|
Tonsil
The tonsils ( ) are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil (or pharyngeal tonsil), two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play an important role in the immune system. When used unqualified, the term most commonly refers specifically to the palatine tonsils, which are two lymphoid organs situated at either side of the back of the human throat. The palatine tonsils and the adenoid tonsil are organs consisting of lymphoepithelial tissue located near the oropharynx and nasopharynx (parts of the throat). Structure Humans are born with four types of tonsils: the pharyngeal tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils. Development The palatine tonsils tend to reach their largest size in puberty, and they gradually undergo atrophy thereafter. However, they are largest relative to the diameter of the throat in youn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Tonsils
Palatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils, are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat in humans and other mammals, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish lumps. Tonsils only present as "white lumps" if they are inflamed or infected with symptoms of exudates (pus drainage) and severe swelling. Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils and will often, but not necessarily, cause a sore throat and fever. In chronic cases, tonsillectomy may be indicated. Structure The palatine tonsils are located in the isthmus of the fauces, between the palatoglossal arch and the palatopharyngeal arch of the soft palate. The palatine tonsil is one of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALT), located at the entrance to the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts to protect the body from the entry of exogenous material through mucosal sites. In consequence it is a site of, and potential focus f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Tonsil
Palatine tonsils, commonly called the tonsils and occasionally called the faucial tonsils, are tonsils located on the left and right sides at the back of the throat in humans and other mammals, which can often be seen as flesh-colored, pinkish lumps. Tonsils only present as "white lumps" if they are inflamed or infected with symptoms of exudates (pus drainage) and severe swelling. Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils and will often, but not necessarily, cause a sore throat and fever. In chronic cases, tonsillectomy may be indicated. Structure The palatine tonsils are located in the isthmus of the fauces, between the palatoglossal arch and the palatopharyngeal arch of the soft palate. The palatine tonsil is one of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues (MALT), located at the entrance to the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts to protect the body from the entry of exogenous material through mucosal sites. In consequence it is a site of, and potentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waldeyer's Tonsillar Ring
Waldeyer's tonsillar ring (pharyngeal lymphoid ring, Waldeyer's lymphatic ring, or tonsillar ring) is a ringed arrangement of lymphoid organs in the pharynx. Waldeyer's ring surrounds the naso- and oropharynx, with some of its tonsillar tissue located above and some below the soft palate (and to the back of the mouth cavity). Structure The ring consists of the (from top to bottom): * 1 pharyngeal tonsil (or "adenoid"), located on the roof of the nasopharynx, under the sphenoid bone. * 2 tubal tonsils on each side, where each auditory tube opens into the nasopharynx * 2 palatine tonsils (commonly called "the tonsils") located in the oropharynx * lingual tonsils, a collection of lymphatic tissue located on the back part of the tongue Terminology Some authors speak of two pharyngeal tonsils/two adenoids. These authors simply look at the left and right halves of the pharyngeal tonsil as two tonsils. Many authors also speak of lingual tonsils (in the plural), because this accumulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
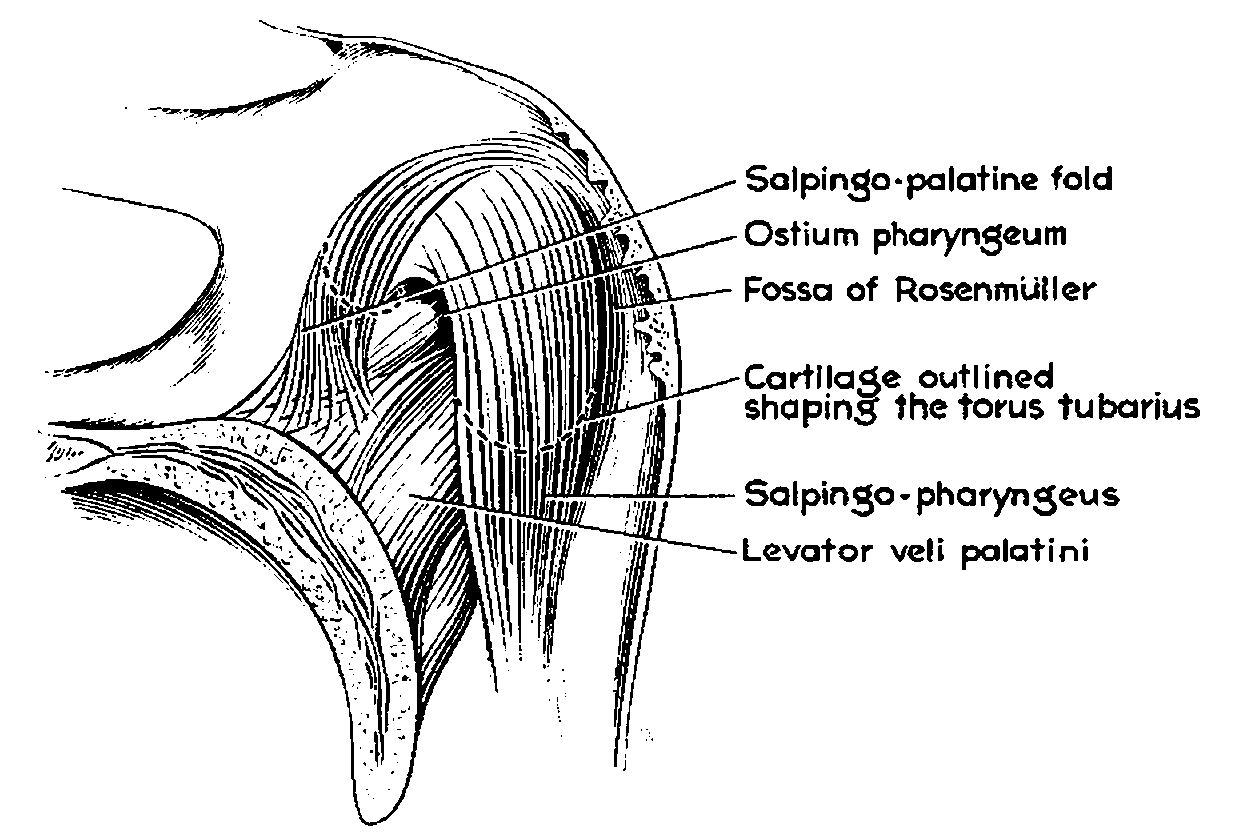
Tubal Tonsil
The tubal tonsil, also known as Gerlach tonsil, is one of the four main tonsil groups forming Waldeyer's tonsillar ring. Structure Each tubal tonsil is located posterior to the opening of the Eustachian tube on the lateral wall of the nasopharynx. It is one of the four main tonsil groups forming Waldeyer's tonsillar ring. This ring also includes the palatine tonsils, the lingual tonsils, and the adenoid. Clinical significance The tubal tonsil may be affected by tonsillitis. However, this usually affects only the palatine tonsils. History The tubal tonsil may also be known as the Gerlach tonsil. It is very close to the torus tubarius The torus tubarius (or torus of the auditory tube) is an elevation of the mucous membrane of the Pharynx#Nasopharynx, nasal part of the pharynx formed by the underlying base of the Eustachian tube, cartilaginous portion of the Eustachian tube, Eu ..., which is why this tonsil is sometimes also called the ''tonsil of (the) torus tubarius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubal Tonsils
The tubal tonsil, also known as Gerlach tonsil, is one of the four main tonsil groups forming Waldeyer's tonsillar ring. Structure Each tubal tonsil is located posterior to the opening of the Eustachian tube on the lateral wall of the nasopharynx. It is one of the four main tonsil groups forming Waldeyer's tonsillar ring. This ring also includes the palatine tonsils, the lingual tonsils, and the adenoid. Clinical significance The tubal tonsil may be affected by tonsillitis. However, this usually affects only the palatine tonsils. History The tubal tonsil may also be known as the Gerlach tonsil. It is very close to the torus tubarius The torus tubarius (or torus of the auditory tube) is an elevation of the mucous membrane of the Pharynx#Nasopharynx, nasal part of the pharynx formed by the underlying base of the Eustachian tube, cartilaginous portion of the Eustachian tube, Eu ..., which is why this tonsil is sometimes also called the ''tonsil of (the) torus tubarius''.E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Tonsils
The lingual tonsils are a collection of lymphoid tissue located in the lamina propria of the root of the tongue. This lymphoid tissue consists of the nodules rich in cells of the immune system ( immunocytes). The immunocytes initiate the immune response when the lingual tonsils get in contact with invading microorganisms (pathogenic bacteria, viruses or parasites). Structure Microanatomy Lingual tonsils are covered externally by stratified squamous epithelium (nonkeratinized) that invaginates inward forming tonsillar crypts. Beneath the epithelium is a layer of lymphoid nodules containing lymphocytes. Mucous glands located at the root of the tongue are drained through several ducts into the crypts of the lingual tonsils. Secretions of these mucous glands keep the crypts clean and free of any debris. Blood supply Lingual tonsils are located on posterior aspect of tongue which is supplied through: * Lingual artery, branch of external carotid artery * Tonsillar artery *Ascendi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonsillar Crypts
The human palatine tonsils (PT) are covered by stratified squamous epithelium that extends into deep and partly branched tonsillar crypts, of which there are about 10 to 30. The crypts greatly increase the contact surface between environmental influences and lymphoid tissue. In an average adult palatine tonsil the estimated epithelial surface area of the crypts is 295 cm2, in addition to the 45 cm2 of epithelium covering the oropharyngeal surface. The crypts extend through the full thickness of the tonsil reaching almost to its hemicapsule. In healthy tonsils the openings of the crypts are fissure-like, and the walls of the lumina are in apposition. A computerized three-dimensional reconstruction of the palatine tonsil crypt system showed that in the centre of the palatine tonsil are tightly packed ramified crypts that join with each other, while on the periphery there is a rather simple and sparse arrangement. The crypt system is not merely a group of invaginations o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Tonsil
The lingual tonsils are a collection of lymphoid tissue located in the lamina propria of the root of the tongue. This lymphoid tissue consists of the nodules rich in cells of the immune system (immunocytes). The immunocytes initiate the immune response when the lingual tonsils get in contact with invading microorganisms (pathogenic bacteria, viruses or Human parasite, parasites). Structure Microanatomy Lingual tonsils are covered externally by stratified squamous epithelium (nonkeratinized) that invaginates inward forming tonsillar crypts. Beneath the epithelium is a layer of lymphoid nodules containing lymphocytes. Mucous glands located at the root of the tongue are drained through several ducts into the crypts of the lingual tonsils. Secretions of these mucous glands keep the crypts clean and free of any debris. Blood supply Lingual tonsils are located on posterior aspect of tongue which is supplied through: * Lingual artery, branch of external carotid artery * Tonsillar art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the Digestion, digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the Human nose, nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen (anatomy), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenoid
In anatomy, the pharyngeal tonsil, also known as the nasopharyngeal tonsil or adenoid, is the superior-most of the tonsils. It is a mass of lymphoid tissue located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof and the posterior wall of the nasopharynx, where the nose blends into the throat. In children, it normally forms a soft mound in the roof and back wall of the nasopharynx, just above and behind the uvula. The term ''adenoid'' is also used to represent adenoid hypertrophy, the abnormal growth of the pharyngeal tonsils. Structure The adenoid is a mass of lymphoid tissue located behind the nasal cavity, in the roof and the posterior wall of the nasopharynx, where the nose blends into the throat. The adenoid, unlike the palatine tonsils, has pseudostratified epithelium. The adenoids are part of the so-called Waldeyer ring of lymphoid tissue which also includes the palatine tonsils, the lingual tonsils and the tubal tonsils. Development Adenoids develop from a subepithelia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oropharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen. They are arranged as an inner layer of longitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |