|
Theca Of Follicle
The theca folliculi comprise a layer of the ovarian follicles. They appear as the follicles become secondary follicles. The theca are divided into two layers, the theca interna and the theca externa. Theca cells are a group of endocrine cells in the ovary made up of connective tissue surrounding the follicle. They have many diverse functions, including promoting folliculogenesis and recruitment of a single follicle during ovulation. Theca cells and granulosa cells together form the stroma of the ovary. Androgen synthesis Theca cells are responsible for synthesizing androgens, providing signal transduction between granulosa cells and oocytes during development by the establishment of a vascular system, providing nutrients, and providing structure and support to the follicle as it matures. Theca cells are responsible for the production of androstenedione, and indirectly the production of 17β estradiol, also called E2, by supplying the neighboring granulosa cells wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Follicle
An ovarian follicle is a roughly spheroid cellular aggregation set found in the ovaries. It secretes hormones that influence stages of the menstrual cycle. In humans, women have approximately 200,000 to 300,000 follicles at the time of puberty, each with the potential to release an egg cell (ovum) at ovulation for Human fertilization, fertilization. These eggs are developed once every menstrual cycle with around 300-400 being ovulated during a woman's reproductive lifetime. Structure Ovarian follicles are the basic units of female reproductive biology. Each of them contains a single oocyte (immature ovum or egg cell). These structures are periodically initiated to grow and develop, culminating in ovulation of usually a single competent oocyte in humans. They also consist of granulosa cells and theca of follicle. Oocyte Once a month, one of the ovaries releases a mature egg (ovum), known as an oocyte. The nucleus of such an oocyte is called a ''germinal vesicle (see picture).' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonadotropic Cell
1. Introduction Gonadotropic cells (also known as gonadotropes, gonadotrophs, delta cells, or delta basophils) are endocrine cells in the anterior pituitary that produce gonadotropins. More specifically, gonadotrophs produce and secrete glycoprotein polypeptide hormones, such as the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which are released due to the positive input of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). These gonadotropins are essential in the development and maintenance of reproductive function in mammals. This control of the reproductive system is coordinated by the electrical activity and signaling pathways of gonadotrophs as well as the tight regulation of gonadotropic cells by both sex steroids and paracrine factors. 2. Formation and Morphology During embryonic development, the anterior and posterior pituitary merge due to regulated cell-to-cell interactions, signaling pathways, and numerous transcription factors. Of the pituitary endo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
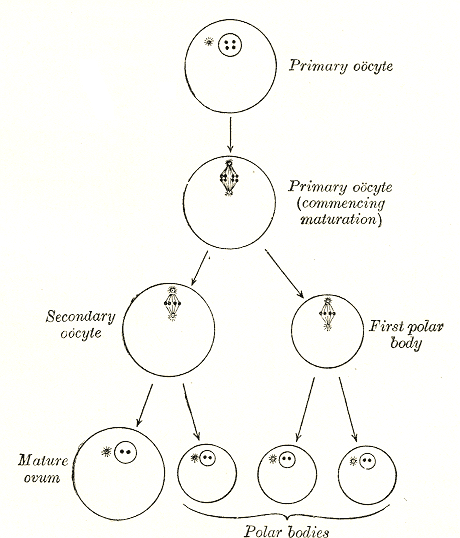
Oocyte
An oocyte (, oöcyte, or ovocyte) is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folliculogenesis
:''Although the process is similar in many animals, this article will deal exclusively with human folliculogenesis.'' In biology, folliculogenesis is the maturation of the ovarian follicle, a densely packed shell of somatic cells that contains an immature oocyte. Folliculogenesis describes the progression of a number of small '' primordial follicles'' into large '' preovulatory follicles'' that occurs in part during the menstrual cycle. Contrary to male spermatogenesis, which can last indefinitely, folliculogenesis ends when the remaining follicles in the ovaries are incapable of responding to the hormonal cues that previously recruited some follicles to mature. This depletion in follicle supply signals the beginning of menopause. Overview The primary role of the follicle is oocyte support. From the whole pool of follicles a woman is born with, only 0.1% of them will rise ovulation, whereas 99.9% will break down (in a process called follicular atresia). From birth, the ovaries of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy And Physiology Of Animals Ovarian Cycle Showing From Top Left Clockwise
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine, and is often studied alongside physiology. Anatomy is a complex and dynamic field that is constantly evolving as discoveries are made. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the use of advan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Luteum
The corpus luteum (Latin for "yellow body"; : corpora lutea) is a temporary endocrine structure in female ovaries involved in the production of relatively high levels of progesterone, and moderate levels of estradiol, and inhibin A. It is the remains of the ovarian follicle that has released a mature ovum during a previous ovulation. The corpus luteum is colored as a result of concentrating carotenoids (including lutein) from the diet and secretes a moderate amount of estrogen that inhibits further release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and thus secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). A new corpus luteum develops with each menstrual cycle. Development and structure The corpus luteum develops from an ovarian follicle during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle or oestrous cycle, following the release of a secondary oocyte from the follicle during ovulation. The follicle first forms a corpus hemorrhagicum before it beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thecoma
Thecomas or theca cell tumors are benign Ovarian cancer, ovarian neoplasms composed only of theca cells. Histogenetically they are classified as sex cord-stromal tumours. They are typically estrogen-producing and they occur in older women (mean age 59; 84% after menopause). (They can, however, appear before menopause.) 60% of patients present with abnormal uterine bleeding, and 20% have endometrial carcinoma. Pathologic features Grossly, the tumour is solid and yellow. Grossly and microscopically, it consists of the ovarian cortex. Microscopically, the tumour cells have abundant lipid-filled cytoplasm. References External links Gynaecological neoplasia {{oncology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracrine
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication (biology), cellular communication in which a Cell (biology), cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to cell signaling by endocrine system, endocrine factors, hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system; juxtacrine signaling, juxtacrine interactions; and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain. Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle and bone mass, and the growth of androgenic hair, body hair. It is associated with increased aggression, sex drive, Dominance hierarchy, dominance, courtship display, and a wide range of behavioral characteristics. In addition, testosterone in both sexes is involved in health and well-being, where it has a significant effect on overall mood, cognition, social and sexual behavior, metabolism and energy output, the cardiovascular system, and in the prevention of osteoporosis. Insufficient levels of testosterone in men may lead to abnormalities including frailty, accumulation of adipose fat tissue within the body, anxiety and depression, sexual performance issues, and bone loss. Excessiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of serine-threonine kinases whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulation of glycogen, sugar, and lipid metabolism. It should not be confused with 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMP-activated protein kinase). History Protein kinase A, more precisely known as adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cyclic AMP)-dependent protein kinase, abbreviated to PKA, was discovered by chemists Edmond H. Fischer and Edwin G. Krebs in 1968. They won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1992 for their work on phosphorylation and dephosphorylation and how it relates to PKA activity. PKA is one of the most widely researched Protein kinase, protein kinases, in part because of its uniqueness; out of 540 different protein kinase genes that make up the human kinome, only one other protein kinase, casein kinase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Amp
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP, cyclic AMP, or 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a second messenger, or cellular signal occurring within cells, that is important in many biological processes. cAMP is a derivative of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and used for intracellular signal transduction in many different organisms, conveying the cAMP-dependent pathway. History Earl Sutherland of Vanderbilt University won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers (such as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP). Synthesis The synthesis of cAMP is stimulated by trophic hormones that bind to receptors on the cell surface. cAMP levels reach maximal levels within minutes and decrease gradually over an hour in cultured cells. Cyclic AMP is synthesized from ATP by adenylate cyclase located on the inner side of the plasma membrane and anchored at vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. They are coupled with G proteins. They pass through the cell membrane seven times in the form of six loops (three extracellular loops interacting with ligand molecules, three intracellular loops interacting with G proteins, an N-terminal extracellular region and a C-terminal intracellular region) of amino acid residues, which is why they are sometimes referred to as seven-transmembrane receptors. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) licence/ref> Ligands can bind either to the extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |