|
Thyrotoxicosis
Hyperthyroidism is a endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Thyrotoxicosis is a condition that occurs due to elevated levels of thyroid hormones of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, heat intolerance, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, hand tremor, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less severe in the elderly and during pregnancy. An uncommon but life-threatening complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature; this often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of the cases of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thyroid Storm
Thyroid storm is a rare but severe and life-threatening complication of hyperthyroidism. It occurs when an overactive thyroid leads to hypermetabolism, which can cause death from cardiac arrest or multiple organ failure. It is characterized by a high fever (temperatures often above ), fast and often irregular heart beat, elevated blood pressure, vomiting, diarrhea, and agitation. Hypertension with a wide pulse pressure occurs in early to mid crisis, with hypotension accompanying shock occurring in the late stage. Heart failure and heart attack may occur. Death may occur despite treatment. Most episodes occur either in those with known hyperthyroidism whose treatment has stopped or become ineffective, or in those with untreated mild hyperthyroidism who have developed an intercurrent illness (such as an infection). The primary treatment of thyroid storm is with inorganic iodine and antithyroid drugs (propylthiouracil or methimazole) to reduce synthesis and release of thyroid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radioiodine Therapy
Iodine-131 (131I, I-131) is an important radioisotope of iodine discovered by Glenn Seaborg and John Livingood in 1938 at the University of California, Berkeley. It has a radioactive decay half-life of about eight days. It is associated with nuclear energy, medical diagnostic and treatment procedures, and natural gas production. It also plays a major role as a radioactive isotope present in nuclear fission products, and was a significant contributor to the health hazards from open-air atomic bomb testing in the 1950s, and from the Chernobyl disaster, as well as being a large fraction of the contamination hazard in the first weeks in the Fukushima nuclear crisis. This is because 131I is a major fission product of uranium and plutonium, comprising nearly 3% of the total products of fission (by weight). See fission product yield for a comparison with other radioactive fission products. 131I is also a major fission product of uranium-233, produced from thorium. Due to its mode of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia, also known as overheating, is a condition in which an individual's body temperature is elevated beyond normal due to failed thermoregulation. The person's body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. When extreme temperature elevation occurs, it becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death. Almost half a million deaths are recorded every year from hyperthermia. The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. Heat stroke is an acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms of the body. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia. Hyperthermia can also be caused by a traumatic brain injury. Hyperthermia differs from feve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Beta Blockers
Beta blockers, also spelled β-blockers, are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia), and to protect the heart from a second heart attack after a first heart attack (secondary prevention). They are also widely used to treat high blood pressure, although they are no longer the first choice for initial treatment of most people. Beta blockers are competitive antagonists that block the receptor sites for the endogenous catecholamines epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) on adrenergic beta receptors, of the sympathetic nervous system, which mediates the fight-or-flight response. Beta-adrenergic receptors are found on cells of the heart muscles, smooth muscles, airways, arteries, kidneys, and other tissues that are part of the sympathetic nervous system and lead to stress responses, especially when they are stimulated by epinephrine (adrenaline). Beta blockers interfere with the binding to the receptor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Synthetic Thyroid Hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are two hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine, derived from food. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood is thyroxine (T4), whose half-life of around one wee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
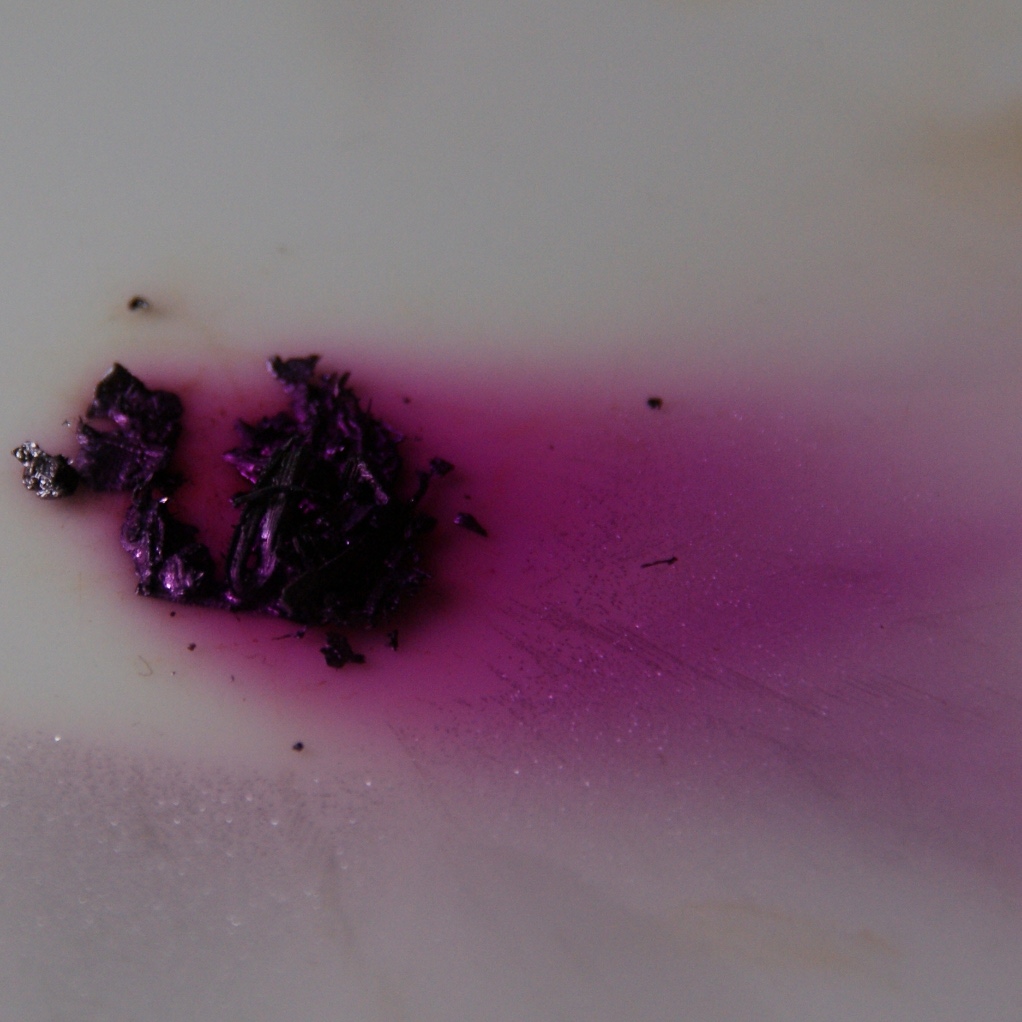
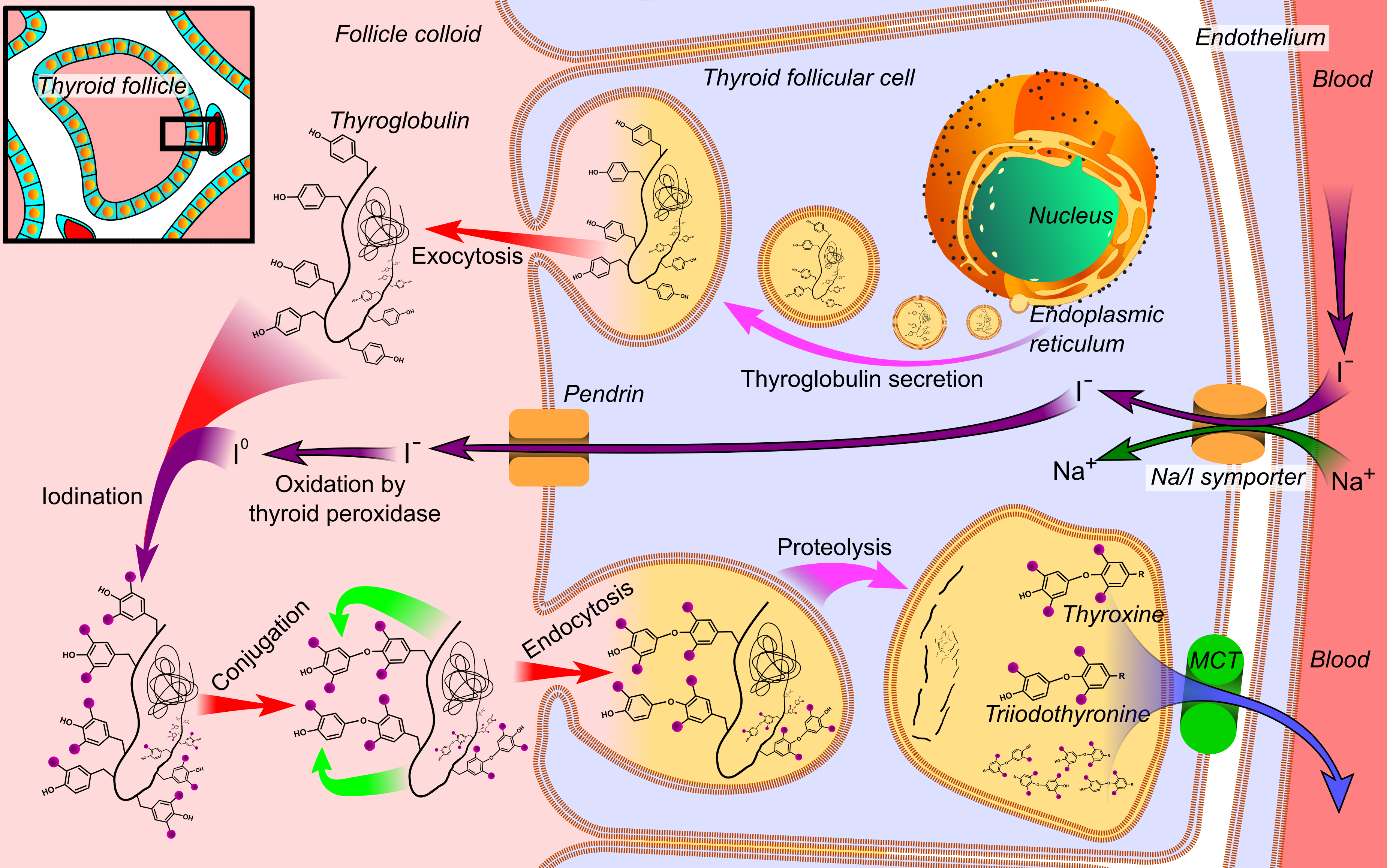
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek , meaning 'violet'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compounds, it has also found favour as a non-toxic radiocontrast material. Because of the spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Graves' Disease
Graves' disease, also known as toxic diffuse goiter or Basedow's disease, is an autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid. It frequently results in and is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It also often results in an enlarged thyroid. Signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea and unintentional weight loss. Other symptoms may include thickening of the skin on the shins, known as pretibial myxedema, and eye bulging, a condition caused by Graves' ophthalmopathy. About 25 to 30% of people with the condition develop eye problems. The exact cause of the disease is unclear, but symptoms are a result of antibodies binding to receptors on the thyroid causing over-expression of thyroid hormone. Persons are more likely to be affected if they have a family member with the disease. If one monozygotic twin is affected, a 30% chance exists that the other twin will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is the inflammation of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located on the front of the neck below the laryngeal prominence, and makes hormones that control metabolism. Thyroiditis is a group of disorders that all cause thyroidal inflammation. Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment depend on the cause of thyroiditis. Forms of thyroiditis are Hashimoto's thyroiditis, postpartum thyroiditis, subacute (de Quervain's) thyroiditis, silent thyroiditis, drug-induced thyroiditis, radiation-induced thyroiditis and acute thyroiditis. Types Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease where the body creates thyroid antibodies. It presents with hypothyroidism due to the destruction of thyroid cells. In Hashimoto's thyroiditis, the hypothyroidism is most often permanent, with symptoms are fatigue, weight gain, depression, dry skin, and constipation. Thyroid hormone replacement is the treatment of hypothyroidism. Silent thyroiditis or painless thyroiditis, also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thyroid Hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine, T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary, Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid, Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are two hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine, derived from food. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid, thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Heat Intolerance
Heat intolerance is a symptom characterized by feeling overheated in warm environments or when the surrounding environment's temperature rises. Typically, the person feels uncomfortably hot and sweats excessively. Compared to heat illnesses like heatstroke, heat intolerance is usually a symptom of endocrine disorders, drugs, or other medical conditions, rather than the result of too much exercise or hot, humid weather. Symptoms * Feeling subjectively hot * Sweating, which may be excessive In patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), heat intolerance may cause a pseudoexacerbation, which is a temporary worsening of MS-related symptoms. A temporary worsening of symptoms can also happen in patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) and dysautonomia. Diagnosis Diagnosis is largely made from the patient history, followed by blood tests and other medical tests to determine the underlying cause. In women, hot flashes must be excluded. Causes Excess thyroid hormone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. What is diarrhea? How is it caused, treated and prevented? (see also script)The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |