|
Tool Steel
Tool steel is any of various carbon steels and alloy steels that are particularly well-suited to be made into tools and tooling, including cutting tools, dies, hand tools, knives, and others. Their suitability comes from their distinctive hardness, resistance to abrasion and deformation, and their ability to hold a cutting edge at elevated temperatures. As a result, tool steels are suited for use in the shaping of other materials, as for example in cutting, machining, stamping, or forging. Tool steels have a carbon content between 0.4% and 1.5%. The presence of carbides in their matrix plays the dominant role in the qualities of tool steel. The four major alloying elements that form carbides in tool steel are: tungsten, chromium, vanadium and molybdenum. The rate of dissolution of the different carbides into the austenite form of the iron determines the high-temperature performance of steel (slower is better, making for a heat-resistant steel). Proper heat treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tool Steels, Data And Tables Appertaining To Electric Tool Steels (1918) (14597078767)
A tool is an object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates back hundreds of millennia, have been observed using tools to make other tools. Early human tools, made of such materials as stone, bone, and wood, were used for the preparation of food, hunting, the manufacture of weapons, and the working of materials to produce clothing and useful artifacts and crafts such as pottery, along with the construction of housing, businesses, infrastructure, and transportation. The development of metalworking made additional types of tools possible. Harnessing energy sources, such as animal power, wind, or steam, allowed increasingly complex tools to produce an even larger range of items, with the Industrial Revolution marking an inflection point in the use of tools. The introduction of widespread automation i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer (passivation (chemistry), passivation) somewhat stabilizes the free metal against further oxidation. Spain, Spanish-Mexico, Mexican scientist Andrés Manuel del Río discovered compounds of vanadium in 1801 by analyzing a new lead-bearing mineral he called "brown lead". Though he initially presumed its qualities were due to the presence of a new element, he was later erroneously convinced by French chemist Hippolyte Victor Collet-Descotils that the element was just chromium. Then in 1830, Nils Gabriel Sefström generated chlorides of vanadium, thus proving there was a new element, and named it "vanadium" after the Scandinavian goddess of beauty and fertility, Vanadís (Freyja). The name was based on the wide range of colors fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
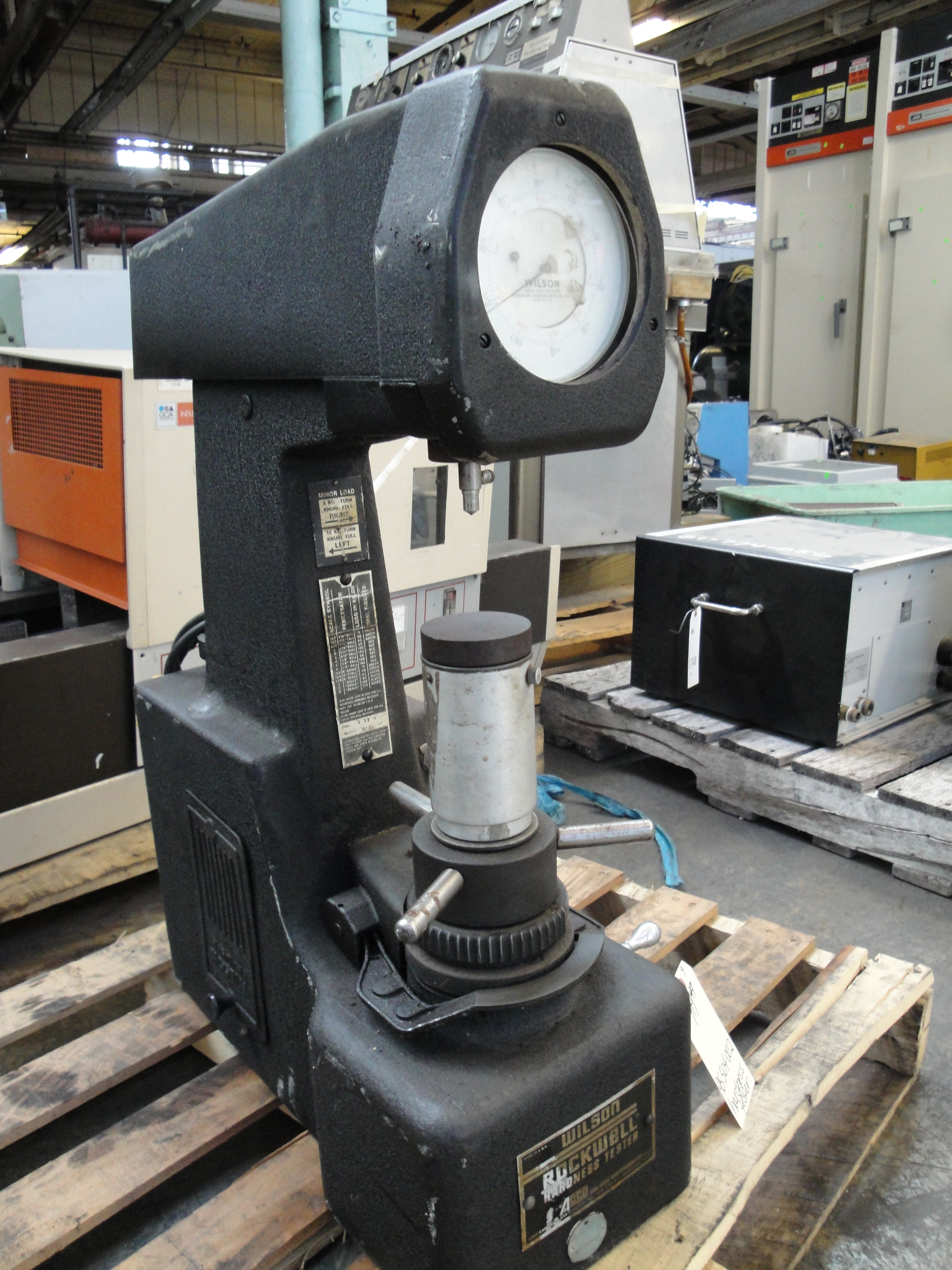
Rockwell Scale
The Rockwell hardness test is a hardness test based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different loads or indenters. The result is a dimensionless number noted as HRA, HRB, HRC, etc., where the last letter is the respective Rockwell scale. Larger numbers correspond to harder materials. When testing metals, indentation hardness correlates linearly with tensile strength. History The differential depth hardness measurement was conceived in 1908 by Viennese professor Paul Ludwik in his book ''Die Kegelprobe'' (crudely, "the cone test"). The differential-depth method subtracted out the errors associated with the mechanical imperfections of the system, such as backlash and surface imperfections. The Brinell scale, Brinell hardness test, invented in Sweden, wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardenability
Jominy test dimensioning Jominy test apparatus Used Jominy test-piece Hardenability is the depth to which a steel is hardened after putting it through a heat treatment process. It should not be confused with hardness, which is a measure of a sample's resistance to indentation or scratching. It is an important property for welding Welding is a fabrication (metal), fabrication process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, primarily by using high temperature to melting, melt the parts together and allow them to cool, causing Fusion welding, fusion. Co ..., since it is inversely proportional to weldability, that is, the ease of welding a material. Process When a hot steel work-piece is quenched, the area in contact with the water immediately cools and its temperature equilibrates with the quenching medium. The inner depths of the material however, do not cool so rapidly, and in work-pieces that are large, the cooling rate may be slow enough to allow th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
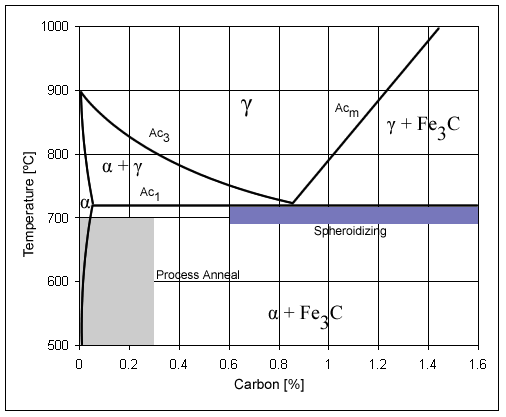
Plain-carbon Steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states: * no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, zirconium, or any other element to be added to obtain a desired alloying effect; * the specified minimum for copper does not exceed 0.40%; * or the specified maximum for any of the following elements does not exceed: manganese 1.65%; silicon 0.60%; and copper 0.60%. As the carbon content percentage rises, steel has the ability to become harder and stronger through heat treating; however, it becomes less ductile. Regardless of the heat treatment, a higher carbon content reduces weldability. In carbon steels, the higher carbon content lowers the melting point. The term may be used to reference steel that is not stainless steel; in this use carbon steel may include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
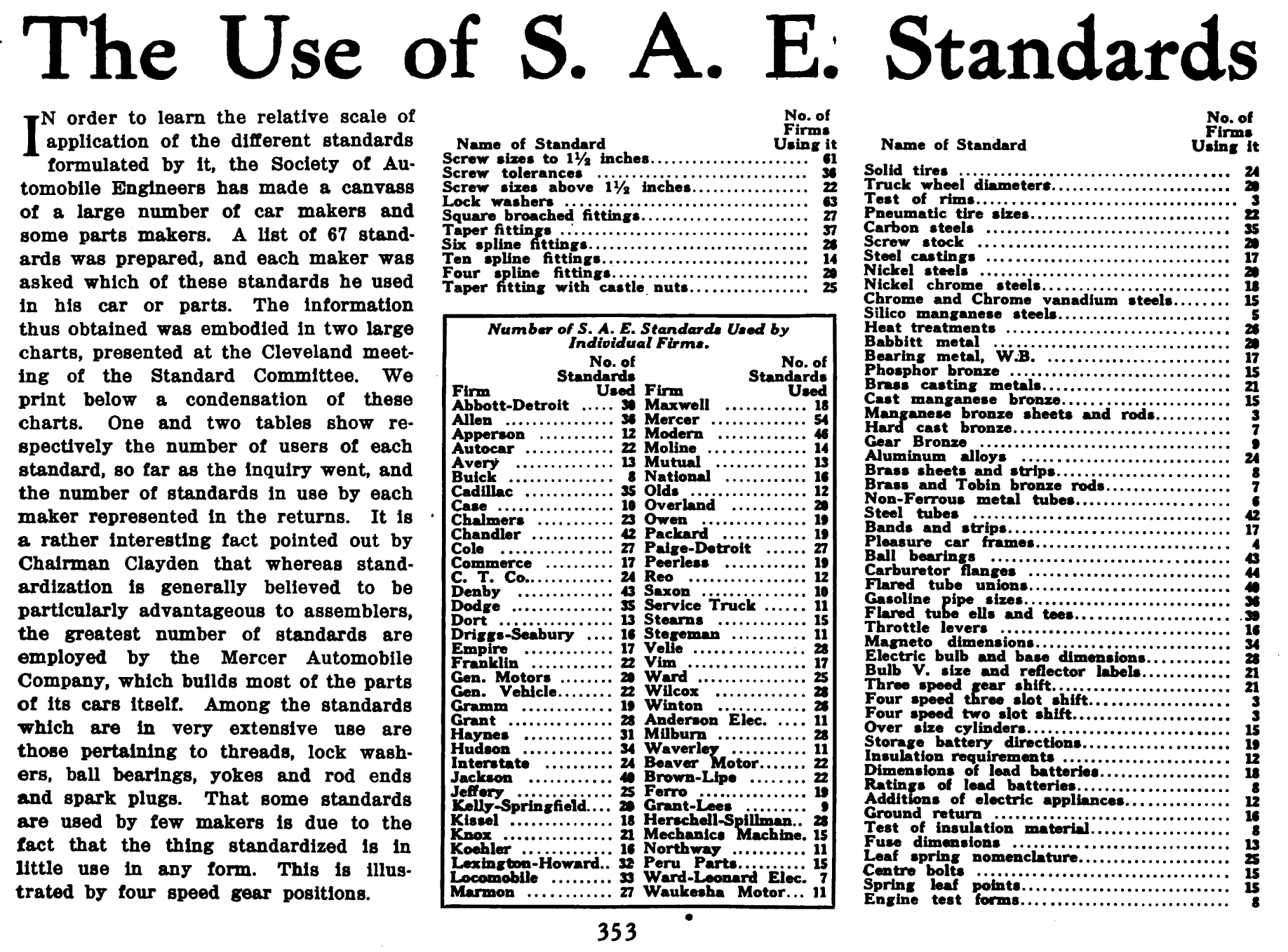
Society Of Automotive Engineers
SAE International is a global professional association and standards organization based in Warrendale, Pennsylvania, United States. Formerly the Society of Automotive Engineers, the organization adopted its current name in 2006 to reflect both its international membership and the increased scope of its activities beyond automotive engineering and the automotive industry to include aerospace and other transport industries, as well as commercial vehicles including autonomous vehicles such as self-driving cars, trucks, surface vessels, drones, and related technologies. SAE International has over 138,000 global members. Membership is granted to individuals, rather than companies. Aside from its standardization efforts, SAE International also devotes resources to projects and programs in STEM education, professional certification, and collegiate design competitions. History In the early 1900s there were dozens of automobile manufacturers in the United States, and many more w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Iron And Steel Institute
The American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) is a trade association of North American steel producers. Including its predecessor organizations, it is one of the oldest trade associations in the United States, dating back to 1855. It assumed its present form in 1908, with Judge Elbert H. Gary, chairman of the United States Steel Corporation, as its first president. Its development was in response to the need for a cooperative agency in the iron and steel industry for collecting and disseminating statistics and information, carrying on investigations, providing a forum for the discussion of problems and generally advancing the interests of the industry. Stainless steel numbering system The AISI maintained a numbering system for wrought stainless steel in which the three digits indicate the various compositions. The 200 and 300 series are generally austenitic stainless steels, whereas the 400 series are either ferritic or martensitic. Some of the grades have a one-letter or two-le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injection Molding
Injection moulding (U.S. spelling: injection molding) is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for which the process is called die-casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (using a helical screw), and injected into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coining (metalworking)
Coining is a form of precision stamping in which a workpiece is subjected to a sufficiently high stress to induce plastic flow on the surface of the material. A beneficial feature is that in some metals, the plastic flow reduces surface grain size, and work hardens the surface, while the material deeper in the part retains its toughness and ductility. The term comes from the initial use of the process: manufacturing of coins. Coining is used to manufacture parts for all industries and is commonly used when high relief or very fine features are required. For example, it is used to produce coins, badges, buttons, precision-energy springs and precision parts with small or polished surface features. Coining is a cold working process similar in other respects to forging, which takes place at elevated temperature; it uses a great deal of force to elastically deform a workpiece, so that it conforms to a die. Coining can be done using a gear driven press, a mechanical press, or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have properties that differ from those of the pure elements from which they are made. The vast majority of metals used for commercial purposes are alloyed to improve their properties or behavior, such as increased strength, hardness or corrosion resistance. Metals may also be alloyed to reduce their overall cost, for instance alloys of gold and Copper(II) sulfate, copper. A typical example of an alloy is SAE 304 stainless steel, 304 grade stainless steel which is commonly used for kitchen utensils, pans, knives and forks. Sometime also known as 18/8, it as an alloy consisting broadly of 74% iron, 18% chromium and 8% nickel. The chromium and nickel alloying elements add strength and hardness to the majority iron element, but their main function is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, gas, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, such as phase transformations, from occurring. It does this by reducing the window of time during which these undesired reactions are both thermodynamically favorable and kinetically accessible; for instance, quenching can reduce the crystal grain size of both metallic and plastic materials, increasing their hardness. In metallurgy, quenching is most commonly used to harden steel by inducing a martensite transformation, where the steel must be rapidly cooled through its eutectoid point, the temperature at which austenite becomes unstable. Rapid cooling prevents the formation of cementite structure, instead forcibly dissolving carbon atoms in the ferrite lattice. In steel alloyed with metals such as nickel and manganese, the eutectoid t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent, as a rubber additive, and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese is commonly found in labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |