|
Tideline
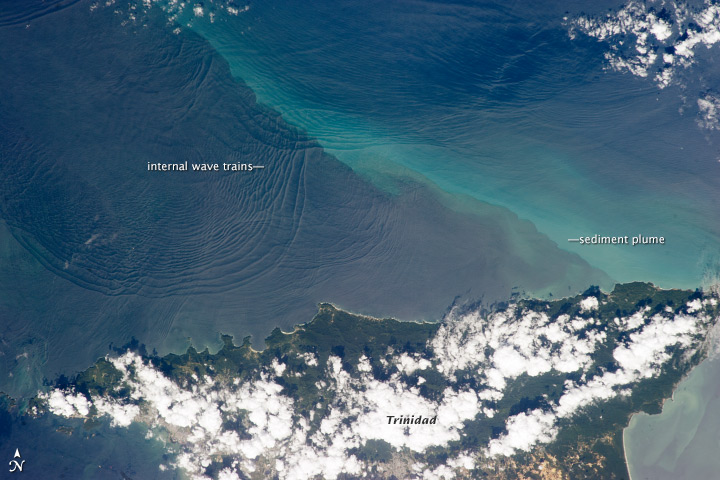
A tideline refers to where two currents in the ocean converge. Driftwood, floating seaweed, foam, and other floating debris may accumulate, forming sinuous lines called tidelines (although they generally have nothing to do with the tide). There are four mechanisms that can cause tidelines to form: # Where one body of water is sinking beneath or riding over top of the surface layer of another body of water (somewhat similar in mechanics to subduction and/or uprisal of the earth plates at continental margins). These types of tidelines are often found where rivers enter the ocean. # Along the margins of back-eddies. # Convergence zones associated with internal gravity waves. # Along adjacent cells formed by wind currents. See also * Langmuir circulation * Ocean circulation * Flotsam and jetsam References * Thomson, R.E. 1981. Oceanography Oceanography (), also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the ocean, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents move both horizontally, on scales that can span entire oceans, as well as vertically, with vertical currents (upwelling and downwelling) playing an important role in the movement of nutrients and gases, such as carbon dioxide, between the surface and the deep ocean. Ocean currents flow for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth's regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean, Antarctic/Southern, and Arctic Ocean),"Ocean." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/ocean . Accessed March 14, 2021. and are themselves mostly divided into seas, gulfs and Lists of bodies of water#Seawater bodies, subsequent bodies of water. The ocean contains 97% of Water distribution on Earth, Earth's water and is the primary component of Earth's hydrosphere, acting as a huge Ocean heat content, reservoir of heat for Earth's energy budget, as well as for its carbon cycle and water cycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or " tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Gravity Waves
Internal waves are gravity waves that oscillate within a fluid medium, rather than on its surface. To exist, the fluid must be stratified: the density must change (continuously or discontinuously) with depth/height due to changes, for example, in temperature and/or salinity. If the density changes over a small vertical distance (as in the case of the thermocline in lakes and oceans or an atmospheric inversion), the waves propagate horizontally like surface waves, but do so at slower speeds as determined by the density difference of the fluid below and above the interface. If the density changes continuously, the waves can propagate vertically as well as horizontally through the fluid. Internal waves, also called internal gravity waves, go by many other names depending upon the fluid stratification, generation mechanism, amplitude, and influence of external forces. If propagating horizontally along an interface where the density rapidly decreases with height, they are specifically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langmuir Circulation
In physical oceanography, Langmuir circulation consists of a series of shallow, slow, counter-rotating vortices at the ocean's surface aligned with the wind. These circulations are developed when wind blows steadily over the sea surface. Irving Langmuir discovered this phenomenon after observing windrows of seaweed in the Sargasso Sea in 1927. Langmuir circulations circulate within the mixed layer; however, it is not yet so clear how strongly they can cause mixing at the base of the mixed layer. Theory The driving force of these circulations is an interaction of the mean flow with wave averaged flows of the surface waves. Stokes drift velocity of the waves stretches and tilts the vorticity of the flow near the surface. The production of vorticity in the upper ocean is balanced by downward (often turbulent) diffusion \nu_T. For a flow driven by a wind \tau characterized by friction velocity u_* the ratio of vorticity diffusion and production defines the Langmuir number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Circulation
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents move both horizontally, on scales that can span entire oceans, as well as vertically, with vertical currents (upwelling and downwelling) playing an important role in the movement of nutrients and gases, such as carbon dioxide, between the surface and the deep ocean. Ocean currents flow for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth's regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flotsam And Jetsam
In maritime law, flotsam'','' jetsam'','' lagan'','' and derelict are terms for various types of property lost or abandoned at sea. The words have specific nautical meanings, with legal consequences in the law of admiralty and marine salvage. A shipwreck is defined as the remains of a ship that has been wrecked, whether it has sunk or is floating on the surface of the water. Overview A wreck is categorized as property belonging to no apparent owner that either sinks to the seabed or floats on the surface of the water, whether it be intentionally cast overboard or as the result of an accident. The term encompasses the hull of the vessel and its fixtures as well as any other form of object on board, such as cargo and stores, and personal effects of the crew and passengers. This also encompasses the narrower definition of salvage, that is, property that has been recovered from a wreckage, or the recovery of the ship itself. There are a number of factors that contribute to the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the ocean, including its physics, chemistry, biology, and geology. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics; fluxes of various chemical substances and physical properties within the ocean and across its boundaries; ecosystem dynamics; and plate tectonics and seabed geology. Oceanographers draw upon a wide range of disciplines to deepen their understanding of the world’s oceans, incorporating insights from astronomy, biology, chemistry, geography, geology, hydrology, meteorology and physics. History Early history Humans first acquired knowledge of the waves and currents of the seas and oceans in pre-historic times. Observations on tides were recorded by Aristotle and Strabo in 384–322 BC. Early exploration of the oceans was primarily for cartography and mainly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tides
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or " tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |