea of the humerus, trochlea and capitulum of the humerus, capitulum), and 3 fossae (radial fossa, coronoid fossa, and olecranon fossa). As well as its true anatomical neck, the constriction below the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus is referred to as its Surgical neck of the humerus, surgical neck due to its tendency to fracture, thus often becoming the focus of surgeons. Etymology The word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thieme Medical Publishers
Thieme Medical Publishers is a German academic publishing, medical and science publisher in the Thieme Publishing Group. It produces professional journals, textbooks, atlases, monographs and reference books in both German and English covering a variety of medical specialties, including neurosurgery, orthopaedics, endocrinology, urology, radiology, anatomy, chemistry, otolaryngology, ophthalmology, audiology and speech-language pathology, complementary medicine, complementary and alternative medicine. Thieme has more than 1,000 employees and maintains offices in seven cities worldwide, including New York City, Beijing, Delhi, Stuttgart, and three other cities in Germany. History Georg Thieme Verlag was founded in 1886 in Leipzig, Germany, by Georg Thieme when he was 26 years old. Thieme remains privately held and family-owned. The company received some early success in 1896 by publishing Wilhelm Röntgen's famous picture of his wife's hand in what is still one of Thieme's and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |