|
Third Cuneiform
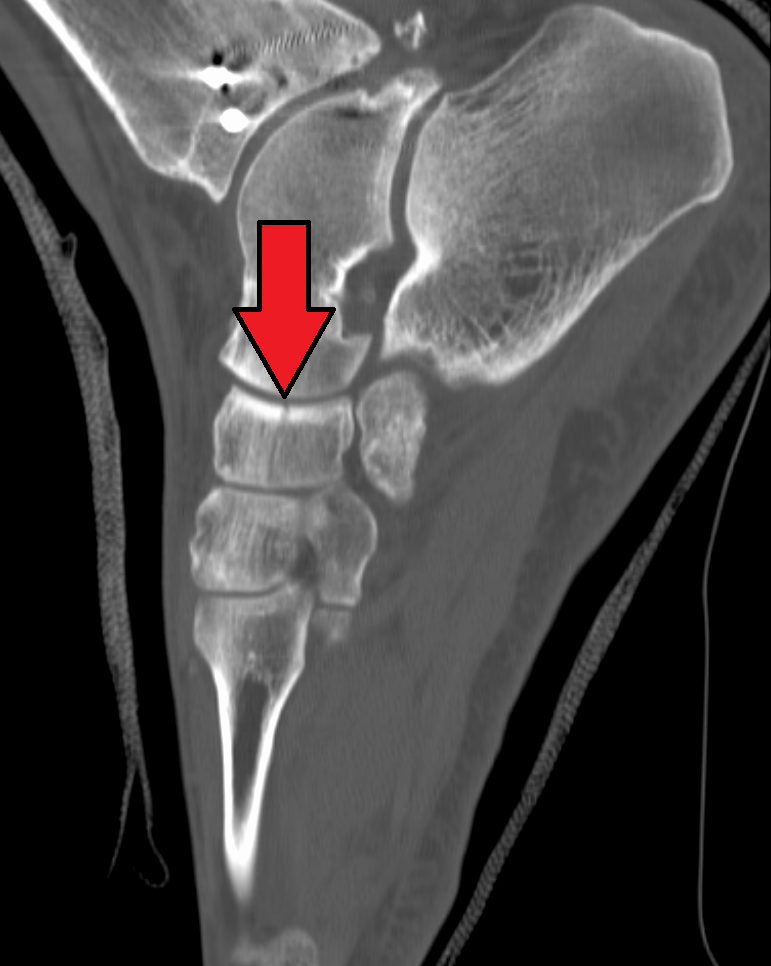
There are three cuneiform ("wedge-shaped") bones in the human foot: * the first or medial cuneiform * the second or intermediate cuneiform, also known as the middle cuneiform * the third or lateral cuneiform They are located between the navicular bone and the First metatarsal bone, first, Second metatarsal bone, second and Third metatarsal bone, third metatarsal bones and are medial to the cuboid bone. Structure There are three cuneiform bones: # The medial cuneiform (also known as first cuneiform) is the largest of the cuneiforms. It is situated at the medial side of the foot, anterior to the navicular bone and posterior to the base of the first metatarsal. Lateral to it is the intermediate cuneiform. It articulates with four bones: the navicular, second cuneiform, and First metatarsal bone, first and Second metatarsal bone, second metatarsals. The tibialis anterior muscle, tibialis anterior and fibularis longus muscle inserts at the medial cuneiform bone. # The intermediate c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform Cartilages
In the human larynx, the cuneiform cartilages (from Latin: ''cuneus'' 'wedge' + ''forma'' 'form'; also known as cartilages of Wrisberg) are two small, elongated pieces of yellow elastic cartilage, placed one on either side, in the aryepiglottic fold. The cuneiforms are paired cartilages that sit on top of and move with the arytenoids. They are located above and in front of the corniculate cartilages, and the presence of these two pairs of cartilages result in small bulges on the surface of the mucous membrane A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It ..., i.e. cuneiform tubercle. Covered by the aryepiglottic folds, the cuneiforms form the lateral aspect of the laryngeal inlet, while the corniculates form the posterior aspect, and the epiglottis the anterior. Function of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navicular
The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals. Human anatomy The navicular bone in humans is one of the tarsus (skeleton), tarsal bones, found in the foot. Its name derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat, caused by the strongly concave Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, proximal joint, articular surface. The term ''navicular bone'' or ''hand navicular bone'' was formerly used for the scaphoid bone, one of the Carpal bones, carpal bones of the wrist. The navicular bone in humans is located on the Anatomical terms of location#Relative directions, medial side of the foot, and articulates proximally with the Talus bone, talus, Anatomical terms of location#Relative directions, distally with the three cuneiform bones, and Anatomical terms of location#Relative directions, laterally with the Cuboid bone, cuboid. It is the last of the foot bones to start ossification and does not tend to do so until the end of the third year in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform scripts are marked by and named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions (Latin: ) which form their Grapheme, signs. Cuneiform is the History of writing#Inventions of writing, earliest known writing system and was originally developed to write the Sumerian language of southern Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). Over the course of its history, cuneiform was adapted to write a number of languages in addition to Sumerian. Akkadian language, Akkadian texts are attested from the 24th century BC onward and make up the bulk of the cuneiform record. Akkadian cuneiform was itself adapted to write the Hittite language in the early second millennium BC. The other languages with significant cuneiform Text corpus, corpora are Eblaite language, Eblaite, Elamit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsus (skeleton)
In the human body, the tarsus (: tarsi) is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot (Cuboid bone, cuboid, medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform bone, cuneiform, and navicular) and hindfoot (Talus bone, talus and calcaneus). The tarsus articulates with the bones of the metatarsus, which in turn articulate with the proximal phalanges of the toes. The joint between the tibia and fibula above and the tarsus below is referred to as the ankle, ankle joint proper. In humans the largest bone in the tarsus is the calcaneus, which is the weight-bearing bone within the heel of the foot. Human anatomy Bones The talus bone or ankle bone is connected superiorly to the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and fibula, to form the ankle, ankle joint or talocrural joint; inferiorly, at the subtalar joint, to the calcaneus or heel bone. Together, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lisfranc Fracture
A Lisfranc injury, also known as Lisfranc fracture, is an injury of the foot in which one or more of the metatarsal bones are displaced from the tarsus. The injury is named after Jacques Lisfranc de St. Martin, a French surgeon and gynecologist who noticed this fracture pattern amongst cavalrymen in 1815, after the War of the Sixth Coalition. Causes The midfoot consists of five bones that form the arches of the foot (the cuboid, navicular, and three cuneiform bones) and their articulations with the bases of the five metatarsal bones. It is these articulations that are damaged in a Lisfranc injury. Such injuries typically involve the ligaments between the medial cuneiform bone and the bases of the second and third metatarsal bones, and each of these ligaments is called Lisfranc ligament. Lisfranc injuries are caused when excessive kinetic energy is applied either directly or indirectly to the midfoot and are often seen in traffic collisions or industrial accidents. Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Cuneiform
There are three cuneiform ("wedge-shaped") bones in the human foot: * the first or medial cuneiform * the second or intermediate cuneiform, also known as the middle cuneiform * the third or lateral cuneiform They are located between the navicular bone and the first, second and third metatarsal bones and are medial to the cuboid bone. Structure There are three cuneiform bones: # The medial cuneiform (also known as first cuneiform) is the largest of the cuneiforms. It is situated at the medial side of the foot, anterior to the navicular bone and posterior to the base of the first metatarsal. Lateral to it is the intermediate cuneiform. It articulates with four bones: the navicular, second cuneiform, and first and second metatarsals. The tibialis anterior and fibularis longus muscle inserts at the medial cuneiform bone. # The intermediate cuneiform (second cuneiform or middle cuneiform) is shaped like a wedge, the thin end pointing downwards. The intermediate cuneiform is situa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibularis Longus Muscle
In human anatomy, the fibularis longus (also known as peroneus longus) is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body ( eversion) and to extend the foot downward away from the body (plantar flexion) at the ankle. The fibularis longus is the longest and most superficial of the three fibularis (peroneus) muscles. At its upper end, it is attached to the head of the fibula, and its "belly" runs down along most of this bone. The muscle becomes a tendon that wraps around and behind the lateral malleolus of the ankle, then continues under the foot to attach to the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal. It is supplied by the superficial fibular nerve. Structure The fibularis longus arises from the head and upper two-thirds of the lateral, or outward, surface of the fibula, from the deep surface of the fascia, and from the connective tissue between it and the muscles on the front and back of the leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Cuneiform
There are three cuneiform ("wedge-shaped") bones in the human foot: * the first or medial cuneiform * the second or intermediate cuneiform, also known as the middle cuneiform * the third or lateral cuneiform They are located between the navicular bone and the first, second and third metatarsal bones and are medial to the cuboid bone. Structure There are three cuneiform bones: # The medial cuneiform (also known as first cuneiform) is the largest of the cuneiforms. It is situated at the medial side of the foot, anterior to the navicular bone and posterior to the base of the first metatarsal. Lateral to it is the intermediate cuneiform. It articulates with four bones: the navicular, second cuneiform, and first and second metatarsals. The tibialis anterior and fibularis longus muscle inserts at the medial cuneiform bone. # The intermediate cuneiform (second cuneiform or middle cuneiform) is shaped like a wedge, the thin end pointing downwards. The intermediate cuneiform is situat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibialis Anterior Muscle
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle of the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It originates from the upper portion of the tibia; it inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert the foot. This muscle is mostly located near the shin. It is situated on the lateral side of the tibia; it is thick and fleshy above, tendinous below. The tibialis anterior overlaps the anterior tibial vessels and deep peroneal nerve in the upper part of the leg. Structure The tibialis anterior muscle is the most medial muscle of the anterior compartment of the leg. The muscle ends in a tendon which is apparent on the anteriomedial dorsal aspect of the foot close to the ankle. Its tendon is ensheathed in a synovial sheath. The tendon passes through the medial compartment superior and inferior extensor retinacula of the foot. Origin The tibialis anterior muscle arises from the upper 2/3 of the lateral surface of the tibia and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Hallucis Brevis Muscle
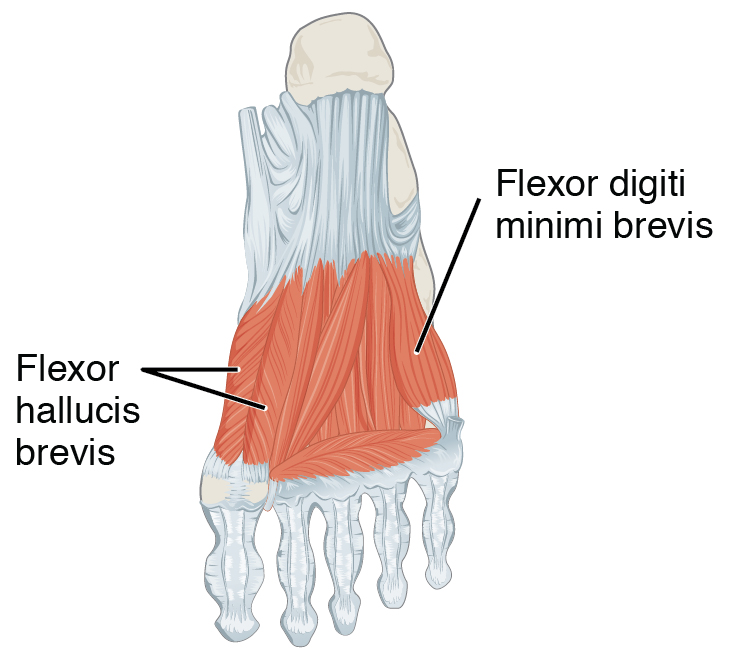
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a muscle of the foot that flexes the big toe. Structure Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone, from the contiguous portion of the third cuneiform, and from the prolongation of the tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle which is attached to that bone. It divides in front into two portions, which are inserted into the medial and lateral sides of the base of the first phalanx of the great toe, a sesamoid bone being present in each tendon at its insertion. The medial portion is blended with the abductor hallucis muscle previous to its insertion; the lateral portion (sometimes described as the first plantar interosseus) with the adductor hallucis muscle. The tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle lies in a groove between the two. Its tendon usually contains two sesamoid bones at the point under the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Innervation Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibialis Posterior Muscle
The tibialis posterior muscle is the most central of all the leg muscles, and is located in the deep posterior compartment of the leg. It is the key stabilizing muscle of the lower leg. Posterior tibial tendonitis Posterior tibial tendonitis is a condition that predominantly affects runners and active individuals. It involves inflammation or tearing of the posterior tibial tendon, which connects the calf muscle to the bones on the inside of the foot. It plays a vital role in supporting the arch and assisting in foot movement. This condition can cause pain, swelling, and potentially lead to flatfoot if left untreated. Structure The tibialis posterior muscle originates on the inner posterior border of the fibula laterally. It is also attached to the interosseous membrane medially, which attaches to the tibia and fibula. The tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle (sometimes called the posterior tibial tendon) descends posterior to the medial malleolus. It terminates by dividin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuboid Bone
In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot. Structure The cuboid bone is the most lateral of the bones in the distal row of the tarsus. It is roughly cubical in shape, and presents a prominence in its inferior (or plantar) surface, the tuberosity of the cuboid. The bone provides a groove where the tendon of the peroneus longus muscle passes to reach its insertion in the first metatarsal and medial cuneiform bones. Surfaces The dorsal surface, directed upward and lateralward, is rough, for the attachment of ligaments. The plantar surface presents in front a deep groove, the peroneal sulcus, which runs obliquely forward and medialward; it lodges the tendon of the peroneus longus, and is bounded behind by a prominent ridge, to which the long plantar ligament is attached. The ridge ends laterally in an eminence, the tuberosity, the surface of which presents an oval facet; on this facet glides the sesamoid bone or cartilage frequently found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |