|
Tobacco Mosaic Virus
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus species in the genus '' Tobamovirus'' that infects a wide range of plants, especially tobacco and other members of the family Solanaceae. The infection causes characteristic patterns, such as "mosaic"-like mottling and discoloration on the leaves (hence the name). TMV was the first virus to be discovered. Although it was known from the late 19th century that a non-bacterial infectious disease was damaging tobacco crops, it was not until 1930 that the infectious agent was determined to be a virus. It is the first pathogen identified as a virus. The virus was crystallised by Wendell Meredith Stanley. It has a similar size to the largest synthetic molecule, known as PG5 with comparable length and diameter. History In 1886, Adolf Mayer first described the tobacco mosaic disease that could be transferred between plants, similar to bacterial infections. In 1892, Dmitri Ivanovsky gave the first concrete e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
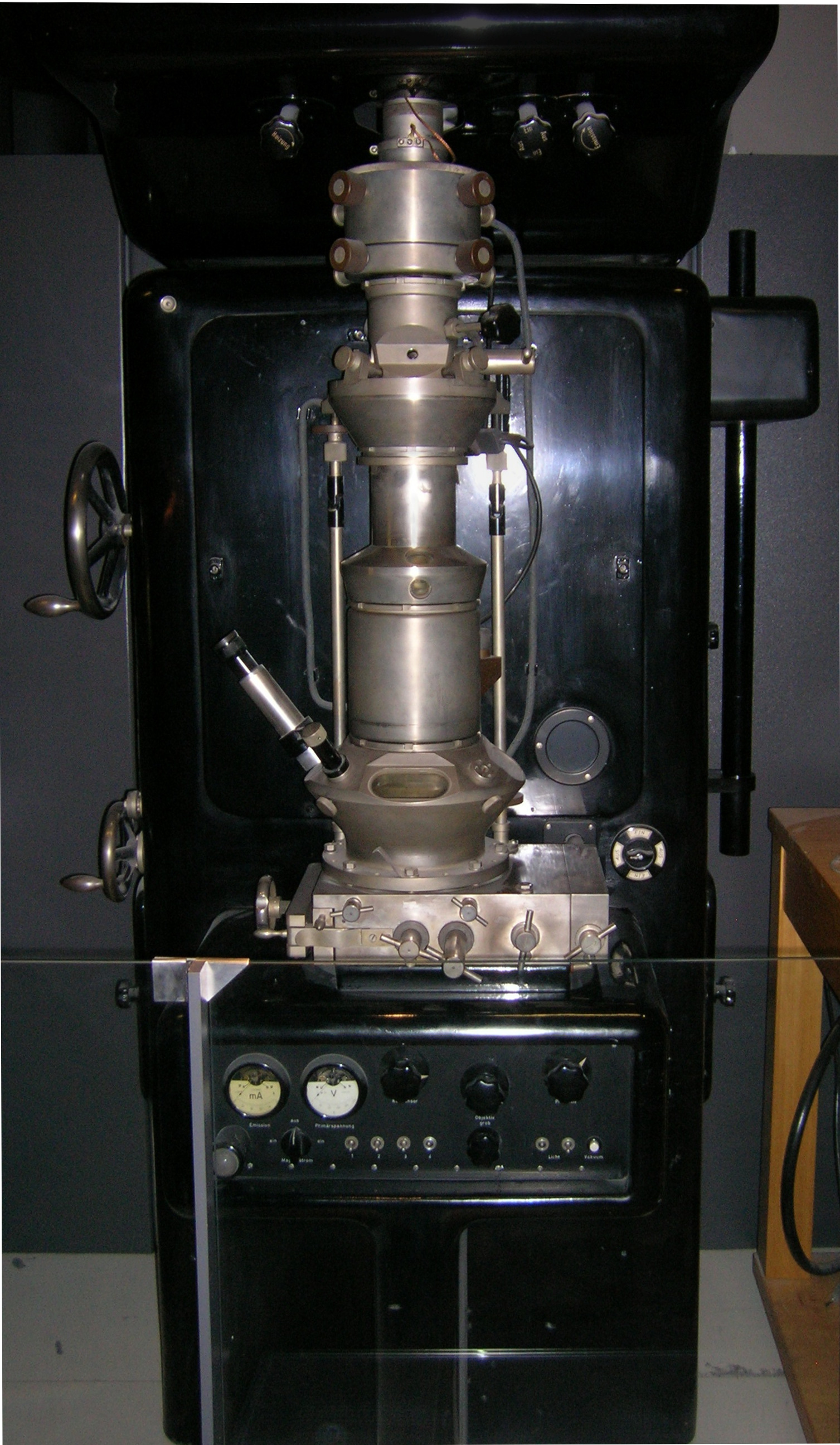
Transmission Electron Micrograph
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and Focus (optics), focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a Detectors for transmission electron microscopy, detector such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device or a direct electron detector. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher Optical resolution, resolution than Optical microscope, light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robley Williams
Robley Cook Williams (October 13, 1908 – January 3, 1995) was an early biophysicist and virologist. He served as the first president of the Biophysical Society. He also served as the president of the Electron Microscope Society of America in 1951. Career Williams attended Cornell University on an athletic scholarship, completing a B.S. in 1931 and a Ph.D. in physics in 1935. While at Cornell, he was selected for membership in the Telluride House and the Quill and Dagger society. Williams began his research career as an assistant professor of astronomy at the University of Michigan, and from 1945, associate professor of physics. A growing fascination with viruses led him to leave Michigan in 1950, when he was invited to the University of California, Berkeley by Wendell Stanley, to serve as a professor at the newly created Department of Virology. Research Together with Heinz Fraenkel-Conrat, Williams studied the Tobacco mosaic virus, and showed that a functional virus cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinz Fraenkel-Conrat
Heinz Ludwig Fraenkel-Conrat (July 29, 1910 – April 10, 1999) was a biochemist, famous for his research on viruses. Early life Fraenkel-Conrat was born in Breslau, Germany. He was the son of Lili Conrat and Professor Ludwig Fraenkel, director of the Women's Clinic of the University of Breslau. His father was a prominent gynecologist and medical researcher who published regarding endocrine function, social gynecology, and sexology during the first decades of the 20th century, and was one of many scientists summarily dismissed from their positions by the Nazis. Academic career He received an MD from the University of Breslau in 1933. Due to the rise of Nazism in Germany he left for Scotland in 1933 and finished his PhD at the University of Edinburgh (1936). After completing his doctorate, he emigrated to the United States, becoming a naturalized citizen in 1941. In the 1940s Fraenkel-Conrat visited his sister and brother-in-law, biochemist Karl Slotta, a pioneer in the stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Ruska
Ernst August Friedrich Ruska (; 25 December 1906 – 27 May 1988) was a German physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986 for his work in electron optics, including the design of the first electron microscope. Life and career Ernst Ruska was born in Heidelberg, Germany. He was educated at the Technical University of Munich from 1925 to 1927 and then entered ''Technische Hochschule Berlin'' (now Technische Universität Berlin), where he posited that microscopes using electrons, with wavelengths 1000 times shorter than those of light, could provide a more detailed picture of an object than a microscope utilizing light, in which magnification is limited by the size of the wavelengths. In 1931, he demonstrated that a magnetic coil could act as an electron lens, and used several coils in a series to build the first electron microscope in 1933. After completing his PhD in 1933, Ruska continued to work in the field of electron optics, first at Fernseh AG in Berlin-Zehlendo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmut Ruska
Helmut Ruska (June 7, 1908, in Heidelberg – August 30, 1973) was a German physician and biologist from Heidelberg. After earning his medical degree, he spent several years working as a physician at hospitals in Heidelberg and Berlin. During this time, he also worked closely with his brother Ernst Ruska (1906-1988) and brother-in-law Bodo von Borries (1905-56), who were both research scientists at Siemens-Reiniger-Werke. Ernst Ruska was the inventor of the electron microscope, and later winner of a Nobel Prize. From 1948 to 1951, Helmut Ruska was a professor at the University of Berlin, in 1952 he moved to the United States where he was a micromorphologist for the New York State Department of Health in Albany. He returned to Germany in 1958 as director of biophysics at the University of Düsseldorf. Through close association with his brother, Helmut Ruska is remembered for developing the electron microscope for biological and medical applications. He was the first scientist to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgar Pfankuch
Edgar is a commonly used masculine English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Edgar'' (composed of '' ead'' "rich, prosperous" and '' gar'' "spear"). Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the Late Middle Ages; it was, however, revived in the 18th century, and was popularised by its use for a character in Sir Walter Scott's ''The Bride of Lammermoor'' (1819). The name was more common in the United States than elsewhere in the Anglosphere during the 19th century. It has been a particularly fashionable name in Latin American countries since the 20th century. People with the given name * Edgar the Peaceful (942–975), king of England * Edgar the Ætheling (c. 1051 – c. 1126), last member of the Anglo-Saxon royal house of England * Edgar of Scotland (1074–1107), king of Scotland * Edgar Alaffita (born 1996), Mexican footballer * Edgar Allan (other), multiple people * Edgar Allen (other), multiple people * Edgar Angara (1934–2018), Fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav Kausche
Gustav, Gustaf or Gustave may refer to: *Gustav (name), a male given name of Old Swedish origin Art, entertainment, and media * ''Primeval'' (film), a 2007 American horror film * ''Gustav'' (film series), a Hungarian series of animated short cartoons * Gustav (''Zoids''), a transportation mecha in the ''Zoids'' fictional universe *Gustav, a character in '' Sesamstraße'' *Monsieur Gustav H., a leading character in '' The Grand Budapest Hotel'' * Gustaf, an American art punk band from Brooklyn, New York. Weapons * Carl Gustav recoilless rifle, dubbed "the Gustav" by US soldiers * Schwerer Gustav, 800-mm German siege cannon used during World War II Other uses * Gustav (pigeon), a pigeon of the RAF pigeon service in WWII *Gustave (crocodile), a large male Nile crocodile in Burundi *Gustave, South Dakota *Hurricane Gustav (other), a name used for several tropical cyclones and storms *Gustav, a streetwear clothing brand See also *Gustav of Sweden (other) *Gustav A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocatalysis
In chemistry, a chemical reaction is said to be autocatalytic if one of the reaction products is also a catalyst for the same reaction. Many forms of autocatalysis are recognized.Steinfeld J.I., Francisco J.S. and Hase W.L. ''Chemical Kinetics and Dynamics'' (2nd ed., Prentice-Hall 1999) pp. 151–2 A ''set'' of chemical reactions can be said to be "collectively autocatalytic" if a number of those reactions produce, as reaction products, catalysts for enough of the other reactions that the entire set of chemical reactions is self-sustaining given an input of energy and food molecules (see autocatalytic set). Examples Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of esters produces carboxylic acids that also catalyze the same reaction. Indeed, the observation of an accelerating hydrolysis of gamma valerolactone to gamma-hydroxyvaleric acid led to the introduction of the concept of autocatalysis in 1890. The oxidation of hydrocarbons by air or oxygen is the basis of autoxidation. Like many radic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outstanding contributions in chemistry, physics, literature, peace, and physiology or medicine. This award is administered by the Nobel Foundation and awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences on proposal of the Nobel Committee for Chemistry, which consists of five members elected by the Academy. The award is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on December 10th, the anniversary of Nobel's death. The first Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded in 1901 to Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff, of the Netherlands, "for his discovery of the laws of chemical dynamics and osmotic pressure in solutions". From 1901 to 2024, the award has been bestowed on a total of 195 individuals. The 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Demis Hassabis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
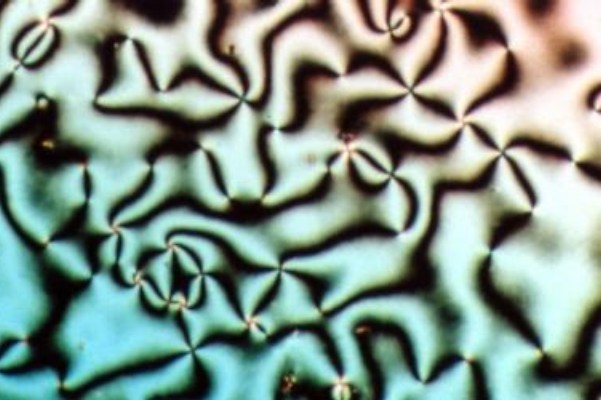
Liquid Crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as in a solid. There are many types of LC Phase (matter), phases, which can be distinguished by their Optics, optical properties (such as Texture (crystalline), textures). The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. An LC material may not always be in an LC state of matter (just as water may be ice or water vapour). Liquid crystals can be divided into three main types: thermotropic, lyotropic, and #Metallotropic liquid crystals, metallotropic. Thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystals consist mostly of organic molecules, although a few minerals are also known. Thermotropic LCs exhibit a phase transition into the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Crystallization
Protein crystallization is the process of formation of a regular array of individual protein molecules stabilized by crystal contacts. If the crystal is sufficiently ordered, it will diffract. Some proteins naturally form crystalline arrays, like aquaporin in the lens of the eye. In the process of protein crystallization, proteins are dissolved in an aqueous environment and sample solution until they reach the supersaturated state. Different methods are used to reach that state such as vapor diffusion, microbatch, microdialysis, and free-interface diffusion. Developing protein crystals is a difficult process influenced by many factors, including pH, temperature, ionic strength in the crystallization solution, and even gravity. Once formed, these crystals can be used in structural biology to study the molecular structure of the protein, particularly for various industrial or medical purposes. Development For over 150 years, scientists from all around the world have known a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |