|
Thin-film Transistor
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is a special type of field-effect transistor (FET) where the transistor is made by thin film deposition. TFTs are grown on a supporting (but non-conducting) substrate, such as glass. This differs from the conventional bulk metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET), where the semiconductor material typically ''is'' the substrate, such as a silicon wafer. The traditional application of TFTs is in TFT liquid-crystal displays. Design and manufacture TFTs can be fabricated with a wide variety of semiconductor materials. Because it is naturally abundant and well understood, amorphous or polycrystalline silicon were (and still are) used as the semiconductor layer. However, because of the low mobility of amorphous silicon and the large device-to-device variations found in polycrystalline silicon, other materials have been studied for use in TFTs. These include cadmium selenide, metal oxides such as indium gallium zinc oxide (IGZO) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by the Austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Vapor Deposition
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high-quality, and high-performance, solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films. In typical CVD, the wafer (electronics), wafer (substrate) is exposed to one or more Volatility (chemistry), volatile wikt:precursor, precursors, which chemical reaction, react and/or chemical decomposition, decompose on the substrate surface to produce the desired deposit. Frequently, volatile by-products are also produced, which are removed by gas flow through the reaction chamber. Microfabrication processes widely use CVD to deposit materials in various forms, including: Single crystal, monocrystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, and Epitaxy, epitaxial. These materials include: silicon (Silicon dioxide, dioxide, silicon carbide, carbide, silicon nitride, nitride, silicon oxynitride, oxynitride), carbon (carbon (fiber), fiber, carbon nanofibers, nanofibers, carbon nanot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
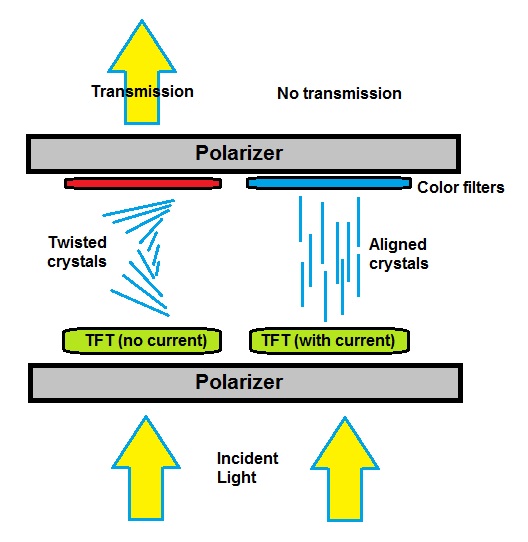
Liquid-crystal Display
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other Electro-optic modulator, electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers to display information. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or Reflector (photography), reflector to produce images in color or Monochrome monitor, monochrome. LCDs are available to display arbitrary images (as in a general-purpose computer display) or fixed images with low information content, which can be displayed or hidden: preset words, digits, and seven-segment displays (as in a digital clock) are all examples of devices with these displays. They use the same basic technology, except that arbitrary images are made from a matrix of small pixels, while other displays have larger elements. LCDs are used in a wide range of applications, including LCD televisions, computer monitors, Dashboard, instrument panels, flight instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TFT LCD
A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display (TFT LCD) is a type of liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film transistor, thin-film-transistor technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven (i.e. with segments directly connected to electronics outside the LCD) LCDs with a few segments. TFT LCDs are used in television sets, computer monitors, mobile phones, video game systems, personal digital assistants, navigation systems, video projector, projectors, and dashboards in some automobiles and in medium to high end motorcycles. History In February 1957, J. Torkel Wallmark, John Wallmark of RCA filed a patent for a thin film MOSFET. Paul K. Weimer, also of RCA, implemented Wallmark's ideas and developed the thin-film transistor (TFT) in 1962, a type of MOSFET distinct from the standard bulk MOSFET. It was made with thin films of cadmium selenide and cadmium s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-temperature Polycrystalline Silicon
Low-temperature polycrystalline silicon (LTPS) is polycrystalline silicon that has been synthesized at relatively low temperatures (~650 °C and lower). LTPS is important for display device, display industries, since the use of large glass panels prohibits exposure to deformative high temperatures. More specifically, the use of polycrystalline silicon in thin-film transistors (LTPS-TFT) has high potential for large-scale production of electronic devices like flat panel LCD displays or image sensors. LTPS is polycrystalline silicon that has been synthesized at ~650 °C and lower, compared to traditional methods (above 900 °C). Development of polycrystalline silicon Polycrystalline silicon (p-Si) is a pure and conductive form of the element composed of many crystallites, or grains of highly ordered crystal structure, crystal lattice. In 1984, studies showed that amorphous silicon (a-Si) is an excellent precursor for forming p-Si films with stable structures and low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMOLED
AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode; ) is a type of OLED display device technology. OLED describes a specific type of thin-film-display technology in which organic compounds form the electroluminescence, electroluminescent material, and active matrix refers to the technology behind the addressing of pixels. Since 2007, AMOLED technology has been used among mobile phones, media players, TVs and digital cameras, and the current progress over this technology is in lower power usage, lower cost, better resolution and specifically for larger screen (e.g. 8k screens). Design An AMOLED display consists of an active matrix of OLED pixels generating light (luminescence) upon electrical activation that have been deposited or integrated onto a thin-film transistor (TFT) array, which functions as a series of switches to control the current flowing to each individual pixel. Typically, this continuous current flow is controlled by at least two TFTs at each pixel (to trigger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Electron Device Letters
''IEEE Electron Device Letters'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published monthly by the IEEE. It was founded in 1980 by IEEE Electron Devices Society. The journal covers the advances in electron and ion integrated circuit devices. Its editor-in-chief is Sayeef Salahuddin (University of California, Berkeley). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 4.1. References External links * Electron Device Letters, IEEE Electrical and electronic engineering journals Academic journals established in 1980 Semiconductor journals English-language journals Monthly journals {{physics-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universidade Nova De Lisboa
NOVA University Lisbon (, ), or just NOVA, is a Portuguese public university whose rectorate is located in Campolide, Lisbon. Founded in 1973, it is the newest of the public universities in the Portuguese capital city, earning its name as the "New" (NOVA) University of Lisbon. The institution has more than 20,000 students, 1,800 professors and staff members distributed through five faculties, three institutes and one school, providing a variety of courses in several fields of knowledge. History NOVA University Lisbon was founded in 1973 and is the newest public university in the Lisbon metropolitan area, with teaching units in Lisbon, Almada, Oeiras, and Cascais. It was founded as a response to ever-increasing demand for higher education in Portugal and in Lisbon in particular. While its early years focused on graduate and specialist programs, NOVA started expanding its teaching and research from 1977 onwards. The structure of NOVA was organized according to a departmental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon State University
Oregon State University (OSU) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Corvallis, Oregon, United States. OSU offers more than 200 undergraduate degree programs and a variety of graduate and doctoral degrees through all 11 of the university's colleges. It has the seventh-largest engineering college in the nation (2023). Undergraduate enrollment for all colleges combined averages over 32,000 while an additional 5,000 students are engaged in post-graduate coursework through the university. In 2023, over 37,000 students were enrolled at OSU, making it the largest university in the state. Out-of-state students typically make up over one-quarter of the student body. Since its founding, over 272,000 students have graduated from OSU. The university is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". Initially chartered as a land-grant university, OS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
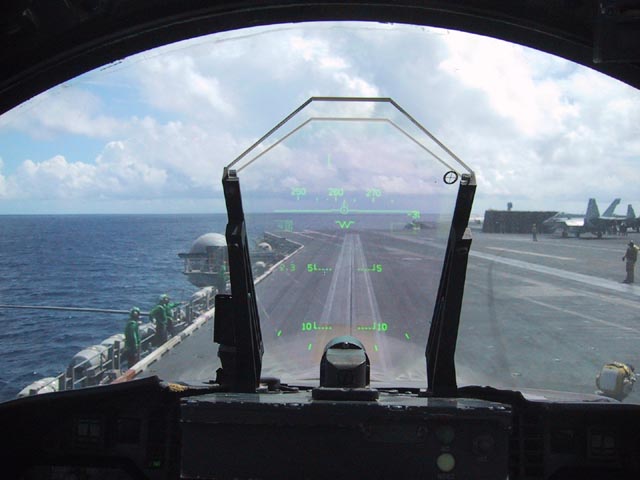
Head-up Display
A head-up display, or heads-up display, also known as a HUD () or head-up guidance system (HGS), is any transparent display that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints. The origin of the name stems from a pilot being able to view information with the head positioned "up" and looking forward, instead of angled down looking at lower instruments. A HUD also has the advantage that the pilot's eyes do not need to refocus to view the outside after looking at the optically nearer instruments. Although they were initially developed for military aviation, HUDs are now used in commercial aircraft, automobiles, and other (mostly professional) applications. Head-up displays were a precursor technology to augmented reality (AR), incorporating a subset of the features needed for the full AR experience, but lacking the necessary registration and tracking between the virtual content and the user's real-world environment. Overview A typical HUD cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Tin Oxide
Indium tin oxide (ITO) is a ternary composition of indium, tin and oxygen in varying proportions. Depending on the oxygen content, it can be described as either a ceramic or an alloy. Indium tin oxide is typically encountered as an oxygen-saturated composition with a formulation of 74% In, 8% Sn, and 18% O by weight. Oxygen-saturated compositions are so typical that unsaturated compositions are termed ''oxygen-deficient ITO''. It is transparent and colorless in thin layers, while in bulk form it is yellowish to gray. In the infrared region of the spectrum it acts as a metal-like mirror. Indium tin oxide is one of the most widely used transparent conducting oxides, not just for its electrical conductivity and optical transparency, but also for the ease with which it can be deposited as a thin film, as well as its chemical resistance to moisture. As with all transparent conducting films, a compromise must be made between conductivity and transparency, since increasing the thickness a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a variety of materials (chemicals) depending on the type of cell. An electrode may be called either a cathode or anode according to the direction of the electric current, unrelated to the potential difference between electrodes. Michael Faraday coined the term "" in 1833; the word recalls the Greek ἤλεκτρον (, "amber") and ὁδός (, "path, way"). The electrophore, invented by Johan Wilcke in 1762, was an early version of an electrode used to study static electricity. Anode and cathode in electrochemical cells Electrodes are an essential part of any battery. The first electrochemical battery was devised by Alessandro Volta and was aptly named the Voltaic cell. This battery consisted of a stack of copper and zinc electrodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |