|
Thyroxin
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are two hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine, derived from food. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4), whose half-life of around one wee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine, also known as -thyroxine, is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4). It is used to treat thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism), including a severe form known as myxedema coma. It may also be used to treat and prevent certain types of thyroid tumors. It is not indicated for weight loss. Levothyroxine is taken orally (by mouth) or given by intravenous injection. Levothyroxine has a half-life of 7.5 days when taken daily, so about six weeks is required for it to reach a steady level in the blood. Side effects from excessive doses include weight loss, trouble tolerating heat, sweating, anxiety, trouble sleeping, tremor, and fast heart rate. Use is not recommended in people who have had a recent heart attack. Use during pregnancy has been found to be safe. Dosing should be based on regular measurements of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and T4 levels in the blood. Much of the effect of levothyroxine is following its conversion to tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid Hormones
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are two hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine, derived from food. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4), whose half-life of arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the isthmus (: isthmi). Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and growth and development in children. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triiodothyronine
Triiodothyronine, also known as T3, is a thyroid hormone. It affects almost every physiological process in the body, including growth and development, metabolism, body temperature, and heart rate. Production of T3 and its prohormone thyroxine (T4) is activated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is released from the anterior pituitary gland. This pathway is part of a closed-loop feedback process: Elevated concentrations of T3, and T4 in the blood plasma inhibit the production of TSH in the anterior pituitary gland. As concentrations of these hormones decrease, the anterior pituitary gland increases production of TSH, and by these processes, a feedback control system stabilizes the level of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream. At the cellular level, T3 is the body's more active and potent thyroid hormone. T3 helps deliver oxygen and energy to all of the body's cells, its effects on target tissues being roughly four times more potent than those of T4. Of the thyroid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
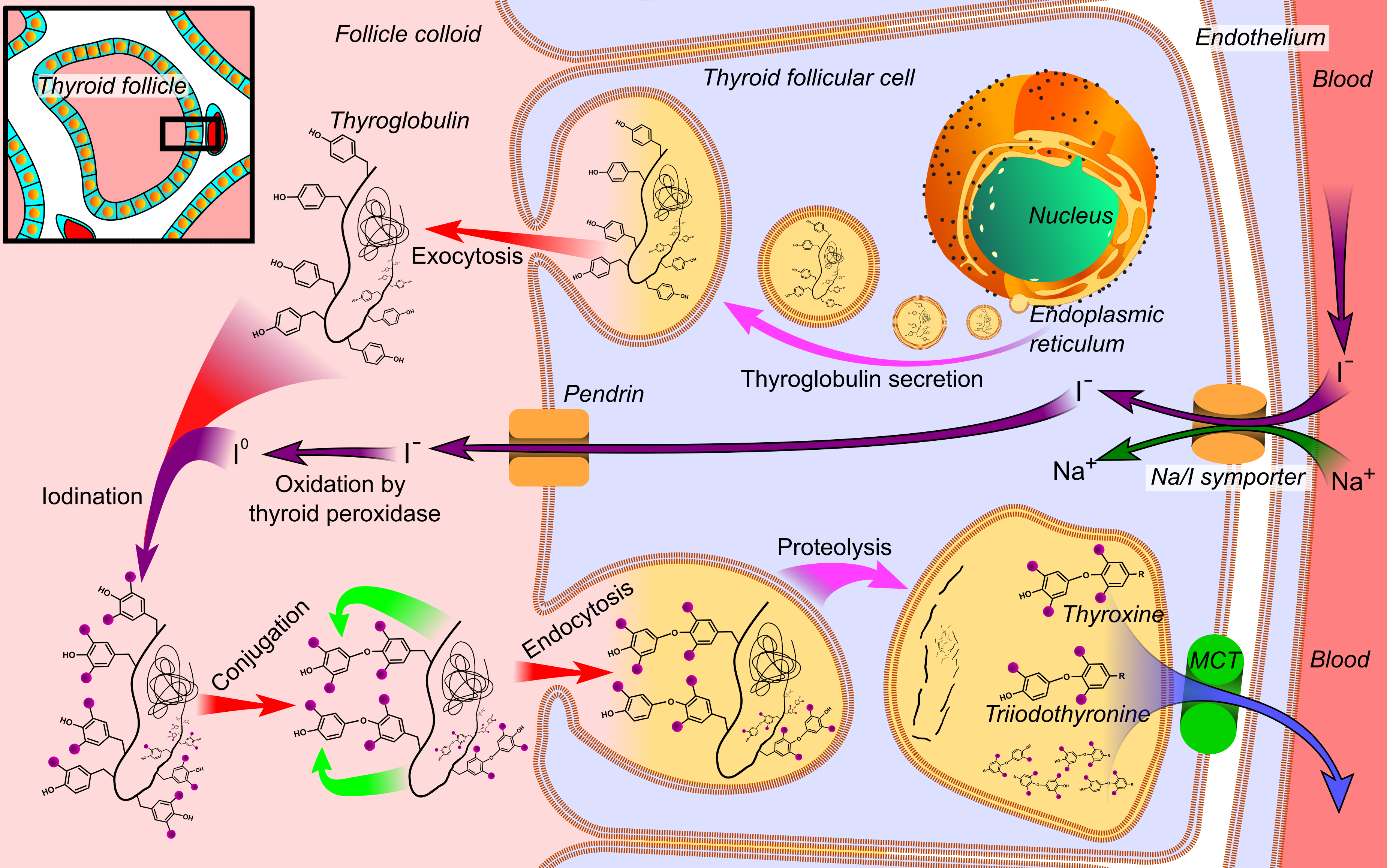
Thyroxine
Thyroxine, also known as T4, is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It is the primary form of thyroid hormone found in the blood and acts as a prohormone of the more active thyroid hormone, triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroxine and its active metabolites are essential for regulating metabolic rate, supporting heart and muscle function, promoting brain development, and maintaining bone health. Regulation Thyroxine has a half-life of approximately one week and hence maintains relatively stable blood levels. Its production and release are controlled through a complex feedback loop involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and thyroid gland. This regulatory system ensures that optimal hormone levels are maintained. Biosynthesis Thyroxine biosynthesis is a multi-step process that occurs in follicular cell within the thyroid gland. The synthesis of thyroxine requires adequate iodine supply and appropriate hormonal control. The process begins with the active uptake o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required for the normal development of animals, plants and fungi. Due to the broad definition of a hormone (as a signaling molecule that exerts its effects far from its site of production), numerous kinds of molecules can be classified as hormones. Among the substances that can be considered hormones, are eicosanoids (e.g. prostaglandins and thromboxanes), steroids (e.g. Estrogen, oestrogen and brassinosteroid), amino acid derivatives (e.g. epinephrine and auxin), protein or peptides (e.g. insulin and CLE peptides), and gases (e.g. ethylene and nitric oxide). Hormones are used to communicate between organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues. In vertebrates, hormones are responsible for regulating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Calvin Kendall
Edward Calvin Kendall (March 8, 1886 – May 4, 1972) was an American biochemist. In 1950, Kendall was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine along with Swiss chemist Tadeusz Reichstein and Mayo Clinic physician Philip S. Hench, for their work with the hormones of the adrenal glands. Kendall not only researched the adrenal glands, he also isolated thyroxine, a hormone of the thyroid gland and worked with the team that crystallized glutathione and identified its chemical structure. Kendall was a biochemist at the Graduate School of the Mayo Foundation at the time of the Nobel award. He received his education at Columbia University. After retiring from his job with the Mayo Foundation, Kendall joined the faculty at Princeton University, where he remained until his death in 1972. Kendall Elementary School, in Norwalk is named for him. Early life and education Kendall was born in South Norwalk, Connecticut in 1886. He attended Columbia University, earning a Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
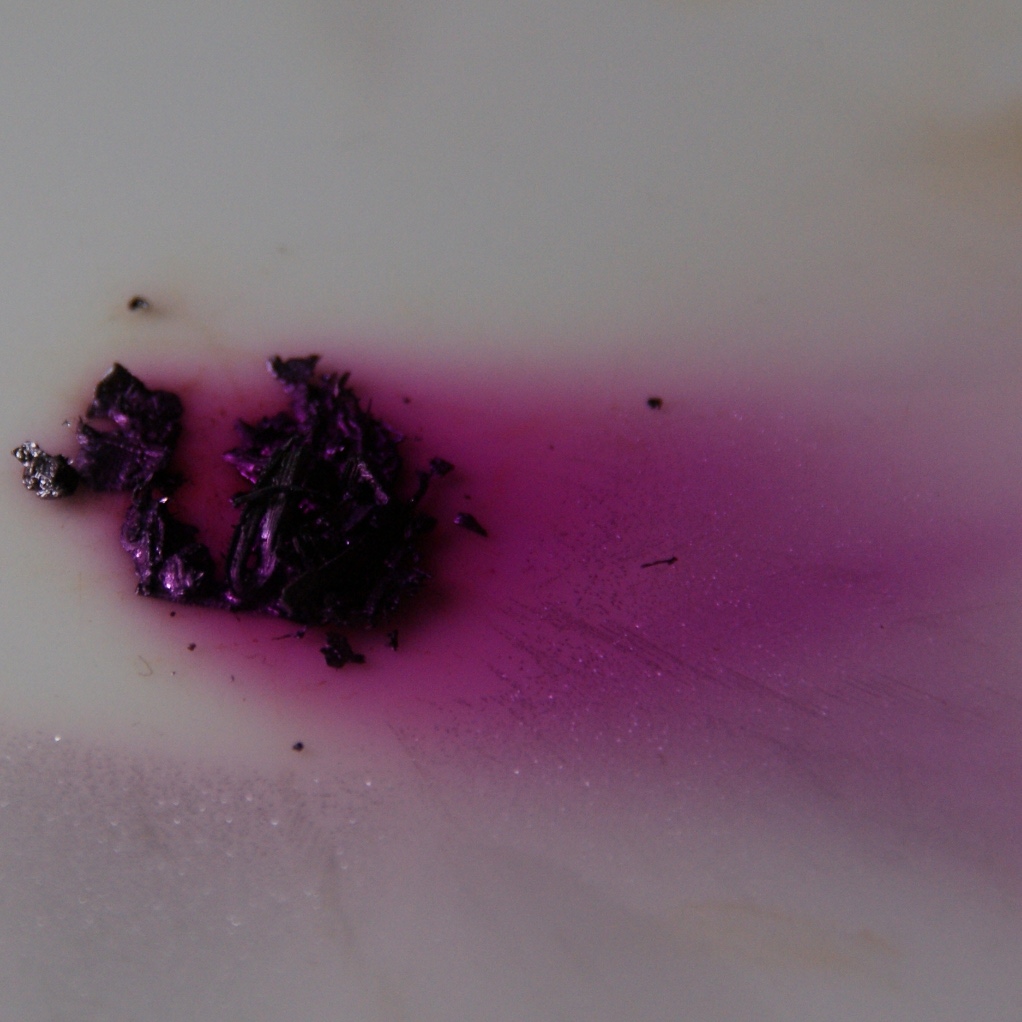
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek , meaning 'violet'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compounds, it has also found favour as a non-toxic radiocontrast material. Because of the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deiodinase
Deiodinase (monodeiodinase) is a peroxidase enzyme that is involved in the activation or deactivation of thyroid hormones. Types Types of deiodinases include: Iodothyronine deiodinases catalyze release of iodine directly from the thyronine hormones. They are selenocysteine-dependent membrane proteins with a catalytic domain resembling peroxiredoxins (Prx). Three related isoforms, deiodinase type I, II, and III, contribute to activation and inactivation of the initially released hormone precursor T4 (thyroxine) into T3 (triiodothyronine) or rT3 ( reverse triiodothyronine) in target cells. The enzymes catalyze a reductive elimination of iodine (the different isoforms attack different thyronine positions), thereby oxidizing themselves similar to Prx, followed by a reductive recycling of the enzyme. Iodotyrosine deiodinase contributes to breakdown of thyroid hormones. It releases iodine, for renewed use, from iodinated tyrosines resulting from catabolism of iodothyronines. Io ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a conditionally essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Greek ''tyrós'', meaning ''cheese'', as it was first discovered in 1846 by German chemist Justus von Liebig in the protein casein from cheese. It is called tyrosyl when referred to as a functional group or side chain. While tyrosine is generally classified as a hydrophobic amino acid, it is more hydrophilic than phenylalanine. It is encoded by the codons UAC and UAU in messenger RNA. The one-letter symbol Y was assigned to tyrosine for being alphabetically nearest of those letters available. Note that T was assigned to the structurally simpler threonine, U was avoided for its similarity with V for valine, W was assigned to tryptophan, while X was reserved for undetermined or atypical amino acids. The mnemonic t''Y''rosine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |