|
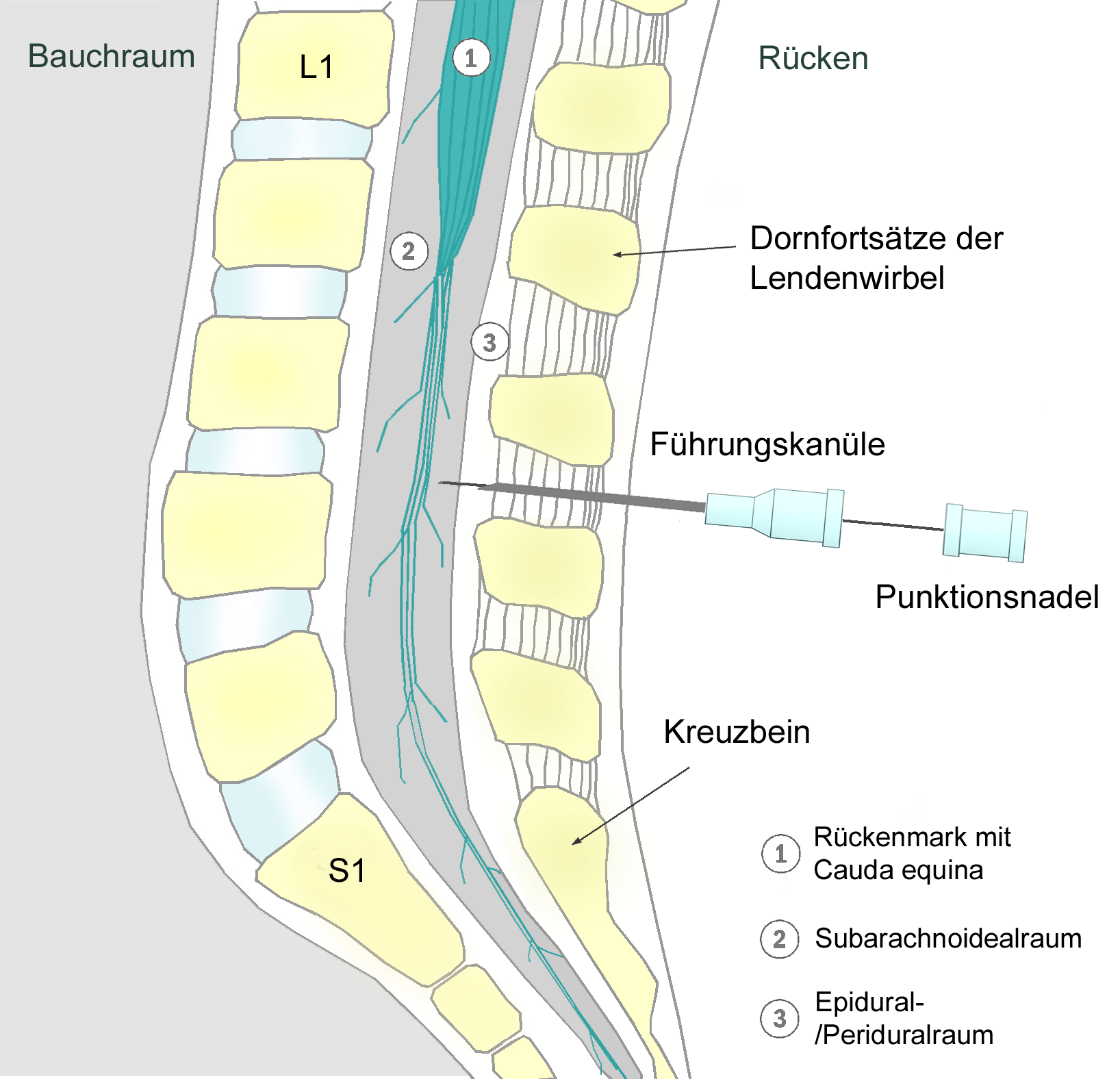
Thecal Sac
The thecal sac or dural sac is the membranous sheath (theca) or tube of dura mater that surrounds the spinal cord and the cauda equina. The thecal sac contains the cerebrospinal fluid which provides nutrients and buoyancy to the spinal cord. From the skull the tube adheres to bone at the foramen magnum and extends down to the second sacral vertebra where it tapers to cover over the filum terminale. Along most of the spinal canal it is separated from the inner surface by the epidural space. The sac has projections that follow the spinal nerves along their paths out of the vertebral canal which become the dural root sheaths. Clinical significance The lumbar cistern is part of the subarachnoid space. It is the space within the thecal sac which extends from below the end of the spinal cord (the conus medularis), typically at the level of the first to second lumbar vertebrae down to tapering of the dura at the level of the second sacral vertebra. The dura is pierced with a nee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Membrane
A biological membrane, biomembrane or cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane that separates the interior of a cell from the external environment or creates intracellular compartments by serving as a boundary between one part of the cell and another. Biological membranes, in the form of eukaryotic cell membranes, consist of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded, integral and peripheral proteins used in communication and transportation of chemicals and ions. The bulk of lipids in a cell membrane provides a fluid matrix for proteins to rotate and laterally diffuse for physiological functioning. Proteins are adapted to high membrane fluidity environment of the lipid bilayer with the presence of an annular lipid shell, consisting of lipid molecules bound tightly to the surface of integral membrane proteins. The cell membranes are different from the isolating tissues formed by layers of cells, such as mucous membranes, basement membranes, and serous membranes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumbar Cistern
The subarachnoid cisterns are spaces formed by openings in the subarachnoid space, an anatomic space in the meninges of the brain. The space is situated between the two meninges, the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. These cisterns are filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Structure Although the pia mater adheres to the surface of the brain, closely following the contours of its gyri and sulci, the arachnoid mater only covers its superficial surface, bridging across the gyri. This leaves wider spaces between the pia and arachnoid and the cavities are known as the subarachnoid cisterns. Although they are often described as distinct compartments, the subarachnoid cisterns are not truly anatomically distinct. Rather, these subarachnoid cisterns are separated from each other by a trabeculated porous wall with various-sized openings. Cisterns There are many cisterns in the brain with several large ones noted with their own name. At the base of the spinal cord is another subarachn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spontaneous Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
A cerebrospinal fluid leak (CSF leak or CSFL) is a medical condition where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that surrounds the brain and spinal cord leaks out of one or more holes or tears in the dura mater. A CSF leak is classed as either spontaneous (primary), having no known cause (sCSF leak), or nonspontaneous (secondary) where it is attributed to an underlying condition. Causes of a primary CSF leak are those of Major trauma, trauma including from an accident or intentional injury, or arising from a medical intervention known as iatrogenic. A basilar skull fracture as a cause can give the sign of CSF leakage from the ear, nose or mouth. A lumbar puncture can give the symptom of a post-dural-puncture headache. A cerebrospinal fluid leak can be either cranial or spinal, and these are two different disorders. A spinal CSF leak can be caused by one or more meninges, meningeal diverticulum, diverticula or CSF-venous fistulas not associated with an epidural space, epidural leak. A spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak
A cerebrospinal fluid leak (CSF leak or CSFL) is a medical condition where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that surrounds the brain and spinal cord leaks out of one or more holes or tears in the dura mater. A CSF leak is classed as either spontaneous (primary), having no known cause (sCSF leak), or nonspontaneous (secondary) where it is attributed to an underlying condition. Causes of a primary CSF leak are those of trauma including from an accident or intentional injury, or arising from a medical intervention known as iatrogenic. A basilar skull fracture as a cause can give the sign of CSF leakage from the ear, nose or mouth. A lumbar puncture can give the symptom of a post-dural-puncture headache. A cerebrospinal fluid leak can be either cranial or spinal, and these are two different disorders. A spinal CSF leak can be caused by one or more meningeal diverticula or CSF-venous fistulas not associated with an epidural leak. A spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leak may occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood–brain Barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that regulates the transfer of solutes and chemicals between the circulatory system and the central nervous system, thus protecting the brain from harmful or unwanted substances in the blood. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the Capillary, capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive transport, passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and Molecular mass, large or Hydrophile, hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmaceutical Drug
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to diagnose, cure, treat, or prevent disease. Drug therapy ( pharmacotherapy) is an important part of the medical field and relies on the science of pharmacology for continual advancement and on pharmacy for appropriate management. Drugs are classified in many ways. One of the key divisions is by level of control, which distinguishes prescription drugs (those that a pharmacist dispenses only on the medical prescription) from over-the-counter drugs (those that consumers can order for themselves). Medicines may be classified by mode of action, route of administration, biological system affected, or therapeutic effects. The World Health Organization keeps a list of essential medicines. Drug discovery and drug development are complex and expensive endeavors undertaken by pharmaceutical companies, academic scientists, and governments. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Route Of Administration
In pharmacology and toxicology, a route of administration is the way by which a medication, drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body. Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. Common examples include oral administration, oral and intravenous therapy, intravenous administration. Routes can also be classified based on where the target of action is. Action may be topical medication, topical (local), enteral administration, enteral (system-wide effect, but delivered through the gastrointestinal tract), or #Parenteral, parenteral (systemic action, but is delivered by routes other than the GI tract). Route of administration and dosage form are aspects of drug delivery. Classification Routes of administration are usually classified by application location (or exposition). The route or course the active substance takes from application location to the location where it has its target effect is usually rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrathecal Administration
Intrathecal administration is a route of administration for drugs via an injection into the spinal canal, or into the subarachnoid space (sin. ''intrathecal space'') so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It is useful in several applications, such as for spinal anesthesia, chemotherapy, or pain management. This route is also used to introduce drugs that fight certain infections, particularly post-neurosurgical. Typically, the drug is given this way to avoid being stopped by the blood–brain barrier, as it may not be able to pass into the brain when given orally. Drugs given by the intrathecal route often have to be compounded specially by a pharmacist or technician because they cannot contain any preservative or other potentially harmful inactive ingredients that are sometimes found in standard injectable drug preparations. Intrathecal pseudodelivery is a technique where the drug is encapsulated in a porous capsule that is placed in communication with the CSF. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Anaesthesia
Spinal anaesthesia (or spinal anesthesia), also called spinal block, subarachnoid block, intradural block and intrathecal block, is a form of neuraxial regional anaesthesia involving the injection of a local anaesthetic with or without an opioid into the subarachnoid space. Usually a single-shot dose is administrered through a fine needle, alternatively continuous spinal anaesthesia through a intrathecal catheter can be performed. It is a safe and effective form of anesthesia usually performed by anesthesiologists and CRNAs that can be used as an alternative to general anesthesia commonly in surgeries involving the lower extremities and surgeries below the umbilicus. The local anesthetic with or without an opioid injected into the cerebrospinal fluid provides locoregional anaesthesia: true anaesthesia, motor, sensory and autonomic (sympathetic) blockade. Administering analgesics (opioid, alpha2-adrenoreceptor agonist) in the cerebrospinal fluid without a local anaestheti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidural Anesthesia
Epidural administration (from Ancient Greek ἐπί, "upon" + '' dura mater'') is a method of medication administration in which a medicine is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord. The epidural route is used by physicians and nurse anesthetists to administer local anesthetic agents, analgesics, diagnostic medicines such as radiocontrast agents, and other medicines such as glucocorticoids. Epidural administration involves the placement of a catheter into the epidural space, which may remain in place for the duration of the treatment. The technique of intentional epidural administration of medication was first described in 1921 by the Spanish Aragonese military surgeon Fidel Pagés. Epidural anaesthesia causes a loss of sensation, including pain, by blocking the transmission of signals through nerve fibres in or near the spinal cord. For this reason, epidurals are commonly used for pain control during childbirth and surgery, for which the technique is con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conus Medularis
The conus medullaris (Latin for "medullary cone") or conus terminalis is the tapered, lower end of the spinal cord. It occurs near lumbar vertebral levels 1 (L1) and 2 (L2), occasionally lower. The upper end of the conus medullaris is usually not well defined, however, its corresponding spinal cord segments are usually S1–S5. After the spinal cord tapers out, the spinal nerves continue to branch out diagonally, forming the cauda equina. The pia mater that surrounds the spinal cord, however, projects directly downward, forming a slender filament called the filum terminale, which connects the conus medullaris to the back of the coccyx. The filum terminale provides a connection between the conus medullaris and the coccyx which stabilizes the entire spinal cord. Blood supply The blood supply consists of three spinal arterial vessels—the anterior median longitudinal arterial trunk and the right and left posterior spinal arteries. Other less prominent sources of blood supply in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |