|
Television In The United States
Television is one of the Mass media in the United States, major mass media outlets in the United States. In 2011, 96.7% of households owned television sets; about 114,200,000 American households owned at least one television set each in August 2013. Most households have more than one set. The percentage of households owning at least one television set peaked at 98.4%, in the 1996–1997 season. In 1948, 1 percent of U.S. households owned at least one television; in 1955, 75 percent did. In 1992, 60 percent of all U.S. households had Cable television in the United States, cable television subscriptions. However, this number has fallen to 40% in 2024. As a whole, the television networks that broadcast in the United States are the largest and most distributed in the world, and programs produced specifically for American networks are the most widely broadcast syndication, syndicated internationally. Because of a surge in the number and popularity of critically acclaimed television ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
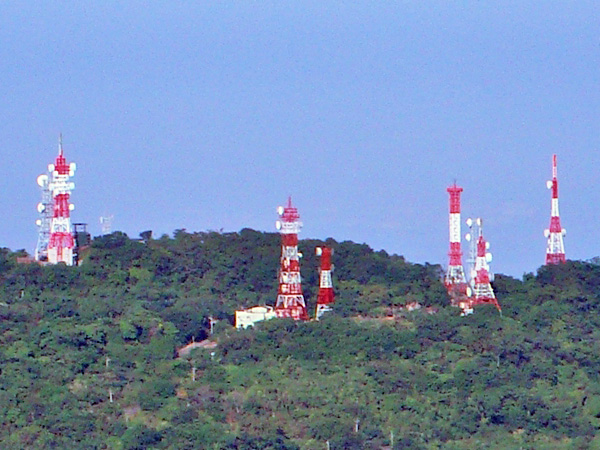
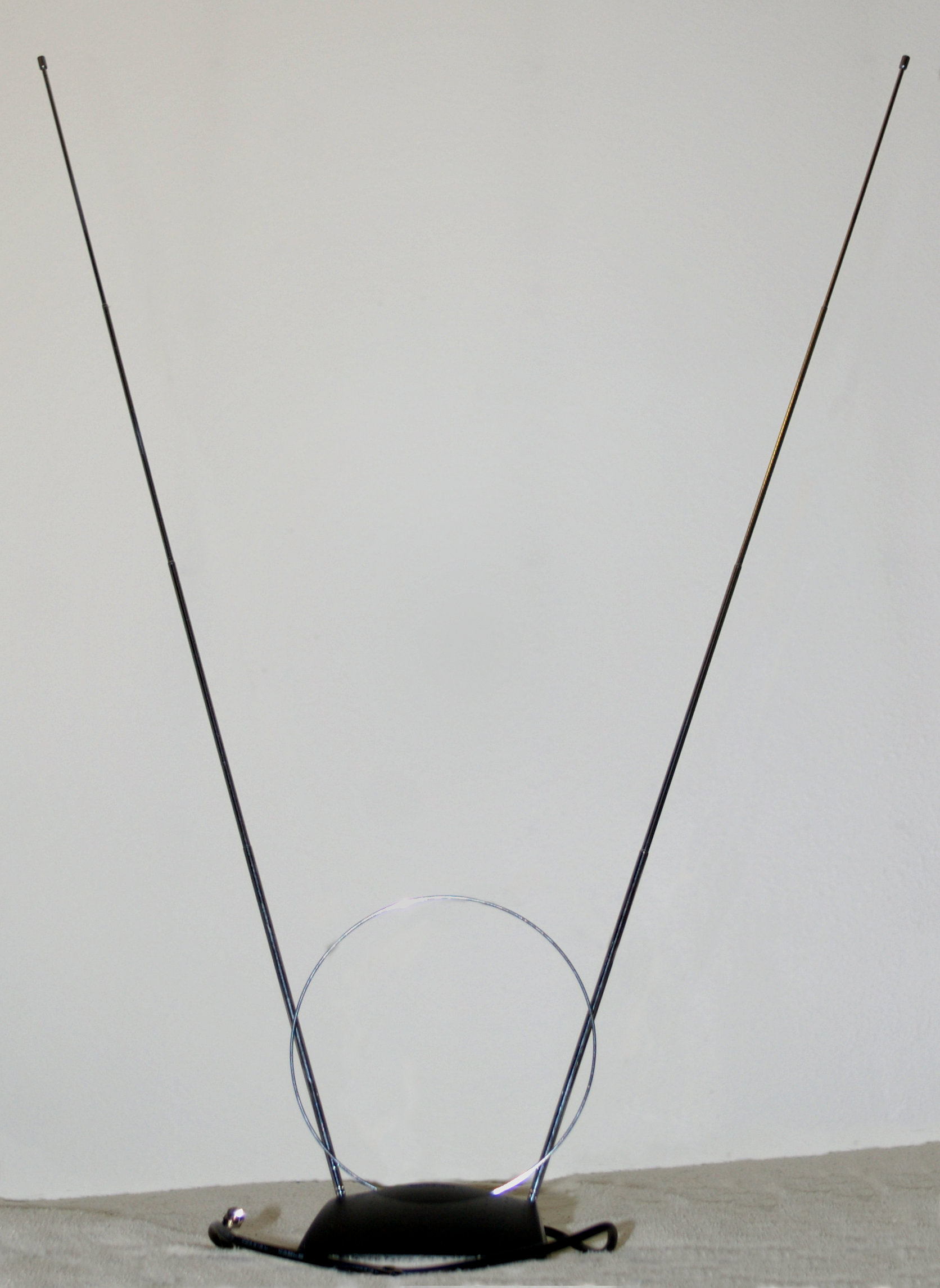
Terrestrial Television
Terrestrial television, or over-the-air television (OTA) is a type of television broadcasting in which the content is signal transmission, transmitted via radio waves from the terrestrial (Earth-based) transmitter of a TV station to a TV receiver having an television antenna, antenna. The term ''terrestrial'' is more common in Europe and Latin America, while in Canada and the United States it is called ''over-the-air'' or simply ''broadcast''. This type of Television broadcasting, TV broadcast is distinguished from newer technologies, such as satellite television (direct broadcast satellite or DBS television), in which the signal is transmitted to the receiver from an overhead satellite; cable television, in which the signal is carried to the receiver through a coaxial cable, cable; and Internet Protocol television, in which the signal is received over an Internet stream or on a network utilizing the Internet Protocol. Terrestrial television stations broadcast on television cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upper limit of audio frequencies that humans can hear (though these are not electromagnetic) and the lower limit of infrared frequencies, and also encompasses the microwave range. These are the frequencies at which energy from an oscillating current can radiate off a conductor into space as radio waves, so they are used in radio technology, among other uses. Different sources specify different upper and lower bounds for the frequency range. Electric current Electric currents that oscillate at radio frequencies (RF currents) have special properties not shared by direct current or lower audio frequency alternating current, such as the 50 or 60 Hz current used in electrical power distribution. * Energy from RF currents in conduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Terrestrial Television
Digital terrestrial television (DTTV, DTT, or DTTB) is a technology for terrestrial television, in which television stations broadcast television content in a digital signal, digital format. Digital terrestrial television is a major technological advancement over analog television, and has largely replaced analog television broadcasting, which was previously in common use since the middle of the 20th century. Test broadcasts began in 1998, and the Digital television transition, changeover to digital television began in 2006 and is now complete in many countries. The advantages of digital terrestrial television are similar to those obtained by digitizing platforms such as cable TV, satellite, and telecommunications: more efficient use of radio spectrum bandwidth, the ability to broadcast more channels than analog, better quality images, and potentially lower operating costs for broadcasters. Different Country, countries have adopted different digital broadcasting standards. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Television
Analog television is the original television technology that uses analog signals to transmit video and audio. In an analog television broadcast, the brightness, colors and sound are represented by amplitude, instantaneous phase and frequency, phase and frequency of an analog signal. Analog signals vary over a continuous range of possible values which means that electronic noise and interference may be introduced. Thus with analog, a moderately weak signal becomes Noise (video), snowy and subject to interference. In contrast, picture quality from a digital television (DTV) signal remains good until the signal level drops below digital cliff, a threshold where reception is no longer possible or becomes intermittent. Analog television may be wireless (terrestrial television and satellite television) or can be distributed over a cable network as cable television. All broadcast television systems used analog signals before the arrival of DTV. Motivated by the lower bandwidth requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MVPD
Multichannel television in the United States has been available since at least 1948. The United States is served by multichannel television through cable television systems, direct-broadcast satellite providers, and various other wireline video providers; among the largest television providers in the U.S. are YouTube TV, DirecTV, Altice USA, Charter Communications (through its Spectrum division, which also includes the former Time Warner Cable and Bright House Networks systems), Comcast (through its Xfinity division), Dish Network, Verizon Communications (through its FiOS division), and Cox Communications. The Telecommunications Act of 1996 defines a multichannel video programming distributor (MVPD) as "a person such as, but not limited to, a cable operator, a multichannel multipoint distribution service, a direct broadcast satellite service, or a television receive-only satellite program distributor, who makes available for purchase, by subscribers or customers, multiple cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks that consists of Private network, private, public, academic, business, and government networks of local to global scope, linked by a broad array of electronic, Wireless network, wireless, and optical networking technologies. The Internet carries a vast range of information resources and services, such as the interlinked hypertext documents and Web application, applications of the World Wide Web (WWW), email, electronic mail, internet telephony, streaming media and file sharing. The origins of the Internet date back to research that enabled the time-sharing of computer resources, the development of packet switching in the 1960s and the design of computer networks for data communication. The set of rules (communication protocols) to enable i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
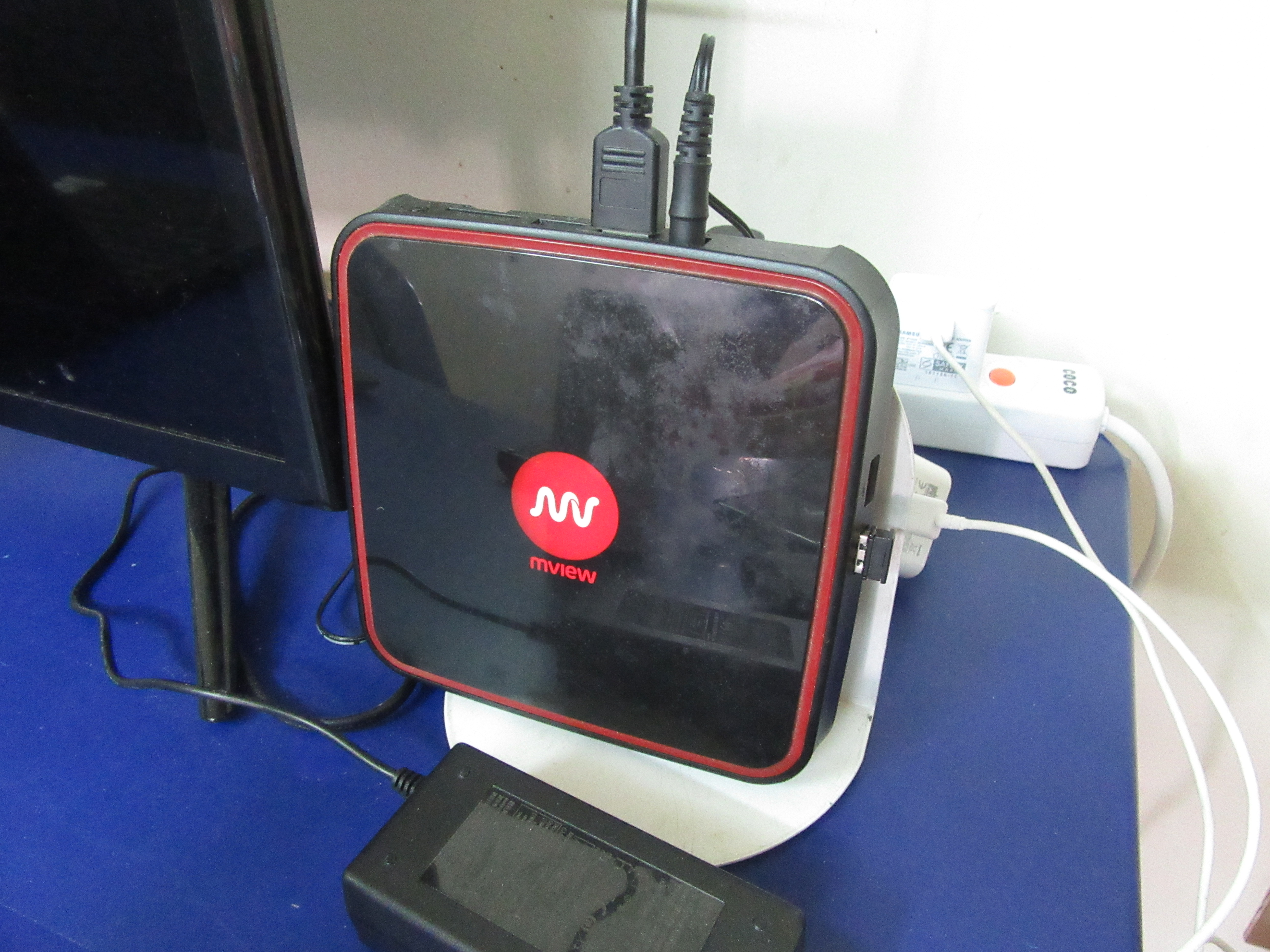
Internet Protocol Television
Internet Protocol television (IPTV), also called TV over broadband, is the service delivery of television over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. Usually sold and run by a telecom provider, it consists of broadcast live television that is streamed over the Internet ( multicast) — in contrast to delivery through traditional terrestrial, satellite, and cable transmission formats — as well as video on demand services for watching or replaying content ( unicast). IPTV broadcasts started gaining usage during the 2000s alongside the rising use of broadband-based internet connections. It is often provided bundled with internet access services by ISPs to subscribers and runs in a closed network. IPTV normally requires the use of a set-top box, which receives the encoded television content in the MPEG transport stream via IP multicast, and converts the packets to be watched on a TV set or other kind of display. It is distinct from over-the-top (OTT) services, which are based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct-broadcast Satellite Television
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location.ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.39, definition: ''Broadcasting-satellite service'' The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna commonly referred to as a satellite dish and a low-noise block downconverter. A satellite receiver decodes the desired television program for viewing on a television set. Receivers can be external set-top boxes, or a built-in television tuner. Satellite television provides a wide range of channels and services. It is usually the only television available in many remote geographic areas without terrestrial television or cable television service. Different receivers are required for the two types. Some transmissions and channels are unencrypted and therefore free-to-air, while many other channels are transmitted with en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-to-air
Free-to-air (FTA) services are television (TV) and radio services broadcast in unencrypted form, allowing any person with the appropriate receiving equipment to receive the signal and view or listen to the content without requiring a subscription, other ongoing cost, or one-off fee (e.g., pay-per-view). In the traditional sense, this is carried on terrestrial radio signals and received with an antenna. FTA also refers to channels and broadcasters providing content for which no subscription is expected, even though they may be delivered to the viewer/listener by another carrier for which a subscription is required, e.g., cable television, the Internet, or satellite. These carriers may be mandated (or OPT) in some geographies to deliver FTA channels even if a premium subscription is not present (providing the necessary equipment is still available), especially where FTA channels are expected to be used for emergency broadcasts, similar to the mandatory emergency phone num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Television
Satellite television is a service that delivers television programming to viewers by relaying it from a communications satellite orbiting the Earth directly to the viewer's location.ITU Radio Regulations, Section IV. Radio Stations and Systems – Article 1.39, definition: ''Broadcasting-satellite service'' The signals are received via an outdoor parabolic antenna commonly referred to as a satellite dish and a low-noise block downconverter. A satellite receiver decodes the desired television program for viewing on a television set. Receivers can be external set-top boxes, or a built-in television tuner. Satellite television provides a wide range of channels and services. It is usually the only television available in many remote geographic areas without terrestrial television or cable television service. Different receivers are required for the two types. Some transmissions and channels are unencrypted and therefore free-to-air, while many other channels are transmitted with enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cable Television
Cable television is a system of delivering television programming to consumers via radio frequency (RF) signals transmitted through coaxial cables, or in more recent systems, light pulses through fibre-optic cables. This contrasts with broadcast television, in which the television signal is transmitted over-the-air by radio waves and received by a television antenna, or satellite television, in which the television signal is transmitted over-the-air by radio waves from a communications satellite and received by a satellite dish on the roof. FM radio programming, high-speed Internet, telephone services, and similar non-television services may also be provided through these cables. Analog television was standard in the 20th century, but since the 2000s, cable systems have been upgraded to digital cable operation. A cable channel (sometimes known as a cable network) is a television network available via cable television. Many of the same channels are distributed throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |