|
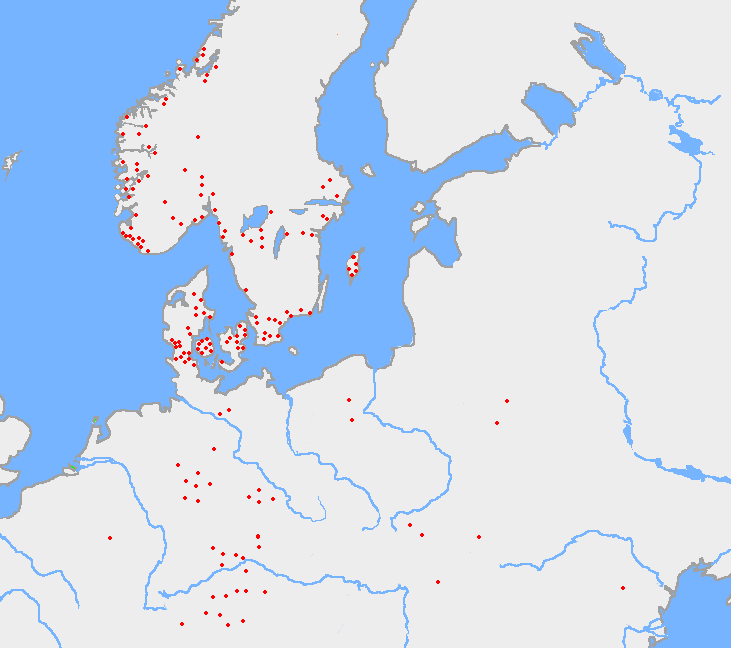
Thorn (letter)
Thorn or þorn (Þ, þ) is a letter in the Old English Latin alphabet, Old English, Old Norse alphabet, Old Norse, Old Swedish and modern Icelandic orthography, Icelandic alphabets, as well as modern transliterations of the Gothic language, Gothic alphabet, Middle Scots, and some dialects of Middle English. It was also used in Middle Ages, medieval Scandinavia but was later replaced with the Digraph (orthography), digraph ''Th (digraph), th,'' except in Iceland, where it survives. The letter originated from the runic alphabet, rune in the Elder Futhark and was called ''thorn'' in the Anglo-Saxon and ''thorn'' or ''Jötunn, thurs'' in the Scandinavian rune poems. It is similar in appearance to the archaic Greek letter Sho (letter), sho (ϸ), although the two are historically unrelated. The only language in which þ is currently in use is Icelandic language, Icelandic. It represented a voiceless dental fricative or its voiced dental fricative, voiced counterpart . However, in mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thurisaz
The rune is called Thurs (Old Norse ''Jötunn, Þurs'', a type of entity, from a reconstructed Common Germanic ') in the Icelandic and Norwegian rune poems. In the Anglo-Saxon rune poem it is called thorn, whence the name of the Thorn (letter), letter þ derived. It is transliterated as ''þ'', and has the sound value of a voiceless dental fricative (the Pronunciation of English th, English sound of ''th'' as in ''thing''). The rune is absent from the earliest Vimose inscriptions, but it is found in the Thorsberg chape inscription, dated to ca. AD 200. The rune may have been an original innovation, or it may have been adapted from the History of the Latin alphabet#Classical Latin period, classical Latin alphabet's ''D'', or from the Rhaetic alphabets, Rhaetic's alphabet's ''Θ''. Name In Anglo-Saxon England, the same rune was called ''Thorn'' or "Þorn" and it survives as the Icelandic orthography, Icelandic letter Thorn (letter), Þ (þ). An attempt has been made to accou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English period. Scholarly opinion varies, but the University of Valencia states the period when Middle English was spoken as being from 1150 to 1500. This stage of the development of the English language roughly coincided with the High Middle Ages, High and Late Middle Ages. Middle English saw significant changes to its vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and orthography. Writing conventions during the Middle English period varied widely. Examples of writing from this period that have survived show extensive regional variation. The more standardized Old English literary variety broke down and writing in English became fragmented and localized and was, for the most part, being improvised. By the end of the period (about 1470), and aided by the movabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Dental Fricative
The voiceless dental non-sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is familiar to most English speakers as the 'th' in ''think''. Though rather rare as a phoneme among the world's languages, it is encountered in some of the most widespread and influential ones. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is T. The IPA symbol is the lowercase Greek alphabet, Greek letter theta, which is used for this sound in post-classical Greek language, Greek, and the sound is thus often referred to as "theta". The dental non-sibilant fricatives are often called "interdental consonant, interdental" because they are often produced with the tongue between the upper and lower teeth, and not just against the back of the upper or lower teeth, as they are with other dental consonants. This sound and its Voiced dental fricative, voiced counterpart are rare phonemes, occurring in 4% of lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icelandic Language
Icelandic ( ; , ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken by about 314,000 people, the vast majority of whom live in Iceland, where it is the national language. Since it is a West Scandinavian languages, West Scandinavian language, it is most closely related to Faroese language, Faroese, western Norwegian dialects, and the extinct language Norn language, Norn. It is not mutually intelligible with the continental Scandinavian languages (Danish language, Danish, Norwegian language, Norwegian, and Swedish language, Swedish) and is more distinct from the most widely spoken Germanic languages, English language, English and German language, German. The written forms of Icelandic and Faroese are very similar, but their spoken forms are not Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible. The language is more Linguistic conservatism, conservative than most other Germanic languages. While most of them hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thurisaz (rune)
The rune is called Thurs (Old Norse '' Þurs'', a type of entity, from a reconstructed Common Germanic ') in the Icelandic and Norwegian rune poems. In the Anglo-Saxon rune poem it is called thorn, whence the name of the letter þ derived. It is transliterated as ''þ'', and has the sound value of a voiceless dental fricative (the English sound of ''th'' as in ''thing''). The rune is absent from the earliest Vimose inscriptions, but it is found in the Thorsberg chape inscription, dated to ca. AD 200. The rune may have been an original innovation, or it may have been adapted from the classical Latin alphabet's ''D'', or from the Rhaetic's alphabet's ''Θ''. Name In Anglo-Saxon England, the same rune was called ''Thorn'' or "Þorn" and it survives as the Icelandic letter Þ (þ). An attempt has been made to account for the substitution of names by taking "thorn" to be a kenning (metaphor) for "giant". It is disputed as to whether a distinct system of Gothic rune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic languages, Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages. Proto-Germanic eventually developed from Germanic parent language, pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic branches during the fifth century BC to fifth century AD: West Germanic languages, West Germanic, East Germanic languages, East Germanic and North Germanic languages, North Germanic. North Germanic remained in language contact, contact with the other branches over a considerable time, especially with the Ingvaeonic languages (including History of English, English), which arose from West Germanic dialects, and had remained in contact with the Proto-Norse language, Norse. A defining feature of Proto-Germanic is the completion of the process described by Grimm's law, a set of sound changes that occurred between its status as a dialect of Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rune Poem
Rune poems are poems that list the letters of runic alphabets while providing an explanatory poetic stanza for each letter. Four different poems from before the mid-20th century have been preserved: the Anglo-Saxon Rune Poem, the Norwegian Rune Poem, the Icelandic Rune Poem and the Swedish Rune Poem. The Icelandic and Norwegian poems list 16 Younger Futhark runes, while the Anglo-Saxon Rune Poem lists 29 Anglo-Saxon runes. Each poem differs in poetic verse, but they contain numerous parallels between one another. Further, the poems provide references to figures from Norse paganism, Norse and Anglo-Saxon paganism, the latter included alongside Christianity, Christian references. A list of rune names is also recorded in the ''Abecedarium Nordmannicum'', a 9th-century manuscript, but whether this can be called a poem or not is a matter of some debate. The rune poems have been theorized as having been mnemonic devices that allowed the user to remember the order and names of each le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jötunn
A (also jotun; plural ; in the normalised scholarly spelling of Old Norse, ; or, in Old English, , plural ) is a type of being in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, are often contrasted with gods (the Æsir and Vanir) and with other non-human figures, such as dwarf (mythology), dwarfs and elf, elves, although the groupings are not always mutually exclusive. The entities included in the category are referred to by several other terms, including , (or ) and if male and or if female. The typically dwell across boundaries from the gods and humans in lands such as . The are frequently attested throughout the Old Norse records, with also featuring in the Old English epic poem ''Beowulf''. The usage of the terms is dynamic, with an overall trend that the beings become portrayed as less impressive and more negative as Christianity becomes more influential over time. Although the term "giant" is sometimes used to gloss the word "" and its apparent synonyms in some transl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark (or Fuþark, ), also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic alphabets. It was a writing system used by Germanic peoples for Northwest Germanic dialects in the Migration Period. Inscriptions are found on artifacts including jewelry, amulets, plateware, tools, and weapons, as well as runestones, from the 2nd to the 8th centuries. In Scandinavia, beginning in the late 8th century, the script was simplified to the Younger Futhark, while the Anglo-Saxons and Frisians instead extended it, giving rise to the Anglo-Saxon runes, Anglo-Saxon futhorc. Both the Anglo-Saxon futhorc and the Younger Futhark remained in use during the Early Middle Ages, Early and the High Middle Ages respectively, but knowledge of how to read the Elder Futhark was forgotten until 1865, when it was deciphered by Norwegian scholar Sophus Bugge. Description The Elder Futhark is named after the initial phoneme of the first six rune names: /f/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runic Alphabet
Runes are the Letter (alphabet), letters in a set of related alphabets, known as runic rows, runic alphabets or futharks (also, see ''#Futharks, futhark'' vs ''#Runic alphabets, runic alphabet''), native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were primarily used to represent a sound value (a phoneme) but they were also used to represent the concepts after which they are named (ideographic runes). Runology is the academic study of the runic alphabets, runic inscriptions, runestones, and their history. Runology forms a specialised branch of Germanic philology. The earliest secure runic inscriptions date from at latest AD 150, with a possible earlier inscription dating to AD 50 and Tacitus's possible description of rune use from around AD 98. The Svingerud Runestone dates from between AD 1 and 250. Runes were generally replaced by the Latin alphabet as the cultures that had used runes underwent Christianisation, by approximately AD 700 in central Europe and 1100 in northern Europe. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the region's westernmost and most list of countries and dependencies by population density, sparsely populated country. Its Capital city, capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which is home to about 36% of the country's roughly 380,000 residents (excluding nearby towns/suburbs, which are separate municipalities). The official language of the country is Icelandic language, Icelandic. Iceland is on a rift between Plate tectonics, tectonic plates, and its geologic activity includes geysers and frequent Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions. The interior consists of a volcanic plateau with sand and lava fields, mountains and glaciers, and many Glacial stream, glacial rivers flow to the sea through the Upland and lowland, lowlands. Iceland i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Th (digraph)
Th is a digraph in the Latin script. It was originally introduced into Latin to transliterate Greek loan words. In modern languages that use the Latin alphabet, it represents a number of different sounds. It is the most common digraph in order of frequency in the English language. Aspirated stop /tʰ/ The digraph was first introduced in Latin to transliterate the letter theta in loans from Greek. Theta was pronounced as an aspirated stop in Classical and early Koine Greek. is used in academic transcription systems to represent letters in south and east Asian alphabets that have the value . According to the Royal Thai General System of Transcription, for example, represents a series of Thai letters with the value . is also used to transcribe the phoneme in Southern Bantu languages, such as Zulu and Tswana. Voiceless fricative /θ/ During late antiquity, the Greek phoneme represented by the letter mutated from an aspirated stop to a dental fricative . Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |